Business Activities and Financial Conduct
Banknotes, Currency, and Cash Movement
Cash Center Operations
Policy for Handling Saudi Banknotes Marked with Security Inks and Compensation
No: 120172/329 Date(g): 12/7/2023 | Date(h): 24/12/1444 Status: In-Force Translated Document
First: Introduction
General framework:
The “Policy for Dealing with and Compensating for Security Marked Banknotes” sets out the rules and controls necessary to organize the mechanism for dealing with and compensating for banknotes marked with security protection inks. The general framework of this policy is summarized in the following main points:
- General controls and specifications for security inks, cash transportation bags and ATM boxes.
- Controls for approving the specifications of cash transportation bags and ATM boxes for service providers.
- Controls for reporting and raising awareness on how to deal with banknotes marked with security inks.
- Controls for receiving seized banknotes.
- Controls for dealing with unseized banknotes.
- Controls for examining and replacing the security-marked banknote.
- Operational cost controls.
- Document retention controls.
Objective:
This policy aims to define the controls and guidelines necessary to organize and control the procedures for handling and replacing Saudi currency banknotes marked with security inks, as well as the general controls and specifications for security inks, cash transport bags and ATM boxes.
Scope:
This policy applies to the Currency Department and all related administrative units, and to dealing with cases of requesting the approval of the specifications of cash transportation bags and ATM boxes, as well as Saudi currency banknotes marked with security inks received by the Central Bank, regardless of whether they are seized or unseized.
Updating and inquiries:
The Currency Department is responsible for updating this policy periodically in coordination with the Center of Excellence, or when there are changes that may impact the policy, as well as responding to any inquiries about it. This policy supersedes any policy or circular related to the content of the policy that was issued prior to the adoption of this policy.
Second: Definitions
Term
Definition
Central Bank Saudi Central Bank. Management Currency management. Marking banknotes Covering some features of Saudi Arabian currency banknotes by self-destructing security ink through self-destruct devices in cash transportation bags or ATM boxes, and the banknotes are considered damaged and unfit for circulation. Seized banknotes Uncirculated banknotes seized subsequent to being marked and identified. Unseized banknotes Banknotes that were circulated among the public after being marked and subsequently seized, but their owner is not identified. Money Carrier Bag A sophisticated bag designed for the secure transportation of money, which facilitates automatic tracking and incorporates a self-destruction mechanism for marking banknotes. Automated teller machine (ATM) boxes Smart boxes are used for the replenishment currency into ATMs and allow for self-destruction by marking the banknotes. The Service Provider the company that imports the cash transportation bags or ATM boxes. The User the organization utilizing the cash bag or ATM box. The Laboratory The laboratory authorized by the authority to test samples of banknotes marked with security inks. The Committee Damaged banknotes compensation committee. DNA Fingerprinting The chemical component in the ink used to mark banknotes and are machine-readable. Third: Policy Content
General Controls and Specifications for Security Inks, Money Bags and ATM Boxes
3.1
Security inks should include the following specifications:
1.1 Have a certificate from an internationally accredited laboratory. 1.2 Must be certified by the Saudi Standards, Metrology, and Quality Organization (SASO). 1.3 It must contain DNA (Taggant). 1.4 Have an integrated Infra-Red (IR) marker. 1.5 Have a dark green color. 1.6 Not being toxic or dangerous to humans. 1.7 Highly stable and impossible to remove with any substance such as: Water, fuel, bleach or cleaning agents. 1.8 Cash Deposit Machines (CDMs), Cash Recyclers (TCRs), self-service machines, and counting and sorting machines should be able to detect and reject counterfeit currency. Cash carriers and ATM boxes must meet the following specifications:
2.1 The materials used in security inkjet technology should not include any materials employed in the production of explosives (according to the requirements of the Ministry of Interior, represented by the Higher Authority for Industrial Security). 2,2 Incorporate a tracking features utilizing satellite or mobile network technology (GPS/GPR Tracking). 2.3 The ability to cover all banknotes with security inks in cash transportation bags and ATM boxes without exception, with a minimum of 20% per banknote once the security inks are activated and dispensed.
Regulations for the approval of specifications for service providers' cash bags and ATM boxes
3.2
- When a service provider applies to the General Directorate of Branches and Cash Centers for a letter of approval regarding the specifications of cash transport cases and ATM boxes, the Directorate must verify the following before granting the approval letter:
1,1 Cash transportation bags and ATM boxes shall use inks in accordance with the specifications for security inks referred to in paragraph (1) of clause (1.3), and cash transportation bags and ATM boxes shall contain the specifications referred to in paragraph (2) of clause (1.3). 1.2 Inform the service provider to bear the operational costs of examining the samples of marked banknotes during the examination. Reporting and Awareness Controls on How to Handle Banknotes Marked with Security Inks
3,3
- The department, in coordination with the Bank Policy Department, must inform the user in a one-time official letter of the following:
1,1 Handing over the seized banknotes to the Central Bank to complete the compensation procedures in accordance with the regulations and procedures approved by the Central Bank. 1.2 Retaining the unseized banknotes, fill out the “Report of a report or seizure of banknotes marked with security inks” form (Annex 3) and send the form with the marked banknotes to the police, and send a copy of the form to the administration. 1.3 Prohibit the circulation of marked banknotes. - The administration must coordinate with the Communication Department to educate the community - in accordance with the approved policies, procedures, and instructions - not to accept marked banknotes, and the need to report any information related to them to the police.
- The administration must take the necessary measures to raise user awareness; to train its employees to identify banknotes marked with security inks and the mechanism for detecting and reporting them.
Controls for Receiving Seized Banknotes
3.4
- Central Bank branches must collect the seized banknotes from the user and hand them over to the administration, and treat them as a cash consignment according to the “Internal and External Cash shipment Policy”.
- The administration must collect the seized banknotes from the user or Central Bank branches and refer them to the committee.
- After submitting an official letter from the user to request compensation for the seized banknotes, the user is required to fill out the “Request for Compensation for Security Marked Banknotes" Form (Annex 1) and the “Declaration of Banknotes for Compensation” form (Annex 2), and the person responsible for receiving the seized banknotes (the cashier) must adhere with the following:
3.1 He shall not receive any controlled banknotes except those of specified number and value. 3.2 Identify the user's name and contact information. 3,3 Receive a copy of the approval letter issued by the Central Bank to the service provider on the conformity of the cash transportation bag or ATM box with the required specifications mentioned in clause (1.3). 3.4 Note the information of manufacturer of the self-destruct device used to mark the seized banknotes and the circumstances under which it was activated. 3.5 Record the serial number of the cash-carrying bag or ATM boxes. 3.6 Request all supporting videos/photos, if any, to be submitted, and a copy of the relevant police report in the event of an attempted takeover. - The seized banknotes shall be presented to the committee to take the necessary measures in accordance with its jurisdiction.
Controls for Dealing with Unseized Banknotes
3.5 - If unseized banknotes are presented to the central bank by:
1,1 The User:
The user is instructed to fill out the form “Banknotes marked with security inks” (Annex 3) and submit the form along with the banknotes to the police, and a copy of the form is sent to the administration.
1.2 Security agencies:
The value of the banknotes should not be reimbursed.
1.3 Individuals:
The value of these banknotes should not be compensated, and they are referred by the administration to the security authorities to ensure that they are not related to a seizure case.
- If unseized banknotes are presented to the central bank by:
Controls for Examining and Replacing Banknotes Marked with Security Inks
3.6
- When the administration receives samples of marked banknotes from the committee for the purpose of examining them, the administration must send the samples to the laboratory to obtain the concentrations of security inks and a detailed report on the results of the examination, and return the samples after completion, and the administration must submit the technical report to the committee.
- The user shall be compensated for banknotes marked with security inks based on the committee's recommendation and the authorization holder's approval of the compensation. Without prejudice to the provisions of this policy, the seized banknotes to be compensated shall be considered as damaged banknotes and compensation shall be subject to the controls contained in the “Damaged Banknotes Compensation Policy".
Operational Cost Controls
3.7
- The Administration shall inform the Service Provider or the User, as the case may be, to bear the cost of examining the samples of the marked banknotes.
- The Administration shall inform the User of the operational costs of replacing the seized banknotes according to the following:
2.1 The value specified in the approval of the authorizing authority for each marked banknote in cases of proven negligence in handling cash transport bags and ATM boxes. 2,2 The cost of transporting the seized banknotes to be compensated in case the user wants the Central Bank to transport them from one of its branches to the main center. Document Retention Controls
8,3
- The original “Request for Compensation for Banknotes Marked with Security Inks” form (Annex 1), “Declaration of Banknotes for which Compensation is requested” form (Annex 2), copies of the rest of the documents, the committee's recommendation for compensation, and the approval of the authority holder thereof shall be retained by the administration for one year in paper form, and then destroyed after being archived in a content management system.
Fourth: References
Reference
Reference Details
Banking Control Law Issued by Royal Decree No. (M/5) dated 22/02/1386 H Mechanism for Compensating Damaged Cash Marked with Security Inks No. (41025174) dated 12/04/1441 H Minister of Finances approval on considering the banknotes marked with private security inks as non-compensable Approval No. (5002) issued on 13/06/1439 H Governor's approval on the circular and compensation No. (43459/80) dated 17/03/1441 H. Damaged Banknote Replacement Policy Version No. 2.0 dated 06/08/1439 H. Criteria and Requirements for Operating a Money Transportation Service No. (53506/198) dated 13/04/1440 H. Fifth: Adjusting the Document
Relevant Department
Related Departments
Advisory Departments
Director of the Department
Currency management
- General Administration of Branches and Cash Centers.
- General Administration of Bank Supervision.
- Communication Department.
- General Department of Legal Affairs.
- Risk and Compliance Department.
- Internal Audit Department.
Dr. Naif bin Abdullah Al-Sharaan
17/03/2023 G
Recommendation of the General Department of Legal Affairs
Signature
Date
Mohammed bin Othman Al-Abduljabbar
18/01/1445 H
Recommendation of the Deputy Governor for Finance and Administrative Affairs
Signature
Date
Abdul Elah bin Abdulaziz Al-Duhaim
11/02/1445 H
Approval of the Governor
Signature
Date
Ayman bin Mohammed al-Siyari
12/02/45 H
List of Releases
Previous Release Date
New Release Date
Original Release Number
New Release Number
Policy for handling and replacing security-marked Saudi Arabian currency banknotes -
12/02/1445 H
-
1,0
Scope of Distribution
Archiving
√ Currency Management
√ General Administration of Branches and Cash Centers.
√ General Directorate of Banking Supervision.
√ Communication Management
√ Central Bank Branches.
√ The original document: To be kept at the Support Services Division.
√ The original document: To be kept at the Center of Excellence.
- General Administration of Branches and Cash Centers.
Annexures
Annexure (1): Form for Requesting Compensation for Banknotes Marked with Security Inks
نموذج طلب تعويض عن الأوراق النقدية الموسومة بالأحبار الأمنية
اسم المستخدم/_________________________________ممثل المستخدم________________________________
رقم الهوية__________________________________________رقم الهاتف___________________________________
رقم الجوال _______________________البريد الإلكتروني_________________ص:ب_________________
الرمز البريدي_______________________ المدينة_______________________
رقم الوكالة وتاريخها ومصدرها_______________________________________________________
ملاحظات: يجب أن تكون الأوراق النقدية الموسومة جافة ومرتبة حسب الفنة، وأن تحتوي كل رزمة على مئة ورقة من الفئة نفسها. مصنع جهاز الإتلاف الذاتي___________________________________________
رقم الحقيبة التسلسلي________________________________
الفئة_______________________________________
عدد الأوراق النقدية______________________________________________________
قيمة المبلغ كتابة____________________________________________________________________________________
أسباب تلف الأوراق النقدية المطلوب التعويض عنها:
• محاولة سرقة • سوء استخدام حقيبة نقل النقود/صندوق أجهزة الصرف الآلي
• أسباب تقنية • أخرى/.....................................
المرفقات المطلوبة:
• تقرير/مشهد من الدفاع المدني- إن وجدت
• تقرير من مزود الخدمة في حال أن التلف ناتج من خلل فني في حقيبة
نقل النقود/صندوق أجهزة الصرف الآل • تقرير/مشهد من الشرطة-إن وجدت
• كل ما يدعم من مقاطع فيديو/صور-إن وجدت • إقرار عن أوراق نقدية مطلوب التعويض عنها
• استلام صورة خطاب الموافقة الصادرة من البنك المركزي لمزود • وكالة
الخدمة على مطابقة حقيبة نقل النقود أو صندوق أجهزة الصرف
الآلي للمواصفات المطلوبة
أرغب في أن يكون تحويل قيمة التعويض المعتمد من صاحب الصلاحية:
للحساب البنكي (رقم آيبان)__________________________________________________________________
لدى مصرف/بنك_________________________________________________________________________
وسيلة أخرى______________________________________________________________________________
أتعهد بتحمل فيمة فحص عيّنات الأوراق النقدية الموسومة بالأحبار الأمنية في المختبر، وقيمة التكاليف التشغيلية لتعويض الأوراق النقدية الموسومة بالأحبار الأمنية. وفق الضوابط التي يضعها البنك المركزي في هذا الشأن.
اسم المستخدم/ الوكيل__________________________________ توقيعه__________________________________
اسم وتوقيع أمين الصرف اسم وتوقيع رئيس العمليات النقدية
________________________________ _____________________________
رقم العملية في النظام الآلي:______________________________________________________________________ الإجراء بالفرع / خزينة المركز بعد اعتماد صاحب الصلاحية لقيمة مبلغ التعويض تم السداد للمستفيد
• التحويل للحساب • أخرى
رقم العملية (الحوالة) الآلية
_________________________________________
اسم أمين الصندوق وتوقيعه ______________________________________________________________
الإجراء في خزينة المركز الرئيسي بعد مرور سنة مالية على اعتماد قيمة المبلغ المعوض لعدم التمكن من التواصل مع المستفيد _______________________________
رقم العملية من النظام الألي ______________________________________________________________________
مستلم النموذج من شعبة العمليات المصرفية ____________________________________________________________
الاسم _______________________________________ التوقيع___________________________________________________
Annexure (2): Declaration of Banknotes to be Compensated
إقرار عن أوراق نقدية مطلوب التعويض عنها
معلومات مندوب المستخدم
الاسم:............................................... رقم الهوية:.....................................
رقم الجوال:........................................ جهة العمل:.....................................................
موقع المراجعة:...................................
تاريخ المراجعة: يوم الموافق / /١٤هـ أتعهد أنا............................................................................................................................. أن بيانات المبلغ النقدي المطلوب التعويض عنه صحيحة حسب الموضح أدناه: مصدر النقد: ..................................................................................................................... ملكية النقد: ................................................................................................... المبلغ التقريبي: ............................................................................................................ الفئات النقدية:............................................................................................................... سبب تلف النقد: ........................................................................................ كما أتعهد بمعرفتي أن تعمد إتلاف العملة السعودية يتم المعاقبة عليها وإذا كانت تحتوي على نقد مزيف فسيتم تطبيق الأنظمة والتعليمات ذات الصلة، وأتعهد بدفع أي تكاليف تشغيلية تفرض وفق تعليمات البنك المركزي. الاسم: ..........................................................................التوقيع,............................................... : خاص بموظفي الخزينة
اسم المسئول: ...............................................................................................................
وظيفة المسئول:.............................................................................................................
التوقيع:................................................................................
Annexure (3): Reporting and Seizure of Banknotes Marked with Security Inks
محضر إبلاغ أوضبط أوراق نقدية موسومة بالأحبار الأمنية
رقم الصادر
/ / 20م
لموافق
/ / 143هـ
التاريخ
ضبط
بلاغ
الحصول على الأوراق النقدية الموسومة عن طريق
أخرى
شخص
مركز الشرطة
الشرطة
محل تجاري
مصرف
بنك
مكان الحصول على الأوراق النقدية الموسومة
الجنسية
البلد
مكان الولادة
العائلة
اسم الجد
اسم الأب
الاسم الأول
مقدم الأوراق النقدية الموسومة
مصدرها
تاريخها
رقمها
نوعها
الهوية
المهنة
التعليم
الحالة الإجتماعية
أنثى
ذكر
الجنس
هاتف
العمل
العنوان
هاتف
السكن
هاتف
الاسم
الكفيل
هاتف
العنوان
وصف الأوراق النقدية الموسومة بالأحبار الامنية
الرقم التسلسلي
العدد
الفئة
نوع العملة (الإصدار)
المبلغ
مستقبل البلاغ
التوقيع
الاسم
الرتبة
الوظيفة
الاسم
البصمة
التوقيع
صورة / لملف القضية.
صورة / للأمن العام / الامن الجنائي / إدارة التحريات والبحث الجنائي - فاكس (0114054216).
صورة / للبنك المركزي السعودي إدارة العملة - Currency@Sama.gov.sa
Providing Small Denominations and Coins
Referring to the instructions of SAMA communicated under Circular No. 341000111354 dated 15/09/1434 H regarding the acceptance and exchange of banknotes and coins by banks operating in the Kingdom to meet public demand.
Accordingly, SAMA emphasizes the need of having sufficient quantities of small denomination banknotes and coins to meet the public's requests for obtaining or exchanging them. This should be made available to everyone at all branches.
For your information and action accordingly, please note that SAMA will conduct field visits to cash centers and bank branches to ensure the availability of various small denominations and coins for individual and corporate customers.
Replacing Damaged Saudi Banknotes
Further to the instructions of SAMA communicated under Circular No. 34734, dated 10/7/1432 H regarding exchanging damaged banknotes from beneficiaries (torn, burned, eroded, incomplete edges or parts, or any of the main features missing due to dirt, adhesive materials, or inappropriate inscriptions, ...).
And based on SAMA's commitment to providing intact banknotes and suitable for circulation, SAMA affirms the acceptance and exchange of various currency denominations after verifying their authenticity with the adoption of the specific mechanism for accepting and compensating damaged currency presented by the public.
1 The replaced banknote must be clearly visible and its area shall not be less than 60% of the size of the original banknote. 2 The two signatures (Minister of Finance and Governor of SAMA) or the two serial numbers must not be missing. 3 If the banknote is not clearly visible due to exposure to fire or other natural factors such as corrosion, the holder must present it to one of the branches of SAMA For your information and action accordingly, and to emphasize to all bank branches, cash centers to circulate intact banknotes and withdraw damaged and invalid cash from circulation, and to coordinate with SAMA's branches to supply it.
Commitment to Employing Citizens in Cash Centers
Further to SAMA Circular No. 341000068320 dated 03/06/1434 H concerning the Compliance with Employing Citizens and the Requirements for Contracting with Recruitment Service Companies, and as stated in clause one, Paragraph (2), which specifies that all positions in branches, remittance centers, and cash centers should be exclusively occupied by Saudis, with the aim of completing the Saudization process by 31/12/2013, it has come to our attention that there are still non-Saudi employees working in cash centers, whether as bank staff or employees of contracted companies, which is a violation to the regulations and exposes banks and companies to severe penalties.
Therefore, we hope you will provide us with proof of compliance with the aforementioned instructions and submit a detailed list of employees working in the bank's cash units and centers, as well as those in exchange companies or centers affiliated with contracted companies, including the following information:
Name Nationality National ID/Residence Number Job Title Name of the Cash Center
Please send the completed form to the Cash Centers and Operations Supervision Department at SAMA within a maximum one week from its date.Techniques to Identify Banknotes
No: 281000041965 Date(g): 4/11/2007 | Date(h): 24/10/1428 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Based on the requirements of Article 4 and Article 5 of The Money Counterfeiting Law 1379H issued by Royal Decree No. (12) dated 21/7/1379H, regarding the establishment of regulations for issuing licenses for currency reproduction in a manner that ensures measures for preventing counterfeiting and protecting it from similar-looking papers and coinages. To ensure the circulation of only genuine currency in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, you will find attached the updated regulations for currency reproduction in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. We hope that you will act according to them and revoke any previous directives issued in this regard. Applications for obtaining reproduction licenses can be submitted through the central bank's website.
First: General Instructions
- It is prohibited for any natural or legal person to clone, photograph, or use images or designs of any Saudi or foreign currency circulated within the Kingdom for commercial, media, or cultural purposes without obtaining prior authorization from the Saudi Central Bank.
- It is strictly prohibited to use images, replicas, or designs of Saudi and foreign currencies circulated within the Kingdom in the form of paintings, crafts, models, product packaging, or in the shape of money and others.
- Anyone who violates the instructions shall be punished in accordance with the provisions of Money Counterfeiting Law issued by Royal Decree No. (12) dated 02/07/1379 H and according to the Anti-Counterfeiting Law issued by Royal Decree No. 114 dated 26/11/1380 H.
The Anti-Counterfeiting Law issued by Royal Decree No. (114) dated 26/11/1380 H. was replaced by The Penal Code for Forgery Offences, issued by Royal Decree No. (M/11), dated 18/02/1435 H.
Second: Controls for Replicating Foreign Currency Legally Circulated within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- To reproduce images of foreign currency that is legally circulated within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia for use in printed or electronic (digital) media, an application must be submitted to the Central Bank to obtain a currency reproduction license.
- To obtain the license, the instructions and regulations issued by the authorities responsible for the issuance of the foreign currency to be reproduced must be followed.
Third: Controls for Replicating Saudi Currency Legally Circulated within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- To reproduce images of Saudi currency in circulation within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in printed or electronic (digital) media, an application must be submitted to the Central Bank to obtain a currency reproduction license.
- To obtain a license to reproduce Saudi currency in circulation inside the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia for use in printed media, the following instructions and controls must be observed:
O Attach the material intended for publication or printing with the request for a currency reproduction license, specifying the technical specifications in terms of shape, color, and size, along with the purpose of publishing the images of the Saudi currency (commercial / media / cultural).
O Do not distort the image of the king in any way (whether by enlarging, shrinking, or changing its coordinates).
O The lack of risk of deceiving the public into thinking it is a genuine currency.
O Images can be of one side of the coin, provided that:
▪ The size of the image should not exceed 75% of the length and width of the original paper, or
▪ The size of the image should not be less than 150% of the length and width of the original document.
O The images can be of both sides of the coin provided that:
▪ The size of the image should not exceed 50% of the length and width of the original paper, or
▪ The size of the image must not be less than 200% of the length and width of the original paper.
▪ Do not display the front side of the banknote against the back side of the same banknote.
O All materials used in the process of producing images from films (negative and positive) and plates must be destroyed immediately after use.
- To obtain a reproduction license Saudi currency Circulated systematically within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia for use in electronic (digital) means, the following instructions and regulations must be observed:
O Clarify the purpose of using images of the Saudi currency (commercial/media/cultural).
O The image of the king should not be distorted in any way (whether by enlarging, reducing, or altering its coordinates).
O The non-use of images of the Saudi currency in an inappropriate context.
O The resolution should be 72 pixels per inch or less.
O The word "SAMPLE" should be printed diagonally and clearly on the image of the banknote in a different color.
O All materials used in the process of issuing images from digital storage media, such as files and others, must be destroyed or removed immediately after their use is complete.
Instructions to Be Followed When Opening, Relocating or Closing Bank Branches, Instant Remittance Centers and ATMs, Whether Operational or Non-Operational
SAMA has recently observed an increase in violations committed by several banks, where certain measures were taken before obtaining prior approval from SAMA. The most significant of these violations include the following:
- Setting up headquarters for main administrations or operational branches, and then writing to SAMA to obtain approval for the move from the original licensed location to the newly prepared site.
2. Opening offices in different locations for specific purposes and for a limited period, or at exhibitions or festivals.
3. Closing operational branches, converting them into offices, or downsizing banking operations within them.
4. Setting up, installing, or operating ATMs without a license.
5. Relocating or deactivating operational or non-operational ATMs without obtaining approval from SAMA.
6. Engaging in speculative activities and bidding on certain locations that have already been licensed to a bank, thereby depriving the location of banking services.
7. Merging ATM licenses with licenses for active or inactive branches.
8. Failure to follow through with the process of opening branches and machines within the nine-month licensing period, and not providing an explanation when requested for renewal about the reasons that prevented the bank from opening the branch or installing the ATM.
And since the banks' adherence to these procedures constitutes a clear violation to The Banking Control Law in accordance with the current applicable regulations in this regard, we hope that you will inform your relevant specialists about the necessity to follow and adhere to the following instructions:
a) No bank may open new branches, other offices, or ATMs in any region of the Kingdom without first obtaining an official prior license from SAMA.
b) When the bank obtains a license from SAMA to open a branch or install an ATM, it is not permissible to relocating it from one location to another without obtaining written approval from SAMA. This applies whether the branch is operational or non-operational, or whether the ATM machine is operational or non-operational.
c) When the bank obtains approval from SAMA to open a branch at any location, installing an ATM at the branch is covered under the branch's license. There is no need to obtain a separate license for the ATM, however SAMA must be informed about it.
d) The license for an independent ATM (outside branch premises) cannot be merged with any branch, regardless of whether it is operational or non-operational.
e) The duration of the license is nine months from the date of approval issuance, and the bank must follow up to complete the opening within this period. If the opening cannot be completed within this time frame, the bank must inform SAMA of the reasons that led to this before expiry of the license period.
f) The licenses for non-operating branches are extended every six months to provide the bank with the opportunity to prepare the site.
g) The bank must provide SAMA at the end of every six months with a report that includes its position regarding the opening of branches or the installation of ATMs.
c) Every bank must attach the following information when requesting approval to open a branch or install an ATM:
- Feasibility study for opening a branch or installing an ATM.
- A sketch drawing showing the exact location of the desired branch or the ATM.
t) SAMA must be notified of the actual opening date of the branch and the commencement of its operations or the date the ATM becomes operational.
Automated Teller Machines
Procedures And Controls to Be Observed in Maintaining ATM Machines
We wish to inform you that SAMA receives from time to time reports from Saudi police about the bank's maintenance of ATM machines. In view of the fact that maintenance workers are sometimes caught without having a permit which indicates their identity and the nature of the work they are doing; and since there are instructions and controls adopted by General Security and communicated to SAMA regarding the maintenance of ATM machines; and in our desire to see the ATM machines well maintained and smoothly operating all the time and the maintenance workers are not subject to questioning and arrest by the police, the banks must abide by the following instructions:
- The police operation room must be advised of the location of the ATM machine to be maintained, the day and hour of the maintenance job so that the police patrol in the area will provide needed protection.
- Maintenance workers must carry permits showing their name and photo stamped by the official stamp of their employer to be presented lo security when requested.
- An office must be assigned and operating around the clock with a Saudi employee in charge and its phone number be communicated to the operation room in case of suspicion.
- The maintenance hours must be fixed between 8:00 A.M and 11:00 PM.
- Maintenance companies and establishments must be required to have a special logo attached to their vehicles and worker uniforms so that the maintenance team is clearly identified by the security patrols.
We further wish to remind you of SAMA's circular No.485/BC/36 dated 7/1/1416, with a copy of the Security guide attached thereto, which includes, in several parts, thereof, the procedures and controls which cover all aspects of ATM safety and security as follows:
- The part related to physical security requirements (P 10 and 11)
- The part related to security and safety requirements (P 16, 17, 18, 25 & 26)
- The part related to internal procedures for the transport of cash (P 10 & 11)
- The part related lo establishments security guide (P14)
The above-mentioned parts included the location of ATM machines and the specifications of protection, feeding and alarm that have to be complied with.
Please be informed, advice same to your departments that are involved in feeding and maintaining the ATM machines and acknowledge receipt.
Cash Feeding Requirements for ATMs
Further to SAMA's instructions issued under Circular No. 361000064350 dated 03/05/1436 H regarding to the procedures for reversal of cash transactions in Automated Teller Machines (ATMs), as well as Circular No. 351000009927 dated 22/01/1435 H concerning the reconciliation and replenishment timelines for banks' ATMs, and Circular No. 27027/Akh dated 19/12/1424 H regarding the distribution of cash denominations in ATMs.
We hereby inform you that, in accordance to the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority Law issued by Royal Decree No. (23) dated 23/05/1377 H, and the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/5) dated 22/02/1386 H, the following has been decided:
- ATM shall be replenished and extension of the period of reconciliation every ten business days, considering cash flow projections, the characteristics of the location, and associated operational risks.
- The Dispense Logic is determined at the bank's discretion, taking into account the characteristics of the location and the needs of the customers. All ATMs situated within bank branches and transfer centers shall be replenished with a minimum of three cash denominations: five hundred, one hundred, and fifty. This arrangement ensures that customers have the option to withdraw cash in any combination of these three denominations. Outdoor ATMs situated in various locations such as roadways and shopping malls are designed to accept a minimum of two different denominations of currency, ensuring that both denominations can be dispensed to the customer during cash withdrawal transactions. The General Administration of Branches and Cash Centers will conduct a reassessment of the distribution of cash denominations six months following its implementation.
- The responsibility for determining the cash replenishment method of ATM lies with the banks. They have the discretion to decide whether to replace all denomination cassettes simultaneously when the machine requires cash or to replace only the denomination box that has been depleted. The box or cassettes shall be prepared at the cash center and maintained under dual surveillance and monitoring via cameras, subsequent to the bank determination of the requisite accounting mechanisms and procedures.
- Banks must automate ATM replenishment procedures by having an automated system to replenish the ATMs. In the absence of such systems, it is advisable to utilize test cards, which enable the replenishment team to conduct a test withdrawal following each replenishment. This procedure is essential to verify that the appropriate cash denominations have been correctly placed within the ATM. Supervisor cards must be utilized to enable the replenishment team at the cash centers to reconcile ATMs in real time, thereby eliminating the need to wait for reconciliation by the bank's support departments.
- Banks shall rectify discrepancies associated with the reversal of denomination cassettes that arise from the replenishment of ATMs. Additionally, they must manage instances where a customer inadvertently receives funds due to either a technical malfunction or human error. The banks bear the responsibility to substantiate the error in the event the customer disputes their actions.
For your information and action accordingly as of its date. SAMA will undertake field visits to verify compliance with these instructions, and in case of any inquiries in this regard, the Advisor to the Deputy Governor for Financial Sector Development can be contacted.
- ATM shall be replenished and extension of the period of reconciliation every ten business days, considering cash flow projections, the characteristics of the location, and associated operational risks.
Requirements for ATM Cash Feeding with Sixth Issuance Currency and Inclusion of 200 Riyal Denomination
Referring to Circular No. 27027/Akh dated 19/12/1424 H regarding the distribution of cash denominations in ATMs local banks, and Circular No. 30902/227 dated 26/08/1440H regarding cash feeding requirements for ATMs, and based on SAMA’s commitment to enhancing the efficiency and quality of circulating cash, and to meet the needs of ATM users with different cash denominations, SAMA emphasizes to all operating banks the importance of ensuring the proper replenishment and safety of cash in the bank’s ATMs and to adhere to the following:
First: Effective January 1, 2022G, ATMs shall be exclusively replenished by sixth-issue denominations.
Second: The SAR 200 denomination from the sixth issue will be added into all internal ATMs situated within branches and transfer centers. The determination to add this denomination into external ATMs will be made at the bank's discretion, considering the unique attributes of the location and the needs of customers, prior to February 2, 2022G.
The Central Bank emphasizes the importance of adhering to the above, and providing the Cash Supervision Department with the bank's plan to insert the (200) riyal denomination in ATMs via e-mail, within two weeks from its date.
Declined Bank Card Transactions at ATMs
We would like to emphasize the role played by the Saudi banking network in providing advanced banking services to citizens and residents facilitating their access to cash easily and conveniently, which enhanced customers' trust and reliance on the banking sector. The Central Bank appreciates the efforts of Saudi banks in providing these services, whether by issuing cards or installing ATMs and POS terminals. The Central Bank is currently studying the Saudi network fees in order to establish a mutually agreeable resolution for all stakeholders involved.
Although the Central Bank had previously issued Circular No. BCT/4593 dated 05/08/1420 H, a copy of which is attached, which stipulates the prohibition of imposing restrictions on the issuance or utilization of Saudi Payments Network cards, it was noticed that certain banks have imposed restrictions on the use of the network, which impacted the network's credibility and led to numerous complaints from customers.
Therefore, we inform you that the bank shall eliminate any restrictions on network usage and remove any current restrictions, noting that as of 05/12/1420 H, the Central Bank will implement a fee of 6.4 riyals for each transaction that is declined beyond the standard rate established by the Central Bank, should the bank fail to comply with the directive to remove the existing restrictions.
Annual Plans to Install ATMs
Referring to the future plans of banks to provide ATM services for customers in all regions of the Kingdom, and the importance of early planning and coordination among the relevant parties in this regard, SAMA will provide the necessary support for banks to implement these plans.
We hope to provide SAMA by the annual plans for installing ATMs in September of each calendar year, along with the plans to benefit from the temporarily suspended site licenses, according to the current requirements among the categories, for review and approval by SAMA.
For inquiries, you can contact specialists in the Currency Supervision Department via email.
Requirements for ATM Receipts Initiative
No: 43067037 Date(g): 6/3/2022 | Date(h): 3/8/1443 Status: In-Force Based on the powers granted to the Saudi Central Bank under its Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/36) dated 11/4/1442 AH, and the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/5) dated 22/2/1386 H, and referring to the ATM Service Level Agreement (Version 2) issued under Central Bank Circular No. (41932/227) dated 15/3/1441 H, and in continuation of the efforts made to develop the payment system infrastructure in the Kingdom.
Attached is the Requirements for ATM Receipts Initiative issued by Saudi Payments, which banks are required to implement on ATMs. The initiative aims to reduce customer requests for paper receipts in ATM transactions by standardizing the workflow across all machines to ensure the following:
- Preserving the environment and the overall appearance.
- Standardizing the user experience across all ATMs.
- The importance of maintaining data privacy for cardholders.
- Reducing costs for service providers.
Accordingly, the Central Bank emphasizes that all banks operating in the Kingdom and members of the Saudi Payments Network must comply with the provisions of the attached initiative. Coordination in this regard can be made with specialists at Saudi Payments via email (onboarding@saudipayments.com).
For your information and action accordingly, effective from 30/06/2022 G.
1. Introduction
In line with SAMA’s and Saudi Payments’ vision to make continuous improvements in payment infrastructure of the Kingdom, ATM Receipts initiative aims to minimize Cardholders’ dependency on paper receipts for ATM transactions.
The sole objectives of this initiative are to:
√ Enable cost efficiency for Acquirers
√ Maximize customer data privacy and protection
√ Save environment and go green!
1.1 Purpose of Document
The purpose of this document is to assign rules and requirements related to ATM Receipts to external stakeholders who play significant roles in the success of this change. This document is intended to govern the responsibilities of mada Members from multiple aspects for the purpose of ensuring the quality of the solution.
1.2 Scope of Document
This document covers the rules and requirements for ATM Receipts initiative. It also contains detailed workflows of the new enhancements on ATM screens. This document, however, does not contain certification procedures nor terms and conditions.
1.3 Audience of Document
The intended audience of this document is mada Members who are familiar with the basic guidelines of ATM functionalities, and who must comply with these rules at all times.
2. Overview
ATM Receipts is an enhancement initiative that drives the market to minimize dependency on receipts for the four (4) most commonly performed transactions on ATMs.
This initiative focusses on improving and unifying the screen workflow across all ATMs (off-us and on-us) in an attempt to unify user experience and reduce demand on receipts as a result. However, paper receipts shall still be available and provided to Cardholders whenever requested.
Currently, the Home page on ATMs-after inserting the card and entering the PIN-displays the four major transactions (Cash Withdrawal, Balance Inquiry, Mini Statement, and Cash Deposit if available). As part of this initiative, the Home page will be limited to whatever is available of those four transactions and must be fixed and unified across all ATMs (including on-us and off-us). In addition to the four transactions, the Home page also provides an 'Others’ option which opens up to any other transaction(s) and/or service(s) (i.e. PIN Change, Transfer...etc.).
The new enhancement on ATM screen flow runs into two streams: (1) Cash Withdrawal transaction stream, and (2) *Non-cash transactions stream. Each of which has its own mechanism to achieve the same goal of receipt reduction.
*Non-cash transactions include (1) Balance Enquiry, (2) Mini Statement, and (3) Cash Deposit -which is currently available for on-us only.
3. New ATM Screen Workflows
3.1 Cash Withdrawal Transaction Stream
Since Cash Withdrawal is the top transaction in terms of initiation and receipt requests, there will be two separate transactions for Cash Withdrawal:
(1) The first transaction is “Cash Withdrawal" which is presented within the Home page on the ATM. This transaction should not provide a receipt upon completion.
(2) The second transaction is "Cash Withdrawal with Receipt” which will be added inside the 'Others' page from the Home page. This transaction should provide a receipt upon completion.
More importantly, after choosing either of the two transactions, if Cardholder selects one of the listed amounts on the screen, card and cash should be collected immediately and without displaying the account balance. However, in case Cardholder chooses "Another amount” and manually enters the amount, an option to "Confirm and Display Balance” will be given to the Cardholder in addition to the default option(s). The new workflow for Cash withdrawal transactions will be as follows:
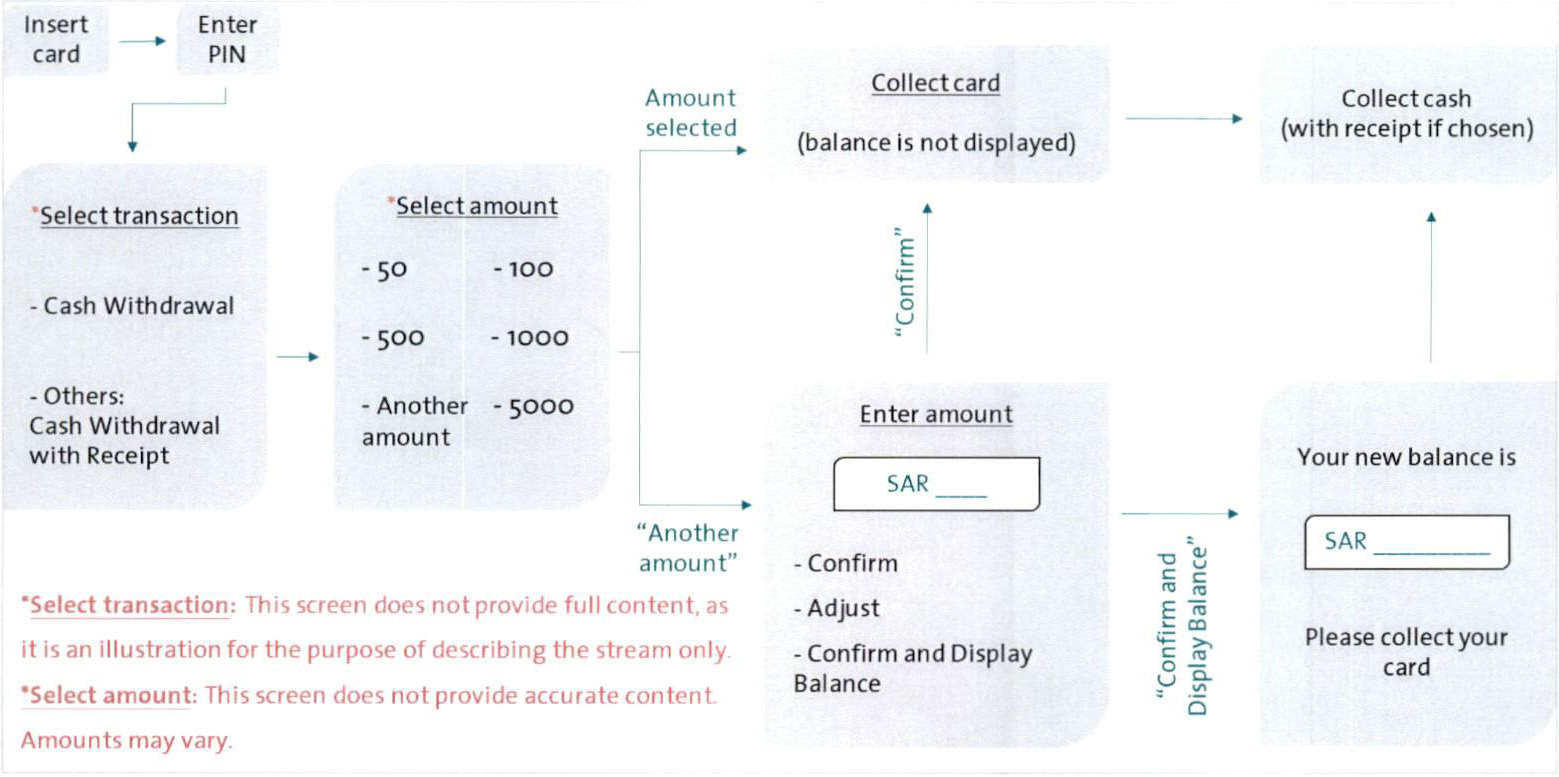
A detailed workflow for the Cash Withdrawal transactions stream can be found in the Appendix.
3.2 Non-Cash Transactions Stream
As mentioned earlier, non-cash transactions include Balance Enquiry, Mini Statement, and Cash Deposit. There will be two changes (or additions) to enhance the screen flow and reduce receipt demand for this stream:
First, upon choosing Balance Enquiry or Mini Statement, the account balance or mini statement, respectively, will be shown on the screen. And upon choosing Cash Deposit, the deposited amount as well as the new balance will be shown on the screen.
Second, at the end of either of the three transactions, a receipt will not be automatically printed. However, an option to "collect a receipt and exit’’ will be given to the Cardholder in addition to the default option(s) - if chosen, the process should be ended and the card should be collected along with the receipt. The new workflow for the non-cash transactions will be as follows:
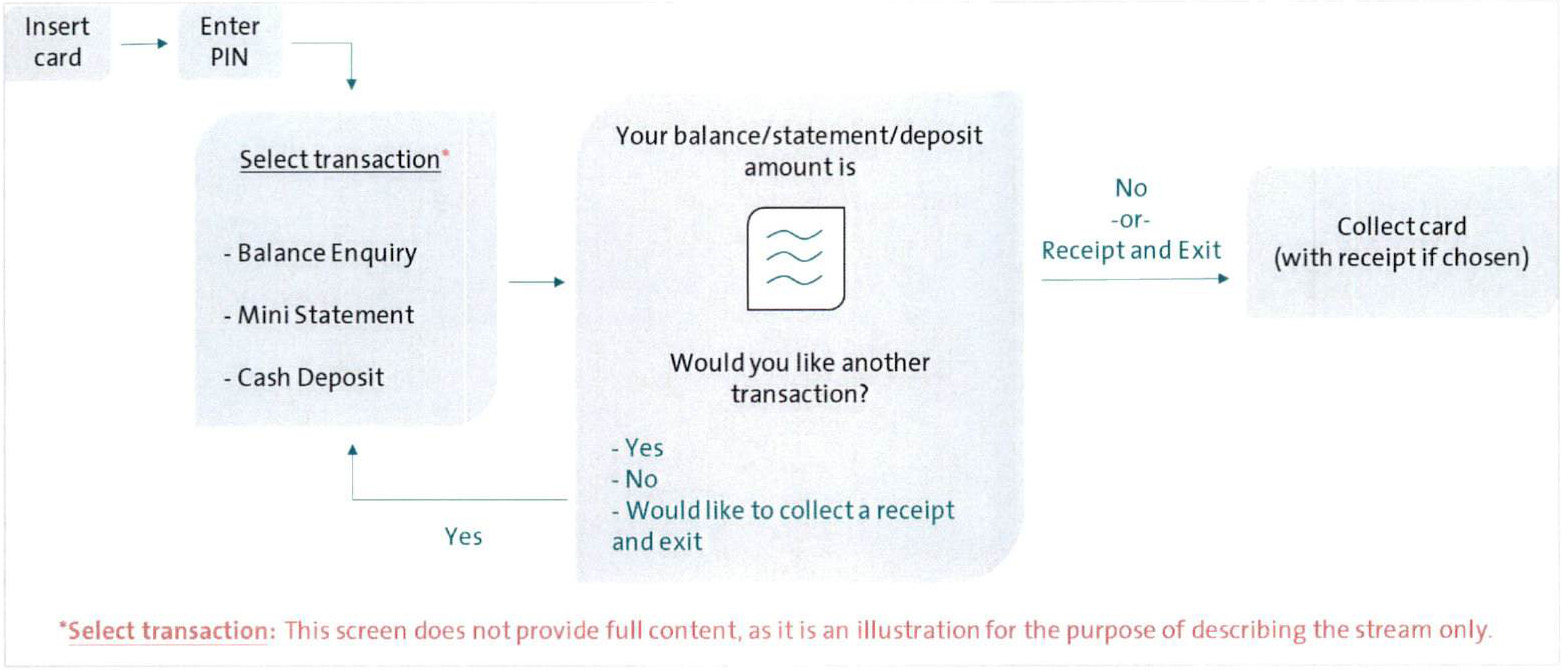
A detailed workflow for the non-cash transactions stream can be found in the Appendix.
4. Appendix
4.1 Workflows for Cash Withdrawal Transactions Stream
4.1.1 Workflow for Cash Withdrawal (without Receipt)


4.1.2 Workflow for Cash Withdrawal with Receipt


4.2 Workflows for Non-Cash Transactions Stream
4.2.1 Workflow for Balance Enquiry

4.2.2 Workflow for Mini Statement

4.2.3 Workflow for Cash Deposit

Adoption of ATM's Electronic Journals
Referring to the discussions held in the Banking Operations Managers Committee (BOOC) regarding the request to cancel the use of paper journals from ATMs and to adopt electronic journals.
We inform you that SAMA has no objection to the adoption of the outputs of the Electronic Data Capture (EDC) for banks wishing to do so when addressing customer claims and complaints, as well as for reconciling and settling ATM transactions instead of using paper journals. It should be noted that in the event of customer claims or complaints and if the bank is unable to obtain a copy of the transaction from either the electronic or paper journal, the bank will bear any resulting responsibilities.
Immediate Response to Any Sudden Power or Communication Disruption in ATMs
Referring to what SAMA recently observed regarding the weak response of some banks to reports of malfunctions related to sudden power or communication disruption in ATMs, and the cash remaining inside the machines for long periods.
Accordingly, SAMA stresses to all banks to respond immediately to any of these cases, and to work on the safety of cash and not to leave it in ATMs for more than 24 hours in the event that it is not possible to resolve problems related to electricity, communications and technical malfunctions.
We also hope that you will inform the relevant departments and your affiliated entities to implement this, act accordingly and include it in your internal procedures as of this date.
SAMA will verify the extent of compliance with these instructions.
Time Out Cash Retract on ATMs
Referring to the Time out-Cash retract in Automated Teller Machines (ATMs), which returns the amount to the ATM in case it is not collected.
We inform you that, due to the emergence of several negative aspects in this feature, banks are required to stop the service as of 1/1/2015.
Maintenance and Feeding of ATMs
Referring to SAMA Circular No. 4567/BCI/123 dated 27/02/1429 H, supplementary to Circular No. 6898/BCI/287 dated 1420 H regarding the procedures and controls to be observed in maintaining ATM machines, including the requirement for ATM maintenance workers to carry permits showing their names and photos, stamped with the official stamp of their organization, and for the companies and institutions performing maintenance to display a specific logo on their vehicles and uniforms. SAMA has observed, during its monitoring of certain ATMs belonging to banks and based on reports from security agencies to SAMA, that some maintenance and feeding workers are using private vehicles and wearing inappropriate clothing that does not comply with the regulations.
Therefore, we hope to confirm adherence to the instructions mentioned in the above circular and inform the contracted companies to comply accordingly. SAMA will monitor compliance with these instructions and apply regulations against any violating banks.
Safety of Cash in ATMs
Based on SAMA's keenness and role in ensuring the safety of cash in circulation and the banks' responsibility for cash in ATMs, SAMA emphasizes to all local banks the necessity of paying sufficient attention to the safety of cash in the ATMs under the bank's jurisdiction, and adhering to the following:
First: Provision of necessary money counting and inspection machines at cash centers, and periodic assurance of the efficiency of these machines and the correctness of their setup (programming).
Second: Compliance With SAMA circular No. 23782/BC/251 dated 14/09/1414 H, and No. 422/M/T and the date 8/11/1413 H, and circular No. 400/B/C/241 and date 21/10/1413 H regarding the inspection of cash and ensuring its safety and quality before feeding it into ATMs.
Third: Increasing bank tellers' awareness of banknotes and their embedded security features, and providing all necessary equipment to verify the safety of the banknotes that are dealt with.
Fourth: ATMs should be fed under dual control and surveillance cameras with TV recording features, with the recorded material retained for at least six months for future reference if needed.
Fifth: Supervision, monitoring, and follow-up by bank officials on the process of feeding ATMs by cash transport companies, and not leaving this to companies only.
SAMA emphasizes the importance of adhering to what has been mentioned above.
ATM Maintenance Procedures
Further to SAMA Circular No. 6898 /BCI/ 287, dated 04/05/1420 H, which outlines the procedures and controls to be observed in maintaining ATM machine, including the requirement for maintenance workers to carry permits with their names and photos stamped with their organization's official stamp, and for maintenance companies and establishments to display a specific logo on their vehicles and uniforms. SAMA has observed, during its monitoring of certain ATM machines belonging to banks and through reports from security agencies, that maintenance and feeding workers have been using their private vehicles and some have not adhered to the regulations.
Therefore, please ensure strict adherence to the instructions outlined in the aforementioned circular and inform your contracted companies of the necessity to comply with these requirements. SAMA will continue to monitor compliance with these instructions and apply regulatory measures against non-compliant banks.
Extension of the Period for Making Inventories of ATMs and Feeding them With Cash
Referring to SAMA Circular No. 2193/BCI/102 dated 13/2/1419 H, which includes internal controls on ATMs and POSs on a daily basis, whether these ATM's are outside the branches or inside them, according to the instructions issued in this regard in the rules and procedures of the Saudi Payments Network (SPAN Business Book) circulated by Circular No. 341000076614 dated 20/6/1434 H. Based on the request submitted by the Bank Operating Officers Committee (BOOC) regarding the extension of the current ATM audit period, and considering the technological advancements in systems and ATMs that support their monitoring and remote access to withdrawal transaction documents, SAMA has decided to extend the scheduled period for making inventory and feeding of ATMs as follows:
• Banks must immediately feed the ATM's when the cash in the ATM reaches 20% of the total cash across all denominations.
• When there are complaints or claims from customers that require the bank to conduct a physical inventory, the bank must do so immediately regardless of the bank's schedule in normal cases.
To review and act accordingly and inform SAMA of what has been done in this regard within a month from its date.
ATM Service Level Agreement (Second Edition)
Based on the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority Law issued by Royal Decree No. 23 dated 23/05/1377 H and the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/02/1386 H, and with reference to Central Bank Circular No. 341000110148 dated 10/09/1434 H on issuing and signing the ATM Service Level Agreement.
We attach to you the ATM Service Level Agreement (second version) approved by the Central Bank, which aims to enhance and elevate the qualiy of ATM services recognizing their significance as a critical electronic channel for facilitating a wide array of banking services. Consequently, the revised agreement will be applied to all ATM services starting from January 1, 2021G. It is imperative to comply with this agreement and any subsequent updates. Therefore, we kindly request that it be signed and returned to the Central Bank within a maximum timeframe of two weeks from the date of receipt.
Note that the bank must send monthly reports in line with the new mechanisms and clauses in the agreement (second version) as of 01/04/2020 G, while continuing to send the current agreement reports as usual until the beginning of the full implementation of the new agreement at the beginning of 2021 G.
Instructions on Forms for Straps of Banknote Stacks of Sixth Edition
No: 42065141 Date(g): 25/4/2021 | Date(h): 14/9/1442 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Referring to the third edition of the instructions for the models of cards for tying the denominations of the sixth series of banknotes, communicated under Circular No. 42018358 dated 22/03/1442 H, and to the issuance of the 200-riyal denomination for circulation on 13/09/1442 H, in order to ensure consistency in the color of the banknote tying cards among banks, and SAMA's branches with the current and previous issues.
Attached is the fourth edition of the instructions for the models of cards for tying the denominations of the sixth series of banknotes, which includes the addition of the card model for tying the 200-riyal denomination, replacing the third edition referenced above.
Please take note and implement this within three months from the date of this notice.
1. General Instructions
1-1 Approve the printing of tying cards for the sixth series of banknotes according to the designs and colour specifications outlined in these instructions.
1-2 These cards must be used for tying the denominations of the sixth series when supplying them to SAMA branches.
2. Requirements to be Included in the Cards
A. The bank's name and logo at the top of the card.
B. The names and signatures of the first and second employees at the bottom of the card.
C. The number of notes and denomination in the center of the card, with the denomination in a larger font size.
D. The issue of the currency in the corner of the card.
3. Colors of the Cards
Distinguish each denomination by printing it in specific colors as follows:
Denomination
Color Value (RGB)
Color Model (RGB)
Color Model (CMYK)
Blue
Green
Red
K
Y
M
C
500 Riyals
230
195
157
10%
0%
15%
32%
100 Riyals
77
77
253
1%
70%
70%
0%
50 Riyals
80
208
146
18%
62%
0%
30%
10 Riyals
131
177
244
4%
46%
27%
0%
5 Riyals
255
204
255
0%
0%
20%
0%
5 Riyals (Polymer)
169
93
211
17%
20%
56%
0%
20 Riyals
202
108
133
21 %
0%
47%
34%
200 Riyals
166
166
166
35%
0%
0%
0%
4. Card Models
No: 42065141 Date(g): 25/4/2021 | Date(h): 14/9/1442 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Attached are the card models for compliance.
Attachments
Compliance with Employing Citizens and the Requirements for Contracting with Recruitment Service Companies
Reference to SAMA Circular No. 1712/BC/88 dated 6/2/1416 H and No. 3851/BC/124 dated 2/4/1410 H and other circulars regarding the implementation of Saudization in jobs within banks, and in continuation of the efforts made by SAMA and the banks in localizing jobs and qualifying Saudis to fill them, and due to the importance of intensifying efforts to achieve the desired goals in line with general directions, SAMA emphasizes the necessity of adhering to the following:
First) Citizens Employment
- The goal is to localize all jobs, of various types and levels, including top leadership and supervisory positions, and not to limit Saudization to certain jobs only. Employment contracts with non-Saudi employees should be considered only if a qualified Saudi candidate is not available at the time, while taking into consideration the stipulations stated in The Labor Law issued by the Royal Decree No. M/51 dated 23/8/1426 H In this regard.
- Appointment and employment in all positions at branches, remittance centers, and cash centers are restricted to Saudis only, without specifying the type of job. Efforts should be made to completely replace non-Saudi employees with Saudi employees by a maximum date of 31/12/2013 G. It is allowed to hire one non-Saudi employee at remittance centers if the bank or money exchange deems the presence of such an employee necessary, provided that their role is limited to assisting and serving customers without having access to the bank's data and automated systems, or conducting banking operations, or opening customer accounts*.
- The appointment to all positions involving financial transactions, the transfer of money, and related roles, as well as positions related to information security and those concerning the combating of money laundering and the financing of terrorism, is restricted to Saudi nationals only across all departments of the bank, exchange offices, branches, and affiliated remittance centers.
- Develop programs and specific timelines for the Saudization of all jobs and provide them to SAMA within three months from this date. Work on recruiting, training, and qualifying national cadres to replace non-Saudis in these positions within a specified period.
- Prohibition of direct and indirect dealings with any entities or individuals working as marketers of banking services within the Kingdom on behalf of foreign banks or financial entities and banning the presence of representatives of such entities within the bank, exchange office, or any of its branches or affiliated centers.
- Develop plans and schedules for training and qualifying Saudis in accordance with the aforementioned instructions and provide them to SAMA within two months from this date.
Second) Adherence to the requirements of contracting with employment service companies
- Selecting companies specialized in providing employment, support services, and verifying the integrity of the contracts concluded with them, as well as ensuring their compliance with and fulfillment of the requirements of SAMA and relevant authorities.
- Ensuring that all employees are working legally and that their job roles correspond to the tasks assigned to them, as well as matching what is recorded in their work permits and residence permits.
Third) Assign the Human Resources Department to develop a plan for the localization of jobs, to train and qualify their occupants, and to begin its implementation. Also, assign the Compliance Department to monitor and oversee its implementation according to the above requirements and to prepare reports at the end of each quarter on the progress of job localization and training until the end of the period.
*According to Circular No. (21755/41) dated 6/4/1440 H, SAMA emphasizes the restriction of all currency exchange business roles (category (A, B)) to Saudis and the necessity of training Saudi employees and enrolling them in suitable training programs that match the nature of their work. Currency exchange institutions and companies must take the necessary measures to ensure full compliance, provided that the time period for Saudization of jobs does not exceed a maximum of January 29, 2020 G. Note that SAMA will take all regulatory measures against exchange institutions and companies that do not adhere to this directive.
According to Circular No. (18910/41) dated 21/03/1440 H, the categories that are treated equivalent to Saudis must be counted in the Saudization rates, in accordance with what is issued by the Ministry of Labor and Social Development and disclosed in the data submitted to SAMA.
Contract with Cash Transfer Companies and Using High-Specification Security Bags
Referring to the letter from His Royal Highness the Crown Prince, Deputy Prime Minister, and Minister of Interior, "may God protect him," No. 225703 dated 28/08/1438 H, regarding the recommendations from the Crime Research Center to require large companies and commercial establishments to contract with cash transfer companies and to use high-specification security bags, and to SAMA Circular No. 371000093183 dated 22/08/1437 H based on the letter from His Royal Highness the Crown Prince, Deputy Prime Minister, and Minister of Interior, "may God protect him," No. 126563 dated 14/05/1437 H, regarding the approval of the results of the security committee formed by the General Security, the Ministry of Finance, and SAMA to review and update the necessary standards and conditions and impose strict and precise controls for conducting the activity of transporting cash, precious metals, and valuable documents to require all companies operating in this field to comply with them. This includes the adoption of using containers for transporting cash, which enable automated tracking and self-destruction of cash if diverted from the proposed route, instead of the current fabric containers.
Therefore, compliance with the instructions mentioned above is required, and cash should only be transported for large companies and commercial establishments through licensed cash transfer companies, using security bags approved by SAMA. Please note that SAMA will conduct field visits to ensure the implementation of these recommendations and impose penalties against violators.
Prohibition on Dealing with Representatives of Private Security Companies and Cash Transport Companies that are non-Saudis
Due to the availability of information regarding certain representatives of private security companies and cash transport companies from non-Saudis negotiating with local banks when seeking to provide security services or cash transport.
SAMA emphasizes to all banks the importance of not engaging or negotiating with any non-Saudi representative of these companies and institutions. They must also inform the relevant authority in the region about the company or institution employing the non-Saudi representative to take the necessary legal actions against them. Furthermore, SAMA reiterates the importance of full compliance with its issued directives regarding compliance with The Law of Private Security Services and its Implementing Regulations, as well as The Law of Transporting Cash, Precious Metals, and Valuable Documents and its Implementing Regulations.
Recommendations for the Cash Transfer System
Referring to the telegram from His Royal Highness the Crown Prince, Deputy Prime Minister, and Minister of Interior (may God protect him), No. 126563, dated 14/05/1437H, which includes the approval of the results of the security committee formed by (Public Security - Ministry of Finance - and SAMA) to review and update the necessary standards and conditions, and to impose strict and precise regulations for practicing the activity of transporting cash, precious metals, and negotiable instruments, requiring all companies operating in this field to comply with them.
Based on this, the committee concluded with a number of recommendations concerning banks and cash transport companies, as follows:
- Require banks to enhance oversight of the performance of contracted companies inside cash centers, adhere to specific procedures and mechanisms for receiving and delivering cash, and impose necessary penalties on violating banks.
- Separate the tasks and responsibilities related to cash transportation from those related to replenishing ATMs:
- Companies must adhere to the regulations and guidelines for the transport vehicle crew involved in cash transportation, consisting of three members (driver, guard, and companion). The guard and companion should be equipped with the necessary firearms.
- When using a transport vehicle for ATM replenishment, the two-person replenishment team (supervisor and replenisher) should never accompany the armored vehicle crew. Instead, they should travel in a civilian vehicle displaying the company logo, following the armored vehicle’s route. This setup will result in a five-person ATM replenishment team (three inside the armored vehicle and two in the civilian vehicle).
- Cash replenishment boxes for ATMs must be filled, secured inside specialized containers, and sealed by an independent team from the cash transport company. This process should be under dual supervision and monitored by CCTV inside cash centers. The ATM replenishment team’s role should be limited to transporting the secured containers and replenishing ATMs according to a preassigned route provided at the start of the workday.
- A separate team (from the bank or the company) at the cash center should be responsible for counting and reconciling the returned cash from ATMs according to the readings from the ATM counters and the bank’s system.
- Companies must adhere to the regulations and guidelines for the transport vehicle crew involved in cash transportation, consisting of three members (driver, guard, and companion). The guard and companion should be equipped with the necessary firearms.
- Implement the use of high-standard cash transport containers as practiced in developed countries, which enable automatic tracking and self-destruction of the cash if the proposed route is altered, replacing the current fabric containers.
- Leverage credit information from the Credit Information Company (SIMAH) to review the credit history of individuals applying for jobs at cash transport companies and other legitimate sources to assess the suitability of employees in this field.
- Provide SAMA with the procedures and mechanisms followed by the bank to monitor the performance of companies contracted for cash transport and ATM replenishment. This includes doubling supervision and monitoring the movement of cash transport vehicles, precious metals, and negotiable instruments, as well as tracking the time allocated for cash transport and ATM replenishment to and from the bank premises. Additionally, review the rotation of employees in cash centers, cash transport, and ATM replenishment, and work on improving training programs to enhance the performance and efficiency of employees in both the contracted companies and banks.
Therefore, we request that you proceed with the swift implementation of the above-mentioned recommendations and provide us with an update within two weeks from this date. It is worth noting that arrangements are currently being made to allow licensed cash transport companies to establish their own cash processing units to serve the ATMs of all the banks they contract with, following the necessary approvals from SAMA and the Ministry of Interior. These units will be governed by unified security standards, procedures, and requirements. The license for operating such cash processing units will be granted for a maximum of three years, renewable, with the aim of improving service levels and preparing local companies to manage and operate unified cash centers, which will be established by SAMA.
- Require banks to enhance oversight of the performance of contracted companies inside cash centers, adhere to specific procedures and mechanisms for receiving and delivering cash, and impose necessary penalties on violating banks.
Mechanism for the Entry and Exit of Saudi and Foreign Currency via King Fahd Causeway
No: 371000035276 Date(g): 3/1/2016 | Date(h): 24/3/1437 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Referring to the agreement with the Customs Authority regarding the mechanism related to handling the entry and exit of Saudi and foreign currency through the King Fahd Causeway customs, please adhere to and implement the following directives:
First: Mechanism for the Entry and Exit of Saudi Currency through King Fahd Causeway Customs
The current mechanism for handling Saudi currency, as agreed upon between the General Customs Authority and SAMA in the coordination and cooperation record dated 10/4/1435H, shall continue. According to this mechanism, customs employees at King Fahd Causeway are responsible for sealing the Saudi currency transported through the customs for banks and exchange companies, and then sending it to SAMA branch in Dammam for inspection, as follows:
- A financial declaration form for the cash amounts (entry) is filled out electronically using the automated financial declaration system. The form indicates the number of containers or packages received, the sequence of their seal numbers, and the total amount sent.
- The financial declaration form is faxed from the King Fahd Causeway customs to SAMA branch in Dammam, and a copy is handed over to the bank representative or the exchange company.
- Upon deposit at SAMA branch, the number of packages and the customs seal numbers provided in the letter of King Fahd Causeway customs is verified by the Treasury Division at SAMA branch in Dammam. The cash packages are then reviewed and accepted under counting and are set aside with the customs letter until they are counted and verified for accuracy.
- King Fahd Causeway customs will be notified by SAMA branch in Dammam in the event of any unusual discrepancy, such as a mismatch between the declared amount and the received funds, concerns about the currency's condition, the failure of the funds to arrive as per the customs letter sent by fax to SAMA branch, or delays in delivering the funds to SAMA.
Additionally, King Fahd Causeway customs will receive a letter from SAMA branch when local banks request to export financial amounts abroad after sealing them in a container or package, detailing the amount and seal numbers. A copy of this letter will be faxed simultaneously to King Fahd Causeway customs and the bank representative.
- A financial declaration form for the cash amounts (entry) is filled out electronically using the automated financial declaration system. The form indicates the number of containers or packages received, the sequence of their seal numbers, and the total amount sent.
Second: Mechanism for the Entry and Exit of Foreign Currency through King Fahd Causeway
After completing the approved immediate clearance procedures at King Fahd Causeway Customs, the following steps are taken:
- The Gulf vehicles transporting foreign currency are sealed with a metal seal by the customs officer.
- A letter is signed by King Fahd Causeway Customs addressed to SAMA branch in Dammam, with a copy sent to the benefiting bank or exchange company.
- The vehicles are allowed to depart to the cash centers of banks and exchange offices. If the vehicle is armored, approval from the General Customs Authority is required, as its entry is restricted.
- In the case of discovering counterfeit currency, SAMA branch in Dammam is notified, which in turn informs King Fahd Causeway Customs and returns the counterfeit amounts to the customs for necessary legal procedures.
- SAMA branch in Dammam is notified, and it will officially inform King Fahd Causeway Customs in case of any unusual violation, such as a discrepancy between the declared and received amounts, the condition of the currency, failure of the amounts to arrive as indicated in the customs letter sent by fax to SAMA, delays in receiving the amounts, or any other reasons.
- The Gulf vehicles transporting foreign currency are sealed with a metal seal by the customs officer.
Third: Regulations for the Entry of Gulf Cash Transport Vehicles into Saudi Arabia
- Gulf vehicles transporting foreign currency into the Kingdom must comply with the technical specifications for the armoring of cash transport vehicles as outlined in the implementing regulations issued by Ministerial Decision No. (4814) dated 09/10/1433H. These specifications pertain to the Transporting Cash, Precious Metals, and Negotiable Instruments Law, issued under Royal Decree No. (81/M) dated 18/10/1428H.
- Entities importing Saudi and foreign currencies (banks/exchange offices) are required to deploy an armed security escort vehicle to accompany the Gulf vehicle transporting foreign currency. The security vehicle must belong to an entity licensed to operate in transporting cash, precious metals, and negotiable instruments, and should be stationed outside the customs area awaiting the foreign currency transport vehicles for escort.
- Gulf vehicles transporting foreign currency into the Kingdom must comply with the technical specifications for the armoring of cash transport vehicles as outlined in the implementing regulations issued by Ministerial Decision No. (4814) dated 09/10/1433H. These specifications pertain to the Transporting Cash, Precious Metals, and Negotiable Instruments Law, issued under Royal Decree No. (81/M) dated 18/10/1428H.
Cash Transfers must be Coordinated with Security Authorities Well Enough in Advance
Further to SAMA's circular No. 5922/BCI/62 dated 08/04/1421H, which includes specific guidelines for feeding ATMs, particularly the paragraph concerning the necessity of coordination and notification of security authorities during the cash transfer, we inform you that SAMA has received a letter from its branch in Buraidah containing observations from the Qassim Region Police on the reporting process. These reports are being received upon the arrival of the feeding officials at the ATMs, which disrupts the work of the security authorities and results in delays in the security agencies carrying out their duties.
Therefore, we hope to inform and ensure coordination with the security authorities for transportation operations in a timely manner so that the security authorities can perform their duties as required in various regions and governorates of the Kingdom.
Internal Controls on ATMs and POSs
In Reference to our previous circulars No. BC/588 dated 24-9-1415, No. BC/353 dated 10-7-1415 and No. BC 214 dated 1-8-1414, regarding internal controls presently applied on ATMs and POSs and the procedures and problems connected therewith; and
In view of the increase of complaints by some people who insist that they are not receiving the money they ask for from ATM; and
In view of the importance of this matter in enhancing public confidence in the banking sector in general and the ATM and POS services in particular,
SAMA would like to emphasize the following:
Banks must conduct a daily inventory of all ATMs, whether inside or outside branch premises.
Banks must use SAMA's ATM Balancing Sheet by those in charge of feeding the ATM, signed by the teller and approved by the section head or the cashier.
Cash surplus found in the ATM (resulting from the daily inventory and belonging to the clients who did not cash it for technical reasons) must be paid immediately to the client without his request. Claims among banks should be settled within one week from the date of the claim through CAPS.
Banks must settle such claims with their clients (debits or credits) within one week from the date of the claim. If the claim is rejected the bank has to explain the reasons.
If requested by SAMA, the bank has to submit the operation receipt, the journal tape and the daily inventory minutes in one week at the latest in order to settle these claims the soonest possible.
In addition to the daily inventory made by those in charge of ATMs, the internal auditors of the bank must conduct monthly surprise inventory of ATMs and keep a record which can be referred to, if needed.
The bank must periodically test and maintain ATMs and POSs to avoid reverse operations and any other technical problems which increase client and bank claims, in view of the negative effects on the services of ATMs and POSs.
The treasury and secret numbers of the ATM should be under dual control and the secret number is disclosed only by management approval.
The bank that issues the card must pay the amount of reverse claims caused by insufficient balance in the account of the card holder at the time of the claim without asking for the receipt of the purchase operation at POS, in order to settle the claims of merchants and banks together and enhance their faith in the POS service. The bank will then follow up with the card holder to recover its money.
One of the bank employees must be appointed as a liaison officer responsible for following up on ATM and POS cases. His name and phone number must be passed on to SAMA within one week.
Please be informed and comply as of this date. In case of a violation of any of these instructions the bank shall be responsible for consequences.
Criteria and Requirements for Operating a Cash Transportation Service
Referring to the telegram of His Royal Highness Prince Abdulaziz bin Saud bin Nayef bin Abdulaziz, Minister of Interior and Chairman of the Supreme Commission for Industrial Security No. 54033 dated 10/3/1440 H, which included the approval of the recommendations of the committee formed by specialists from the Ministry of Interior, the Ministry of Finance and SAMA to review and update the standards and conditions necessary for practicing the activity of transferring cash, precious metals and valuable documents, and to SAMA’s circular No. 371000093183 dated 22/8/1437 H, which included recommendations for the cash transfer law.
Accordingly, His Highness’s telegram included a number of final recommendations and specified the tasks required of the parties concerned with this activity, as follows:
- All licensed cash and precious metals transport companies and institutions are required to have their vehicles fully armored, including sides and roofs, and with standard bulletproof armor of type (Vpam6) as a minimum issued by the European Committee for Standardisation and in accordance with the approved technical terms and specifications attached to the circular. Note that armoring of cash transport vehicles is optional if the feature of using high-specification containers and security inks for transporting cash is available, after obtaining the approval of the General Secretariat of the Supreme Commission for Industrial Security.
- Cash transport vehicles must have an independent security permit issued by the General Secretariat of the Supreme Authority for Industrial Security (Central Security Licensing Unit). The Secretariat also issues permits for armoring vehicles, establishing factories and importing requests for armored vehicles through its electronic portal. Cash transport companies must submit a license renewal request three months before its expiration. It is prohibited to practice the activity with an expired license. Cash transport companies must carry out periodic preventive maintenance on their vehicles on an ongoing basis, and the expected life of cash transport vehicles must not exceed five years from the date of their entry into service.
- Banks, currency exchangers and Cash Transfer Companies are committed to strengthening control over the work of companies contracted to transport cash within cash centers and to inform the security authority (Public Security) of any company that violates the application of the law against it, and to adhere to the procedures and mechanisms for receiving and delivering cash.
- Banks, currency exchangers and cash transfer companies and institutions are committed to the laws and regulations specified for the cash transfer vehicle crew, which consists of only three individuals (driver - guard - companion), provided that the guard and companion are armed. In the event that cash transfer vehicles are used in the activity of replenishment ATMs, the companion who works within the armored vehicle crew is responsible for replenishment the ATMs, and this requires the availability of electronic locks on the device safes.
- It is necessary for workers on cash transfer vehicles to use encrypted communication devices that are difficult to hack.
- Cash transfer companies are obligated to register cash transfer contracts and employees at the Central Security Licensing Unit at the General Secretariat of the Supreme Authority for Industrial Security and to screen employees for security.
- Banks, and Currency Exchangers are obligated to install surveillance cameras covering all facades of their sites, customer parking lots, the delivery and receipt area for cash transfer vehicles and all sensitive areas such as ATMs, and to connect them to the television camera recording unit so that the recording is kept for a period of no less than six months.
- When receiving and delivering shipments, the vehicle must be stopped in the closest place to the receiving and delivery point, so that the vehicle door is in front of the bank or merchant.
- The ATM replenishment cassettes must be filled and placed in the designated containers and secured by an independent work team under dual supervision and under the recording of the television cameras inside the cash centers, so that the role of the field replenishment team is limited to transporting the cash containers for the ATM and replenishment them to the machine according to a route given to them at the beginning of the work day and the security authorities are informed of the route. The aforementioned independent work team shall undertake to reconciliation and verification the ATM's with the cash returned from the ATM's according to the readings of the ATM meters and the bank law, and this shall be under the recording of the television cameras.
- The ATM replenishment process should be limited to replacing the cassettes equipped with cash only, and no transfer of currency from one box to another should be carried out during the ATM replenishment process, regardless of any cash amounts in the replaced box, and ATM maintenance should not be linked to the teller replenishment process, while emphasizing to workers the need to quickly complete the replenishment task as quickly as possible.
- Cash transfer companies, banks, Currency Exchangers are committed to using high-specification containers for cash transfers when receiving and delivering cash to and from branches, cash centers, remittances, Currency Exchangers and the retail sector, which allow automatic tracking and self-destruction with security inks for cash in the event of changing the specified route, or attempting to forcefully open it, tampering with it or vandalizing it in an irregular manner according to the approved technical terms and specifications attached to the circular, within six months from its date.
- Working hours for replenishment and maintaining ATMs are throughout the week, including official holidays and weekends, and around the clock for the main cities (Makkah, Madinah, Riyadh, Jeddah, Dammam and Khobar), commercial centers, airports and train stations, while the rest of the cities of the Kingdom are from seven in the morning until ten in the evening, except for what is specified by the security authorities.
Attached are the terms, requirements and technical standards for the design and manufacture of armored vehicles for transporting cash, precious metals and valuable documents, specifications for inks and security cash transport containers, and general requirements.
We hope to work quickly to implement the recommendations, terms, requirements and technical standards attached to you, and in the event of any difficulties you may face, we hope to coordinate this with the Advisor to the Deputy Governor for Banking Operations.
Follow-up circular on Instructions to Be Followed When Opening, Relocating or Closing Bank Branches, Instant Remittance Centers and ATMs, Whether Operational or Non-Operational
Further to the Central Bank Circular No. BCP/214 dated 25/4/1416 H regarding the Central Bank's observations made by various banks, as well as Central Bank Circular No. (485/BC/36) dated 07/01/1416 H attached to the Security Safety Manual, the Central Bank emphasizes the necessity of compliance with all outlined directives.
1-The bank must adhere to the security safety requirements outlined in the aforementioned guide for all new branches, offices, or ATMs and provide the Central Bank with a certificate from the security consultant confirming compliance with these requirements.
2-No bank is allowed to open new branches, offices or ATMs in any region of the Kingdom without obtaining an official license from the Central Bank.
3-Upon obtaining the Central Bank's license to open a branch or install an ATM, any relocation of the branch or ATM, regardless of its operational status or non-operational, is prohibited without obtaining a written approval from the Central Bank.
4-When the bank obtains the Central Bank's approval to open a branch in any location, the installation of the ATM in the branch is subordinate to the branch license, and there is no requirement to secure a separate license for the ATM; however, it is necessary to notify the Central Bank of this installation.
5-It is not permissible to merge an independent ATM license (outside the branch premises) with any branch, whether operational or non-operational.
6-The license is valid for a period of nine months from the date of its approval. The bank shall ensure the completion of the opening process within this period. Should the bank be unable to finalize the opening within the stipulated period, it shall notify the Central Bank of the reasons for the delay prior to the expiration of the license.
7-Licenses for non-operational branches are extended every six months to allow the bank to equipe the location.
8-A bank shall submit a report to the central bank biannually, detailing its status regarding the establishment of new branches and the installation of ATMs.
9-When requesting approval to open a branch or install an ATM, each bank must attach the following data
- A feasibility study for opening a branch or installing an ATM.
- A blueprint or showing the exact location of the requested branch or the exact location of the ATM.
10-The Central Bank must be notified of the actual date on which the branch opens and begins operations, or the date on which the ATM becomes operational.
Operational Rules
Account Opening Rules
No: 65681/67 Date(g): 3/7/2019 | Date(h): 1/11/1440 Status: In-Force Arabic shall be the language used in construing these Rules.Chapter I. Definitions
The following terms and phrases, wherever mentioned herein, shall have the meanings
assigned thereto unless the context otherwise requires:1. SAMA:
The Saudi Central Bank
2. Rules:
Rules for Bank Accounts.
3. Bank Account:
An accounting record maintained by a bank licensed to operate in Saudi Arabia. Such a record is generated under a contract called "Account Opening Agreement" between the bank and the account holder (the Customer) or its representative. The Agreement sets out the rights and obligations of each party including accounting entries posted by the bank in accordance with the applicable regulations and the acceptable rules and practices agreed upon under the account opening agreement, other agreements signed by the two parties, and other instructions given by the account holder to the bank.
4. Freezing of Account:
A temporary suspension of withdrawal/transfer or the like from a bank account/relationship due to the expiration of the customer’s ID; non update by the customer or his representative of KYC data or violation of any provision of the Account Opening Agreement.
5. Bank Verification:
Placing the bank official stamp or the like in addition to the bank employee signature and stamp on a copy of a document or ID card to confirm that it is a copy of the original.
6. Special Purposes Entities
Entities established and licensed under Rules for Special Purposes Entities, issued by the Capital Market Authority.
7. Government Entities:
Government entities, public institutions, authorities, funds and the like, whether they have appropriations in the State general budget or not.
8. Foreign Schools:
Schools licensed by the Ministry of Education that apply non-Saudi curriculum and are subject to the Regulation for Foreign Schools in Saudi Arabia. They are different from educational institutions of foreign embassies.
9. International Multilateral Organizations:
International organizations in Saudi Arabia that exist under a headquarters agreement (license), signed by Saudi government, such as the Muslim World League, World Assembly of Muslim Youth and the like.
10. Chambers of Commerce and Industry:
Non-profit organizations that represent commercial and industrial interests before public entities and protect and develop such interests. They have their own Boards of Directors.
11. Freelancer:
A self-employed person (who gets paid per hour, day, or work) rather than working for an employer in exchange for a monthly salary.
12. Minor:
A male or female under the age of 18 Hijri years.
13. Curator:
A person appointed by a Guardianship Deed issued by the competent courts to be a guardian of a minor.
14. Guardian:
The father of a minor or a person appointed by the court under a Guardianship Deed.
15. Custodial Person:
A person appointed by the court under a Custody Deed authorizing him/her to receive the allowances provided by public or private entities to a child in his/her custody.
16. Legally Incompetent Person:
A person not allowed to manage his/her money under a court deed that proves the lack or loss of mental capacity.
17. Private Associations and Foundations:
Associations and foundations as defined in the Civil Associations and Foundations Law.
18. Philanthropic/Charitable Committees:
Committees licensed by local government entities to serve the public, such as Patients’ Friends Committee and Disabled Persons Committee and the like.
19. National Societies and Committees:
Societies and committees established pursuant to a royal approval or a resolution by the Council of Ministers to perform specialized roles to serve the public interests.
20. Cooperative Associations and Funds:
- Cooperative associations:
An associations formed by individuals in accordance with the provisions of the Law of Cooperative Associations to improve the social and economic conditions of its members in production, consumption, marketing or services through the joint efforts of the members using cooperative principles.
- Cooperative funds:
Funds established by the employees of a government agency or a company in accordance with the provisions of Cooperative Funds. The source of funding is member contributions. Such funding is mainly used to cover social, cultural and sport activities of the Fund's members.
21. Foreign Endowment(2):
Endowment for specific Saudi individuals or Saudi charities inside Saudi Arabia owned by natural or juristic non-Saudi persons with one or more Saudi legal agents.
22. Escrow accounts for off-plan sale or rental real estate projects (6):
A bank account for depositing the amounts paid by financiers, buyers or tenants for the project.
23. Escrow Accounts for Real Estate Contributions Project (7):
A bank account for depositing real estate contribution funds.
24. Scientific Societies (3):
Societies established in Saudi universities under their direct management and supervision in accordance with the Rules for Scientific Societies in Saudi universities.
25. Professional Associations (3):
Juristic and financially independent associations established to improve specific professions and work under the supervision of a government entity authorized to do so.
26. Payment Service Providers (1):
Any entity qualified and licensed by SAMA to provide one or more payment services in the Kingdom in accordance with SAMA'S relevant instructions.
27. Debt-Based Crowdfunding Company (4) (5):
a joint-stock company licensed to engage in Debt-Based Crowdfunding activity.
28. Finance Amount (4) (5):
funds raised from Participants via a Debt-Based Crowdfunding Platform to be provided for an Institutional Beneficiary.
(1) This paragraph has been added pursuant to the circular No. (42073085), Dated 21/10/1442H, corresponding to 01/06/2021G.
(2) This paragraph has been amended according to the circular No. (41042946), Dated 19/06/1441H, corresponding to 13/02/2020G.
(3) This paragraph has been added pursuant to the circular No. (41039895), Dated 08/06/1441H, corresponding to 02/02/2020G.
(4) This paragraph has been added pursuant to the circular No. (42075950), Dated 29/10/1442H, corresponding to 09/06/2021G.
(5) This paragraph has been amended according to the circular No. (000046024651), Dated 19/04/1446H, corresponding to 22/10/2024G.
(6) This paragraph has been amended according to the circular No. (46028059), Dated 08/05/1446H, corresponding to 09/11/2024G.
(7) This paragraph has been added pursuant to the circular No. (46028059), Dated 08/05/1446H, corresponding to 09/11/2024G..
Chapter II. Supervisory Rules and Controls
1. Electronic Record
For the purpose of setting up a unified electronic database for bank accounts, all banks shall establish an electronic registration system in accordance with the classification set forth in Appendix (C) and its updates and based on the information provided in the approved IDs. This system serves as an electronic record, and should include the requirements provided in the paragraphs below as well as the detailed requirements provided in Chapters III and IV herein, as a basis for opening, operating, and following up bank accounts.
1.1 Saudi Natural Persons
- Banks must have in place an electronic record for all Saudi nationals having, as a minimum, the following:
a. The full name (first, second, third and family name) as shown in the ID.
b. ID number.
c. ID expiry date.
d. National address and contact information.
e. Employer (if any).
- Information used shall be based on the national ID, family register for minors, or birth certificate for people of special circumstances staying at housing centers of the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development and shall be obtained from reliable sources.
1.2 GCC Natural Persons
- Banks must maintain an electronic record for all GCC nationals having, as a minimum, the following:
a. The full name as shown in the national ID.
b. National ID number.
c. National ID expiration date.
d. Nationality.
e. Address and contact information.
f. employer (if any).
- Information shall be obtained from the national ID and from reliable sources.
1.3 Non-Saudi Natural Persons
- Banks must maintain an electronic record for all non-Saudi natural persons having, as a minimum, the following:
a. The full name as in the passport or Iqama and in the same language according to the following priority (Arabic - English- Latin alphabets). If the name is in any other language, the name provided in the entry visa granted by Saudi embassies and consulates should be used.
b. Nationality.
c. Iqama No. and validity date.
d. National address and contact information.
e. Employer (if any).
- For persons holding Iqama cards with five-year validity period that is given to some tribe members, the full name, number and validity date of the card shall be written.
- No accounts may be opened for expatriates holding Saudi passports except with the approval of the Ministry of Interior through SAMA.
1.4 Juristic Persons
- Banks must maintain an electronic record for all juristic persons having, as a minimum, the following:
a. The official full name of the juristic person as per official documents.
b. Commercial register number or license number if the activity does not require a CR, (if the account is opened for the main commercial register, the main commercial register number shall be written. However, it the account is opened for a subsidiary commercial register, the subsidiary commercial register number shall be written. The main commercial register accounts shall be electronically linked with the subsidiary commercial register accounts).
c. The ID numbers of the owners as indicated in the last update of memorandum of association and persons authorized to manage the accounts (owners of joint stock companies are exempted from providing their ID numbers).
d. Signature of the person authorized to manage the account.
e. The national address of the juristic person.
f. Tax No. (if any).
g. Legal Entity Identifier (if any).
- For accounts opened pursuant to official approvals or applications, the reference number, date and name of body issuing such approval or making such application shall be recorded.
2. Requirements for Inspection Purposes
Banks shall use an electronic search system to perform the routine search according to information required in the electronic records under each category. Such search shall cover all transactions, relationships, products and services offered to customers in addition to express transfers and investment deposits.
3. Freezing of Bank Accounts Upon Expiration of Identification Documents
3.1 Freezing of Bank Accounts
As a rule between banks and customers, the relationship must start and continue under valid identification documents and IDs for all transactions, whether those covered by the definition of bank account in Chapter I or other contractual relations or account-related services.
3.1.1 Saudi Natural Persons
Banks must freeze all accounts held by Saudi natural persons upon the expiration of the documents provided below unless the account holder presents a renewed document or a valid ID card. A bank may verify ID renewal without requiring the customer attendance via trusted and independent source and it shall document that. The following are the documents to be presented by Saudi customers prior to opening or maintaining a bank account:
- National ID Card: The account opened by an ID card shall be frozen after the elapse of (90) days from expiry date and shall not be reactivated except after renewal.
- Family Register for Minors: An account opened for a minor under a family register shall be frozen upon the elapse of five years from the account opening date or five years from last account update. Presence of the minor is not required as the presence of his/her guardian or curator will suffice. The bank shall inform the guardian or curator, (90) calendar days prior to the minor reaching the age of (15) Hijri years, to update such account and present a valid national ID of the minor.
- Birth Certificate of Children of Special Circumstances: The account must be frozen when the minor reaches the age of (15) Hijri years and may be reactivated when he/she is issued a valid ID card or when a letter is received from the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development requesting continuation of the account until the minor reaches (18) Hijri years.
3.1.2 Non-Saudi Natural Persons
Banks shall freeze all accounts and transactions of all non-Saudi natural persons after (90) days of the expiration of the documents mentioned below. After (180) days of the expiration of the ID, the account balance shall be transferred to an unified account created by the bank for such cases. After 5 years from the date of last transaction/dealing carried out by the customer in his/her account, the balance shall be transferred to the suspense account created for unclaimed accounts and all outstanding obligations of the customer during and after this period shall be met. Also, all accounts of expatriates must be closed upon their final exit. The documents are as follows:
- National ID Card for GCC citizens.
- Iqama for expatriates.
- Diplomatic card for diplomats.
3.1.3 Juristic Persons
All banks must:
- Freeze all accounts of juristic entities after (90) days from the expiration date of the respective authorization to practice their activity (license, commercial registration, etc.) unless the customer provides a renewed authorization or any document valid for (90) days from a the responsible authority proving that it is being renewed.
- Freeze all accounts of juristic persons and organizations whose documents of opening their accounts do not contain a validity date, such as the accounts of charity and welfare societies or organizations, government accounts and licensed schools and the like upon the lapse of five years from the date of opening the account or the date of last update to the account until the account data is updated.
- Freeze the relationship with correspondent banks upon the end of the period specified in Rule (4) and until all requirements of KYC and AML/CFT are fulfilled.
- Monitor the ID validity of the directors and authorized signatories of juristic person accounts and freeze and suspend their powers to operate the account only, depending if they are Saudis or non-Saudis, until the renewal of IDs. This shall also be applicable to sole proprietorship owners.
3.2 General Instructions for Freezing of Bank Accounts
- The bank must ensure that the account opening agreement, contractual relationships and services state that the bank has the right to freeze the account upon the expiration of the customer’s ID and/or when the customer does not update his/her personal and financial data and addresses.
- The bank must notify the customer of the account freezing date at least (30) days in advance, and must have adequate processes in place to ensure the same with respect to each customer or authorized person acting on his behalf and such processes should be documented.
- A joint account with a single or joint signature must be frozen upon the expiration of the ID card of either of the account holders.
- Freezing order issued due to the expiry of identification documents other than the national ID may be lifted upon presentation of a valid national ID. However, banks shall not lift freezing order on accounts opened by a national ID if other identification document is presented.
- Natural or juristic persons shall have the right to close their own accounts or any accounts they are authorized to operate (only single transaction) that are frozen due to the expiry of IDs or failure to update their data, provided that the customer completes a form prepared by the bank for this purpose and that the procedures stated in account closure instructions are applied.
- If the request to freeze the account of an expatriate is made after his final exit from Saudi Arabia, and if the account balance is less than SAR (50,000), banks may transfer the money to the owner with the approval of the bank's compliance department, according to procedures set by the bank depending on the customers, their countries and signature checks. However, if the account balance is over SAR (50,000), the money shall only be transferred to the owner upon a request approved by the correspondent bank of the local bank or the branch of the resident foreign bank. Banks are not allowed to transfer only part of the balance. The balance shall only be transferred abroad to the account holder or the legal agent of his/her heirs upon the approval of the compliance department.
- In case an expatriate customer requests the bank to transfer the balance of his/her account immediately after his/her previous final exit and presents a visa other than the work visa, the balance exceeding SAR (50,000) may only be paid upon the approval of the compliance department after evaluating the account. If such a customer directly applies to the bank and submits a new Iqama issued under the same passport or a new passport, the frozen account shall be closed if it is still within the freezing duration, before (180) days, and a new account shall be opened for him/her and the amount shall be transferred to the new account, and thereafter he/she shall be allowed to deal on such account.
3.3 Freezing Exceptions
Banks shall not allow a customer or its authorized person to carry out transactions from his/her accounts after the expiration of his/her ID, unless upon renewal thereof or updating his/her KYC data. The following shall be exempted from freezing:
- Personal deposits or deposits received through clearing and local and international transfers, SARIE payments/ collections and salaries of employees.
- The customer existing obligations already effected by the bank with or on behalf of the customer in favor of the bank or third parties (government or non-government) before the expiration of the ID of account holder or authorized representative. Such obligations include, but are not limited to, payment of credit cards, loans, direct debit payments, standing regular instructions for payments such as payment of utility bills, letters of credit and letters of guarantee etc. These also include high risk investment transactions due to price fluctuations that are likely to inflict damages to the customer, in which case the customer would be called upon by a bank officer and given a maximum period of (60) days from the date of executing the transaction to have his ID renewed.
- Standing instructions governing Saudi account not related to outstanding obligations are allowed to continue after the freezing of the account subject to the approval of the operation manager at the bank's Head Office, for a limited number of times and for a maximum period of (180) days as of the ID's expiry date. The bank should lay down the procedures and the policies which ensure control and activation of these cases in terms of limits and number of times.
- Accounts of Saudi (male and female) diplomats, students on scholarship abroad, patients with chronic diseases staying at hospitals or other places and their accompanying family members, prisoners and the like, soon after the bank becomes aware of them, in which case they may be given (180) days from the date of expiration of ID for unlimited number of times after obtaining the approval of the bank’s compliance department manager. In order to extend the period specified, an approval from the bank’s CEO/general manager and the compliance department must be obtained. Banks shall contact their customers using the preferred method of contact according to their files or the procedures banks deem appropriate to encourage customers to renew their IDs.
- For the accounts of the State employees whose salaries are delivered through banks and whose accounts are frozen and are not able to present national IDs because of certain formality problem in respect therewith, they shall be allowed a 180 days' delay period after the date of expiration of their identification documents or updating due date, after presenting the official employment card or an official reference letter.
4. Updating Account Data
Customer identification must be established at the outset of relationship. As a measure of control, banks must require all their customers to update the database of their accounts with the bank according to the cases and the periods provided in these Rules. The updating process must include the customer ID, personal information, national address, financial information including personal information of the customer’s authorized representatives/agents and information of the beneficiary of legal persons. Banks shall establish permanent procedures and policies for the updating process which shall be carried out as follows:
4.1 Updating the Customer’s ID
a. Updating official identification cards and documents by type/duration.
- Identification cards and documents that are valid for less than five years shall be updated upon expiration, such as commercial register or license.
- Identification cards and documents that are valid for more than five years shall be updated every 5 years or upon expiration, whichever comes first.
- Accounts opened under official approvals or letters, such as accounts of government entities, embassies and the like and international organizations and the like, or under open-term licenses and registrations, such as accounts of private associations, foundations and schools, shall be updated every 5 years maximum.
b. Updating identity information online:
- Banks, at their discretion, may update identity information online for customers*.
- Incompetent persons or the like shall not be allowed to use this service.
- Banks shall check the validity of and document the identification documents by using documents, data or information obtained from reliable and independent sources.
* This paragraph has been amended according to the circular No. (42033441), Dated 20/05/1442H, corresponding to 03/01/2021G.
4.2 Updating Customer Information
a. Banks may update the customer information in any of the following cases:
- The customer information is outdated (the period specified has ended), or there is a change in the customer information, for example, a change in the commercial entity’s board of directors;
- The customer's behavior in executing financial transactions on the account has changed.
- The bank performs due diligence in case of ML/FT risks.
b. Banks shall understand that official identification documents and approvals can be used to update account approvals; however, using such documents only is not sufficient to update the customer information.
c. Accounts of correspondent banks shall be updated every three years maximum.
d. Banks may accept updating the information of the customer via electronic banking services (e.g. online or phone banking) for those subscribing to such services, provided that the identification information is verified and documented using documents, data or information obtained from reliable and independent sources*.
* This paragraph has been amended according to the circular No. (42033441), dated 20/05/1442H, corresponding to 03/01/2021G.
5. Inoperative Accounts
This rule has been respectively amended according to the circular No. (44071426), Dated 07/09/1444H, corresponding to 28/03/2023G, and circular No. (46015210), Dated 06/03/1446H, corresponding to 09/09/2024G.Accounts, relationships and transactions shall be considered non-moving after two calendar years from the date of the last financial transaction carried out by the customer, his/her authorized representative, or his/her heirs. Inoperative accounts are divided into three types as described in this Rule. The purpose of this Rule is to keep accounts active, save the customer assets (money) that have not been used for a financial transaction (withdrawal or deposit – depending on the nature of the relationship), recorded debit transactions, or documented correspondences during the period specified in Article (5.2). The Rule also supports communicating with customers, returning the rights to their owners upon request immediately after the completion of documents and necessary procedures, changing account status to abandoned if banks are unable to reach the account holder after using all methods of contact. Accounts of government entities shall be excluded from the provisions of this Rule in respect of the phase of abandoned accounts only as set forth in paragraph (5.2.4), and the bank accounts for enforcement courts that are established for the purpose of collecting enforcement amounts are excluded from all three stages of classification outlined in Article (5.2). Accounts of statutory reserve deposited by financial institutions supervised by SAMA, whose balances are not allowed to be disposed of without prior written permission from SAMA, shall also be excluded from the provisions of this Rule.
5.1 Transactions Subject to this Rule
This Rule applies to all assets (accounts, banking relationships, transactions, etc.) in cash and in-kind for natural and juristic persons which are deposited in banks operating in Saudi Arabia. Such assets include the following:
1. Inoperative current and saving accounts on which no financial transaction (withdrawal or deposit) has been carried out by the customer, his/her authorized representative, or his/her heirs*.
2. Automatically renewed investment deposits whose owners do not visit the bank after the completion of the agreed-upon period and cannot be reached by the bank.
3. Bank transfers (SARIE, Swift, remittance membership, etc.) that have not been settled, deducted or received from the date they are made.
4. Shares, bonds and title deeds of properties pledged against banking facilities that are fully paid by their owners, but they do not contact the bank to regain their ownership.
5. Safe deposit boxes (lockers) rented by banks to customers with contracts that have not been renewed from the date of the customer’s last visit, and banks were unable to reach the owners by using direct contact or other methods of contact or checking the customer’s other accounts and information in the bank. SAMA instructions on safe deposit boxes shall be applicable.
6. Unpaid amounts and profits due to customers on their investments in different types of investment funds managed, or was managed, or held by the bank for customers whose investment periods have expired and their owners have not received the amounts due because they do not visit the bank to receive such amounts and profits, they do not have active accounts for the bank to deposit such amounts and profits, or they can not be reached by the bank after they have been notified in writing.
7. Prepaid services accounts, in a way that does not conflict with the Regulatory Rules for the Prepaid Payment Services.
8. Amounts on credit cards that are not used or claimed by customers.
9. Leasing finance settlement accounts.
10. Amounts held against letters of guarantee and letters of credit as of their expiry date.
11. Other amounts due to customers and the accruals related thereof.
* This paragraph has been amended according to the circular No. (44071426), Dated 07/09/1444H, corresponding to 28/03/2023G. Please refer to the Arabic version of this paragraph to read the last updated version.
5.2 Durations, Periods and Requirements for Dealing with Inoperative Accounts
5.2.1 Active Accounts
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (44071426), Dated 07/09/1444H, corresponding to 28/03/2023G. Please refer to the Arabic version of this rule to read the last updated version.Accounts shall be considered active if no more than (24) calendar months have passed since the last recorded financial transaction (withdrawal or deposit, depending on the nature of the relationship) carried out by the customer, his/her authorized representative, or his/her heirs, or since the last reliable and documented correspondence.
5.2.2 Dormant Accounts
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (44071426), Dated 07/09/1444H, corresponding to 28/03/2023G. Please refer to the Arabic version of this rule to read the last updated version.Accounts shall be considered dormant after completing (24) calendar months from the date of the last recorded financial transaction (withdrawal or deposit, depending on the nature of the relationship) carried out by the customer, his/her authorized representative, or his/her heirs, or the last reliable and documented correspondence.
Requirements for dealing with dormant accounts:
- Activation of dormant accounts shall be subject to double supervision with higher authority, one of which includes the branch manager or the branch operation manager.
- Withdrawal and transfer transactions on a dormant account shall only be accepted in the presence of the customer (natural person), the customer’s legal agent holding a deed allowing him/her to operate the account, the agent of the customer’s heirs or the person authorized to operate the account if the account is for a juristic person. As an exception, fax number or e-mail address registered in the bank records shall be accepted. In addition, carrying out financial transactions using electronic services, such as online services and phone banking, shall also be accepted. The status of the account and the nature of the executed transaction shall be clear to the customer.
- Dormant accounts shall be allowed to accept all deposits, domestic and international transfers and dividends made by another person other than the account holder. The account status shall not be changed from dormant to active due to carrying out such transactions.
- This shall be applied to all customers, including those who have other active accounts. Banks are required to contact customers and inform them of the action to be taken on his/her account before completing five years if such customers have other active accounts. Customers shall also be asked to activate the account by carrying out a transaction. If the account is not activated during the specified period, the requirements of unclaimed accounts shall be applied.
5.2.3 Unclaimed Accounts
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (44071426), Dated 07/09/1444H, corresponding to 28/03/2023G. Please refer to the Arabic version of this rule to read the last updated version.Accounts shall be considered unclaimed after completing five years (60 months), including the dormant phase, from the date of the last recorded financial transaction (withdrawal or deposit, depending on the nature of the relationship) carried out by the customer, his/her authorized representative, or his/her heirs, or the last reliable and documented correspondence, and the bank becoming unable to reach the customer after using all methods of contact.
Requirements for dealing with unclaimed accounts:
- Banks shall transfer the balance of the account within the month following the five-year period to the bank’s suspense account created for unclaimed accounts.
- Such accounts shall be classified in the suspense account to be easy to deal with and manage according to the different communication policies and procedures and supervision aspects.
- Unclaimed accounts shall be allowed to accept all deposits, domestic and international transfers and dividends made by another person other than the account holder.
- Banks shall completely conceal the customer signature and balance from the branch screens during this phase. Supervision on such accounts shall be limited to the Head Office.
- If the customer visits the bank to activate the account or withdraw the balance, the customer may open a new account to which the outstanding balance in the bank’s records can be transferred, or may receive the balance by check or bank transfer after confirming the identity of the customer; legal agent; the agent of the customer’s heirs or the person authorized to manage and operate the account (as the case may be).
- Banks shall establish policies and procedures to ensure double supervision over the files of such accounts, with a supervision level higher than that applied to the other files. Banks shall also save such files separately from the other files and provide the necessary safety tools to protect the files from recordkeeping risks.
- Balances of such accounts shall be recorded as liabilities in the bank balance sheet. Banks shall not take any action regarding the balances regardless of the balance limit, the subsequent period and the account type.
- Outstanding debt obligations on such accounts shall be deducted before transferring the balance to the suspense account.
- The bank may close customer accounts whose balances are equal to (1,000) riyals and less, provided that the customer is notified a month prior to the date of closing, and notifies him when closing, document the notices and save them in his file. The bank must keep all the data of these customers and the amounts of their balances in the combined account; to hand it over to them when they go back to the bank.
5.2.4 Abandoned Accounts
Accounts shall be considered abandoned after completing the periods specified in this paragraph from the date of classifying the accounts as unclaimed, and the banks becoming unable to reach the customer after observing the account movements and his/her other transactions with the bank and using all methods of contact according to the communication policies and procedures provided in the Rules. The periods of such accounts shall be as follows:
- Unclaimed for a period of ten years (total of 15 years as of the last transaction) for current accounts, saving accounts, investment deposits, balances of deceased persons and credit amounts in credit cards.
- Unclaimed for a period of five years (total of ten years as of the last transaction) for bank transfers, safe deposit boxes, retained earnings, unpaid amounts and profits due to customers on their investments, shares; bonds and title deeds of properties pledged against banking facilities that are fully paid by their owners, but they do not contact the bank to regain their ownership, amounts held against letters of guarantee and letters of credit as of their expiry date, leasing finance settlement accounts, prepaid services accounts, and other amounts due to customers and the accruals related thereof
Requirements for dealing with abandoned accounts:
- Banks shall change the account status to abandoned within the month following the completion of the periods specified.
- Such accounts shall be under direct supervision of an authorized official from the bank senior management.
5.3 General Requirements
For inoperative accounts:
a. Account commissions and profits shall continue to be calculated as agreed upon or at market rates.
b. Accounts shall be checked and classified and the procedures stipulated in the Rules thereon shall be taken according to the periods specified for each.
c. Copies of documents and records of all the amounts and dues shall be kept as per the regulatory period of record-keeping.
d. Detailed records of accounts shall be kept. Such records must include, as a minimum, the following:
- Customer full name as shown in the identification document.
- Customer ID number as shown in bank records.
- Amount of assets and time periods related thereto.
- Nature of customer assets (current accounts, investment deposits, remittances, etc.).
- The national address, residence address and contact numbers, if any.
- Bank account number, relationship number or the serial number in safe records, if any.
- Ownership certificate numbers, if any or relevant.
- Any other data about the customer, if available or necessary.
e. Personal and financial data shall be kept by the bank in electronic records according to the technical specifications set by SAMA for easy future reference. A copy of such data shall be submitted to SAMA.
f. Provisions containing the periods and procedures for freezing accounts and other funds mentioned in these Rules shall be added to contracts, agreements, account opening forms signed by customers, as well as account statements sent to customers.
g. The role of the compliance department shall be supervisory at all phases and periods stated to ensure the fulfillment of the requirements of such accounts. In addition, rights shall be returned by the bank operation department.
5.4 Communication Policy and Procedures for Inoperative Account Holders
5.4.1 The Communication Policy and Procedures Shall Be Implemented in Accordance with the Customer Classification and Legal Nature, as a Minimum, as Follows
- Resident natural persons, including Saudis, GCC nationals, expatriates and politically exposed persons residing in Saudi Arabia.
- Non-resident natural persons, including Saudis, GCC nationals and foreigners not residing in Saudi Arabia, including those who leave Saudi Arabia and still have balances in their accounts.
- Resident juristic persons.
- Non-resident juristic persons.
- Commercial banks, including international accounts.
- Correspondent banks.
- Accounts of government entities.
5.4.2 Methods of Contact
Banks shall communicate with and try to reach customers, without disclosing any financial data, in all time periods specified by all possible legal means, for example:
- SMS.
- Email.
- Available phone numbers.
- Official letter sent by the mail to customers inside and outside Saudi Arabia.
- On-site visits by the bank relation staff.
- Messages on bank statements showing the account status and the actions required from the customer.
- Available public search tools and official information centers that help reaching customers by providing banks with the customer new contact numbers not registered with the bank, or informing banks of the customer status if alive, left Saudi Arabia, or if his/her business and financial activity was terminated.
- Media awareness advertisements explaining the relevant regulations, the actions required from dormant account holders, and balance search procedures.
- Inquiries to competent official authorities.
- Banks shall communicate with customers using the above mentioned methods during the different phases of inoperative accounts at intervals. Therefore, customers shall be contacted, at least, two times during each phase. If the customer is not responding and cannot be reached, banks shall stop communication a year after each stage and document the methods of contact used.
5.4.3 Bank Communication Unit
Banks shall establish a unit (formally established or defined) to implement the communication policy effectively. The tasks of the unit shall include implementing communication procedures and documentation, taking all related responsibilities and preparing periodic reports on communication and the results thereof.
5.4.4 Stages and Steps of Implementing Communication Policy and Procedures for Inoperative Account Holders
Banks shall comply with the following when communicating with customers according to each phase:
a. Dormant accounts:
- Banks shall inform customers, using their preferred methods of contact, of their account status, the required actions, and the procedure that will be taken by the bank in case customers fail to cooperate, including changing the account status to unclaimed.
- Government entities and private associations shall be officially informed, a year before changing the account status from dormant to unclaimed, without prejudice to the provisions of paragraph (4.2), of the procedures to be taken if there are no transactions in the account.
- Embassies, consulates, their educational institutions, and resident diplomats shall be officially informed, a year before changing the account status from dormant to unclaimed, of the procedures to be taken if there are no transactions in the account.
b. Unclaimed accounts:
- A bank check shall be issued with the unclaimed account balance of the government entity to the Ministry of Finance's account with SAMA. The check shall be sent to SAMA under an official letter and a copy of the check to the government entity and the Deputy Ministry for Financial and Accounts Affairs.
- Banks shall inform customers, using the preferred methods of contact based on the results of communication in the previous phase, of the unclaimed account status and that they are required to contact the bank to receive the balance and open alternative new accounts.
- A bank check shall be sent to embassies, consulates and their educational institutions with the account balance. Such procedure shall be documented.
c. Abandoned accounts:
- Banks shall inform customers, using the preferred methods of contact based on the results of communication in the previous phase, of the abandoned account status.
5.5 Internal Audit Control and Reports
Unclaimed and abandoned accounts shall be subject to the internal audit program once every two years, as a maximum. In addition, audit reports shall be submitted to the Audit Committee and the annual audit program shall not be linked to any other periodic programs related to such accounts.
5.6 Annual Statistical Reports Required by SAMA
Banks shall submit an annual report to SAMA at the end of March in accordance with the schedule sent by SAMA. The report shall cover all unclaimed and abandoned accounts, including the nature, type and number of the account as of the end of December of the previous year, without disclosing any personal information.
6. Application of KYC Principle and AML/CFT Requirements
- Banks shall fully apply the KYC principle, provided that the primary purpose of the application is for the bank to be fully aware and have a complete picture of the customer and the nature of his/her activities and transactions, prior to or during the business relationship or the process of opening the account, or prior to carrying out a transaction to a customer with whom it has no business relationship, by assessing the risks that the customer may impose on the bank and the level of such risks. The identification of customers and assessment of risks shall be made while ensuring the fulfillment of all statutory requirements of opening accounts or starting business relationship.
- Banks shall establish, define, review and update the necessary procedures for the application of the KYC principle in accordance with the relative significance and degree of risk assessment made by the bank.
- Banks shall ensure that staff has the experience and training required to identify and assess the customer’s level of risks.
- These Rules shall be read in conjunction with the requirements of the Anti-Money Laundering Law and its Implementing Regulations, the Law on Terrorism Crimes and Financing and the Guidelines issued thereunder.
- The Compliance Department shall have the authority and right to timely access the customer identification data, due diligence information, transaction records and other relevant data.
7. Curators, Legal Agents, Custodians and Authorized Persons (Natural or Juristic)
Banks shall ascertain the nature of the relationship for natural curators, legal agents, custodians and authorized persons when opening accounts and check the validity of the documents submitted.
8. On-Going Monitoring of Accounts and Transactions
- Without prejudice to the provisions of the Anti-Money Laundering Law and its Implementing Regulations, the Law on Terrorism Crimes and Financing and the Guidelines issued thereunder, Banks should have appropriate systems in place to monitor the customer’s transactions and activities and identify any suspicious or wrong behavior. Manual transaction monitoring is not sufficient and banks shall invest in developing electronic systems in accordance with the best standards in monitoring and information security and protection to continuously monitor customers’ transactions.
- Banks shall continuously assess internal risk-based controls in order to benefit from unusual activities that have been detected.
- The electronic systems used in banks should be suitable for the nature of the bank's risk profile, and the monitoring system should be integrated with the bank's core systems. In case of incompatibility between the two systems due to integration, the bank shall be prepared to take the necessary precautions and manual procedures to address the incompatibility.
- If the bank suspects that banking accounts are being used illegally or that the source of the money deposited is found to be earned from illegal business, the bank must notify the Saudi Arabia Financial Investigation Unit of such case.
9. Training as a Key Principle for these Rules
- Banks should not assign any teller or customer service staff before attending courses on KYC, AML/CFT measures, and ethical and professional behavior of bankers.
- Banks should put in place continued training programs to provide on-job training to employees in these areas. Banks should include extensive training on the contents of these Rules and their applications in their training programs.
10. Disclosure of and Enforcement on Bank Accounts, Balances and Relationships
- Subject to SAMA’s instructions on providing government and non-government entities with documents, information and data of customer bank accounts, the disclosure of and enforcement on bank balances, accounts and relationships (such as, blocking and compulsory deduction) shall be made by an order from SAMA upon the request of the competent authorities.
- Enforcement on banking relationships means blocking, compulsory deduction, check issuance and money transfer from the bank's customer accounts.
- Procedures taken for the disclosure of and enforcement on bank balances, accounts and relationships at all stages shall be strictly confidential. Such requests shall be received only by SAMA except for cases stated in SAMA’s instructions.
- Banks shall carry out requests for disclosure and enforcement according to the form, manner and period specified by SAMA.
10.1 Disclosure of Bank Balances, Accounts and Relationships
For the purpose of disclosing bank balances, accounts and relationships upon SAMA’s request and according to the relevant instructions, banks shall search for all relationships between the bank and the customer, including all active; closed and suspended accounts, inoperative accounts, deposits, valuable boxes, credit cards, remittance accounts (remittance membership) and any other relationships or products offered by the bank. Banks shall ensure that the search is made based on the customer name, ID or the document under which the account is opened according to the following:
- The search shall include sole proprietorships owned by the person inquired about and his/her participation in companies. Banks shall state in the statements submitted to SAMA that the search included such accounts and transactions. However, if the disclosure is requested for a certain relationship/transaction, banks shall only include the requested relationship/transaction in the statement.
- The validity of information sent to SAMA in compliance with the requirements of this Rule shall be checked.
- In case of requesting the disclosure of balances, accounts and relationships of a natural person, the disclosure shall include all the information required above in this Rule, in addition to institutions and stores owned by the natural person pursuant to the principle of full financial disclosure. If disclosure is requested for a specific institution or store, disclosure shall include the relationships related to such institution or store not the owner.
- In case of requesting the disclosure of balances, accounts and relationships of a natural person, disclosure shall be limited to the name of the company and the percentage of ownership. The accounts and balances of companies the natural person co-owns or in which he/she owns shares shall not be disclosed. The same shall apply to joint accounts by disclosing only the number of the account and the percentage of ownership of the customer subject of the disclosure request, unless otherwise provided in SAMA's request.
10.1.1 Attachment of Bank Balances, Accounts and Relationships
Banks shall comply with the following when attaching bank accounts, balances and relationships upon the request of SAMA in accordance with the relevant instructions:
- If a specific amount of money is requested to be attached from the customer’s account, the bank shall, from the receipt of the request, commit to attaching only the amount of money specified from the outstanding balance if the amount is available. In case the amount is not available, the bank shall not allow the customer to make debit transactions from the outstanding balance in the customer’s accounts (withdrawal, transfer, etc.) or open new accounts. Only credit transactions shall be allowed until the amount is available again in the account.
- Attachment shall include all credit balances in the bank accounts and relationships, except the accounts of the companies that the customer co-owns directly or indirectly, and the joint accounts, unless otherwise provided in SAMA's request.
- If the request includes precautionary or executive attachment of a specific amount of money, attachment shall be enforced only on the amount specified. Once the amount requested to be attached is available, SAMA shall be informed and attachment of other accounts and amounts of money shall be lifted.
- If attachment is requested for a specific period of time, attachment shall be automatically lifted upon the expiry of the period.
- Banks shall, when imposing attachment, comply with the instructions issued on deduction. If deducting from an employee, the amount of money seized shall not exceed one third of the net monthly salary, except for the alimony debt if provided for in SAMA’s instructions. If deducting from a retiree, the amount of money seized shall not exceed one quarter of the net monthly pension, except for the alimony debt if provided for in SAMA’s instructions. Banks shall also comply with the instructions issued on bank accounts opened for or receive government compensation and subsidy for citizens, as well as any other instructions on the amounts excluded from attachment. In addition, banks shall allow the withdrawal of such amounts form ATMs.
10.1.2 Instructing Banks to Stop Dealing with Customers
- Upon receipt of requests to stop dealing with customers, banks shall ban such customers from managing their existing banking relationships and shall not
- be allowed to establish new relationships or carry out debit transactions. The ban shall be imposed in respect of the customer’s funds and in his/her personal capacity only,
- and shall not include the fact that the customer is a guardian, curator, legal agent or a person authorized to manage accounts not opened in his/her name, unless otherwise provided in SAMA's request.
- If the stop dealing order is issued for a specific period of time, the order shall be automatically lifted upon the expiry of the period.
- If the stop dealing order is issued with an attachment order, the stop dealing order shall be automatically lifted upon lifting the attachment order by the bank.
10.1.3 Compulsory Deduction from Accounts
- Compulsory deduction shall be enforced by an order issued from SAMA to the bank at the request of the authorized entities. Upon the request, the bank shall deduct a specified amount on a monthly basis from the bank's customer account to a specific beneficiary account.
- Compulsory deductions and expenses are considered priority and must be carried out or deducted before any other debts. Necessary steps shall be taken by banks to ensure the execution of such action.
- SAMA’s deduction request for expenses or debts is to be made on the customer bank account to which salary payments are credited. The deduction shall be made promptly upon crediting such payments to the account. Necessary steps shall also be taken to ensure the execution of such action. The only exception here, however, is when SAMA’s request states that such deductions shall be made from another bank account.
10.2 Freezing in the Event of Death, Bankruptcy or Loss of Legal Competence
10.2.1 Official Notice on Freezing by Reason of Death, Loss of Legal Competence, Starting Any Liquidation or Administrative Liquidation Procedures Under the Bankruptcy Law, or Going into Liquidation Under Companies Law
I. In accordance with the applicable laws, the bank must stop all dealings related to the account and freeze the balance therein if it becomes aware of, or receives official notification from a competent authority about, any of the following:
a. Death of the account holder or one of the account holders.
b. Restriction on the legal competence of the account holder or one of the account holders.
c. Issuance of a judicial order or a decision from the company’s general assembly or partners to liquidate the company that owns the account.
d. Starting any liquidation or administrative liquidation procedures under the Bankruptcy Law for the account holder.
II. When carrying out the above, the following shall be considered.
- The absence of a provision in the company’s memorandum of association and articles of association that allows the company to continue if any of the cases mentioned in Paragraphs (a) and (b) of Item (I) stated above occurs.
- The account must be operated in accordance with Paragraph (c) of Item (I) stated above by the liquidator appointed by a judicial liquidation decision or a decision of the company’s general assembly or partners. The decision should include the appointment of the liquidator, restrictions imposed on its power and the period needed for liquidation (provided that such period shall not exceed five years if the decision is issued by the company’s general assembly or partners). The exception to the provisions of this paragraph and Paragraph (c) of Item (I) above is when the company’s memorandum of association, its articles of association, or partners’ agreement contain(s) a provision on how to liquidate the company. In such case, the liquidation should be performed thereby, as the case may be.
- The account shall be operated in accordance with Paragraph (d) of Item (I) above by the liquidator or bankruptcy committee as determined in the decision of the competent court.
- Checks issued before the occurrence of any of the cases mentioned in Item (I) above should be considered, unless otherwise stated by a court order issued thereon.
10.2.2 Request of Heirs, Guardians and Curators to Banks to Disclose Transactions and Account Balances of their Deceased or Incompetent Persons and the Like
10.2.2.1 Inquiring About and Operation of a Deceased’s Account
- If any person requests a bank to disclose transactions, accounts’ balances or banking relationships of his/her legator, the bank must respond to the request after verifying the existence of the necessary documents, which empower him/her to act so, including, as a minimum, the death certificate and determination of heirs deed (or an original copy thereof) that defines the names of heirs, including the person requesting the disclosure. If the requesting person is a legal agent of all the heirs or of one of them, he should produce the original power of attorney of his heirs or any of them that gives him the right to inquire about the legator's balances. The inquirer should be provided with the answer in a written form. The statement provided should be accurate and should include all banking relationships pertaining to the deceased. The Bank should keep a copy of the statement after being signed by the recipient.
- To operate the accounts of a deceased after freezing balances and stopping dealings because of death, the bank must verify the persons who have the right to the account of the deceased. Disbursement should be made based on legal practices and documents, including, as a minimum, the provision of the determination of heirs deed (or an original copy thereof) and the presence of heirs or their representatives collectively or individually, provided that such representatives have a power of attorney thereon. In addition, the decision of disbursement or distribution made by mutual agreement or by the competent court should be presented to the bank. If it is impossible to provide any of the required documents in connection with the deceased expatriate, the bank, after obtaining an attested death certificate, should issue a banking check with the amount of the balance in the name of the deceased’s country’s embassy to hand it to his/her heirs. The bank must comply with the requirements and procedures for heirs’ accounts set forth in Rule (200.1.1).
- Providing heirs or their representative with the deceased’s account statements or account activity for the period preceding the date of death is prohibited unless SAMA informs the bank of the issuance of a judicial order requiring so.
10.2.2.2 Inquiring About Incompetent Persons’ Accounts
If any person contacts a bank to inquire about or require disclosing of transactions, accounts’ balances or banking relationships of an incompetent person, the bank must respond to the request after verifying the existence of the necessary empowering documents, including, as a minimum, a legal document that proves the person’s guardianship or custody over the incompetent person. The inquirer should be provided with the answer in a written form. The statement provided should be accurate and should include all banking relationships pertaining to the incompetent person. The bank should keep a copy of the statement after being signed by the recipient. Providing curators or guardians with the incompetent person’s account statements or account activity information for the period preceding the issuance of the custody or guardianship deed is prohibited. For account operation, the provisions of the related rules should be applied on a case-by-case basis (interdicted, disabled, etc.).
11. Providing Services to Customers with Disabilities and Giving them Priority
The bank should give the optimum priority and care to customers with disabilities in a way that facilitates the procedures of providing banking services thereto.
Chapter III. Procedural Rules
100. General Instructions for Opening Bank Accounts
1. Customer ID
- The bank must obtain copies of all required documents and compare them with their originals in order to ensure conformity and authenticity. All copies of documents must also be stamped to confirm their authenticity.
- The bank must obtain customer’s signature on the photocopy of his/her ID, confirming the authenticity of the photocopy and the original. The bank must ensure that no transaction shall be carried out for any customers before examining the customer’s ID and verifying its validity as prescribed for the identification documents of customers set forth herein.
- The bank must identify and examine persons authorized to sign for bank accounts.
2. Documents Required to Open a Bank Account are as Follows
a. An original copy of the ID of natural or juristic customer.
b. Account opening agreement form which is prepared according to the requirements hereof. The agreement should include, as a minimum, the following:
- Customer's personal data: Name, nationality, ID number, validity date of ID, national address, occupation, and contact details.
- Financial information: Source of income (primary/additional), the expected size of financial movement on the account (deposits/withdrawals), and the purpose of opening the account.
- Terms and conditions of the agreement between the two parties (i.e. the bank and the account holder), along with customer signature thereon placed in the designated space.
- A specimen signature (personal signature, thumbprint, or personal stamp) which the customer will use for his/her transactions with the bank.
- Details and identity document of the guardian or representative and the like, and their signatures.
- A declaration by the customer of the following:
■ That he/she is not legally prohibited to be dealt with, that all information and data he/she has given is true and reliable, and that he/she has understood the terms, conditions and other provisions of the account opening agreement.
■ That he/she would be liable before the competent authorities for the funds deposited in his/her account by him/her personally or deposited by others with or without his/her knowledge, whether or not he/she used such funds, and when he/she failed to formally report to the bank the existence of such funds. That the funds deposited are from legal sources, that he/she is liable for their being free from any forgery or counterfeiting, and that if the bank receives from him/her (the customer) any illegal or counterfeit notes, he/she will not be refunded or compensated.
■ That he/she commits himself/herself to updating his/her personal data when requested by the bank or from time to time (as specified by the bank), provided that the interval shall not exceed 5 years. The customer also undertakes to provide a renewed ID before the expiration of its existing validity, and he/she acknowledges that if he/she fails to do so, the bank will freeze his/her account.
■ That the bank reserves the right to freeze the account or an amount of money credited to the account if the bank suspects that the bank account is being used illegally or that the amounts deposited are from financial fraud.
■ That he/she is the real beneficiary. The bank should verify such information.
- The bank must ensure that the account opening agreement (for juristic persons) contains, at a minimum, the following information:
■ Information on members of the board of directors.
■ Information on managers of the juristic person as per its status.
■ Information on authorized signatories, and their specimen signatures.
■ Verification of the ownership structure to identify the actual beneficiary, in addition to the structure of control and ownership.
3. Rules for Remote Opening of Bank Accounts for Natural Persons
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (42009017), Dated 18/02/1442H, corresponding to 05/10/2020G.1. Opening bank accounts remotely for customers with existing accounts in the same bank is not allowed.
2. The service is provided for individual citizens (national ID holders) and residents (Iqama holders).
3. The bank is responsible for verifying the identity of customers by using documents, data or information acquired from a reliable and independent source.
4. Risks associated with such accounts shall be assessed, policies and procedures for mitigating the associated risks shall be established periodically, and preventive measures to mitigate risks commensurate with the risk assessment results shall be developed and implemented.
5. The bank must set a clear and secure mechanism to activate the ATM card used for the bank account.
6. Documents and requirements referred to in Paragraph (2) above must be submitted and fulfilled by the customer, except the following:
■ An original copy of the ID of the natural or juristic customer.
■ A specimen signature (personal signature, thumbprint, or personal stamp) that the customer will use for his/her transactions with the bank.
4. Rules for Remote Opening of Bank Accounts for Sole Proprietorships
This rule has been added pursuant to the circular No. (41027515), Dated 20/04/1441H, corresponding to 17/12/2019G, and amended according to the circular No. (42009017), Dated 18/02/1442H, corresponding to 05/10/2020G.1. The bank is responsible for verifying the identity of the enterprise and its owner by using documents, data or information acquired from a reliable and independent source.
2. Risks associated with such accounts shall be assessed, policies and procedures for mitigating the associated risks shall be established periodically, and preventive measures to mitigate risks commensurate with the risk assessment results shall be developed and implemented.
3. The bank must set a clear and secure mechanism to activate ATM card used for the bank account.
5. Rules for Remote Opening of Bank Accounts for Resident Corporations
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (42009017), Dated 18/02/1442H, corresponding to 05/10/2020G.1. The bank is responsible for verifying the identity of the corporation by using documents, data or information acquired from a reliable and independent source. The following at least shall be checked: The name and legal form of the corporation, the powers that regulate and govern its work, the corporation's capital, its owners and the ownership percentage of each owner (except for the partners of a listed joint-stock company), the members of the board of directors if any, the directors, and the persons authorized to open and operate the accounts.
2. Appropriate standards must be set to manage risks associated with these accounts before approving the opening of such accounts in order to avoid opening an account for a company or a person with whom dealing is prohibited, for an incompetent person or the like.
3. The bank must set a clear and secure mechanism to activate the ATM card used for the bank account.
6. Rules for Remote Opening of Bank Accounts for Foreign Companies According to Foreign Investment Law
This rule has been added pursuant to the circular No. (43058341), Dated 01/07/1443H, corresponding to 02/02/2022G.1. Verifying the identity of the company by using documents, data or information acquired from a reliable and independent source as follows: The commercial register and the license obtained from the Ministry of Investment (MISA), the name and legal form of the company, the powers that regulate and govern its work, the capital, the owners and the ownership percentage of each one, and the members of the board of directors/executives.
2. The service shall only be provided to the general director of the company whose name and powers are stated in the company’s memorandum of association, including the opening and managing of bank accounts. Additionally, the identity of the general director shall be verified by using documents, data or information acquired from a reliable and independent source.
3. As an exception to Chapter 4 requirements concerning the operation of bank accounts, the authorized general director may operate the account with the passport, provided that the Iqama is presented after (90) days from the account opening date.
4. Risks associated with such accounts shall be assessed, policies and procedures for mitigating the associated risks shall be established and reviewed periodically, and preventive risk mitigation measures commensurate with the assessment results shall be developed and implemented.
7. Account Information Card
The bank must provide the customer (using any appropriate means) with account information, including the customer's name, account number and IBAN as evidence of opening the account.
8. Opening an Account without Making a Deposit
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (46015210), Dated 06/03/1446H, corresponding to 09/09/2024G.The bank must agree to open an account for any customer if the required documents and conditions are submitted and satisfied. The bank must not require the customer to deposit any amounts as a condition for opening the account. If no amount is deposited in the customer account within a period of 90 days, then the bank must close such account. The exception is being made to government entities’ accounts that the Ministry of Finance (MOF) approves opening without the need to deposit any amounts for a period specified by the MOF, As well as the bank accounts for enforcement courts that are established for the purpose of collecting enforcement amounts.
9. Blind and Illiterate Customer Service and Dealing
- The bank must open an account for any blind or illiterate customers who request so. The bank must also provide the blind or illiterate customer with an ATM card, in addition to a checkbook upon his/her request. The blind or illiterate customer has the right to obtain any banking services (telephone banking and/or Internet banking), provided he/she has been advised of the terms and conditions governing these services. Further, his/her signature must be obtained in this regard, confirming that such services are provided for him/her upon his/her request and choice, that he/she is aware of the risks associated with the use of such services, and that he/she is legally liable for all dealings being conducted through such type of services.
- Both the blind customer and illiterate customer must present a personal reference to introduce them to the banking procedures taken and documents and papers required by the bank. Such personal reference shall have an ID, be 15 years old or older, and be able to read out to the blind or the illiterate and to act as a witness. The bank must obtain from the personal reference a copy of his/her ID, in addition to his/her national address and signature.
- Should the blind or illiterate customer request to go through banking procedures without the presence of the personal reference, then the banking procedures will be introduced to him/her by one of the customer service representatives at the bank. Such introduction will be certified by one of the branch’s authorized signatories (branch/operations manager), confirming that the customer has been introduced to all necessary information and terms and conditions for the opening of accounts as well as the account management controls and that such terms and conditions and controls have been read out to him/her.
- Both the blind customer and illiterate customer must provide a thumbprint and a personal stamp as his/her specimen signature. Should either of them wish to use the (manual) personal signature as a specimen signature, he/she will be permitted to do so. In this case, it should be documented that this procedure has been taken at his request and choice and on his/her own responsibility.
10. Foreign Currency Accounts
Customers may open accounts in any available foreign currency. They may deposit and withdraw funds in a foreign currency. If such foreign currency is not available, payments can be made in Saudi riyal. Normal fees and expenses involved in such transactions will be borne by the customer.
11. Multiple Bank Accounts
The customer may have more than one account at the same bank, provided that all accounts bear one Customer Information File (CIF) number. Using the same account number for a new customer is not permitted.
12. Presence of Customer
Subject to the provisions hereof, as a basic rule, no account should be opened for new customers without their presence at the bank. The exception is being made to cases where there are powers of attorney explicitly authorizing the opening of bank accounts and containing the personal information of both parties. Furthermore, this rule (the presence of customer) shall also be applied when updating Know Your Customer (KYC) details for the account.
13. Visiting the Customers in Exceptional Cases
In exceptional cases where the customer is unable to visit the bank for reasons beyond his/her control, the bank may delegate two or more of its staff (with different powers) to meet the customer on-site and obtain relevant information and documents as required herein. The bank must develop the appropriate procedures and policies to ensure correct implementation.
14. Transfer and Check Services
14.1 Outgoing Transfers and Sold Checks
Banks are not allowed to render outgoing transfer and sold check service except to customers maintaining accounts therewith. Customer number is sufficient in the Express Transfers System as a substitute for bank account for customers of this service only, provided that the bank, upon the initiation of membership, obtains the personal data of customers on a special form designated for this service and uses a separate file. In addition, the bank must obtain the customer specimen signature and valid ID certified by both the customer and the bank employee pursuant to these Rules. Customer Number should be based on the ID number. Moreover, the Transfers System should be subject to regulatory procedures for accounts, such as freezing, verification of the ID validity and customer’s name, and limits placed on concerned customers. Membership account shall also be linked to transactions monitoring systems.
14.2 Incoming Transfers and Purchased Checks
Incoming transfers and purchased checks may be accepted in the following cases:
- If the transfer or check is made or issued from an account with the bank to a natural or juristic beneficiary account in one of the branches of the same bank, the transfer or check may be paid in cash to the beneficiary or his/her legal agent.
- If the transfer or check is from a local bank to another local bank, then payment shall be from the account of transferor to the account of the transferee.
- If the transfer is coming from outside Saudi Arabia in the personal name of the beneficiary, money transferred shall be paid through a bank account only.
15. Time Period for Opening the Bank Accounts
This rule has been added pursuant to the circular No. (75362/67), Dated 27/12/1440H, corresponding to 28/08/2019G.Banks shall open bank accounts for natural and juristic persons, for whom no approvals from bank’s concerned departments are required, within one business day if they meet all bank requirements and within two business days for those who need approvals. The applicant must be informed in writing of any missing or additional requirements upon application.
200. Rules for Opening Accounts for Natural Persons
200.1 Natural Persons Residing in Saudi Arabia
Natural persons are allowed to open accounts and use services provided by banks operating in Saudi Arabia pursuant to conditions regulating such services, as follows:
200.1.1 Saudi Natural Persons
• Male and female citizens:
Male and female citizens may open bank account by presenting their national ID (or family register for minors).
• Saudi natural persons exempted from personal photographs:
No accounts shall be opened by a national ID containing a statement on exempting its holder from providing personal photo, unless SAMA receives from the Ministry of Interior an official letter to this effect and informs the bank thereof.
• Minors:
Bank accounts may be opened for minors as follows:
1. The bank account shall be opened through the guardian, curator, or custodial person.
2. The account shall be in the name of the minor, while it is operated by the guardian, curator or custodial person.
3. The bank shall receive a copy of the custodianship deed issued by the competent court for the curator, or a copy of the guardianship deed where the guardian is not the father, or a copy of the custody deed for the custodial person.*
4. The bank shall obtain and verify the data of the family register to which the customer’s information is added, as well as the national identity information of the guardian, curator or custodial person.
5. When the minor reaches the age of (18) Hijri years and is still incompetent, the bank must receive a copy of the legal deed that proves the minor's condition as well as a copy of the guardianship continuation deed for the guardian or a copy of the custodianship deed for the curator.
6. As an exception of Paragraphs (1) and (2), a minor who has reached the age of (15) Hijri years and has a national ID may open and operate a bank account himself/herself, provided that the bank obtains the consent of the guardian or curator to open the account for the minor. In this case, no checkbook shall be issued until he/she reaches the age of (18) Hijri years.
• Bank accounts of people with disabilities-upper-limb disabled/ people with no upper limbs:
Bank accounts may be opened for upper-limb disabled people and people with no upper limbs, who cannot write or sign, subject to the following conditions and requirements:
1. A copy of the person’s national ID or Iqama must be submitted to the bank.
2. The bank should approve the customer’s seal instead of the personal signature on all documents and bank transactions.
3. Withdrawals from the account shall be made only in the presence of the customer personally at one of the bank's branches. If the customer requests an ATM card, e-banking service, telephone banking service, or/and a checkbook, the bank should provide him/her with these services, upon receiving the customer’s declaration and undertaking carrying his/her own seal and upon submission of a testimony by two of the bank branch’s employees (one of them should be the branch manager or his deputy) stating that the services are granted under the customer’s own responsibility.
4. Procedures should be introduced, if necessary, to the customer by two of the branch’s employees (one of them should be the branch manager or his deputy). Such employees should sign on each transaction, contractual relationship, or deposit or withdrawal document.
• Legally Incompetent Person:
A bank account may be opened for a legally incompetent person by his/her legal representative who shall be the one authorized to sign for and operate such account. The legal representative must present the original documents supporting the authority given to him/her, along with the originals of his/her own personal identification documents as well as those of the legally incompetent person.
• Children with special circumstances:
- These are children born in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia from unknown parents, illegitimate children, and children deprived of care from parent(s) or relatives due to death, divorce of parents, imprisonment of mother, suffering of mother from mental illness or chronic or contagious physical illness, or any other similar reason that prevents the mother from properly looking after her children. Such children are staying at housing centers of the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development (MHRSD), such as social nurseries, social education homes, model educational institutions, or charities caring for orphans, or living with substitute families as per a status letter from the MHRSD. Such children are Saudi and are given certificate of birth, in addition to the right to have a national ID when reaching the age of 15 Hijri years.
- A bank account may be opened for such children, upon a letter from the General Manager of Orphan Welfare or the General Manager of Social Affairs at the MHRSD. In addition, a copy of the child’s birth certificate authenticated by the housing center, the MHRSD or the bank (where the original is presented to the bank for verification) must be submitted. Drawing/disbursing funds from such account shall be made possible only by presenting a letter from either the Deputy Minister for Social Development or the Assistant Deputy Minster for Welfare Affairs. If the child is living with a foster family (substitute family sponsoring him/her) and the family requests opening a bank account for the child, an account may be opened in the child’s name after obtaining a letter from the MHRSD issued by the General Manager of Orphan Welfare or the General Manager of Social Affairs in the concerned region in Saudi Arabia. The letter should specify the name of the child and the names of both spouses of the family sponsoring the child. Additionally, certified copies of the child’s birth certificate and the sponsoring family’s identification documents as well as other relevant personal information of such family must be submitted to the bank. Such account shall be operated by the sponsoring family in all drawing and depositing transactions until the child reaches the legal age of 18 Hijri years. When the child reaches the age of (15) Hijri years, his/her national ID shall be accepted if presented instead of the birth certificate.
• Prisoners:
Bank accounts may be opened for prisoners if they approach banks escorted by officers of the General Directorate of Prisons. The bank must obtain from the accompanying officers a letter by the prison management in the city where the prison is located. The letter should be addressed to the bank branch, indicating the prisoner’s name and ID or Iqama number and the desire of the prisoner to open a bank account. The branch shall assign its senior teller, customer service representative or any other higher senior officer to receive the security car outside the premises of the branch, meet the prisoner, complete all regular procedures for opening the account as stipulated in Rule (100), and enable the prisoner to perform transactions and benefit from services offered by the bank. The prisoner shall also be permitted to operate his/her account following the same applicable manner and procedures. For female prisoners who do not present a national ID, the prison management’s letter introducing the female prisoner may be accepted.
• Prisoners’ trust accounts:
Opening of bank accounts for depositing and withdrawing of Prisoners’ Trusts shall be allowed according to the following controls:
1. The account shall be opened by a letter from the General Director of Prisons or his authorized representative. The letter shall be addressed to the bank branch at which the account will be opened, clearly indicating the purpose of opening the account.
2. The name of the account shall be “The General Directorate of Prisons, Prisons of (.....) Region, (name of) Prison-Holding Prisoners’ Trusts”. The same regular procedures for account updating shall be applied to this account.
3. The account shall be operated by a joint signature of at least two persons: the prison warden or his deputy and the officer in charge of the prisoners’ trusts or his deputy. Copies of the authorized signatories’ IDs and specimen signatures shall be obtained.
4. Withdrawal from the account shall be made only by checks signed by the authorized persons, by transfer from the prisoners’ trust account to the prisoner's own account, or to the enforcement court according to a court ruling**.
5. Deposit shall be made in cash through the bank branch or by a check if the trust is a check drawn to the order of the prisoner. Deposit shall be made by the authorized person or the person he/she may authorize. The cash deposit service can be offered by ATMs, if available at the prison department. Cash deposit card can be issued in the name of “(.....) Prison- Prisoners’ Trusts”. The PIN of the deposit card shall be handed to the of the prison warden. ATM cards and credit cards shall not be issued for such account**.
6. The bank may, at its discretion and upon its approval, offer online banking and telephone banking services, based on a formal letter from the entity operating the account, for only checking account balances and inquiring about transactions.
• Bank accounts of heirs:
If the bank receives an official notice of, or becomes aware of, the death of an account holder, it should apply the following measures based on the applicable regulations:
1. The provisions of the supervisory Rule (10.2) should be applied.
2. The name of the account should be changed to "Heirs of , or a new account should be opened under this name.
3. The determination of heirs deed (or an original copy thereof) should be accepted as, and considered, an ID for maintaining the existing account or for opening a new account for the balances.
4. In completing the account information, the ID number is the number of the determination of heirs deed, the date of the ID is the date of such deed, and the place of issue is the court issuing the deed.
5. The person authorized to sign shall be the heirs themselves or their agent(s), collectively or individually. The bank is required to register the personal data of heirs and authorized agent(s) as well as including copies of their respective IDs and the legal power(s) of attorney in the account file.
6. The account shall be valid for one year from the date of determining the authorized persons as per the abovementioned paragraphs. The account shall be annually updated. If the account has had no activity for five years starting from the date of death, the provisions set forth in Rule (5) of the Supervisory Rules and Controls shall be applied.
7. Only checkbooks can be issued for such accounts and not ATM cards or credit cards.
• Receiver:
Opening accounts for a receiver is permitted upon completing the following:
1. Submitting a copy of the court order appointing the receiver and stating his powers.
2. Submitting a copy of the national ID of the receiver.
3. Submitting a copy of the receiver’s license unless appointed by the concerned parties.
4. Submitting a copy of each document pertaining to the subject of dispute under receivership (for which the court order of receivership was issued). Such documents include the determination of heirs deed if the dispute is over an heirloom, or the memorandum of association and its annexes if the dispute is over a company. The document(s) required in other cases should be based on the distinction made in the previous point.
5. The name of the account should indicate its purpose, in addition to including the expression "Under Receivership”.
6. The court order should be used as an ID for opening the account or maintaining its use.
7. In completing the account information, the ID number is the number of the court order, the date of the ID is the order date, and the place of issue is the court issuing the order.
8. The authorized signatory for the account shall be the receiver or as specified by the court order.
9. The account shall be valid for one year from the date of the court order. The account shall be updated annually by the authorized signatory in accordance with Paragraph (8). If the account has had no activity for five years from the date of its opening, the provisions provided for in Rule (5) of the Supervisory Rules and Controls shall be applied.
10. Only checkbooks can be issued for such accounts and not ATM cards or credit cards.
* In accordance with circular No. (44086644), Dated 15/11/1444H, the Saudi Central Bank confirms that all banks must accept conciliation documents issued by the conciliation Center, including proof of custody, in banking transactions that the custodian conclude on behalf of the child. reconciliation documents can be verified electronically through the Taradi platform portal.
** Amended according to the circular No. (12426/67), Dated 25/02/1441H, corresponding to 24/10/2019G.
200.1.2 GCC Natural Persons
The bank may open accounts for GCC natural persons, after obtaining a copy of the customer’s national ID, his/her address in Saudi Arabia (proved by a service invoice, residential lease agreement, real estate ownership deed-or an original copy thereof, or a testimony by a Saudi person stating that the customer resides in the mentioned address), and his/her address in his/her home country. A GCC natural person is allowed to authorize a Saudi person or a another GCC citizen to open and operate his/her bank accounts.
200.1.3 Expatriates in Saudi Arabia
This rule has been amended according to the circular No.(42078428), Dated 10/11/1442H, corresponding to 19/06/2021G.• Expatriate holding residence permit (Iqama):
The bank may open bank accounts for expatriates holding residence permits (Iqama) after obtaining a copy of Iqama. Such Iqamas might be issued by the Passport Department against the applicable fees or free of charge, such as Iqamas issued to students of universities, students of military colleges, and students of institutes, who obtained scholarships or training approvals, or might be issued by the Protocol Affairs at the Ministry of Foreign Affairs or the like. In addition, the bank should obtain the expatriate’s address in Saudi Arabia as well as his/her address in his/her mother country.
• Expatriate dependents (whose Iqamas include a statement indicating that they are dependents and are “not authorized to work”):
The bank may open bank accounts for expatriate dependents whose Iqamas indicate that they are dependents and not authorized to work in Saudi Arabia. The bank shall comply with instructions related to expatriates’ bank accounts. If the bank suspects that the bank account is being used for illegal purposes or it finds out that the deposited funds are from the work of those dependents and not from their families, then the bank must inform the Saudi Arabia Financial Investigation Unit (SAFIU).
- If the expatriate whose Iqama indicates that he/she is a dependent and not authorized to work in Saudi Arabia is a son/daughter of a Saudi mother but a Non-Saudi father, then he/she is allowed to open a salary account, provided that he/she submits official documents proving that his/her mother is Saudi. The requirements mentioned above shall also be fulfilled.
- If the expatriate whose Iqama indicates that he/she is a dependent and not authorized to work in Saudi Arabia works for a licensed educational institution and wishes to open a salary account, then the bank account might be opened for him/her upon satisfying the following requirements:
1. Submitting a copy of Iqama.
2. Completing an account opening form by the customer for the purpose of receiving salary from the contracting institution.
3. Providing a written undertaking by the customer to notify the bank upon the expiration or termination of his/her contract.
4. Submitting a letter of employment from the general management of the educational institution contracting with the account applicant. Such letter should provide basic information about the expatriate and his/her salary and bonuses and should also state that he/she is currently employed by the educational institution by an “Ajeer” notice (work permit). Moreover, the letter should indicate that it is provided for the purpose of opening a salary account. Further, the following documents should be attached to the letter:
a. A copy of the valid Ajeer notice issued in the expatriate’s name and verified by the contracting institution.
b. A copy of the contracting institution’s license as issued by the supervising body.
c. A copy of the validity certificate issued in the expatriate’s name by the supervising body and verified by the contracting institution.
d. An undertaking to notify the bank upon expiration or termination of the account holder’s contract.
5. The bank account shall be valid for a period identical to the validity period of the account holder’s Iqama or Ajeer notice, whichever expires first.
6. The approval of compliance department for opening the bank account shall be obtained.
- If the expatriate whose Iqama indicates that he/she is a dependent and not authorized to work in Saudi Arabia is a minor (under the age of 15 years), then his/her account shall be operated by the main, sponsoring expatriate residing in Saudi Arabia. However, if the main expatriate is a woman and her husband is her escort, the minor’s account in this case shall be operated by his/her father since he is the legal guardian. If the minor reaches the age of 15 Hijri years, receives an independent Iqama, and applies directly for opening a bank account, the bank shall seek the approval of the guardian or curator for opening the account. In this case, no checkbook shall be issued until the minor reaches the age of 18 years.
- This type of bank accounts shall be classified as a high-risk account.
• Expatriate with a temporary (90-day) work visa in his/her passport:
Bank account may be opened for expatriates whose employers are individuals, institutions, official entities, or companies in order to transfer or deposit their salaries and financial entitlements during the temporary residence period in accordance with the following:
1. The account is to be opened for the expatriate employee upon receiving an official request from the employer. Such request shall state that the holder(s) of the account(s) works/work for the employer and that no Iqama was issued for the expatriate due to not completing 90 days from the date of arrival in Saudi Arabia. The request shall also specify the occupation and task of the expatriate, why the account is needed, sources of money to be deposited in the account, and his/her salary. The bank shall check the original passport(s) including work visa.
2. The employer shall undertake to notify the bank once the account holder leaves Saudi Arabia (on a final exit visa) during this period (the first three months of arrival in Saudi Arabia). Once notified, the bank must immediately freeze the account and contact the customer to submit to him/her the balance left and close the account. If the communication is not possible, the account freeze should continue and after the elapse of 90 days starting from the end of the 3-month period (the first three months from the date of expatriate’s arrival) or starting from the date of the account freeze due to the expatriate’s final exit, the account shall be dealt with according to the requirements of Rule (3) on Freezing of Bank Accounts.
3. The bank must meet the expatriate (account holder) in person and obtain his/her signature on an account opening agreement. The bank must also obtain documents and data needed to open the account (except Iqama). The customer shall sign an undertaking to submit his/her Iqama once issued (during the three legal months). The bank may also request the customer to agree on any other requirements the bank deems appropriate in relation to balance, transfer, and/or account closing. Additionally, the bank should inform the customer that his/her account will be frozen if his/her Iqama is not submitted during the first three months of arrival in Saudi Arabia.
4. Approval of the manager of compliance department at the bank shall be sought.
5. This type of bank accounts shall be classified as of high risk.
6. The bank account shall be valid for a period identical to the validity period of the visa. Only issuing an ATM card and performing transfer transactions are permitted for the account. No checkbooks, credit cards and/or any other services shall be issued or provided for this account during this period.
7. Operating the account after three months from the expatriate’s (account holder) arrival in Saudi Arabia is not allowed unless the bank meets the account holder and verifies his/her Iqama. After meeting the customer and verifying his/her Iqama, his/her account will have the same procedures implemented on other bank accounts.
• Expatriates with a visit visa to carry out certain assignments for entities in Saudi Arabia:
A bank account may be opened in Saudi riyal for an expatriate holding a government visit visa to carry out certain assignments for a government or quasi-government entity or for any other juristic entity contracting with a government or quasi-government entity in Saudi Arabia, for an expatriate holding a business visit visa (provided for employees of companies and institutions), or for an expatriate holding scientific or professional visit visa and the like after fulfilling the following requirements:
1. A copy of the valid passport including the visit visa should be submitted.
2. A letter from the inviting entity (endorsed by the Chamber of Commerce if it is a business visit visa) should be submitted. The letter should clarify the mission of the individual, the reasons for not issuing a residence permit for him/her, why the account is needed and its validity period, and sources and amounts of money to be deposited therein.
3. The account shall be valid for a period identical to the validity period of the visa. If the visa is for a single entry, the account shall be immediately closed once the visa expires. If the visa is for multiple entries, the account validity shall be for (6) months from the date of entry to Saudi Arabia and should be renewed for the same period or less, taking into consideration the validity of the visa. The bank must obtain a written undertaking from the inviting entity to inform the bank when the expatriate leaves Saudi Arabia permanently in order to close the account.
4. It is permitted to provide the expatriate with an ATM card that only operates on the Saudi Payment Network (MADA). However, no checkbook shall be provided for this account.
5. This type of accounts shall be classified as of high risk and shall be subject to the supervision of compliance officers.
6. Approval of the manager of compliance department for opening the account shall be sought.
7. If the expatriate leaves Saudi Arabia permanently and then comes back with a new visa to carry out any of the assignments mentioned above for the same entity or for any other entity, the bank shall apply all the requirements set forth in the paragraphs above. The old account shall be treated according to Rule (3.2) on General Instructions for Freezing of Bank Accounts stated in Chapter II on Supervisory Rules and Controls, taking into account the account balance.
• Foreign pilgrims:
A foreign natural person having a Hajj identification card issued by the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah, pilgrim guiding institutions, or others, permitting him/her to perform Hajj, is not allowed to open bank accounts.
• Transfer via bank account or transfer membership:
After the elapse of the first three months of the expatriate’s arrival in Saudi Arabia or after he/she obtains an Iqama during that period, all banks are prohibited from carrying out any transfers, issuing any checks or exchanging any currencies for the expatriate, except through a bank account opened in his/her name. Customer number is sufficient in the Express Transfers System as a substitute for bank account for customers of this service only, provided that the bank obtains the personal data and Iqama of customers. In addition, customer number should be based on Iqama number. Moreover, the Transfers System should be subject to regulatory procedures for accounts, such as freezing, verification of the ID validity, checking customer’s name against his/her passport for expatriates holding non-magnetic Iqama, limits placed on concerned customers, etc.
• Transfer limit during the 3-month work visa:
The maximum amount of a transfer or a check which banks may effect for an expatriate during the first three months of his/her arrival in Saudi Arabia for work and before obtaining an Iqama and opening an account in his/her name shall be ten thousand Saudi riyals (SAR 10,000). This limit is applicable to professionals, such as physicians, engineers and senior administrative officers whose salaries are commensurate with such limit or are above. For individuals in normal jobs or workers, the maximum limit of each transfer should be commensurate with the type of profession specified in the work visa placed in the passport. The bank shall use the passport number as a reference for the transactions executed during such period.
• Expatriates exempted from working for their sponsors:
An expatriate having a valid Iqama including a statement to the effect that its holder is exempted from working for his/her sponsor may open a bank account by providing his/her Iqama and an employment letter from the person or entity for which he/she works.
• Expatriates working in Saudi Arabia without Iqama:
No bank account may be opened for an expatriate working under (monthly or annual) employment contract for any entity in Saudi Arabia without a valid Iqama. In this case, an explicit approval from the Ministry of Interior must be obtained for each case and should then be communicated to the bank through SAMA along with any applicable procedures.
• Valid Iqama holders without passport:
Bank accounts may be opened and maintained for expatriates having valid Iqama including the word “without” next to the “nationality”, by providing their Iqama only. No passport, copy or number thereof, shall be required.
• Expatriates having Saudi passports
No bank account may be opened by presenting a Saudi passport issued to some expatriate individuals. Such an expatriate must present a valid Iqama, and the validity of his/her Saudi passport shall not be required. However, where the expatriate has no identification document except his/her Saudi passport, the approval of SAMA shall be obtained for opening the account. Such approval shall include a reference to the approval of the Ministry of Interior. Once the account is opened, SAMA shall be provided with the number of the account and address of the expatriate. The bank shall classify this type of accounts as of high risk to be subject to continuous monitoring.
• Authorization by expatriate to others, or opening joint accounts by expatriate:
An expatriate may neither authorize another person to open a bank account in his/her name, nor may he/she open a joint account with others, except in the following cases:
- The expatriate husband and his expatriate wife and vice versa, and their first-degree expatriate relatives.
- The female expatriate working in Saudi Arabia and her legal escort, provided that the Iqama of the legal escort or any other official document states that he is the legal escort of the female expatriate.
- The female expatriate and her Saudi husband.
- The female expatriate and her Saudi father, mother, son or daughter.
- The male expatriate and his Saudi wife.
- The male expatriate and his Saudi father, mother, son or daughter.
The male or female expatriate and his/her abovementioned relatives should hold valid Iqamas. The bank should record the number of Iqama for each male or female expatriate as an electronic reference number for the expatriate.
• Standing instructions on the account of an expatriate*:
Expatriates may set up and renew standing orders for one year only through e-banking services. The personal information of the client shall be verified using documents, data or information acquired from a reliable and independent source. Such information shall be documented as well. Expatriates may set up standing orders to make regular domestic or international money transfers. The standing order payment shall be made once a month only and the amount shall be determined by the bank according to the client’s risk assessment.
* This paragraph has been amended according to the circular No.(42078428), Dated 10/11/1442H, corresponding to 19/06/2021G.
200.1.4 Tribe Members: Displaced Tribes/Ar Rub' Al-Khali Tribes
The bank may open accounts for those tribal individuals residing in Saudi Arabia, and the validity of their accounts should be linked to the validity of their Iqamas. The bank must obtain the individual’s Iqama which has a statement in the “nationality” space that reads “tribe members”, “displaced tribes”, or “Ar Rub’ al-khali tribes”. The supervisory and control requirements implemented on expatriates residing in Saudi Arabia, stated herein, shall apply to this category of customers.
200.1.5 The Beluchis and Turkistanians
Bank accounts may be opened for Beluchis and Turkistanians by presenting a valid Iqama. The bank should not require such customers to present the original passport or a copy thereof. Before opening a new account, updating an existing one or effecting any other banking transactions, the bank shall require the customer to identify his/her address in Saudi Arabia and submit an employment letter. Such letter should be authenticated by the Chamber of Commerce or the official organization the customer is employed under its supervision. If the customer does not work and his/her Iqama has no employer mentioned, he/she shall be required to present a letter from the mayor of the area (district, governorate or town) where he/she lives, duly authenticated by the police station of the area of such mayor. In addition, the addresses mentioned in such letter should be clear enough to allow easy access to him/her when necessary. Such requirements shall be updated annually.
200.1.6 Expatriate Stewards and Stewardesses of the National Airlines, Expatriate Ship Crews and the Like
Bank accounts may be opened for expatriate stewards and stewardesses of the national airlines, expatriate ship crews and the like by presenting a valid visa included in the passport. The visa should be checked against the identification card provided to such individuals by their employers. The bank account validity shall be identical to the validity period of visa or renewal period thereof.
200.1.7 Bank Accounts for Employees of Enterprises Wishing to Pay Employee Salaries Through Prepaid Electronic Records
The bank may allow its customers to pay the salaries of their employees through prepaid electronic records. In doing so, the bank must comply with the provisions of the Regulatory Rules for the Prepaid Payment Services in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
200.1.8 Credit Cards for Non-Resident Foreigners Employed by Resident Saudi Companies
The bank may issue credit cards to a selected, limited category of non-resident foreigners employed by a limited category of major Saudi companies having relationship with the bank. Such employees should have jobs that necessitate moving from a place or country to another (such as private airline pilots, stewards and stewardesses), and they do not have residence cards for any country where they go, including Saudi Arabia. The Saudi company hiring such employees is responsible for covering their local and international transportation expenses by credit cards. In this case, the bank shall observe the following conditions when issuing such credit cards for those employees:
1. The credit cards shall be issued through the resident Saudi company for which such employees work.
2. The Saudi company shall have good creditworthiness and a sound financial position.
3. All individuals, for whom credit cards or debit cards are required to be issued, shall be employed by the Saudi company, and documents proving such shall be obtained.
4. The Saudi company shall ensure in writing that the said cards will be properly used and that the company will bear all implications of use thereof by its employees.
5. The Saudi company, rather than the employees to whom the cards are delivered, shall pay all due payments related to the cards.
6. The maximum credit limit per card shall not exceed the limit allowed to other customers, corresponding to card category.
7. Dealing under this system shall be based on a formal agreement entered into between the bank and the company prior to the issuance of such cards.
8. The company shall provide the bank with the agreement, signed by the company and its employees, that determines the responsibility related to the issuance and use of such cards.
200.1.9 Opening Bank Accounts to Raise Blood Money to Be Paid for Reconciliation in Murder Cases
The bank must comply with the following when opening and operating such bank accounts:
I. Any activity aimed at raising funds for reconciliation shall not be undertaken without the consent of the Minister of Interior, after reporting of such activity by the emirate of the concerned region.
II. If the approval of the Minister of Interior is issued, the emirate of the region shall communicate with SAMA and request opening of a bank account at a specified bank to raise blood money. The following requirements shall be satisfied:
1. Approval of the Ministry of Interior for opening the bank account shall be obtained. The approval should indicate the period of the account validity.
2. A copy (or an original copy) of the legal deed indicating that the victim’s heirs waive the right of legal retribution (Qisas) and agree to receive the required amount of monetary compensation (Diyah), shall be submitted. Such legal deed shall indicate the time agreed upon to submit such compensation.
3. The bank account to raise blood money shall be subject to the supervision of the emirate of the concerned region, and no party of the case shall have any rights thereon, whatsoever.
4. The emirate of the concerned region shall specify the names of persons authorized to manage the account (supervision of the account and following-up of deposits); copies of their IDs, specimen signatures (joint signature) and contact details shall also be included.
5. The bank shall not issue checkbooks or ATM cards for the account. Further, no transfers from the account shall be allowed.
6. The name of the account shall be as follows (the Emirate of... Region, Diyah Money Raising for... (the full name of the murdered shall be written)”.
7. The bank shall stop the account automatically once the required amount of blood money is reached, and the account shall not accept any extra money.
8. The account shall be valid for one year, as a maximum, starting from the date of opening the account. After one year, it shall be deactivated. The account may continue to operate for another year by a letter from SAMA upon the request of the emirate of the concerned region.
9. If the amount of blood money is completely raised, the emirate of the concerned region should request a bank check and hand it to the beneficiary through the court.
10. If the victim’s heirs reduce the amount agreed upon in the original legal waiving deed, this reduction shall be recorded in a similar legal deed or expressly added to the original legal waiving deed that includes the previously agreed-upon amount.
11. If the amount of blood money is not completely raised and the victim’s heirs are not satisfied therewith, or if the victim’s heirs waive the amount, the funds raised shall be returned to their depositors whose names are known through deposit slips. As for anonymous deposits, the emirate of the concerned region shall present the case to the Mufti to give a formal legal opinion (Fatwa) regarding how to handle such funds. (The bank shall satisfy this requirement upon receiving the direction of the emirate of the concerned region, which is delivered to the bank by authorized individuals.)
12. Only one bank account shall be opened for each case involving raising blood money (Diyah). In addition, opening more accounts in other banks for the same case is not allowed.
13. The account shall be closed once the amount of the blood money is completely raised. Then a bank check of the amount shall be issued.
14. This rule also applies to bank accounts dedicated to raising funds to be paid as compensation in injury cases.
200.2 Natural Persons Outside Saudi Arabia
200.2.1 Saudi Citizens Residing Outside Saudi Arabia
Saudi citizens residing outside Saudi Arabia for study, medical treatment or official work (such as in embassies, consulates, or multilateral organizations) may open bank accounts upon the following:
1. Providing a copy of the passport.
2. Providing a copy of the national ID.
3. Submitting a specimen signature.
4. Completing the account opening form or authorizing a Saudi citizen to open the bank account.
5. Obtaining verification of such documents from the Saudi embassy or consulate in the foreign country.
- Saudi individuals residing in a GCC country may provide such data via the correspondent GCC bank for the bank operating in Saudi Arabia.
200.2.2 GCC Nationals Not Residing in Saudi Arabia
Bank accounts may be opened for GCC nationals who are not residing in Saudi Arabia, directly by themselves or by a Saudi or GCC citizen authorized by a power of attorney. The bank should obtain the following documents from such individuals:
1. A copy of the valid national ID.
2. A copy of the valid passport (if any).
3. An employment letter from the entity for which he/she works, or from his/her personal business.
4. A completed account opening form.
5. A specimen signature.
- Such documents shall be obtained by the employees of the local bank directly or by the correspondent GCC bank in the GCC country where such individual resides. The GCC bank shall authenticate all documents obtained, and all deposit, withdrawal and transfer transactions shall be effected through the correspondent bank. Receiving such documents and effecting deposit, withdrawal and transfer transactions are also possible through a correspondent bank in the GCC country where the GCC citizen resides. No cash deposits by third party shall be accepted.
- No checkbook, ATM card or credit card may be given to such individual unless he/she comes to Saudi Arabia and presents to the bank adequate data proving his/her residence in Saudi Arabia. In this case, Rule (200.1.2) shall be applied to such customer, and his/her account status shall be changed.
200.2.3 Non-Saudi and Non-GCC Natural Persons Not Residing in Saudi Arabia
The bank shall not open an account in Saudi riyal or in any foreign currencies, or any other account, for non-Saudi and non-GCC natural persons not residing in Saudi Arabia unless written approval from the Ministry of Interior or the Ministry of Foreign Affairs is received through SAMA. If so, the account may be opened by the passport of the individual.
300. Rules for Opening Bank Accounts for Juristic Persons
300.1 Resident Juristic Persons (Including Embassies and Multilateral Organizations)
300.1.1 Licensed Businesses and Shops
This rule has been respectively amended according to the circular No. (41042946), Dated 19/06/1441H, corresponding to 13/02/2020G ,and circular No. (42053614), Dated 02/08/1442H, corresponding to 15/03/2021G.The bank may open bank accounts for these licensed businesses and shops upon completing the following:
1. Obtaining a copy of the entity’s commercial register, or license if it is the only item required for practicing the entity's business without the need for a commercial register.
2. Verifying the identity of the owner of the entity against his/her name in the commercial register or license, and checking the information and validity of the owner’s ID.
3. Obtaining copies of the IDs of individuals authorized to mange and operate the accounts.
• If the owner of entity or shop is an endowment or private societies/foundations or cooperative associations, the bank must then request the following, in addition to the aforementioned requirements:
1. A copy of a valid endowment registration certificate issued by the General Authority of Awqaf, including at minimum the following: Name of endowment, endowment deed number and date, and names of administrators and their ID numbers (for endowments); or a copy of the license issued by the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development, a copy of the decision of the board of directors of the society/foundation (meeting minutes) approving the establishment of the business, entity or shop, and the approval for the account’s authorized signatories (for private societies/foundations or cooperative associations).
2. Copies of the IDs of administrators whose names are stated in the endowment registration certificate (for endowments).
3. This type of accounts shall be classified as a high-risk account. 300.1.1.1 Special-Purpose Entities
The bank may open accounts for these special-purpose entities upon completing the following:
1. Obtaining a copy of the license of the special-purpose entity, issued by the Capital Market Authority (CMA).
2. Obtaining a copy of the license (if any) or commercial register of the owner, issued by the concerned authority.
3. Obtaining a copy of the entity’s articles of association.
4. Checking the IDs (for natural persons) and licenses or commercial registers (for juristic persons) of registered board members.
5. Obtaining a copy of the decision made by the authorized signatory in such entity, authorizing specific individuals to manage and operate the accounts.
6. Obtaining copies of the IDs of individuals authorized to mange and operate the accounts; and
7. Checking the IDs (for natural persons) and licenses or commercial registers (for juristic persons) of the special-purpose entity’s owners whose names are stated in its articles of association and amendments thereto.
300.1.1.2 Foreign Schools
The bank may open accounts for these resident foreign schools upon completing the following:
1. Receiving a letter from the board chairman or school principal, containing a request to open a bank account and the names of the account’s authorized signatories (a joint signature), along with copies of their IDs attached.
2. Receiving the approval of the Ministry of Education for opening the bank account and for the authorized signatories.
3. Obtaining a copy of the school’s license that is issued by the Ministry of Education.
4. Receiving a copy of the decision of forming the school board, approved by the Ministry of Education, and copies of members' Iqamas.
5. The account shall be valid for a period identical to the validity period of school license and the term specified for the school board as per its formation decision approved by the Ministry of Education.
6. The signatories shall be the school principal and its financial officer (who shall be employed in the same school), or one of them and a school board member, provided that such member is not a diplomat or an embassy employee. Such member may be from outside this school as an exemption from Paragraph (3) of Rule (4) of Chapter IV on the General Rules for Operation of Bank Accounts, regarding controls for authorizing non-Saudis.
7. Withdrawal from these accounts shall be as per dual control, and in case of withdrawal by checks, check shall be payable to the first beneficiary.
8. ATM cards or credit cards shall not be issued for such accounts.
300.1.1.3 E-Commerce Businesses with No Official Premises
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (75357/67), Dated 27/12/1440H, corresponding to 28/08/2019G.The bank may open accounts for e-commerce businesses as per the requirements of Rule (300.1.1) on Licensed Businesses and Shops. The following shall also be observed:
1. The account name shall be as shown in the commercial register of the business, and the purpose of opening the account shall be “e-commerce”.
2. The e-platform of the business shall be as shown in the commercial register.
3. The national address of the entity or its owner shall be obtained.
4. This type of bank accounts shall be classified as of high risk and shall be updated every two years.
300.1.1.4 Freelance Job Permit Holder
The bank may open bank accounts for freelancers upon completing the following:
1. Obtaining a copy of the freelancer’s permit issued by the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development.
2. Obtaining a copy of the national ID of the person holding the freelance job permit.
3. Obtaining the national address of the freelancer.
4. The bank account shall be in the name of the person holding the freelance job license. The work type stated in such license shall also be added to the name of the account.
5. The account shall be for one person only and shall not have signatories.
6. This type of accounts shall be classified as of high risk, and the purpose of opening such account shall be specified.
7. The account shall be valid for a period identical to the validity period of the freelance job license.
300.1.2 Licensed Money Changers
The bank may open accounts for licensed money changers upon completing the following:
1. Copies of licenses issued by SAMA shall be obtained. The account shall be valid for a period identical to the validity period of the license issued by SAMA.
2. A copy of the commercial register shall be obtained.
3. The bank shall verify the information contained in the commercial register or in the license issued by SAMA matches the information contained in the owner’s ID card.
4. A copy of the owner’s ID shall be obtained.
5. Copies of the IDs of individuals authorized to mange and operate the accounts shall be obtained.
300.1.3 Resident Companies
This rule has been respectively amended according to the circulars No. (41042946), Dated 19/06/1441H, corresponding to 13/02/2020G, circular No. (42053614), Dated 02/08/1442H, corresponding to 15/03/2021G, and circular No. (44061480), Dated 28/07/1444H, corresponding to 18/02/2023G.The bank may open accounts for companies residing in Saudi Arabia upon completing the following:
1. A copy of the commercial register shall be obtained.
2. Obtaining a copy of the memorandum of association or the articles of association and their annexes.
3. Obtaining a copy of the ID of the manager in charge.
4. Verifying the identity of board members.
5. Obtaining the power of attorney issued by a notary public or a notary (or the authorization made in the bank by the person/persons who, by virtue of memorandum of association, partners’ decision or board of directors’ decision, has/have the power to authorize), authorizing natural persons to sign for and operate the accounts.
6. Obtaining copies of the IDs of individuals authorized to sign for and operate the accounts.
7. Verifying the IDs of the owners of the company, whose names are included in the last update of the memorandum of association. Public joint-stock companies are excluded from this requirement.
• Where the owner or one of the owners of the company is an endowment, private society/foundation or cooperative association, according to the memorandum of association, the bank must then fulfill the following, in addition to the above requirements:
1. Obtaining a copy of a valid endowment registration certificate issued by the General Authority of Awqaf, including at minimum the following: Name of endowment, endowment deed number and date, and names of administrators and their ID numbers (for endowments); or a copy of the license issued by the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development and the decision of the board of directors of the society/foundation (meeting minutes) approving the establishment of the company (for private societies/foundations or cooperative associations).
2. Obtaining copies of the IDs of administrators whose names are stated in the endowment registration certificate (for endowments).
3. This type of accounts shall be classified as of high risk if the ownership of endowments, private societies/foundations or cooperative associations exceeds 50% of the company's capital.
300.1.3.1 Joint-Stock and Simplified Joint-Stock Companies
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (44061480), Dated 28/07/1444H, corresponding to 18/02/2023G, please refer to the Arabic version of this rule to read the last updated version.• Companies under formation:
The bank accounts for depositing and retaining the capital of these companies under formation shall be opened as follows:
1. A letter from the founders, including at a minimum: a request to open the account stating its purpose as "Depositing the capital of the company (…name of the company) Under Formation," the names of the founders, and the ownership percentage of each founder in the company's capital.
2. The name of the account shall be as follows :"Founders Account of the Company (name of the company) "
3. Verifying the identity of the company's founders.
4. Payment from the account shall only be allowed by the company's board of directors after its registration in the commercial register and the bank's completion of the required documents in accordance with the requirements of Rule (300-1-3) related to resident companies. In the event the company's formation is not completed, the bank must return the amounts to each founder according to their share of the capital.
• Licensed companies:
Documents required are as specified in (300.1.3) above.
300.1.3.2 Limited Liability Companies
Documents required are as specified in (300.1.3) above.
300.1.3.3 General Partnerships
Documents required are as specified in (300.1.3) above.
300.1.3.4 Limited Partnerships
Documents required are as specified in (300.1.3) above.
300.1.3.5 GCC Commercial Non-Banking Companies Residing in Saudi Arabia
Should a GCC company acquire a commercial register in Saudi Arabia (without investment license issued by the Ministry of Investment), such company shall be treated as a resident company, subject to the same requirements applicable to Saudi resident companies. Consequently, such GCC company shall submit the required documents specified in (300.1.3) above.
300.1.3.6 Rules for Opening Escrow Accounts for Real Estate Development Projects
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (46028059), Dated 08/05/1446H, corresponding to 09/11/2024G.The bank may open escrow accounts for real estate projects (sale or rental of off-plan real estate projects or real estate contributions) after fulfilling the following documents and procedures:
1. Verifying and identifying of the real estate developer, consulting office/engineering consultant, and certified public accountant in the legal form for each of them.
2. A written undertaking shall be made by the real estate developer stating that no disbursement shall be made from the account for purposes other than those concerning the project determined or its returns in the escrow account.
3. A written undertaking shall be made by the real estate developer stating its consent to amend the escrow account agreement to comply with any relevant laws, regulations, or instructions.
- Controls related to Opening and Managing Escrow Accounts for Off-Plan Sale or Rental Real Estate Projects:
1. Only one account shall be opened for each individual project and shall be named as follows: "name of project" Project- Escrow Account for "name of real estate developer”. Sub-accounts linked to the main account of the project may be opened, such as administrative and marketing expenses account, savings account, construction cost account, incentives account and finance account.
2. Payment shall be made from the project's escrow account based on the payment document submitted by the real estate developer to the bank. Such documents shall be certified by the consulting office and the certified public accountant and shall include the required amounts and justifications for their expenditure. Payment documents may be processed through secure technological means.
3. By exception to the provision in paragraph (2) above, payment may be made from the escrow account upon request from the Real Estate General Authority. The bank shall be notified through the Saudi Central Bank.
4. Payment from the account shall be made by check or transfers only and shall be within the limits stated in Paragraphs (2) and (3) above.
5. Deposits in the account shall be made by buyers, tenants, or financiers via any means of payment accepted by the bank other than cash.
- Controls for Opening and Managing Escrow Accounts for Real Estate Contribution Projects:*
1. Only one account shall be opened for each individual project and shall be named as follows: "name of project" Project- Escrow Account for "Real Estate Contribution”. Sub-accounts linked to the main account of the contribution may be opened, such as: reserve account, revenue account, and any other sub-accounts for the purpose of the contribution project, such as a finance account.
2. Payment shall be made from the project's escrow account based on the payment document submitted by the real estate developer to the bank. Such documents shall be certified by the engineering consultant and the certified public accountant and shall include the required amounts and justifications for their expenditure. Payment documents may be processed through secure technological means.
3. Payment from the account shall be made by check or transfers only and shall be within the limits stated in Paragraph (2) above.
4. Payment shall be made from the reserve account based on the payment document submitted by the real estate developer to the bank. Such documents shall be certified by the engineering consultant and the certified public accountant and shall include the required amounts and justifications for their expenditure, along with the approval from the shareholders' association.
5. Payment shall be made from the revenue account based on the disbursement document submitted by the real estate developer, which must be recorded on the shareholders' register and certified by the certified public accountant. The document must include the required amounts and be accompanied by the completion certificate from the consultant or proof of the liquidation of the real estate contribution.
6. Deposits into the main and sub-accounts shall be made by the relevant financial market institution for issuing contribution certificates, financiers, or buyers, or from proceeds of the liquidation of the real estate contribution, by any accepted method, and cash deposits are not permitted.
- General Provisions:
1. The bank shall not activate the escrow account for the real estate project unless the license issued by the “Authority” to engage in the off-plan sale or rental of real estate projects or to offer the real estate contribution is submitted.
2. Project’s sub-accounts shall be used only for receiving/making deposits and transfers from and (in)to the main account.
3. No funds may be transferred from the escrow account to any other accounts other than that of its sub-accounts whose purposes are specified.
4. Checkbooks may be issued for this account at the request of the real estate developer. However, ATM cards and/or credit cards shall not be issued for this account.
5. The bank shall not attach the account for its own interest or that of the creditors of the real estate developer.
6. The bank shall not close the escrow account for the project except after obtaining approval from the relevant authority, without prejudice to the provisions of SAMA's instructions and the agreements in place.
* This rule has been added pursuant to the circular No. (46028059), Dated 08/05/1446H, corresponding to 09/11/2024G.
300.1.3.7 Collection Accounts for Depositing and Retaining the Funds of Payment Companies’* Clients
This rule has been added pursuant to the circular No. (42073085), Dated 21/10/1442H, corresponding to 01/06/2021G.The collection accounts for depositing and retaining the funds of payment companies’ clients shall be opened and managed in accordance with the following requirements:
1. A letter from the Chairperson of the Board of Directors of the company or their authorized representative to the bank, stating the purpose of opening the account under the name “Deposit and Retention of the Funds of (name of payment company)‘s Clients”, and identifying the persons authorized to manage the account.
2. A copy of SAMA’s non-objection letter to open a collection account for the company for the purpose of depositing and retaining the funds of their clients.
3. Copies of all the company’s incorporation documents, including the memorandum of association, articles of association and Board formation decision.
4. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to manage the account.
5. The name of the account shall be “Deposit and Retention of the Funds of (name pf payment company)‘s Clients”.
6. The account shall be separate and independent from the accounts opened for managing the company’s business, including the fees and commissions collected by the company. The account shall not be used for any financial obligations or rights of the company.
7. Payment transactions and transfer of money to other accounts, other than the payment orders made by clients, shall only be made after submitting SAMA’s non-objection for such transaction.
8. Cash deposits to or withdrawals from the account shall not be allowed.
* Payment Service Providers
300.1.3.8 Collection Accounts for Managing the Finance Value of Debt-Based Crowdfunding Companies
This rule has been added pursuant to the circular No. (42075950), Dated 29/10/1442H, corresponding to 09/06/2021G, and amended by circular No. (000046024651), dated 19/04/1446H, corresponding to 22/10/2024G.The collection accounts for collecting funds from participants in order to extend credit to beneficiaries shall be opened and managed in accordance with the following requirements:
1. A letter from the Chairperson of the Board of Directors of the company or their authorized representative to the bank, stating the purpose of opening the account under the name “Management of the Finance Amount of (name of debt-based crowdfunding company)”, and identifying the persons authorized to manage the account.
2. Copies of all the company’s incorporation documents, including the memorandum of association, articles of association and Board formation decision.
3. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to manage the account.
4. The name of the account shall be “Management of the Finance Amount of (name of debt-based crowdfunding company).”
5. The account shall be separate and independent from the accounts opened for managing the company’s business, including the fees and commissions collected by the company. The account shall not be used for any financial obligations or rights of the company.
6. Transfer of money to other accounts without the approval of the participants shall only be made after submitting SAMA’s non-objection for such transaction.
7. Cash deposits to or withdrawals from the account shall not be allowed.
300.1.3.9 Companies in the Special Logistics Zone
The bank may open accounts for companies that are established and registered in the Special Logistics Zone of the General Authority of Civil Aviation (GACA)- under Companies Regulations for the Special Integrated Logistics Zone- after submitting the following documents:
- A copy of the commercial register issued by the GACA.
- A copy of the company’s memorandum of association and appendixes.
- Verifying the IDs of the board members/executives.
- A power of attorney issued by a notary public or a notary or an authorization made in the bank by the person(s) who has the authority, by the memorandum of association or partners’ decision or board/executives’ decision, to authorize natural persons to sign and operate accounts.
- Copies of the IDs of individuals authorized to sign for and operate the accounts.
300.1.4 Residents Investing Under Foreign Investment Law
No: 65681/67 Date(g): 3/7/2019 | Date(h): 1/11/1440 Status: In-Force This rule has been respectively amended according to the circular No. (41029537), dated 27/04/1441H, corresponding to 24/12/2019G ,and circular No. (44082632), dated 28/10/1444H, corresponding to 18/05/2023G,please refer to the Arabic version of this rule to read the last updated version.The bank may open accounts for entities wholly owned by a foreign investor or jointly owned by a foreign investor and a Saudi investor upon receiving the following:
300.1.4.1 Joint-Venture Entities Owned by a Saudi Investor and a Foreign Investor
This rule has been respectively amended according to the circular No. (41029537), dated 27/04/1441H, corresponding to 24/12/2019G ,and circular No. (44082632), dated 28/10/1444H, corresponding to 18/05/2023G,please refer to the Arabic version of this rule to read the last updated version.• Joint-venture entity owned by a foreign investor (natural or juristic) and a Saudi investor (natural or juristic):
1. A copy of the license issued by the Ministry of Investment.
2. A copy of the commercial register without the need to acquire the business license, or a copy of the professional license of the entity if the entity is a service provider.
3. A copy of the memorandum of association or the articles of association and its annexes.
4. A copy of the ID of the manager in charge in the entity. A copy of the passport can be sufficient, provided that a copy of the Iqama is submitted (90) days after opening the account.
5. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to operate and manage the account, and verification of their authorization by identifying them in the memorandum of association, the articles of association, or a decision from the board of directors or partners – or their equivalent. If the authorized person for the account is an agent acting on behalf of the principal, a copy of the power of attorney issued by a notary public or a notary in Saudi Arabia must be provided, or the power of attorney must be authenticated by the Saudi embassy or with an Apostille Authentication if issued outside Saudi Arabia.
6. Understanding the ownership structure and identifying the partners whose names are mentioned in the memorandum of association or the articles of association, and verifying them using documents, data, or information from a reliable and independent source. -In cases where money laundering risks are lower-, the verification process can be completed later, after the account is opened, provided that it is done as quickly as possible. Any delay in identity verification must be necessary to avoid disrupting normal business procedures, and appropriate and effective measures should be applied to control money laundering risks.
300.1.4.2 Entities Wholly Owned by a Foreign Investor
This rule has been respectively amended according to the circular No. (41029537), dated 27/04/1441H, corresponding to 24/12/2019G ,and circular No. (44082632), dated 28/10/1444H, corresponding to 18/05/2023G,please refer to the Arabic version of this rule to read the last updated version.• Branches of foreign corporations or companies:
1. A copy of the license issued by the Ministry of Investment.
2. A copy of the commercial register without the need to acquire the business license, or a copy of the professional license of the entity if the entity is a service provider.
3. A copy of the ID of the manager in charge in the entity. A copy of the passport can be sufficient, provided that the Iqama is submitted (90) days after opening the account.
4. A copy of the commercial register or professional license, as well as the memorandum of association or the articles of association of the entity in the home country, certified by the Saudi embassy or with an Apostille Authentication.
5. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to operate and manage the account, along with verification of their authorization by identifying them in a mandate from the main office of the company or corporation in the home country. The authorization must name the persons authorized to sign on behalf of the company in Saudi Arabia regarding the bank accounts.
6. Understanding the ownership structure and identifying the partners of the entity in the home country, whose names are mentioned in the memorandum of association or the articles of association, and verifying them using documents, data, or information from a reliable and independent source. -In cases where money laundering risks are lower-, the verification process can be completed later, after the account is opened, provided that it is done as quickly as possible. Any delay in identity verification must be necessary to avoid disrupting normal business procedures, and appropriate and effective measures should be applied to control money laundering risks.
• An entity owned by a foreign investor or jointly owned by more than one foreign investor:
1. A copy of the license issued by the Ministry of Investment.
2. A copy of the commercial register without the need to acquire the business license, or a copy of the professional license of the entity if the entity is a service provider.
3. A copy of the memorandum of association or the articles of association and its annexes.
4. A copy of the ID of the manager in charge in the entity. A copy of the passport can be sufficient, provided that the Iqama is submitted (90) days after opening the account.
5. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to operate and manage the account, and verification of their authorization by identifying them in the memorandum of association, the articles of association, or a decision from the board of directors or partners – or their equivalent. If the authorized person for the account is an agent acting on behalf of the principal, a copy of the power of attorney issued by a notary public or a notary in Saudi Arabia must be provided, or the power of attorney must be authenticated by the Saudi embassy or with an Apostille Authentication if issued outside outside Saudi Arabia.
6. Understanding the ownership structure and identifying the partners whose names are mentioned in the memorandum of association or the articles of association, and verifying them using documents, data, or information from a reliable and independent source. -In cases where money laundering risks are lower-, the verification process can be completed later, after the account is opened, provided that it is done as quickly as possible. Any delay in identity verification must be necessary to avoid disrupting normal business procedures, and appropriate and effective measures should be applied to control money laundering risks.
• Foreign individual investor (Sole proprietorships):
1. A copy of the license issued by the Ministry of Investment.
2. A copy of the commercial register without the need to acquire the business license.
3. A copy of the Iqama for the manager in charge and the investor, owner of the entity. A copy of the passport can be sufficient, provided that the Iqama is submitted (90) days after opening the account.
4. The full address of the investor in his/her home country.
5. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to operate and manage the account, as identified in a power of attorney certified by a notary public or a notary if issued inside Saudi Arabia and by the Saudi embassy or Apostille Authentication if issued outside Saudi Arabia, in the case of an agent or authorized person other than the owner of the entity.
300.1.5 Rules for Non-Profit Sector, Hajj and Umrah Entities, and Public Entities
The bank may open accounts for non-profit sector, Hajj and Umrah entities, and public entities upon fulfilling the requirements set forth for each activity as outlined below. Only residents in Saudi Arabia are allowed to operate the accounts of these licensed entities, with the exception of individuals authorized to operate Hajj and Umrah accounts as per Rule (300.1.5.1). Copies of the IDs of such persons must be obtained for account opening.
300.1.5.1 Hajj, Umrah and Visiting the Prophet’s Mosque in Madinah
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (46032385), Dated 29/05/1446H, corresponding to 30/11/2024G.• Pilgrim affairs offices:
a. Requirements for opening a bank account:
1. Bank accounts shall be opened in Saudi riyal only.
2. The Hajj organizer shall present to the bank a letter from the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah approving opening a bank account for the pilgrim affairs office and including the office’s information as follows:
■ The official name of the pilgrim affairs office.
■ Names of the persons authorized to sign for the account (joint signature), provided that they shall be members of the pilgrim affairs office or shall be officials in the embassy of the country of such office.
■ The position of each account signatory and his/her information as per his/her passport.
■ The bank account shall be limited to Hajj purposes only.
■ The office’s bank account number in its home country or in the country designated by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah ,and the name of the bank transferring the money, which the office deals with in its home country or in the country designated by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah, shall also be stated.
3. The bank shall conclude an account opening agreement with the authorized signatories specified in the letter of the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah, addressed to the bank.
4. The account signatories shall determine, in Saudi riyal, the approximate total amount that their respective office will transfer for Hajj purposes.
5. Upon meeting the above requirements by the bank, the bank’s compliance department shall submit an application to SAMA along with all necessary documents to obtain SAMA approval for opening the bank account.
6. The bank shall ensure that such accounts are subject to dual control.
7. The bank shall provide the pilgrim affairs office and the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah with the IBAN number of the office’s bank account.
8. If the requirements for opening a bank account are not met, the bank branch manager must inform the applicant of the necessary requirements for opening a bank account. Such process shall be documented in a special file designed for this purpose in the bank branch. In addition, measures taken in this regard shall be reported to the compliance department at the head office of the bank on the same day.
9. If the requirements for opening a bank account are met, the documents shall be submitted on the same day to the compliance department at the bank’s head office. Consequently, the compliance department, in turn, shall submit such documents to SAMA on the same day or at the beginning of the following working day, at the most.
10. The pilgrim affairs office may open multiple accounts, provided that these accounts are opened in the same bank only - with an explanation of the account's purpose -, The office may not open other accounts in other banks. If the office requests to transfer its accounts from one bank to another, it shall provide compelling justifications that are not related to meeting the requirements. Approval of the Ministry Hajj and Umrah and SAMA for that matter shall be secured.
b. Requirements for account operation and management:
1. The account shall be operated under a new approval letter from the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah to the bank on the account operation. The letter should specify the operation period, which should be from the beginning of Rabi II up till the end of Muharram of the following year. The letter shall be accompanied by a list provided by the pilgrim affairs office. This list shall include the names of Saudi natural persons, companies and establishments that the office will be dealing with for petty expenses, and it shall be attested by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah.
2. Deposits shall be made in the accounts of the pilgrim affairs office via remittances from a bank in the office’s home country or countries designated by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah, the purpose of such remittance shall be specified as “office’s expenses related to Hajj only”.
3. Deposits may be made in the account via checks under collection, drawn by the office itself on a bank in the office’s home country only.
4. Remittances, checks or cash deposits from entities inside Saudi Arabia shall not be accepted, except in the following cases:
■ By persons whose names are included in the list, submitted in advance to the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah by the pilgrim affairs office and attached to the ministry's letter to the bank. Such list should include the names of service providers dealing with the pilgrim affairs office. The amounts of such remittances, shall be less than or equal to the amounts stated in contracts concluded with each beneficiary (at the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah’s discretion).
■ By authorized persons, provided that such an amount is within normal limits, i.e. is less than or equal to the withdrawn amount as petty expenses (at the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah’s discretion).
■ The amounts (in SAR/foreign currencies) disclosed at ports of entry (land ports, seaports, or airports) shall be delivered to the bank branch at the port or the bank representative in the seasonal office at the port as per a document from the Saudi Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority. Such document shall include the name of the pilgrim affairs office and its account number (IBAN) in Saudi Arabia, as well as the name of the cash carrier and a copy of his/her passport. The bank employee shall give the depositor a deposit or transfer receipt attested by the bank.
5. Transfers from the office’s account to the electronic pathway of the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah are made for services contracted through the electronic pathway. Direct transfers from the office’s account in its country—or in countries designated by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah—to the electronic pathway account of the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah for external pilgrims are allowed for contracting purposes related to Hajj arrangements and any other purposes specified by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah, in compliance with all requirements stated in this rule.
6. The organizer may pay authorized signatories by checks for petty expenses (within the estimated amounts approved by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah).
7. The approval of the bank’s compliance department is required for the operation of the office’s account.
8. The office shall not use its account balances for investments.
c. Operating the pilgrim affairs office’s account after Hajj season:
1. At the end of the Hajj season (end of Muharram), amounts left in the account of the pilgrim affairs office shall be returned to a bank in the office’s home country or to a bank in one of the countries designated by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah in case they were the source of these funds at the request of the authorized persons in the office. Such a request shall be indicated in the bank account opening agreement signed by the office.
2. If the office wants to keep the balance in the same account to be used in the subsequent Hajj year, the account will be frozen at the end of Muharram until the beginning of the subsequent Hajj season (which is to be specified by the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah).
3. In exceptional cases, operating the account of the pilgrim affairs office may be allowed during the period in which using the account is originally prohibited, provided that the bank obtains SAMA written approval therefor.
d. Reactivating and operating the pilgrim affairs office’s account in the following Hajj year:
To reactivate the pilgrim affairs office’s bank account in the following Hajj year, the bank shall obtain a letter from the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah, including the same information specified in the form filled out by the ministry when it first approved the account opening. In particular, the information should include the names of authorized persons and their information. The approval letter should be obtained along with the list provided by the pilgrim affairs office for the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah, stating the parties that the office has contracted with in the Hajj year and that the office will write checks and make payments for. This list shall be attested by the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah.
• Tourism companies and travel agencies organizing pilgrim arrival from outside Saudi Arabia:
a. Requirements for opening a bank account:
1. Bank accounts shall be opened in Saudi riyal only.
2. The Hajj organizer shall present to the bank a letter from the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah approving opening a bank account for the pilgrim affairs office and including the office’s information as follows:
■ Official name of the organizer (tourism company, agency or association approved to organize pilgrims’ arrival) in Arabic and English.
■ The computer number given to the organizer by the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah.
■ Name(s) of person(s) authorized to manage the bank account, provided that they are officials in the tourism company, agency or association approved to organize for pilgrim arrival. Full names shall be written in English and Arabic as shown in their passports, along with their passport number.
■ The authorized person’s title shall be a “Hajj organizer".
■ The bank account shall be limited to Hajj purposes only.
■ The organizer’s bank account number in its home country or or in the country designated by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah, shall be specified, as well as the name of the bank transferring funds, which the organizer deals with in its home country or in the country designated by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah.
3. A copy of the organizer’s commercial register and/or license issued for the organizer in its home country shall be submitted. Such commercial register and/or license shall be attested by the concerned Saudi embassy and/or the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
4. The bank must obtain copies of the passports of person(s) authorized to operate the bank account for dual control.
5. The bank shall conclude an account opening agreement with the authorized signatories.
6. The organizer shall determine, in Saudi riyal, the approximate total amount that it will transfer for Hajj purposes.
7. Upon meeting all the above requirements by the bank, the bank’s compliance department shall submit an application to SAMA along with all necessary documents to obtain SAMA approval for opening the bank account.
8. The bank shall ensure that such accounts are subject to dual control.
9. The bank shall provide the organizer and the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah with the IBAN number of the organizer's account on a form designed for this purpose.
10. If the requirements for opening a bank account are not met, the bank branch manager must inform the applicant of the necessary requirements for opening a bank account. Such process shall be documented in a special file designed for this purpose in the bank branch. In addition, measures taken in this regard shall be reported to the compliance department at the head office of the bank on the same day.
11. If the requirements for opening a bank account are met, the documents shall be submitted on the same day to the compliance department at the bank’s head office. Consequently, the compliance department, in turn, shall submit such documents to SAMA on the same day or at the beginning of the following working day, at the most.
12. Where all requirements are met, the period for opening a bank account shall not exceed two working days.
13. The Hajj organizer may open multiple accounts, provided that these accounts are opened in the same bank only - with an explanation of the account's purpose - The organizer may not open other accounts in other banks. If the organizer requests to transfer its accounts from one bank to another, it shall provide compelling justifications that are not related to meeting the requirements. Approval of the Ministry Hajj and Umrah and SAMA for that matter shall be secured.
b. Requirements for account operation and management:
1. The account shall be operated under a new approval letter from the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah to the bank on the account operation. The letter should specify the operation period, which should be from the first day of Rabi I up till the last day of Muharram of the following year. The letter shall be accompanied by a list provided by the Hajj organizer. This list shall include the names of Saudi natural persons, companies and establishments that the organizer will be dealing with for petty expenses, and it shall be attested by the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah.
2. Deposits shall be made in the account of the Hajj organizer via remittances from a bank in the organizer’s home country or countries designated by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah, the purpose of such remittance shall be specified as “organizer’s expenses related to Hajj only”.
3. Deposits may be made in the account via checks under collection, drawn by the organizer itself on a bank in the organizer’s home country only.
4. Remittances, checks or cash deposits from entities inside Saudi Arabia shall not be accepted, except in the following cases:
■ By persons whose names are included in the list, submitted in advance to the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah by the organizer and attached to the ministry's letter to the bank. Such list should include the names of service providers dealing with the organizer. The amounts of such remittances, checks or cash deposits shall be less than or equal to the amounts stated in contracts concluded with each beneficiary (at the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah’s discretion).
■ By authorized persons, provided that such an amount is within normal limits, i.e. is less than or equal to the withdrawn amount as petty expenses (at the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah’s discretion).
■ The amounts (in SAR/foreign currencies) disclosed at ports of entry (land ports, seaports, or airports) shall be delivered to the bank branch at the port or the bank representative in the seasonal office at the port as per a document from the Saudi Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority. Such document shall include the name of the organizer and its account number (IBAN) in Saudi Arabia, as well as the name of the cash carrier and a copy of his/her passport. The bank employee shall give the depositor a deposit or transfer receipt attested by the bank.
5. Transfers from the office’s account to the electronic pathway of the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah are made for services contracted through the electronic pathway. Direct transfers from the office’s account in its country—or in countries designated by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah—to the electronic pathway account of the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah for external pilgrims are allowed for contracting purposes related to Hajj arrangements and any other purposes specified by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah, in compliance with all requirements stated in this rule.
6. The organizer may pay authorized signatories by checks for petty expenses (within the estimated amounts approved by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah).
7. The approval of the bank’s compliance department is required for the operation of the organizer’s account.
8. The organizer shall not use its account balances for investments.
c. Operating the organizer’s account after Hajj season:
1. At the end of the Hajj season (end of Muharram), amounts left in the account of the organizer shall be returned to a bank in the office’s home country or to a bank in one of the countries designated by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah in case they were the source of these funds at the request of the authorized persons. Such a request shall be indicated in the bank account opening agreement signed by the organizer.
2. If the organizer wants to keep the balance in the same account to be used in the subsequent Hajj year, the account will be frozen at the end of Muharram until the beginning of the subsequent Hajj season (which is to be specified by the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah).
3. In exceptional cases, operating the account of the organizer may be allowed during the period in which using the account is originally prohibited, provided that the bank shall obtain SAMA written approval therefor.
d. Reactivating and operating the organizer’s account in the following Hajj year:
To reactivate the organizer’s bank account in the following Hajj year, the bank shall obtain a letter from the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah, including the same information specified in the form filled out by the ministry when it first approved the account opening. In particular, the information should include the names of authorized persons and their information. The approval letter should be obtained along with the list provided by the organizer for the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah, stating the parties that the organizer has contracted with in the Hajj year and that the organizer will write checks and make payments for. This list shall be attested by the Ministry of Hajj and Umrah.
• Saudi establishments and companies organizing the arrival of Umrah performers and visitors of the Prophet's Mosque:
- Documents required from those Saudi establishments are as specified in Rule (300.1.1) above.
- Documents required from those Saudi companies are as specified in Rule (300.1.3) above.
- All bank accounts of Saudi establishments and companies licensed to offer Umrah and holy site visit services shall be separated from one another, in that bank accounts designated for Umrah and holy site visit services shall be separate from other bank accounts designated for other activities and services. In addition, all bank transactions related to Umrah services shall be separate from those related to other services and activities that such establishments and companies may carry out.
300.1.5.2 Private Associations
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (106878603), Dated 01/07/1446H, corresponding to 31/12/2024H. Please refer to the Arabic version of this rule to read the last updated version.
The bank may open accounts only in Saudi riyal for private associations. The requirements are as follows:a. Requirements and controls for opening and managing main bank accounts:
- Requirements for opening main account:
1. A copy of the registration certificate issued by the National Center for the Development of the Non-Profit Sector (NCNP) (the Center).
2. A copy of the association's bylaws, approved by the Center.
3. A copy of the decision to form the board of directors and appoint the officials, which is approved by the Center, along with the verification of the board members' identities.
4. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to operate and manage the account, and verification of their authorization by identifying them in the decision of the board of directors; such authorization shall allow for joint signature by two officials, and obtaining the approval of the Center when the authorized persons are from outside the board.
5. Approval of the bank’s senior management to open the account in cases where required -in accordance with the provisions of the Guidance of Anti Money Laundering and Combating Terrorist Financing-.
- Controls for managing the main account:
1. Cash donations or donations made via electronic channels may be accepted as long as these donations come from banking sources inside Saudi Arabia only, through which donor’s information can be retrieved.
2. If disbursement is made by a check, the check shall be payable to the first beneficiary.
3. ATM and/or credit cards shall not be issued for such accounts.
4. No transactions (e.g. remittance, collection of checks, etc.) from the association’s accounts to any beneficiaries outside Saudi Arabia shall be made, except for transferring money for the purpose of managing the association’s activities. For example, remittance for paying fees of consulting services or of participation in external symposiums, conferences and the like may be made after the bank obtains the official approval therefore from the Center (NCNP).
5. Remittances or checks coming from outside Saudi Arabia to the association’s account at the bank -or coming to other banks operating in Saudi Arabia via the bank- shall not be accepted, unless official approval therefore is obtained from the Center (NCNP).
6. Sub-accounts may be opened for investing the association’s funds in activities with financial returns that would help the association achieve its objectives. To do so, the bank must first obtain the association’s rules that govern the investment of its surplus funds, which are approved by its general assembly.
b. Requirements and controls for opening and managing sub-accounts:
Sub-accounts may be opened for the various purposes of the association, such as the collection of Zakat, as follows:
1. Only the documents for opening and managing the main account shall be required.
2. These accounts shall be used only for the purpose for which they were opened.
3. Cash donations or donations made via electronic channels may be accepted as long as these donations come from banking sources inside Saudi Arabia only, through which donor’s information can be retrieved.
4. In case there are branches of the association, one sub-account may be opened for each branch of the association, with the primary purpose being "Expenses-Branch Name", as follows: a. A copy of the approval of the Center (NCNP) for establishing the branch for which a sub-account is to be opened. b. A copy of the organizational structure decision for the branch and the names of the employees in its management, approved by the Center (NCNP), with Verifying their identities. c. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to operate and manage the bank account, and verification of their authorization by identifying them in the decision of the association's board of directors; such authorization shall allow for joint signature by two officials, and obtaining the approval of the Center when the authorized persons are from outside the board. d. The sub-account shall be named “Branch of... Association/Office in (City)-Subaccount of Periodic Advance”. e. Disbursements from the account shall be limited to the following: - bank checks withdrawn only by the first beneficiary. - Transfers made to the bank accounts of beneficiaries of charity inside Saudi Arabia only. The transfer forms shall be filled out by the persons authorized to sign for the advances’ account. In addition, the transfers shall be monitored by the bank to ensure that they go in line with the nature of the branch’s activities. - Paying salaries of the association branch’s staff. - Paying utility bills and government invoices. f. ATM and/or credit cards shall not be issued for such accounts. g. Approval of the bank’s senior management to open the account in cases where required -in accordance with the provisions of the Guidance of Anti Money Laundering and Combating Terrorist Financing-. h. Cash donations or donations made via electronic channels may be accepted as long as these donations come from banking sources inside Saudi Arabia only, through which donor’s information can be retrieved. 300.1.5.3 Private Foundations
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (106878603), Dated 01/07/1446H, corresponding to 31/12/2024H. Please refer to the Arabic version of this rule to read the last updated version.The bank may open accounts only in Saudi riyal for private Foundations. The requirements are as follows:
a. Requirements and controls for opening and managing main bank accounts:
- Requirements for opening main account:
1. A copy of the registration certificate issued by the National Center for the Development of the Non-Profit Sector (NCNP) (the Center).
2. A copy of the foundation's bylaws, approved by the Center.
3. A copy of the trustee board formation decision and verifying the identities of the members.
4. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to operate and manage the bank account, and verification of their authorization by identifying them in the decision of the trustees board; such authorization shall allow for joint signature by two officials, and obtaining the approval of the Center when the authorized persons are from outside the board.
5. Approval of the bank’s senior management to open the account in cases where required -in accordance with the provisions of the Guidance of Anti Money Laundering and Combating Terrorist Financing-.
- Controls for managing the main account:
1. If disbursement is made by a check, the check shall be payable to the first beneficiary.
2. ATM and/or credit cards shall not be issued.
3. A prepaid card may be issued and funded based on the joint signature of the authorized persons on the account.
4. The foundation is not allowed to accept gifts, bequests, donations, endowments, grants, or Zakat from parties other than the founders specified in its bylaws, unless the approval of the Center is obtained. Additionally, private foundations are not allowed to carry out any cash dealings.
5. No transactions (e.g. remittance, collection of checks, etc.) to any beneficiaries outside Saudi Arabia shall be made, except for transferring money for the purpose of managing the foundation’s activities. For example, remittance for paying fees of consulting services or of participation in external symposiums, conferences and the like may be made after the bank obtains the official approval therefore from the Center (NCNP).
6. Remittances or checks coming from outside Saudi Arabia to the foundation’s account at the bank shall not be accepted, unless official approval therefore is obtained from the Center (NCNP).
7. Sub-accounts may be opened for investing the foundation’s funds in activities with financial returns that would help the foundation achieve its objectives, after obtaining approval from the Board of Trustees.
b. Requirements and controls for opening and managing sub-accounts:
Sub-accounts may be opened for the various purposes of the foundation, as follows:
1. Only the documents for opening and managing the main account shall be required.
2. These accounts shall be used only for the purpose for which they were opened.
3. In case there are branches of the foundation, one sub-account may be opened for each branch of the foundation, with the primary purpose being "Expenses-Branch Name", as follows:
a. A copy of the approval of the Center (NCNP) for establishing the branch for which a sub-account is to be opened.
b. A copy of the organizational structure decision for the branch and the names of the employees in its management, approved by the Center (NCNP), with Verifying their identities.
c. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to operate and manage the account, and verification of their authorization by identifying them in the decision of the Board of Trustees of the Foundation; such authorization shall allow for joint signature by two officials, and obtaining the approval of the Center when the authorized persons are from outside the board.
e. Disbursements from the account shall be limited to the following:
- bank checks withdrawn only by the first beneficiary.
- Transfers made to the bank accounts of beneficiaries of material support inside Saudi Arabia only. The transfer forms shall be filled out by the persons authorized to sign for the expense sub-account. In addition, the transfers shall be monitored by the bank to ensure that they go in line with the nature of the branch’s activities.
- Paying salaries of the foundation branch’s staff.
- Paying utility bills and government invoices.
f. ATM cards and/or credit cards shall not be issued for such accounts.
g. A prepaid card may be issued and funded based on the joint signature of the authorized persons on the account.
h. Approval of the bank’s senior management to open the account in cases where required -in accordance with the provisions of the Guidance of Anti Money Laundering and Combating Terrorist Financing-.
- Civil Society Organizations established pursuant to royal orders:
This rule has been added pursuant to the circular No. (450651330000), dated 14/10/1445H, corresponding to 22/04/2024G. Please refer to the Arabic version of this rule to read the last updated version.
Bank accounts may be opened for Civil Society Organizations established pursuant to royal orders as follows:
1. A copy of the approval from His Majesty the King for the establishment of the civil society organization.
2. A copy of the articles of association of the organization.
3. A copy of the trustee board formation decision and verifying the identities of the members.
4. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to manage and operate the bank account, with verification of their authorization by identifying them in a decision by the Board of Trustees. The signature should be joint for two officials, unless the organization's articles of association state otherwise.
5. Any transactions (e.g. remittance, collection of checks, etc.) outside Saudi Arabia may be made after verifying that these transactions align with the activity or main purpose for which the organization was established, as per its articles of association.
6. No transactions (e.g. remittance, collection of checks, etc.) outside Saudi Arabia shall be made for an organization if it is evident that the transaction does not align with its activity or main purpose under its articles of association, except for transferring money for the purpose of managing the organization’s activities. For example, remittance for paying fees of consulting services or of participation in external symposiums, conferences and the like may be made after obtaining approval from the National Center for Non-Profit Sector.
• Family funds:
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (43074912), dated 26/08/1443H, corresponding to 29/03/2022G.and the circular No. (106878603), Dated 01/07/1446H, corresponding to 31/12/2024H. Please refer to the Arabic version of this rule to read the last updated version.The bank may open accounts only in Saudi riyal for family funds. The requirements are as follows:
a. Requirements and controls for opening and managing main bank accounts:
- Requirements for opening main account:
1. A letter from the chairman of the trustee board of the family fund (or their authorized representative) to the bank in which the account is to be opened clearly indicating the purpose of opening the account.
2. A copy of the registration certificate issued by the National Center for the Development of the Non-Profit Sector (NCNP).
3. A copy of the fund's bylaws, approved by the Center.
4. A copy of the trustee board formation decision approved by the Center, and verifying the identities of the members.
5. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to operate and manage the bank account, and verification of their authorization by identifying them in the decision of the trustees board and the approval of the Center. The signature should be joint for two officials.
Controls for managing the main account: 1. disbursement from the fund shall be in accordance with the methods and conditions stipulated in the fund's bylaws.
2. The family fund may accept funds, gifts, bequests, Zakat and subscriptions (if any) from its founders and family members only, provided that the bank obtains a pledge from the chairman of the fund’s trustee board to comply with this requirement.
3. No transactions (e.g. remittance, collection of checks, etc.) to any beneficiaries outside Saudi Arabia shall be made, except for transferring money for the purpose of managing the fund’s activities. For example, remittance for paying fees of consulting services or of participation in external symposiums, conferences and the like may be made after obtains the official approval therefor from the Center.
4. The family fund is allowed to invest its money according to the provisions stipulated in the fund’s bylaws.
5. Approval of the bank’s senior management to open the account in cases where required -in accordance with the provisions of the Guidance of Anti Money Laundering and Combating Terrorist Financing-.
b. Requirements and controls for opening and managing sub-accounts:
Sub-accounts may be opened for the various purposes of the fund, such as the collection of Zakat, as follows:
1. Only the documents for opening and managing the main account shall be required.
2. These accounts shall be used only for the purpose for which they were opened.
3. Cash donations or donations made via electronic channels may be accepted as long as these donations come from banking sources inside Saudi Arabia only, through which donor’s information can be retrieved.
4. In case there are branches of the fund, one sub-account may be opened for each branch of the fund, with the primary purpose being "Expenses-Branch Name", as follows:
a. A copy of the approval of the Center (NCNP) for establishing the branch for which a sub-account is to be opened.
b. A copy of the organizational structure decision for the branch and the names of the employees in its management, approved by the Center (NCNP), with Verifying their identities.
c. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to operate and manage the bank account, and verification of their authorization by identifying them in the decision of the fund's Board of Trustees; such authorization shall allow for joint signature by two officials, and obtaining the approval of the Center when the authorized persons are from outside the board.
d. The sub-account shall be named “Branch of... Fund/Office in (City)-Subaccount of Periodic Advance”.
e. Disbursements from the account shall be limited to the following:
- bank checks withdrawn only by the first beneficiary.
- Transfers made to the bank accounts of beneficiaries of charity inside Saudi Arabia only. The transfer forms shall be filled out by the persons authorized to sign for the advances’ account. In addition, the transfers shall be monitored by the bank to ensure that they go in line with the nature of the branch’s activities.
- Paying salaries of the fund branch’s staff.
- Paying utility bills and government invoices.
- Prepaid cards and deposits may be issued, provided that their issuance is based on a joint signature from the authorized persons on the bank account, and that the prepaid card is funded with a joint signature from the authorized persons
g. Approval of the bank’s senior management to open the account in cases where required -in accordance with the provisions of the Guidance of Anti Money Laundering and Combating Terrorist Financing-.
h. Cash donations or donations made via electronic channels may be accepted as long as these donations come from banking sources inside Saudi Arabia only, through which donor’s information can be retrieved.
• Charitable activities of (civil and military) government bodies:
The bank may open accounts only in Saudi riyal for charitable activities of (civil or military) government bodies. The following requirements and controls shall be met and applied:
1. The bank shall obtain, through SAMA, the approval of the Ministry of Finance for opening a bank account or for maintaining the operation of an existing account, if the account’s funds (or part of them) are from public funds.
2. The bank shall receive a request from the ultimate authority in the government body carrying out the charitable activity or the person he/she authorizes to open the account, if the account’s funds are not from public funds.
3. The bank shall receive from the ultimate authority or his/her authorized representative a letter containing the names of the persons authorized to manage the bank account (by joint signature), provided that such authorized persons are Saudi employees of the same government body.
4. Such government body shall not raise funds or accept donations, aids or gifts from anyone except from its staff.
5. Deposits are accepted in cash, by checks, and through domestic direct transfer. In addition, deposits can be carried out using ATMs, Internet or credit cards. In all deposits, depositor’s information shall be obtained.
6. No ATM cards and/or remittance membership shall be issued/granted for the account.
7. The government body wishing to open such bank account shall undertake that the beneficiaries of such account are from its staff and their families.
8. Disbursement from the account shall be made by checks payable to the first beneficiary, or via wire transfer from the main account to the first beneficiary’s account.
9. Sub-accounts under the main account may be opened. Sub-accounts shall be used only for receiving deposits and making transfers to the main account. Checkbooks shall not be issued for such sub-accounts. Moreover, neither withdrawal nor transfer from these sub-accounts shall be allowed except to the main account.
10. Approval of the manager of compliance department for opening the account shall be sought.
- Civil Society Organizations established pursuant to royal orders:
300.1.5.4 Public Welfare Committees (e.g. Committees of Patients’ Friends, Committees Caring for People with Disabilities or Blind People, Committees of Academic Excellence Awards, Charitable Warehouses Licensed by Regional Governors, and the Like)
- The bank may open accounts for these committees only in Saudi riyal upon obtaining a copy of the committee’s license issued by the concerned official authority as per its jurisdiction, such as the Ministry of Education, the concerned emirate of the region, etc. Bank accounts for such committees shall be opened and managed under a joint signature of the committee chairman (or secretary) and its financial manager. Further, the bank shall obtain copies of the IDs of those two officials (the committee chairman/secretary and the financial manger), along with copies of the IDs of the members of the board of directors (or board of trustees). Copies of the bylaws of the committee/organization shall also be submitted to the bank. Approval of the manager of compliance department for opening the account shall be sought. Additionally, SAMA shall be informed about opening such accounts.
- Bank accounts may be opened for annual or seasonal public welfare activities, such as festivals, celebrations and the like, whose funds are not from the state budget. In this case, the bank shall receive a formal request from the concerned official entity organizing such activity to open the bank account. Such bank account shall be opened and managed under a joint signature of the person authorized to manage the activity and the financial manager; copies of their IDs shall also be obtained. In addition, the bank shall obtain copies of the IDs of the activity committee members. Moreover, the validity period of the account shall be specified; after such period the account shall be closed. Further, approval of the manager of compliance department for opening the account shall be sought. SAMA shall be informed about opening the account.
- Transferring funds from such accounts to parties outside Saudi Arabia is not permitted.
300.1.5.5 Bank Accounts for Collection of Shoppers' Donations of Remaining Halalas (Change) in Favor of Charities
1. Donation collection service shall be restricted to commercial enterprises with commercial registers.
2. Charities that can benefit from such voluntary donation shall be licensed to operate in Saudi Arabia, and its articles of association or bylaws shall permit collection of donations.
3. No commercial enterprise shall be allowed to provide the voluntary donation service of remaining halalas (change) in favor of charities (whether societies, foundations, committees or others) wishing to receive such donations without official permission from the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development or the authority supervising the charity.
4. The supervisory authority's permission shall include (or have enclosed therewith) the license number for collection of donations and its validity period, as well as the name of the commercial enterprise and its commercial register number.
5. Collection of donations of remaining halalas shall be subject to a two-party contract, i.e. a contract between the commercial enterprise collecting donations of remaining halalas and the charity receiving such donations. The contract shall state obligations of both parties, including that the commercial enterprise will not charge any fees for providing such service.
6. The contract may be extended for more than one period with the consent of the authority supervising the charity. In this case, all previous licenses of donation collection and their related accounts shall be revoked or settled prior to granting renewal approval at the end of the financial year.
7. Donations collected shall be submitted to the concerned charity by a crossed check or a bank transfer to its account at the end of each quarter of the Gregorian calendar year. In addition, the supervisory authority shall be furnished with copies of paid checks or bank transfer receipts.
8. The commercial enterprise shall state in the crossed check or transfer slip the name or account number of the charity and that the amount presented is the donation of remaining halalas by shoppers.
9. The halala-donation procedures, automatic system, and controls of the commercial enterprise shall consider the following:
■ Using a separate special payment means (e.g. cash/sale points) for donation of halalas.
■ Allocating a separate bank account under the name of the commercial enterprise with the clause "remaining halalas" for keeping amounts donated by costumers. This account shall include sub-accounts; each of which shall be designated for one charity with which the commercial enterprise has contracted.
300.1.5.6 Cooperative Associations and Funds
• Cooperative associations
a. Cooperative associations under establishment:
A Saudi Riyal trust account may be opened for a cooperative association under establishment for the purpose of capital raising. The following requirements shall be satisfied:
1. The bank shall receive a letter from the competent authority at the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development (MHRSD), stating that the cooperative association is under establishment and that the MHRSD agrees on opening an account for the association to raise its capital. The letter shall specify the name of the cooperative association under establishment and the name and ID number of the founding committee’s chairman, who is in charge of communicating with the bank for the account opening. In addition, a copy of the association’s preliminary memorandum of association shall be submitted to the bank with the letter.
2. The trust account shall be opened only for six months. The bank may extend this period for another six months upon receiving a request from the concerned authority at the MHRSD.
3. If the association is not registered and established within the period specified in Paragraph (2) above, amounts deposited in the trust account shall be returned upon the approval of the concerned authority at the MHRSD. The approval shall specify the method of returning such amounts and their recipient.
4. If the association is registered and established, the bank shall fulfill the requirements of Paragraph (b) below and shall convert the trust account into a current account.
b. Licensed cooperative associations:
The bank may open a Saudi Riyal account for cooperative associations upon fulfilling the following conditions and requirements:
1. Receiving a request of the association’s board chairman to open a bank account; the account to be opened shall be managed under a joint signature of the board chairman (or his/her vice-chairman) and the treasurer (principal signatory).
2. Obtaining a copy of the association registration and establishment decision (the association registration certificate) issued by the MHRSD.
3. Obtaining a copy of the entity’s board formation decision that is issued, approved or attested by the MHRSD.
4. Obtaining a copy of the entity’s memorandum of association.
5. Obtaining a copy of the entity’s bylaws.
6. Obtaining copies of the board members’ IDs.
• Cooperative funds:
The bank may open accounts for the cooperative funds upon fulfilling the following conditions and requirements:
1. Obtaining a copy of the decision allowing or approving the establishment of the fund, issued by the concerned minister, general director or sector head.
2. Naming the fund after the organization establishing it.
3. Ensuring that the account is opened and operated by the manager and treasurer of the organization that owns the fund.
4. Obtaining a copy of the regulations governing the fund, issued by the concerned government body.
5. Obtaining a copy of the regulations governing the fund, issued by the concerned government body.
300.1.5.7 Homeowners’ Associations/Housing Societies Licensed by the Real Estate General Authority
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (42003746), Dated 22/01/1442H, corresponding to 09/09/2020G.Banks may open bank accounts for homeowners’ associations/housing societies upon obtaining the following:
1. A letter from the real estate manager requesting the opening of the account, including the names of those authorized to manage and operate the account, certified by the chairman of the association/society.
2. A copy of the articles of association of the association/society.
3. A copy of the association/society registration certificate issued by the Real Estate General Authority.
4. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to manage and operate the account.
300.1.5.8 Endowments and Bequests
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (41042946), Dated 19/06/1441H, corresponding to 13/02/2020G.Without prejudice to Rules (300.1.1) and (300.1.3), bank accounts shall be opened in Saudi Riyal for endowments and bequests as follows:
1. Endowments:
a. Endowments under the administration of the General Authority for Awqaf:
1. A letter by the Governor of the General Authority for Awqaf, requesting the opening of a bank account under the name of “Revenues’’ shall be submitted. The persons authorized to operate the account shall be identified, and dual authorization shall be applied. The financial powers of or right to delegate for the persons authorized must be specified.
2. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to operate the account shall be submitted.
b. Endowments not under the administration of the General Authority for Awqaf:
1. The bank shall receive a copy of the valid endowment registration certificate issued by the General Authority for Awqaf, including at minimum, the following: name of endowment, endowment deed number and date, and names of administrators and their ID numbers.
2. A copy of the legal deed of the endowment shall be submitted.
3. A letter from the authorized signatory under the endowment deed, specifying the persons authorized to operate the account, shall be submitted.
4. Copies of the IDs of persons authorized to operate the account shall be submitted.
5. Copies of the IDs of administrators whose names are stated in the endowment registration certificate shall be submitted.
6. No transactions (e.g. remittance, collection of checks, etc.) from the endowment accounts to any beneficiaries outside Saudi Arabia shall be made, except for transferring money for the purpose of managing the association’s activities. For example, remittance for paying fees of consulting services or of participation in external symposiums, conferences and the like may be made after the bank obtains the official approval therefor from the General Authority for Awqaf.
c. Foreign endowments:
1. The bank shall receive a copy of the valid endowment registration certificate issued by the General Authority for Awqaf, including at minimum, the following: name of endowment, endowment deed number and date, and names of administrators and their ID numbers.
2. The bank shall receive a letter from the endowment administrator or agent (Saudi national), requesting the opening of a bank account. The letter shall be accompanied by a request from the authority responsible for endowments in the home country of the foreign endowment (or by a request from the ambassador of that country) and by the approval of the General Authority for Awqaf.
3. The bank shall receive a copy of the endowment’s legal deed stating that the property is allocated as Waqf (endowment) and registered with the competent authority in Saudi Arabia.
4. The bank shall receive a copy of the administration deed/power of attorney issued by the competent authority in Saudi Arabia, which provides for the full right to handle endowment and fulfill the donor's conditions. The administration deed does need to contain a provision for opening bank accounts, as the endowment administration includes this authority.
5. The bank shall receive a copy of the national ID of the endowment administrator/agent.
6. The bank account shall be in the name of the endowment as stated in the endowment deed and the registration certificate issued by the General Authority for Awqaf.
7. SAMA must be informed when the account is opened.
8. Withdrawal from this account shall be made by checks.
9. Transferring funds or issuing personal/bank checks from this account to beneficiaries outside Saudi Arabia shall not be allowed.
10. ATM cards and/or credit cards shall not be issued for such accounts.
11. Receiving remittances or checks from beneficiaries outside Saudi Arabia shall not be permitted without written approval from the General Authority for Awqaf.
2. Bequests:
1. The bank shall receive a copy (or a certified copy) of the guardianship deed, which provides for the bequests.
2. The bank shall receive a copy of the national ID of the trustee(s).
3. The account shall be in the name of the bequest (Bequest of..).
300.1.5.9 Cultural, Sports and Social Clubs and Youth Hostels
• Sports clubs licensed by the General Sports Authority:
The bank may open Saudi Riyal accounts for sports clubs licensed by the General Sports Authority upon receiving the following documents:
1. The approval of the Ministry of Finance for opening the account.
2. A copy of the license issued by the General Sports Authority.
3. A copy of the decision to form the club’s board of directors.
4. A copy of the authorization letter by the board of directors (joint signature), allowing specific persons to open and operate the account.
5. Copies of the IDs of the authorized persons and board members.
- Bank accounts for contributions of the club's members of honor and fans may be opened without the approval of the Ministry of Finance. Such accounts may be opened in Saudi Riyal or foreign currencies, but they shall be separated from the government subsidy account.
• Youth hostels:
Requirements for the sports clubs licensed by the General Sports Authority shall also apply to youth hostels.
• Cultural and literary clubs supervised by the Ministry of Culture:
The bank may open Saudi Riyal accounts for cultural and literary clubs supervised by the Ministry of Culture upon receiving the following documents:
1. The approval of the Ministry of Finance for opening the account.
2. A copy of the license issued by the supervisory authority.
3. a copy of the decision to form the club’s board of directors;
4. The authorization letter by the board of directors, allowing specific persons to open and operate the account under a joint signature.
5. Copies of the IDs of the authorized persons and board members.
• Camel Club, and its branches and offices:
The bank may open Saudi Riyal accounts for camel club and its branches and offices upon receiving the following documents:
1. A copy of the decision to form the club’s board of directors, issued by the Council of Ministers.
2. A copy of the authorization letter by the board of directors, allowing specific persons to open and operate the account.
3. Copies of the authorized signatories’ IDs.
4. Copies of the board members’ IDs.
5. Payment from the main account shall be made only for the purposes for which the account was established.
300.1.5.10 Public Corporations and Public Sector Institutions
The bank may open accounts for public corporations and public institutions (see Appendix "B" for further information on such entities and their names) upon obtaining the following documents:
1. A copy of the decision to form the entity’s board of directors, issued by the Council of Ministers.
2. A copy of the authorization letter by the board of directors, allowing specific person(s) to operate the account, along with copies of those persons’ IDs and their specimen signatures.
300.1.5.11 Chambers of Commerce and Industry
The bank may open accounts for chambers of commerce and industry upon obtaining the following documents:
1. A copy of the decision to form the chamber’s board of directors.
2. A copy of the authorization letter by the board of directors, allowing specific person(s) to open and operate the account, along with copies of those persons’ IDs and their specimen signatures.
300.1.5.12 Building, Renovating or Expanding Small and Large Mosques
The bank may open bank accounts designated for building, renovating or expanding small or large mosques. The following requirements shall be fulfilled:
1. The bank shall receive a letter from the Ministry of Islamic Affairs, Dawah and Guidance (MoIA) or any of its branches in the concerned region, requesting the opening of a bank account and indicating its purpose.
2. The bank shall obtain a copy of the approval of the MoIA or any of its branches in the concerned region for building, renovating or expanding a small or large mosque.
3. The bank shall obtain the decision made by the MoIA or any of its branches in the concerned region to form a committee to supervise the mosque construction, renovation or expansion process. The committee formed shall be chaired personally by the branch manager of the MoIA and include two members of the officials of MoIA branch in the concerned region.
4. The account shall be named “Branch of the Ministry of Islamic Affairs, Dawah and Guidance in... (building, renovating or expanding) (name of the mosque)”.
5. The account shall be operated personally by the manager of MoIA branch in the concerned region (principal signatory) with one or both of the committee members indicated above.
6. The bank shall obtain copies of the IDs of committee members who are authorized to sign for the account.
7. If funds are donations, the approval of the concerned authority shall be submitted.
8. Disbursement from the account shall be made only by checks, under a joint signature. In addition, ATM cards and/or credit cards shall not be issued for this account.
9. The account shall be valid for a period identical to the period specified by the MoIA for the mosque construction, renovation or expansion. Should there be a need to extend the validity period of the account, a letter to this effect shall be submitted to the bank by the MoIA or its concerned branch.
10. If account funds are from the state budget, as per a request from the MoIA, the approval of the Ministry of Finance shall be communicated to the bank through SAMA.
11. Approval of the manager of compliance department for opening the account shall be sought.
300.1.5.13 National Societies and Committees
The bank may open accounts for national societies and committees, such as the National Society for Human Rights and the National Prevention of Blindness Committee, upon completing the following:
1. Receiving a request from the chairman of the society/committee for opening a bank account.
2. Obtaining a copy of the royal approval or the resolution of the Council of Ministers, allowing the society or committee to exercise its activities.
3. Obtaining a copy of the articles of association of the society/committee.
4. Obtaining a copy of the society’s/committee’s regulations governing its financial affairs.
5. Obtaining copies of the IDs of society’s/committee’s executive council members.
6. The names of authorized signatories shall be determined by the chairman of the society/committee. The bank shall obtain copies of those signatories’ IDs and their specimen signatures. Such copies shall be attested as true copies of the original by both the society/committee and the bank. Changing the authorized signatories requires sending a letter from the chairman of the society/committee to the bank where the account is opened.
7. Withdrawal from these accounts shall be as per dual control, and in case of withdrawal by checks, check shall be payable to the first beneficiary.
300.1.5.14 Trial and Enforcement Courts
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (42036451), Dated 01/06/1442H, corresponding to 14/01/2021G.Bank accounts for trial courts, such as commercial courts and family courts, may be opened for the purpose of managing the cases pending before such courts and for the enforcement courts for the purpose of depositing execution funds as follows:
1. The bank shall receive a letter from the Deputy Minister of Justice for Enforcement or his authorized representative (for the bank accounts of enforcement courts), or a letter from the Deputy Minister of Justice for Judicial Affairs or his authorized representative (for the bank accounts of trial courts). The letter shall be addressed to the bank, requesting the opening of a bank account and stating the names of persons authorized to manage and operate the account under a joint signature (two signatories are required).
2. The bank shall obtain copies of the authorized signatories’ IDs and their specimen signatures.
3. The account shall be separate from other accounts of each court.
4. Disbursement from the account shall be made by checks payable to the first beneficiary, by transfers to the collection accounts such as the account opened under the name “Ministry of Justice/Deputyship for Enforcement) and designated for receiving funds via SADAD system, or by transfers to beneficiaries’ accounts. Where checks are used, the purpose of the check and the case number and date shall be written on the check.
5. ATM cards and/or credit cards shall not be issued for such accounts.
6. Transferring funds from these accounts to beneficiaries outside Saudi Arabia shall not be allowed. The exception to this rule is when the beneficiary is a foreign (natural or legal) person residing outside Saudi Arabia and the approval of the concerned deputy minister or the chief judge is obtained for the transfer.
300.1.5.15 Property Conveyancing Processes
The bank may open collection accounts for the purpose of property conveyancing and for enforcement of related decisions. The following requirements and controls shall be met and applied:
1. The bank shall receive a letter from the Minister of Justice or his delegate, specifying the names of persons (two as a minimum) authorized to manage the account under a joint signature.
2. The account shall be named “Property Conveyancing for....”. The account shall also be separate from the accounts of the Ministry of Justice.
3. The bank shall obtain copies of the authorized signatories’ IDs and specimen signatures.
4. Bank transfers related to the electronic property conveyancing, whether made to the collection accounts opened under the name (Property Conveyancing) or to the accounts of beneficiaries, shall be made using electronic banking services. Withdrawal from the account shall be made only by checks payable to the first beneficiary. The purpose of the check and the ID number of the payee shall be written on the check.*
5. ATM cards and/or credit cards shall not be issued for such accounts.
6. Transferring funds from these accounts to beneficiaries outside Saudi Arabia shall not be allowed.
This paragraph has been amended by circular No. (42009020), dated 18/02/1442H, corresponding to 27/09/2020G.
300.1.5.16 Civil Rights–Personal Debt Settlement Account
Bank accounts in Saudi Riyal only may be opened for any verdict execution administrations, divisions or sections, or for rights units at police centers. The following requirements shall be fulfilled:
1. The bank shall receive a letter from the head of the verdict enforcement administration, division or section, or from the head of the police center, requesting opening a bank account and specifying its purpose and authorized signatories.
2. The account name shall be “the Ministry of Interior, Public Security, Verdict Enforcement Administration in … (Region/City/Governorate)-Personal Debt Settlement Account”.
3. The account shall be operated under a joint signature of at least two persons. One of them shall be the head of the verdict enforcement administration, division or section (or the head of the police center) or his/her deputy. The other signatory shall be the treasurer or his/her deputy (principal signatory).
4. The bank shall obtain copies of the authorized signatories’ IDs and their specimen signatures.
5. Funds shall be deposited in the account only by the debtor, his/her family, and their representatives via the following means:
■ Bank checks in the following form: “Pay to the order of Civil Rights Department in … Region/ City/Governorate-Personal Debt Settlement Account”. The purpose of the check shall be written on it as follows: “Repaying the debt of... (debtor’s name and national ID number), Case/Verdict/Resolution No. ... dated ...”.
■ Bank transfers, provided that all the required information of the transferor and the transfer purpose are indicated.
■ Points of sale.
■ Cash acceptance machines.
6. Withdrawal from the account shall be made only by checks signed by the authorized persons mentioned in point (3) above. The check shall be in the following form: “Pay to... (name of the creditor)”. The purpose of the check shall also be written on it as follows: “Repaying the debt of ... (debtor’s name and national ID number), Case/Verdict/Resolution No. ... dated...”.
7. ATM cards and/or credit cards shall not be issued for this account. Moreover, fund transfer from such account shall not be allowed.
8. The compliance officer at the bank shall ensure that all the abovementioned requirements are fulfilled and documents are verified.
9. The bank shall send a free detailed account statement to the concerned civil rights department every month, or whenever requested.
300.1.5.17 Scientific Societies
This rule has been added pursuant to the circular No. (41039895), Dated 08/06/1441H, corresponding to 02/02/2020G.The bank accounts of scientific societies may be opened as follows:
1. The bank shall receive a letter from the chairman of the society’s board of directors requesting opening of the account. The letter must specify the persons authorized to manage and operate the account under a joint signature of the chairman (or his/her deputy) and the chief financial officer.
2. The bank shall receive a copy of the university council’s decision to form the society.
3. The bank shall receive a copy of the decision to form the board of directors approved by the university council.
4. The bank shall receive a copy of the society’s bylaws.
5. The bank shall receive copies of the IDs of the members of the board of directors and those authorized to manage and operate the account.
6. Acceptance of deposits shall be as determined by the bylaws (or financial regulations) of the society.
7. Transferring money to or receiving money from outside Saudi Arabia shall not be accepted, except for transferring money for the purpose of managing the society’s activities. For example, remittance for paying fees of consulting services or of participation in external symposiums, conferences and the like may be made after the bank obtains the official approval therefor from the university council.
8. ATM cards and/or credit cards shall not be issued for such accounts.
300.1.5.18 Professional Associations
This rule has been added pursuant to the circular No. (41039895), Dated 08/06/1441H, corresponding to 02/02/2020G.The bank accounts of professional associations may be opened as follows:
1. The bank shall receive a letter from the Secretary General of the association, requesting the opening of the account. The letter must specify the persons authorized to manage and operate the account under a joint signature of the chairman of the board (or his/her deputy) and the secretary general.
2. The bank shall receive a copy of the decision to form the board of directors approved by the government authority "competent authority” that supervises the work of the association.
3. The bank shall receive a copy of the association’s bylaws.
4. The bank shall receive copies of the IDs of the members of the board of directors and those authorized to manage and operate the account.
5. Acceptance of deposits shall be as determined by the bylaws (or financial regulations) of the association.
6. Transferring money to or receiving money from outside Saudi Arabia shall not be accepted, except for transferring money for the purpose of managing the association’s activities. For example, remittance for paying fees of consulting services or of participation in external symposiums, conferences and the like may be made after the bank obtains the official approval of the competent authority.
7. ATM cards and/or credit cards shall not be issued for such accounts.
300.1.6 Rules for Foreign Embassies, Consulates, Diplomats, Airlines, Multilateral Organizations, and their Employees
300.1.6.1 Embassies, Consulates, and their Educational Institutions and Employees
- Foreign embassies and consulates and educational institutions operating under their auspices are permitted to open bank accounts. However, they are not permitted to open accounts for or on behalf of other entities, including businesses and charities.
- The bank shall receive a letter from such diplomatic entities, requesting to open a bank account. The letter shall specify the name and nature of the account as well as names of residents authorized to operate the account. Copies of the diplomatic cards of such authorized residents and of the ambassador/consul shall be authenticated and stamped by the embassy/consulate and attached to the letter. Alternatively, the letter may be certified by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, authenticating the identity of official in charge and the name of embassy. In either case, the entity shall also complete the account opening agreement and submit it to the bank. If the embassy is under formation in Saudi Arabia, the bank may open an account for it upon receiving a letter from the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The letter shall specify the name of the embassy, the name of the person authorized to open the account, and the type and number of his/her ID. The bank shall update the information related to the embassy and its staff once the embassy/consulate is set up.
300.1.6.2 Resident Diplomats
Subject to the provisions of the Anti-Money Laundering Law and its Implementing Regulations, the Law of Terrorism Crimes and Financing and its Implementing Regulations, and the guidelines issued thereunder concerning politically exposed persons, bank accounts may be opened for resident diplomats working at foreign embassies and consulates. Such diplomats must present to the bank copies of their diplomatic cards, issued by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, and copies of their diplomatic passports for verification. The bank shall keep such copies in the customer information file. Further, the bank may open accounts for diplomats whose embassies in Saudi Arabia are still under establishment upon receiving a letter from the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The letter shall specify the name of the embassy, the name of the diplomat, and his/her ID information. A copy of his/her diplomatic passport shall also be submitted to the bank. Once the embassy is set up, the customer information file shall be updated.
300.1.6.3 Diplomats on Temporary Visit
The bank may open accounts for diplomats visiting Saudi Arabia to carry out official temporary tasks. In addition to obtaining documents indicated in Rule (300.1.6.2) above, the bank shall receive from or through the embassy a letter of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, specifying the term of the diplomat’s task. Moreover, approval of the manager of the bank’s compliance department for opening the account shall be sought. SAMA must be informed about opening the account. Such accounts must be closed when the visit (the assignment) term expires. Upon the expiration of the visit term and if no extension is granted and the account balance remains unsettled, the bank shall then obtain a letter from the customer, addressed to the bank and attested by the concerned embassy. The letter shall indicate that the account holder has left Saudi Arabia and shall specify the suitable method to return the account balance to him/her. However, the bank is not permitted to open accounts for visitors coming for other purposes other than the official tasks or visitors coming to engage in official tasks but for a few days.
300.1.6.4 Foreign Airlines and their Employees
Foreign airlines can open bank accounts to serve their basic objectives. However, they are not permitted to open accounts for or on behalf of any other juristic entities, including corporations, organizations, businesses and charities. To open accounts for foreign airlines, the following requirements shall be met:
1. The person authorized to open the bank account for the airline shall be a resident of Saudi Arabia. If such person is non-Saudi, he/she must be under the sponsorship of the company or present the license of the agency (for agents).
2. The bank shall receive a copy of the approval or permission of the General Authority of Civil Aviation.
3. The bank shall receive a copy of the license issued by the Ministry of Investment to the company if the company directly undertakes its business without an agent, except GCC airlines.
4. The bank shall obtain a copy of the company’s commercial register according to which the business is performed.
5. The account shall be used only for receiving business proceeds and for paying expenses to agents and other suppliers.
- Accounts of airlines employees shall be subject to Rule (200.1).
300.1.6.5 Rules for International Multilateral Organizations
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (41041589), Dated 15/06/1441H, corresponding to 09/02/2020G.
• The Muslim World League and its affiliated councils and organizations:
• The Muslim World League (MWL):
Banks accounts may be opened for the Muslim World League (MWL) as follows:
I. Main account:
a. Requirements for opening main account:
1. The bank shall receive a letter from the Secretary General or Vice Secretary General of the MWL, requesting opening of the account. The letter shall define the purpose of the account, provided that the persons authorized to operate it under a joint signature are the Secretary General or Vice Secretary General of the MWL and the chief financial officer (principal signatory).
2. The bank shall obtain a copy of the MWL Saudi Arabia Headquarters Agreement and the appended protocol.
3. The bank shall obtain a copy of the decision to form the MWL board of directors, appoint its executives and determine their powers.
4. The bank shall obtain copies of the IDs of the Secretary General of the MWL, Vice Secretary General, chief financial officer and board members. Such copies shall be attested by the MWL.
5. Only one main account shall be opened under the entity’s name as stated in its Headquarters Agreement for deposit, withdrawal and transfer.
6. Approval of the manager of compliance department at the bank for opening the account.
7. Telephone banking and e-banking services shall be limited to balance inquiry and transfer from sub-accounts to the main account only.
8. SAMA shall be informed when the account is opened.
b. Deposit controls:
1. Deposited cash amounts to the MWL main account and sub-accounts from MWL official staff may be accepted.
2. The bank may accept cash deposits, checks and transfers to the main account and sub-accounts from non-official staff of MWL or MWL branches inside Saudi Arabia only if they are gift, subsidy or endowment and not donation.
3. Amounts incoming to the MWL main account or sub-accounts from outside Saudi Arabia clearly stating their purpose as gifts, subsidy or donation may be accepted. Such amounts shall not be deposited in the MWL accounts unless after the MWL submits to the bank the approval of the competent authority in Saudi Arabia to deposit the amounts, whether they are, for example, transfers or checks under collection.
c. Withdrawal controls:
Disbursement from the main account shall be limited only to checks or transfers to entities inside or outside Saudi Arabia. Transactions (remittance, issuance of checks, etc.) made to outside Saudi Arabia shall be only for the purpose of managing the MWL or implementing its programs or projects.
d. Balance investment:
The MWL may open accounts to invest its excess funds in activities that have financial return to help achieving its objectives.
II. Sub-accounts for MWL branches and its various activities:
- Sub-accounts of or linked to the MWL main account for the same purposes of the branches or the activities of the MWL shall be opened after meeting and providing the following conditions and documents:
1. A letter from the MWL Chairman or the Vice Chairman to the bank to open the sub-account specifying the purpose and persons authorized to manage the account.
2. A copy of the official approval from the competent authority in Saudi Arabia to open a MWL branch or practice sub-activity.
3. Copies of the authorized signatories IDs attested by the MWL.
4. The MWL Chairman or the Vice Chairman may authorize members from the MWL staff to manage the account as the authorization shall be limited to making transfers from the sub-accounts to the main account.
- Documents required to open and update the main account shall be sufficient for sub-accounts as they are nested under the main account.
• Institutions and organizations affiliated with the MWL, including the International Organization for Relief, Welfare and Development:
Bank accounts may be opened for such entities as follows:
I. Main account:
a. Requirements for opening a main account:
1. A letter from the Chairman of the MWL affiliated entity to the bank requesting opening a main account or maintaining and updating the existing account specifying the purpose of the account, provided that the persons authorized to manage the account under a joint signature are the Chairman or the Vice Chairman of the entity and the chief financial officer (principal signatory).
2. A copy of the MWL Saudi Arabia Headquarters Agreement and the appended protocol.
3. A copy of the decision to form the Board of Directors of the entity and the appointment of its officials and their powers.
4. A copy of the by-law and procedures of the entity.
5. Copies of the IDs of the Chairman, Vice Chairman, Chief Financial Officer and the board members attested by the entity.
6. One main account only shall be opened under the entity’s name as stated in the license for deposit, withdrawal and transfer.
7. Approval of the manager of compliance department at the bank for opening the account.
8. Telephone banking and e-banking services shall be limited to balance inquiry and transfer from sub-accounts to the main account only.
9. SAMA shall be informed when the account is opened.
b. Deposit controls:
1. Deposited cash amounts to the entity’s main account and sub-accounts from MWL official staff may be accepted.
2. The bank may accept cash deposits, checks and transfers to the main account and sub-accounts from non-official staff of the entity or its branches inside Saudi Arabia only if they are gift, subsidy or endowment and not donation.
3. Amounts incoming to the entity main account or sub-accounts from outside Saudi Arabia clearly stating their purpose as gifts, subsidy or donation may be accepted. Such amounts shall not be deposited in the entity accounts unless after entity submits to the bank the approval of the competent authority in Saudi Arabia to deposit the amounts, whether they are, for example, transfers or checks under collection.
c. Withdrawal controls:
Disbursement from the main account shall be limited only to checks or transfers to entities inside or outside Saudi Arabia. Transactions (remittance, issuance of checks, etc.) made to outside Saudi Arabia shall be only for the purpose of managing the MWL or implementing its programs or projects.
d. Balance investment:
The entity may open accounts to invest its excess funds in activities that have financial return to help achieving its objectives.
II. Sub-accounts for the branches of the institution or organization and their various activities:
- Sub-accounts of or linked to the entity’s main account for the same purposes of the branches or the activities of the entity shall be opened after meeting the following conditions and documents:
1. A letter from the entity’s Chairman or the Vice Chairman to the bank to open the sub-account specifying the purpose and persons authorized to manage the account.
2. A copy of the official approval from the competent authority in Saudi Arabia to open a branch of the entity or practice sub-activity.
3. The entity’s Chairman or the Vice Chairman may authorize members from the entity staff to manage the account as the authorization shall be limited to making transfers from the sub-accounts to the main account.
4. Copies of the authorized signatories IDs attested by the entity.
- Documents required to open and update the main account shall be sufficient for sub-accounts as they are nested under the main account.
• World Assembly of Muslim Youth (WAMY):
Bank accounts shall be opened for the WAMY upon fulfilling the following conditions and procedures:
I. Main account:
a. Requirements for opening a bank account:
1. A letter from the president of the WAMY affiliated entity to the bank requesting opening a main account or maintaining and updating the existing account specifying the purpose of the account and that the persons authorized to manage the account are the Chairman or Secretary General with joint signature and the Chief Financial Officer with main signature.
2. A copy of the WAMY Saudi Arabia Headquarters Agreement.
3. A copy of the protocol appended to the WAMY Headquarters Agreement.
4. A copy of the decision to form WAMY Board of Trustees and the appointment of its officials and their powers.
5. A copy of the by-law and procedures of WAMY.
6. The authorized persons must fulfil the account opening agreement (contract) determining the purpose of the account, the sources of income and the real beneficiaries.
7. Copies of the IDs of the Chairman, Secretary General, Chief Financial Officer and the members of the Board of Trustees attested by the entity.
8. One main account only shall be opened under WAMY’s name as stated in Headquarters Agreement for deposit, withdrawal and transfer. The account shall be opened at the bank head office or main branch in the region.
9. Approval of the CEO/general director and the manager of compliance department of the bank to open the account or to maintain and update the existing account.
10. Telephone banking and e-banking services shall be limited to balance inquiry and transfer from sub-accounts to the main account only.
11. SAMA must be informed when the account is opened.
b. Deposit controls:
1. Deposited cash amounts to WAMY’s main account and sub-accounts from WAMY official staff may be accepted.
2. The bank may accept cash deposits, checks and transfers to the main account and sub-accounts from non-official staff of WAMY or WAMY branches inside Saudi Arabia only if they are gift or subsidy.
3. Deposits or transfers for donation incoming to the bank from inside Saudi Arabia shall not be accepted.
4. Amounts incoming to the WAMY’s main account or sub-accounts from outside Saudi Arabia clearly stating their purpose as gifts, subsidy or donation may be accepted. Amounts received by the bank to be transferred to other banks operating inside or outside Saudi Arabia may also be accepted. Such amounts shall not be deposited in the WAMY’s accounts or transferred to other banks unless after the WAMY submits to the bank the approval of the competent authority in Saudi Arabia to deposit the amounts, whether they are, for example, transfers or checks under collection.
c. Withdrawal controls:
Disbursement from the main account shall be limited only to checks or transfers to entities inside or outside Saudi Arabia through the main account or by the remittance membership linked to the main account for transfers.
d. Balance investment:
WAMY may open accounts to invest its excess funds in activities that have financial return to help achieving its objectives.
II. Sub-accounts for WAMY branches and their various activities:
Sub-accounts of or linked to WAMY’s main account for the same purposes of the branches or the activities of WAMY shall be opened after meeting and providing the following conditions and documents:
1. A copy of the official approval from the competent authority in Saudi Arabia to open a branch of WAMY or practice sub-activity.
2. A letter from WAMY Chairman or Secretary General to the bank to open the sub-account specifying the purpose and persons authorized to manage the account.
3. WAMY Chairman or Secretary General may authorize members from WAMY staff to manage the account as the authorization shall be limited to making transfers from the sub-accounts to the main account.
4. Copies of the authorized signatories IDs attested by WAMY.
5. Documents required to open and update the main account shall be sufficient for sub-accounts as they are nested under the main account.
• Islamic Development Bank (IsDB):
Current bank accounts shall be opened for IsDB upon fulfilling the following conditions and procedures:
1. Request to open the account by a letter from the President or Vice President of the bank.
2. A copy of the bank Saudi Headquarters Agreement (permission).
3. Signature shall be joint.
4. Copies of the IDs of the authorized persons, the bank President or Vice President according to the request submitted.
5. Check books may be provided to the bank and its employees to cover the administrative expenses. The bank accounts are not required to be correspondent.
6. A copy of the procedures of money laundry and terrorist financing applied in the bank.
• Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) and its affiliated entities:
Bank accounts shall be opened for OIC upon fulfilling the following conditions and procedures:
1. Obtain a request to open the account from OIC Secretary-General or Vice Secretary-General specifying the names and functions of the persons authorized to open and manage the account of OIC or the affiliated entity.
2. A copy of the OIC Saudi Arabia Headquarters Agreement (or any other document for this purpose).
3. Signature shall be joint.
4. Copies of the IDs of the authorized persons, OIC Chairman or Vice-Chairman according to the request submitted.
5. OIC may transfer money related to its programs or projects to accounts outside Saudi Arabia.
• Permanent Mission of the Russian Federation to the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation:
Bank accounts shall be opened for the Mission after meeting and providing the following conditions and documents:
1. Submit a request approved by OIC to open an account in SAR or other currency to the bank in which the account is to be opened.
2. A certified copy of the approval of opening the Mission Office in Saudi Arabia stating the purpose of the Mission to OIC.
3. A letter from the Chairman of the Mission approved by the OIC specifying the person or persons authorized to manage the account.
4. Copies of the diplomatic cards or residence cards (Iqama) of the authorized persons to open and manage the account according to the identity card issued to them in Saudi Arabia.
5. The Mission may only receive and transfer money related to its purposes and programs.
• Arab Red Crescent and Red Cross Organization (ARCO):
Bank accounts shall be opened for ARCO upon fulfilling the following conditions and procedures:
1. Obtain a request to open the account from the Secretary-General or Vice Secretary-General of ARCO, office or program in Saudi Arabia.
2. A copy of ARCO Saudi Headquarters Agreement (permission).
3. Signature shall be joint.
4. Copies of the IDs of the persons authorized to manage the account, in addition to the ID of the Chairman or Vice-Chairman of ARCO, office or program according to the request submitted.
5. Approval of the CEO/general director and the manager of compliance department to open the account.
6. SAMA must be informed when the account is opened.
7. OIC may transfer money related to its programs or projects to accounts outside Saudi Arabia.
• Other international multilateral organizations and funds:
Bank accounts shall be opened according to the following conditions for international multilateral organizations and funds of a political, developmental or service nature, such as the United Nations, the Islamic World Conference, the World Bank and its affiliates, the International Monetary Fund and its affiliates, the Gulf Cooperation Council, the Arab League and Arab satellite broadcasters:
1. Obtain a request to open the account from the Chairman, Deputy or Vice-Chairman.
2. A copy of ARCO Saudi Headquarters Agreement (permission).
3. Signature shall be joint.
4. Copies of the IDs of the organization/fund Chairman, Deputy or Vice-Chairman according to the request submitted.
• Personal accounts of staff of such organizations:
The bank shall not require SAMA approval for opening accounts for the permanent staff of such organizations as the conditions and procedures stated in Rule (200-1) shall be applicable. However, conditions stated in Rule (300-1-6) shall be applicable to diplomats.
300.1.6.6 Bank Accounts of Relief Committees and Campaigns
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (42060703) Dated 25/08/1442H, corresponding to 07/04/2021G. Please refer to the Arabic version of this rule to read the last updated version.Bank accounts shall be opened for designated relief campaigns and committees, as well as for the King Salman Humanitarian Aid and Relief Center "the Center", for the purposes of managing its operations and humanitarian relief campaigns abroad as follows:
1. A copy of the approval from His Majesty the King for the establishment of the designated fundraising committee/campaign, and the approval of SAMA to open one main account under the name of the committee or campaign, after determining the persons authorized for the account (joint signatures) and providing copies of their IDs and specimen signatures. If the account is to be opened for the Center, a letter must be obtained from the General Supervisor of the Center addressed to the bank, determining the persons authorized to manage the account (at least two persons) with joint signatures, and providing copies of their IDs and specimen signatures. The request must specify that the sources of the account’s funds do not include amounts from the state budget or the Center’s budget.
2. Authorized persons in the center, or in the relief committees and campaigns are permitted to open sub-accounts linked to the main account for the purposes of collecting donations and conducting relief activities.
3. The bank accounts of the center for the purposes of employee salaries, operational expenses, or its humanitarian activities, which are funded by the state’s general budget or the center’s budget, shall be separated from the accounts of the center that are funded from sources other than the state’s budget or the center’s budget. The instructions outlined in Rule (500-1-1) regarding the opening and management of government entity accounts shall be applied to the center's accounts that are funded by the state’s budget or the center’s budget.
4. Deposits into such accounts may be accepted through all means, including cash, checks, or local transfers. The center is also permitted to accept electronic donations through electronic payment gateways via different methods, including credit cards (both domestically and internationally).
5. ATM or credit cards shall not be issued for such accounts.
6. Money transfer to accounts outside Saudi Arabia or receiving transfers from there shall not be accepted after obtaining approval from SAMA, except for the Center's accounts, to which this paragraph does not apply.
300.1.6.7 Bank Accounts of Committees of Friendship and Foreign Official Relationships of Saudi Arabia
Bank accounts shall be opened for such committees according the following controls:
1. An official directive from the Minister of Foreign Affairs approving the establishment of the committee.
2. A direction from SAMA to the bank, stating the name and purpose of the account and the names of persons authorized to manage the account.
3. Copies of the IDs of the authorized persons or a letter from the Ministry of Foreign Affairs containing their personal data.
300.1.6.8 Economic and Technical Liaison Offices in Saudi Arabia
Bank accounts shall be opened for foreign economic and technical liaison offices and their branches licensed by the Ministry of Investment in Saudi Arabia upon meeting and providing the following conditions and documents:
1. A request from the director of the office explaining the purpose of the account.
2. A copy of the license issued for the office by the Ministry of Investment.
3. Signatures of the persons authorized to manage the account and copies of their IDs.
4. The account name shall be (the economic/ technical liaison office of. ) and shall be linked to the validity of the license and renewable by a letter for extension or renewal issued by the Ministry of Investment.
5. The account shall be managed by Saudis who work at the office. If the account is managed by non-Saudis, they must be residing in Saudi Arabia under valid residence permits (Iqama).
6. The account shall be used only for the purposes specified in the license. Such offices shall not open accounts for or on behalf of other entities, such as companies or charities.
7. The persons authorized to manage the account shall only be replaced by the approval of the embassy of the office country and the approval of the Ministry of Investment.
8. Approval of the manager of compliance department for opening the account shall be sought.
9. SAMA must be informed when the account is opened.
300.1.7 Bank Accounts for Liquidation and Financial Restructuring
The bank may open bank accounts for liquidation, for depositing the proceeds of the sale of the bankruptcy assets covering the debtor’s debt in case of a financial restructuring under the Bankruptcy Law, or for liquidation under the Companies Law. The following conditions and documents shall be met and provided:
I. Commencement of any liquidation procedures under the provisions of Bankruptcy Law
1. The bank shall receive the court order that includes the following:
- Commencing any liquidation or administrative liquidation procedures against a natural or juristic person.
- Appointing one or more bankruptcy officeholder and specifying their names and powers, or forming a bankruptcy committee to manage the administrative liquidation procedures.
2. The bank shall receive a request to open the account from the liquidation officeholder or the representative of the bankruptcy committee, as the case may be, stating the purpose of the account.
3. The name of the account shall be (name of the natural or juristic person under liquidation... - Liquidation Account).
4. The bank shall receive copies of the commercial register and memorandum of association and its annexes for the juristic person under liquidation, and a copy of the national ID or Iqama for the natural person under liquidation.
5. The bank shall receive copies of the national ID and commercial register or license of the liquidation officeholder. In case of administrative liquidation, a letter shall be obtained from the bankruptcy committee that includes the data of the person authorized to manage the account and a copy of his/her national ID.
6. The account shall be operated by the liquidation officeholder or the representative of the bankruptcy committee, as the case may be, in accordance with the court order to commence any liquidation procedure.
7. Checkbooks may be issued for such accounts at the request of the liquidation officeholder or the representative of the bankruptcy committee, as the case may be. ATM cards and/or credit cards shall not be issued for such accounts unless the court order to commence the procedure otherwise provides.
8. The bank, the liquidation officeholder or the representative of the bankruptcy committee, as the case may be, must confirm that the IDs and documents are true copies of the originals.
9. Account validity:
a. Liquidation procedure: The account shall be valid until a court order to complete the procedure is issued. The account shall be closed by a letter from the liquidation officeholder based on the court order to complete the liquidation procedure.
b. Administrative liquidation procedure: The account shall continue to be valid according to the period stipulated in the Bankruptcy Law. Renewal shall be effected after the end of this period by a letter from the bankruptcy committee based on a court order, stating that the procedure is not completed and the period needed for completion. The account shall be closed upon the completion of the administrative liquidation procedure by a letter from the bankruptcy committee, stating that the committee has issued a decision to complete the procedure.
II. Liquidation for the termination reasons stated in Article 16 of Companies Law
1. The court order to liquidate a company shall be obtained. In case of a voluntary liquidation by partners, the decision issued by the partners or general assembly of the company to approve liquidation shall be obtained.
2. A request from the liquidator to open a bank account shall be obtained.
3. The liquidator (name and restrictions on powers) shall be appointed by a court order or decision of the company’s partners or general assembly.
4. The bank shall receive copies of the commercial register and memorandum of association and its annexes of the company under liquidation.
5. The bank shall receive copies of the IDs of the owners of the company under liquidation, whose names are mentioned in the memorandum of association and its annexes. Listed joint-stock companies are excluded from this requirement.
6. The bank shall receive copies of liquidator’s national ID and the commercial register or license.
7. The name of the account shall be (name of company under liquidation... -Liquidation Account).
8. The account shall be operated by the liquidator or as stated in the company liquidation decision.
9. Checkbooks may be issued for such accounts at the request of the liquidator. ATM cards and/or credit cards shall not be issued unless the company liquidation decision states otherwise.
10. The bank and the liquidator shall confirm that the IDs and documents are true copies of the originals.
11. The validity period of the account shall be as set forth in the court liquidation order. In case of voluntary liquidation, such period shall not exceed a maximum period of five years. Renewal shall be effected by a letter from the liquidator based on a court order, stating that liquidation procedure has not been completed and the period needed for completion.
12. The account shall be closed upon completion of liquidation procedure by a letter from the liquidator, to which a statement confirming the approval of the entity appointing the liquidator on the liquidation completion report is attached.
III. Accounts for proceeds from the sale of the bankruptcy assets covering the debtor's debt in case of financial restructuring
1. The bank shall receive the court order that includes the following:
- The commencement of the financial restructuring procedure “the procedure” for the natural or juristic person “the debtor”.
- The appointment of a financial restructuring officeholder “the officeholder".
2. The bank shall receive a request to open the account from the officeholder, stating the purpose of the account “Depositing the proceeds of selling the bankruptcy assets covering the debtor’s debt for which the procedure is commenced” and the validity period of the account. The account shall be closed based on the court order to complete the procedure.
3. The bank shall obtain a copy of and verify the national ID of the officeholder.
4. The name of the account shall be “Account of proceeds from sale of bankruptcy assets covering the debt of (name of the debtor) subject to financial restructuring”.
5. The account shall be operated by the officeholder specified in the court order in accordance with the provisions of Article 82 of the Bankruptcy Law. Checkbooks may be issued for such accounts at the request of the officeholder. ATM cards and/or credit cards shall not be issued for such accounts.
6. The bank shall receive an undertaking from the officeholder to notify the bank once a court order to dismiss him/her or accept his/her resignation request is issued. The bank must enable the new officeholder to manage the account in accordance with the provisions of this clause after receiving the court order appointing him/her. The bank must also obtain a copy of and verify the national ID of the new officeholder.
300.2 Non Resident Juristic Persons
300.2.1 Non-Banking GCC Companies Not Residing in Saudi Arabia
300.2.1.1 Current Accounts and Deposits for Business and Credit Purposes
Bank accounts shall be opened for GCC companies for business and credit purposes according to the following conditions and requirements:
1. A copy of the license/commercial register issued by the government authority in the GCC country of residence.
2. Submitting a request to open a bank account stating the business purpose of the account which should conform to the purposes of the company according to the memorandum of association and license.
3. Verifying the national ID(s) of the owner(s) of the GCC establishment (excluding listed joint stock companies).
4. The memorandum of association and its annexes which clearly indicate the composition of both the capital and the establishment’s management and that the ownership of GCC citizens (natural or juristic) exceeds 50% of the company's capital.
5. Verifying the IDs of the members of the board of directors, provided that the majority of members shall be GCC citizens or from GCC establishments.
6. Copies of IDs of the authorized managers and their nationalities.
7. A copy of the authorization issued by the board of directors authorizing persons to manage the bank account unless specified in the memorandum of association.
8. The person authorized to manage the bank account shall be a GCC citizen. If the purpose of the account is to receive facilities from a bank licensed to operate in Saudi Arabia, the person authorized may be a non-GCC individual working in the company and residing in the company's country.
9. Approval of the Saudi embassy in the company’s GCC country for all the above requirements.
10. The above documents shall be completed by the bank's employees directly by interviewing the clients personally (authorized persons) or by a national GCC correspondent bank residing in the country of the company. The correspondent bank shall verify that copies provided for all the required documents, even documents certified by the Saudi embassy, are true copies of the original documents. Deposit, withdrawal and transfer shall be carried out by the correspondent bank. Documents may be completed by a correspondent bank residing in the GCC country of the company that is one of the Saudi bank partners in capital and technical management or by the branches of Saudi banks in the GCC country. The final responsibility for the customer data shall rest with the bank operating in Saudi Arabia.
11. Once the above documents are provided and the requirements satisfied, the bank shall apply the KYC principle.
12. Approval of the CEO/general director and the manager of compliance department to open the account.
13. The permission to open accounts includes all GCC companies and those carrying out commercial, industrial, service, agricultural and real estate businesses.
14. Banks, money changers (other than correspondent accounts), investment companies, financial institutions, independent or affiliated investment funds, insurance companies, sole proprietorships and licensed shops are prohibited from opening bank accounts.
300.2.1.2 Bank Accounts of GCC Juristic Persons for the Purpose of Trading in Securities Listed in the Saudi Stock Exchange
Bank accounts may be opened for these juristic persons after carrying out and providing the following:
- An application for opening a bank account shall be submitted, specifying that it is for the purpose of investment in joint-stock companies shares or securities. The bank shall ascertain that the investment purpose conforms with the company’s objectives as specified in its memorandum of association and license. It shall also ensure that the company’s memorandum of association and articles of association are free of any restrictions that might prevent or limit the company’s ownership of shares of joint-stock companies.
a. GCC companies:
1. A copy of the license / commercial register issued by a competent government authority in the GCC country of residence and attested as a true copy of the original.
2. The company’s articles of association or memorandum of association, or the decision issued by a shareholders’ association or the company partners, must provide that the company is allowed to invest in securities.
3. Real beneficiaries holding ultimate control shall be identified and verified (as a minimum, a natural owner holding 25% as specified in the company’s memorandum of association and its annexes or according to the available data).
4. A copy of the company’s memorandum of association and its annexes clearly showing the company’s capital structure and management and that the share of GCC citizens (natural and juristic) shall exceed 50% of the company capital.
5. Verifying the identity of board members.
6. Copies of IDs of the authorized managers and their nationalities.
7. A copy of the authorization issued by the company’s board of directors empowering the persons concerned to manage accounts and investment portfolios, unless such authorization is included in the company’s memorandum of association.
b. GCC investment institution:
Documents of establishment which prove that the institution is owned by the government, including its memorandum of association, decision to form its board of directors, names of those authorized to manage the accounts and copies of their ID cards.
c. Pension and social insurance organizations:
Documents pertaining to the establishment of these organizations, board formation decision, names of those authorized to manage the accounts and their authorization decision as well as copies of their IDs.
d. Affiliated investment funds:
1. A copy of the fund’s or the managing fund’s articles of association or memorandum of association and any amendments thereto.
2. Documents relating to the license to establish the fund, received either from a capital market authority or a central bank in a GCC Country.
3. Names of the board members responsible for managing the fund and its policy.
4. The resolution nominating those empowered to operate the fund and copies of their IDs.
5. A copy of the fund’s or the managing fund’s memorandum of association and its annexes which clearly show the structure of its capital and its management and that the share of GCC citizens (natural or juristic) exceeds 50%.
- The documents mentioned in a, b, c and d shall be received by directly meeting the customers (authorized persons) in person or through a GCC agent.
- The AML/CFT form shall be completed by a GCC agent. However, when meeting customers (authorized persons) in person, in the case of a GCC company and an investment fund only, such form shall be completed by these two parties themselves as applicable.
- The bank shall apply the KYC principle and exercise due diligence.
- The bank shall obtain a declaration from a GCC agent in which the agent undertakes to provide the bank or the supervisory authorities in Saudi Arabia with any information about customer investors at any time upon request. This is in the case that the bank is dealing with a GCC customer through a GCC agent.
300.2.2 Non-Resident, Non-Banking (Non-GCC) Companies and Businesses with No Contracts or Projects in Saudi Arabia
Banks are not permitted to open any account for such companies and businesses, except for the intermediary accounts allowed under Rules (400.1) and (400.2). An exception is companies and institutions which have SAMA’s approval to obtain facilities, finance or loans from banks operating in Saudi Arabia according to the following conditions and controls:
1. Providing copies of the following documents:
a. License/commercial register issued by the government authority in the country of residence.
b. Memorandum of association and its annexes, clearly showing the structure of capital and company management.
c. Authorization issued by the company’s board for persons to handle credit processes and manage bank accounts, unless this is specified in the memorandum of association.
2. Providing a list of names and copies of the identities of board members and authorized managers showing their nationalities.
3. Determining the (natural) real beneficiary of ownership.
4. Verifying the ownership of any politically exposed person, if any, and verifying its source of funds.
5. Opening an intermediary account with the bank for the purpose intended, named (.........Company Loan Account).
6. The intermediary account shall be managed by officers from the executive level in the bank.
7. The account shall not provide any kind of services (checks, ATM cards, etc.)
8. Requests of a customer who obtains a finance loan (borrower) to withdraw from the account shall be made through any of the following:
- A SWIFT message from the customer through the correspondent bank which the customer deals with in its home country.
- Written instructions signed by two authorized persons in the company obtaining the finance, whose names are included in the finance request.
9. Repayment is made through remittances from the borrower’s country or from banks in the Kingdom by a resident customer specified in the loan agreement. Cash deposits, checks and transfers from domestic accounts with the same bank are not permitted.
300.2.3 Non-Resident and Non-Banking Companies and Businesses with Contracts or Projects in Saudi Arabia
When a non-resident business or company has a contract or a project in Saudi Arabia, it may have accounts with a bank in Saudi Arabia for the duration of the project or the contract according to the following conditions:
1. Obtaining permission from the Ministry of Commerce and/or a provisional license from the Ministry of Investment and approval from the company’s head office. This approval must be certified by the Saudi embassy in the company's country of origin.
2. A copy of company's memorandum of association duly attested by the Saudi embassy in the company's home country.
3. A recommendation from a bank rated by an approved rating agency with which it deals in the country of origin.
4. A copy of the authorization from the company’s head office certified by the Saudi embassy, nominating the persons authorized in Saudi Arabia to sign on behalf of the company for all financial transactions (including opening and operating accounts and checks), along with copies of their Iqamas.
5. Approval of the CEO/general director and the manager of compliance department to open the account.
- Banks must close all such accounts upon expiry of the contract. In order to manage post-project receivables and payables, including zakat and income tax payments, special accounts can be maintained specifically for this purpose until completion. After that, such accounts must be closed according to the following:
1. Considering such account as a trust account under the control of the operations manager at the bank's head office only.
2. Obtaining a letter from the company’s head office, duly attested by the Saudi embassy in its home country, identifying the authorized signatories to sign for the trust account after completion of the company’s business and specifying the method for transferring the remaining amounts and paying zakat or income tax.
3. Limiting deposits in such account to the amounts payable to the company by other parties such as the Ministry of Finance (government checks) or a private entity if the contract is made with a private or semi-government business sector.
4. Classifying this account as of high risk.
300.2.4 Non-Resident and Non-Banking Companies and Businesses Leasing Spaces in Deposit Areas in Saudi Arabia
Banks may open accounts for companies and institutions licensed to sell and reexport commodities in deposit areas at local ports in Saudi Arabia, whether leasing was directly through contracts with the Saudi Ports Authority or through concession. This shall be for a period equal to the duration of the lease contract and according to the following requirements:
1. A copy of the lease contract attested by the Chamber of Commerce and Industry and the port management.
2. A copy of the lessee’s commercial register issued by the country of origin and attested by the Saudi embassy in addition to the full address of the entity.
3. A letter from a bank in the lessee’s country of origin.
4. The persons authorized to manage the entity’s account must be Saudis or non-Saudis with valid Iqamas.
5. The purpose of the account must be specified through a letter from the lessee to the bank.
6. The account must be closed by the bank upon expiry of the lease period if a renewal notification is not received.
300.2.5 Non-Resident Commercial Banks (Including GCC Banks)
Correspondent accounts may be opened for non-resident commercial banks (including GCC banks), including correspondent accounts for central banks, in accordance with the following conditions:
1. Approval of the CEO/general director and the manager of compliance department to open the account.
2. SAMA must be informed when the account is opened.
3. Obtaining license documents (except for situations where the correspondent is the central bank itself) issued by the competent foreign licensing authority of the foreign correspondent bank, such as the central bank or the banking control commission in the country of origin.
4. Banks should refuse to enter into or continue a banking relationship with a correspondent bank in a country where it has no physical presence and which is not affiliated with a regulated financial group (e.g. shell banks).
5. Banks should select or approve correspondent banks whose countries apply strong measures to identify customers and cooperate in combating money laundering. These correspondent banks should be under the control of competent authorities. Moreover, it is possible to have an easy access to information related to such banks’ management, main line of business, locations, reputation and the level of control applied by their regulators.
6. Banks shall obtain a completed AML/CFT form from each correspondent bank, stating that such bank is committed to the AML/CFT policies and procedures regarding relations with new banks as well as existing relations. Banks shall also access the correspondent bank’s internal controls to combat these crimes and ensure their adequacy and effectiveness and that the correspondent bank does not allow shell banks to use its accounts.
7. Banks should ensure, through publicly available information and research (such as media), that the correspondent banks, which a bank plans to deal with or continue to deal with, are not subject to any investigation on money laundering or terrorist financing, involved in cases brought against them in this regard, or subject to any legal action.
8. Banks are not allowed to start new relations with any correspondent bank or open a correspondent account without the approval of their senior management.
9. Banks should ensure that operating these accounts is restricted to dealings among correspondent banks only. Such accounts shall not be used or treated as current accounts and no check books should be issued for them. Additionally, they may not be used for cash depositing or by a third party to conduct activities for its own account.
300.2.6 International Investment Companies and Mutual Funds and Other Nonresident Financial Institutions (Including GCC Institutions)
Banks may not open any bank account for foreign investment companies, mutual funds or financial institutions, including GCC investment companies and brokers who illegally sell their products in Saudi Arabia and raise funds in Saudi riyals and other foreign currencies. Saudi banks may not facilitate the business of such entities in any way. An exception to this is the cases and categories permitted by the CMA, in which investment in the shares of Saudi joint-stock companies is allowed.
300.2.7 Non-Resident Insurance Companies and Money Changers
Saudi banks may not open bank accounts for such juristic entities except in the following cases after obtaining approval of the CEO/general director and the manager of compliance department to open the account and informing SAMA when opening the account:
• A non-resident insurance company with an agreement with a Saudi bank to offer insurance products:
Such company may only open an escrow account in Saudi riyal and other foreign currencies with the partner bank to facilitate its business under the agreement.
• A non-resident money changer:
It may only open a correspondent account after providing the documents related to practicing (banking activities) currency exchange activities as specified in Rule (300.2.5).
300.2.8 Payment Card Companies Not Residing in Saudi Arabia and Not GCC Affiliated
Banks are not permitted to open accounts for such companies. However, after obtaining approval of the CEO/general director and the manager of compliance department to open a bank account and informing SAMA when opening such account, the bank may hold intermediary accounts in Saudi riyals for these companies to enable them to pay the value of customer purchases to the merchants in Saudi Arabia. Banks should also obtain authenticated licenses or registration documents from these companies in order to be able to identify them.
400. Rules for Opening Bank Accounts for Resident and Non-Resident Foreign Investors Not Covered by the Foreign Investment Law
400.1 Rules for Opening Bank Accounts for the Purpose of Linking Investment Deposits Only or Linking Investment Deposits for Issuing Letters of Guarantee to Non-Resident Juristic Persons
Banks may open accounts for non-resident juristic persons (for instance, sovereign wealth funds, mutual funds, cash funds, investment companies, and the like) for the purpose of linking investment deposits only or linking investment deposits for issuing letters of guarantee in banks operating in Saudi Arabia. Banks shall take into consideration the provisions of Article (11) of the Anti-Money Laundering Law and Article (66) of the Law of Terrorism Crimes and Financing. Non-resident foreign investors’ documents shall be obtained by the correspondent banks outside Saudi Arabia. The correspondent bank’s verification of all documents is required in addition to identifying the customer’s account number held by the bank. This should be subject to the following conditions:
1. Obtaining copies of the following documents:
a. License\commercial register issued by the competent authority in the country of origin.
b. Memorandum of association and its annexes or the founding document in the case of sovereign wealth funds and the like, clearly showing the structure of capital and management.
c. The authorization issued by the board for the persons authorized to open and operate the bank account, unless this is specified in the memorandum of association.
2. Obtaining a list of names and copies of the identities of board members and authorized managers showing their nationalities.
3. Identifying and assessing ML/TF risks, applying preventive measures, and exercising due diligence when handling such accounts.
4. Opening an intermediary account with the bank for the purpose intended, named (investment deposit account).
5. The account shall not allow any kind of services (checks, ATM cards, etc.).
6. The customer’s request to break the deposit or issue a bank guarantee shall be made through any of the following:
a. A SWIFT message from the customer through the correspondent bank which the customer deals with in its home country.
b. Written instructions signed by two authorized persons in the non-resident foreign company, whose names are included in the deposit request.
c. The beneficiary shall be the same juristic person.
7. Cash deposits, checks and transfers from domestic accounts with the same bank are not permitted.
8. The bank shall confirm that all IDs and documents are true copies of the originals, and documents issued outside Saudi Arabia shall be verified by relevant authorities, the Saudi Embassy in the relevant country and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs in Saudi Arabia.
9. Obtaining approval of the CEO and the manager of compliance department to open the account.
10. SAMA must be informed when the account is opened.
11. The account must only be used for purposes of deposits, and it is not allowed to be used to carry out any other transactions.
400.2 Rules for Opening Intermediary Investment Accounts
- A bank offering among its investment products and services pooled accounts managed by professional intermediaries or lawyers (such as mutual funds, cash funds, deposit funds, etc.) shall obtain from the intermediary ID documents of beneficiaries of the account where there are sub-accounts for each real beneficiary. The bank shall also ensure that the intermediary is subject to the same regulatory requirements applicable to banks pertaining to AML/CFT and KYC principle.
- Banks must obtain copies of the intermediary’s licenses to practice business attested by the correspondent bank or the Saudi Embassy.
- Approval of the CEO/general director and the manager of compliance department to open the account.
- SAMA must be informed when the account is opened.
400.3 Rules for Opening Bank Accounts for Juristic Persons (Licensed Companies, Institutions and Shops) Owned by Foreign Residents Permitted to Practice Business But Not Included in the Foreign Investment Law
Banks may open bank accounts for this category after obtaining the following:
1. A copy of the commercial register issued by the Ministry of Commerce.
2. A copy of the license if it is the only requirement or if it is required along with the commercial register.
3. A copy of the memorandum of association and its annexes (if any).
4. A copy of the business owner’s Iqama or national ID card (for GCC citizens). The information (name, ID number and expiry date) contained in the commercial register and/or license provided by a non-Saudi merchant must be verified.
5. A list of owners as mentioned in the memorandum of association (if any) as well as copies of their IDs.
6. Non-Saudi owner of an entity is not allowed to authorize others (Saudis or non-Saudis) to manage the accounts of the entity.
400.4 Rules for Opening Bank Accounts for Foreign Financial Institutions Qualified to Invest in Securities Listed in the Saudi Stock Exchange
Banks may open bank accounts for this category after the following is met:
1. An application is submitted by a person authorized by CMA or a qualified foreign investor in accordance with the Rules for Qualified Foreign Financial Institutions Investment in Listed Securities issued by CMA, in which it is specified that the account is for investment in the securities listed in the Saudi Stock Exchange.
2. Obtaining a copy of the foreign investor’s license or commercial register issued by a competent authority in the state of origin, where applicable.
3. Obtaining a copy of the foreign investor’s business license to practice the activity in the country of origin issued by a supervising body (CMA or SAMA counterpart), where applicable.
4. Obtaining a copy of the articles of association and its annexes and/or memorandum of association and its annexes, where applicable.
5. Real beneficiaries holding ultimate control shall be identified and verified (as a minimum, a natural owner holding 25% as specified in the memorandum of association and its annexes or according to the available data).
6. Identifying the control and ownership structure.
7. Obtaining a list of names and copies of ID cards of the legal entity managers and the persons authorized to sign on behalf of the foreign investor regarding account transactions.
8. Obtaining an authorization from the foreign investor’s board specifying the persons authorized to sign on his/her behalf regarding account transactions, where applicable.
9. Completing the KYC principle and AML/CFT form (prepared by SAMA).
10. Obtaining a declaration from the foreign investor and/or authorized person to provide the Saudi supervisory authorities with any information at any time upon request, in accordance with relevant laws and regulations.
11. A copy of the notice issued by the person authorized to confirm acceptance of the investor as a qualified customer.
12. Approval of the bank’s senior management to open the account for the foreign investor.
13. The account shall not provide any kind of services (checks, ATM cards, etc.).
14. Cash withdrawals and deposits shall not be accepted.
15. Banks may open accounts only for licensed foreign investors or foreign founders (where applicable) whose countries apply strong measures to identify customers and cooperate in combating money laundering and terrorist financing. Amounts transferred to accounts in Saudi Arabia’s banks must come from a foreign investor’s account in a country applying such measures (to be specified in the account opening agreement if possible) and be transferred again to the same account. Applications submitted by foreign investors whose countries never (or insufficiently) apply the FATF Recommendations, or some decisions have been issued against them by the Security Council, shall not be accepted.
500. Rules for Opening Bank Accounts for Government Entities
500.1 Rules for Opening Bank Accounts for Ministries and Saudi Government Entities
500.1.1 Ministries and Government Entities Listed in Appendix (A) and the Like
Banks may open Saudi riyal accounts for government entities subject to the following:
1. The government entity shall submit an account opening application to the Ministry of Finance (the Deputyship for Financial and Accounts Affairs). In order to complete the opening application process or activate the account, a list of existing bank accounts with SAMA and other banks must be attached so as to avoid replication of accounts with the same purpose. After considering the application, the Ministry of Finance shall inform SAMA about opening the account, and the government entity shall provide the bank with the names, specimen signatures and ID copies of the authorized persons.
2. Name of the beneficiary shall be included in the payment order related to deposits to the account (Due to the order of the bank, Account No…).
3. The bank account shall be in the name of the government entity, not a natural person or his/her position or job, and its purpose shall be specified in order to differentiate it from other accounts.
4. If a government entity wishes to change its account name, it shall submit an application in this regard to the Ministry of Finance (the Deputyship for Financial and Accounts Affairs) to make a decision of approval or disapproval and then notify SAMA of such decision to be communicated to the bank.
5. A checkbook shall be requested by an official letter signed by those authorized to withdraw funds.
6. Authorization to deposit and withdraw amounts shall be issued by the concerned party. Authorized persons may not delegate their power to others unless authorized to do so by the concerned party. Official letters addressed to the bank by authorized persons to issue bank checks or make internal or external transfers in the official entity’s forms or the approved bank forms may be accepted, provided that such letters are jointly signed by the authorized persons only.
7. Withdrawal from the account shall be as per dual control, and in the case of withdrawal by checks, the check shall be jointly signed by the authorized persons.
8. E-services provided to government entities must include the following: Viewing and extracting of account statements, internal and external transfers, and payment of bills.
9. A government entity may not open any account in a foreign currency unless this is included in an approval given by the Ministry of Finance and communicated to the bank by SAMA.
10. Banks may not extend to any government entity any loans or facilities or allow any overdraft of more than the amounts drawn under payment orders upon the Ministry of Finance, whether for salaries or for any other purposes, except on approval of the Council of Ministers.
11. Government accounts shall not be transferred from one bank to another unless the approval of the Ministry of Finance is obtained therefor and communicated to the bank through SAMA. In addition, there shall be cogent reasons supporting the transfer. If the purpose of the account is fulfilled and the account is no longer needed, the Deputyship for Financial and Accounts Affairs at the Ministry of Finance shall be informed in order to request SAMA to close the account.
12. Signatories of the accounts of Saudi government entities and agencies shall be Saudis only. No authorization shall be granted to no-Saudis in this regard.
500.1.2 Rules for Opening Bank Accounts for Government Entities to Receive Donations for their Own Account
The bank may open Saudi Riyal accounts for government entities to receive gifts and donations for their own account. The following requirements shall be met:
1. The request to open a bank account shall be submitted after obtaining the approval of the Ministry of Finance notified through SAMA. Such request shall indicate that the purpose of opening the account is to receive donations for the government entity.
2. Two signatories shall be determined by the concerned minister or the head of the entity, in addition to the financial controller in the government entity. The bank shall obtain IDs copies and specimen signatures of such authorized persons. Those copies shall be attested as true copies of the original by both the government entity and the bank. Changing the signatories or financial controller requires sending a letter from the concerned minister or the head of the entity or his authorized representative to the bank where the account is opened.
3. Deposit in the account shall be by checks only. The name of the payee shall be the government entity, and such checks shall be presented for deposit through the signatories.
4. A checkbook shall be requested by an official letter signed by those authorized to withdraw funds.
5. Withdrawal from the account shall be made only by checks signed jointly by the authorized signatories and the financial controller.
This rule has been amended according to the circular No. (45070397), Dated 13/11/1445H, corresponding to 20/05/2024G.500.1.2.1 Bank Accounts of Government Entities, Designated for Activities and Services Financed Through Sources Other Than the State Budget
The bank may open separate accounts for academic and specialized government entities (e.g. universities, institutes and research centers) for the purposes of research works, studies, consultation, specialized services and the like that are funded by beneficiaries (not through the state budget). The following requirements shall be met:
1. The bank shall receive a request from the rector/head of the entity (university, institute, scientific center, and the like) to open an account; such request shall indicate that the account is designated for an activity to be funded through sources other than the state budget.
2. The government entity shall specify the purpose of the account and, if possible, the reasons supporting being contracted with or assigned to carry out advisory or technical tasks.
3. The name of the account shall reflect its purpose.
4. Signatories shall be determined by the government entity’s rector/head. The bank shall obtain IDs copies and specimen signatures of such authorized persons. Those copies shall be attested as true copies of the original
5. by both the government entity and the bank. Changing the signatories requires sending a letter from the entity’s rector/head to the bank where the account is opened.
6. The bank shall obtain a copy of the government entity’s regulations governing the financial affairs of the financed activity (university, institute ...).
7. The account shall be opened for the duration of the project or for a period of one year where the duration is not defined. The validity of the account may be extended for another period/additional periods by a letter from the rector/head of the entity to the bank, requesting an extension and including supporting reasons.
500.1.3 Bank Accounts to Invest the Funds of Persons Covered by the Law of the General Commission for the Guardianship of Trust Funds for Minors and their Counterparts (Wilayah)
Bank accounts for these entities shall be opened after fulfilling the following requirements:
1. The bank shall receive a letter from SAMA, requesting the opening of a specific bank account for investing funds of those covered under Wilayah’s law (unknown persons, minors, mentally ill persons, etc).
2. The concerned division at Wilayah shall provide the bank with the names of persons authorized to operate the account under a joint signature, copies of their IDs and their specimen signatures. Further, the bank shall also ensure that the account opening agreement is completed and signed by such persons.
500.2 Bank Accounts of Countries and Non-Saudi and Non-Resident Government Entities
500.2.1 GCC Countries and GCC Government and Quasi-Government Entities
The bank may open accounts for GCC government and quasi-government entities. The following requirements shall be met:
1. The bank shall obtain a copy of the ministerial resolution issued by the GCC country, requesting opening of a bank account.
2. The concerned GCC entity shall send a letter to its Saudi counterpart, the Saudi Ministry of Finance or the Saudi Ministry of Foreign Affairs, requesting opening of a bank account.
3. The bank shall obtain copies of the IDs of persons authorized to sign jointly for the account.
4. The bank shall obtain the signatories’ specimen signatures.
5. The bank shall receive SAMA’s approval for opening the bank account.
500.2.2 Non-GCC Countries and Non-GCC, Non-Resident Government and Quasi-Government Entities, Except Hajj Missions
Banks operating in Saudi Arabia shall not open bank accounts for non-GCC countries and non-GCC, non-resident government and quasi-government entities, except Hajj missions, unless official approval of the Minister of Foreign Affairs is granted and communicated to the bank through SAMA. Such approval shall indicate the name of the account, sources of funds, names of signatories and how to change them. Changing the signatories requires the approval of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs unless the approval for opening the account as communicated through SAMA has clearly allowed changing such signatories by a specific person(s) or entity. The bank shall classify such accounts as of high risk.
600. Clearance Bank Accounts
The bank may open clearance accounts, which are designated for those wishing to discharge their liability toward public funds. The following requirements shall be met:
1. The account shall be named “Clearance Account for (name of the concerned entity shall be specified here)”.
2. The account shall be valid for one year only.
3. The account shall be monitored by the bank’s compliance officer and shall be classified as of high risk.
4. The bank shall present to SAMA a detailed report of the account at the end of the year.
5. Before operating the account, the bank shall coordinate with the entity requesting such account to provide SAMA with the mechanism that will be used for announcing the account creation.
6. To withdraw funds from the account, the entity shall submit a request thereon to the bank. Such request shall be signed, and one of the signatories shall be the chairman of the entity.
7. The bank shall obtain the necessary documents required for opening such accounts, as per the requirements of the rules for opening bank accounts and subject to the classification of the entity.
8. The bank shall submit to SAMA all the aforementioned documents to receive its approval for opening the account.
Chapter IV. General Rules for Operation of Bank Accounts
1. The bank account shall be operated originally by the account holder or other persons authorized by the account holder and approved by the bank. Where applied, the authorization remains valid until the account holder notifies the bank of its cancellation, it expires (after five years), or the authorized person’s ID expires and no renewed ID is presented to the bank. The authorization for operating and cancelling the bank account shall be granted through a power of attorney or an authorization letter prepared at the bank. E-services may be used to verify the authorization.
2. Saudi individuals (whether account holders or authorized to operate the account) are not allowed to operate bank accounts, encash personal checks, make transfers, or carry out any other credit transactions to their order or to the order of a third party unless their valid national IDs are registered in the bank’s automated system. The exceptions to this rule are customers of bank branches at airports, who are traveling abroad; in such case, the customer is required to present his/her passport and boarding pass, and the bank branch shall in turn check customer’s name against documents submitted.
3. The authorization to operate bank accounts on behalf of juristic entities shall be granted by competent individuals who are permitted to give such authorization. The official approval for such authorization shall be granted by the concerned public or private entity. The approval may come from the board of directors, the partners, the employer, any person designated by the owner (or the person in charge) of the entity, a party determined in the agreement concluded between the bank and the concerned entity, or other parties as per the jurisdiction.
4. Authorization by a Saudi (natural or juristic) person to a non-Saudi or non-GCC individual to manage his/her accounts shall be subject to the following conditions:
• Natural persons and their sole proprietorships:
Any authorization granted by a Saudi individual to a non-Saudi or a non-GCC individual to operate his/her personal accounts shall not be accepted by the bank. The only exception is when a Saudi individual authorizes his/her non-Saudi wife/husband, father, mother, son or daughter, provided that the authorized person has a valid Iqama.
• Companies, factories, joint ventures, international trademark agencies, and other similar institutions:
*Companies may authorize an expatriate employee who is under their sponsorship and residing in Saudi Arabia to manage their bank accounts. However, such expatriate employee may not be authorized to manage the accounts of another company, whether a subsidiary or sister company.
*Factories and trademark agencies wishing to authorize an expatriate employee working under their sponsorship shall be treated in accordance with their legal status indicated in their licenses/commercial registers issued by the concerned authority. Legal entities licensed as sole proprietorships shall be subject to the provisions of Paragraph (1) of Rule (4) on Natural Persons and their Sole Proprietorships while legal entities licensed as companies shall be subject to the provisions of Paragraph (2) of Rule (4) on Companies.
5. Management of investors' accounts under the Foreign Investment Law shall be subject to the following conditions:
- The Saudi investing partner may authorize his/her foreign investing partner holding a valid Iqama or any of the non-Saudi expatriate employees working for his/her entity to manage and operate the entity's bank accounts.
- The foreign investor may authorize a Saudi and/or a non-Saudi expatriate to manage the entity's bank accounts, provided that the non-Saudi expatriate is an employee of that entity and has a valid Iqama.
- The Saudi investor and his/her foreign partner may authorize any other resident party to manage the entity's bank accounts.
6. The bank shall not accept any authorization given by an expatriate coming for work or investment in Saudi Arabia to others to manage and operate his/her personal accounts, except in the following cases:
- The expatriate husband and his expatriate wife and vice versa, and their first-degree expatriate relatives.
- The female expatriate working in Saudi Arabia and her legal escort, provided that the Iqama of the legal escort or any other official document states that he is the legal escort of the female expatriate.
- The female expatriate and her Saudi husband.
- The female expatriate and her Saudi father, mother, son or daughter.
- The male expatriate and his Saudi wife.
- The male expatriate and his Saudi father, mother, son or daughter.
- The male or female expatriate and his/her abovementioned relatives should hold valid Iqamas. The bank should record the number of Iqama for each male or female expatriate as an electronic reference number for the expatriate.
7. As for companies, the account will be operational when the company becomes legal.
8. The following banking rules regarding checks shall be observed:
- The name of the beneficiary must match the name shown on his/her ID.
- Provisions of the Commercial Papers Law, including those related to payment term, shall be complied with.
- Crossing out, erasure, or using chemical materials on the check is not permitted.
- When amendment to a check is needed, the part that needs to be amended shall be crossed out, correction shall be written, and the signature of the drawer shall be placed next to the corrected mistake.
9. Rules for Deposits in Bank Accounts
9.1 Deposits Through Bank Tellers
The bank should give importance to cash and check deposits equal to that given to cash and check withdrawals. Aa a minimum requirement, the bank shall obtain full personal information of the depositor and his/her signature. A due consideration should be given to the volume and nature of other information that the bank should collect from depositors. Such information varies according to the type and nature of the deposited funds, deposit volume and recurrence, and the relationship between the depositor and the person/business receiving such deposit. Below are examples of different situations and how the bank should respond:
- When a natural person wants to deposit funds (personally in his/her name or in the name of another natural person) in his/her bank account, another natural person’s account or juristic person’s account, the bank in this case shall obtain the personal information of the depositor. Such information includes the depositor’s full name, address, telephone number, signature, and ID number in accordance with the provisions of Rule (3.1.1) and Rule (3.1.2) of Chapter II herein.
- When a natural person wants to deposit funds in a bank account on behalf of a juristic person (e.g. establishment, company, shop or any other entity) he/she does not own or is not authorized to manage its accounts, the bank shall then obtain the abovementioned information from the depositor in addition to the following:
■ The purpose of the deposit clearly identified in the deposit slip.
■ The name of the principal depositor (the juristic person) and the name and information of the representative (depositing on behalf of the juristic person) as stated above. Such information shall be contained in the deposit slip. The bank shall not limit the deposit slip information to only the names of the company and depositor.
■ A copy of the authorization granted to the depositor (natural person) by the principal depositor (juristic person), not by the beneficiary. The authorization may be attested by the chamber of commerce or made on the bank’s special form and the signature contained is certified by the bank. The authorization can also be in a form of a power of attorney issued by a notary public or a notary, permitting such natural person to deposit funds on behalf of the principal depositor (juristic person) in the bank account(s) of other natural or juristic persons. The authorization copy shall be certified by the bank as a true copy of the original and shall be kept in a separate file or attached to the deposit slip in the bank’s daily work record.
- Banks shall not continue to use the word “himself/herself next to the “customer’s name” if the depositor is the account holder. In such case, the bank shall write the full name of the depositor and all data contained in the deposit slip. However, the exception to this provision is when the depositor’s signature on the deposit slip is the same as that of the account holder, provided that the bank employee shall verify the authenticity of the depositor's signature and certify that he/she is the holder of the account.
9.2 Deposits Via Cash Acceptance Machines (CAM) and Automated Teller Machines (ATM)
9.2.1 Deposits Through ATMs, Using ATM Card and Personal Identification Number (PIN) Only
All banks shall comply with the following controls on the acceptance of cash deposits through ATMs:
1. Cash deposits through ATMs shall be accepted only when using an ATM card and the associated PIN or using a credit card. The exceptions to this rule are the payment of utility bills, payment made to government entities (whether by bank customers or others), and other payments approved officially by SAMA.
2. The bank shall comply with the instructions related to amount limits and number of banknotes and coins that can be deposited in one transaction or per day. In addition, the bank shall ensure that the procedures implemented are in line with data and results of customer risk assessment. Moreover, the bank shall adhere to controls and guidelines of the ATM operation manual.
3. ATMs used for deposits must support obtaining information on the source of cash deposited and the purpose of deposit. If envelope-free deposits are to be made, the ATM must be able to detect counterfeit banknotes through checking security features.
9.2.2 Deposits Through ATMs, Using Cash Deposit Card
Banks may issue smart cards to be used for cash deposit through the ATMs of the issuing bank. Such cards shall use PIN. The following controls shall be applied:
1. The purpose of deposit shall be identified.
2. The cash deposit cards shall be issued to a selected category of customers (companies and establishments) determined by the bank according to its risk assessment.
3. The business of such customers shall include sales or collections representatives. The bank shall be responsible for obtaining from such customers and checking the necessary documents proving their lines of business. The number of representatives shall be consistent with the entity’s business and size.
4. Such accounts shall be subject to constant monitoring by the compliance officer at the bank according to risk assessment. The monitoring process aims to ensure that the deposit transactions agree with the customer’s business. Through reports of internal audit and monitoring process, the bank can prevent any suspicious financial transactions.
5. The cash deposit card(s) shall be restricted to a single account. In case of multiple accounts for a company, the bank may, at the request of the customer, issue one cash deposit card or more for each account. The cash deposit card shall be used for its associated account only.
6. The cash deposit card service shall be provided upon an official request from the person authorized to manage the account or from the authorized person in the entity.
7. The cash deposit card shall be issued only to the representatives of the entity upon presenting valid IDs. The entity’s representative shall present his/her ID to the bank in person. If he/she is an expatriate, he/she shall be subject to expatriate authorization provisions. If he/she is Saudi, he/she shall present his/her employment card or an employment letter from the entity for which he/she works.
8. The cash deposit card shall be issued in the names of the entity and the representative who will use the card (...Company/representative’s name). Personal photo of the representative shall, as possible, be placed on the cash deposit card.
9. The cash deposit card shall be valid for a period identical to the validity period of the ID or the entity’s documents, whichever expires first. However, the validity period of the cash deposit card shall not exceed two years.
10. The bank shall obtain from both the entity and the cardholder a written undertaking that the card will be used only by the person to whom it is issued and only for cash deposits, but not for any other banking transactions.
11. Each cash deposit card held by each representative shall have a unique PIN.
12. The cash deposit card shall be used for deposits in the associated current account through the ATMs of the issuing bank only.
13. The cash deposit card shall be subject to the same procedures applied to other cards in terms of technical (in relation to deposit transactions only) and security specifications.
14. The cash deposit card shall not be used for deposits through the bank tellers.
15. The cash deposit card shall be used for direct cash deposit with no need to use sealed envelopes.
16. The cash deposit card and its associated PIN shall be delivered to the representative directly by the bank, and not through the entity.
17. The bank shall set procedures to change the card’s PIN periodically pursuant to the nature of the entity, potential risks, and discretion of the departments of compliance and risk management at the bank.
18. The bank shall, based on risk assessment in terms of customer’s activity and category, set a maximum limit for daily deposits for each account, taking into consideration the risks associated with carrying large amounts of cash.
19. The bank shall obtain SAMA preliminary approval for providing such product (service).
10. Account Closure
1. If the customer wishes to terminate his/her relationship with the bank, he/she should submit a request to the bank to close his/her account and should return checkbooks, the ATM card and the account information card. If the customer is unable to return them to the bank, the bank shall obtain a liability acknowledgement from the customer. The bank shall cut up the checkbooks and cards in the presence of the customer and return to him/her the account’s funds. The bank may decline the customer's request if there are outstanding financial liabilities associated with the account, such as letters of guarantee, letters of credit and discounted bills with financial significance and effects that necessitate the continuation of the account. In this case, the bank shall explain to the customer when he/she will be able to submit an account closing request.
2. If problems related to the verification of the banking relationship occur after opening the account and the problems are not solved or if the relationship with the bank is used for other purposes other than its intended one, the bank shall terminate the banking relationship with the customer and return the account’s funds to the source. If the verification problem or the misuse of the banking relationship is related to suspicious transactions carried out by the customer (such as money laundering, terrorism financing and the like), the bank shall implement the Rules Governing Anti-Money Laundering and Combating Terrorist Financing, including reporting suspicious transactions.
3. If the account is opened, the customer deposits funds into it and then reduces his/her balance to zero, and the account has remained inactive or with zero balance for 4 years, the bank shall then close the account after verifying that it has no related commitments or obligations. Prior to account closure, the bank shall send one month’s notice to the customer. Another notice shall be sent to the customer upon account closure. The bank must document and keep all notices sent in the customer’s file. Further, the bank shall include terms on bank account closure in the main body of the account opening agreement or add such terms as an attachment appended thereto if it is difficult to modify the account opening agreement.
Chapter V. Concluding Provisions
1. Any update to the Rules will be published immediately on SAMA’s website.
2. These Rules shall supersede the Rules Governing the Opening of Bank Accounts and General Operational Guidelines in Saudi Arabia (4th Update) and any supplementary circulars.
3. The Rules shall supersede any provisions to the contrary.
4. The Rules, and any updates thereto, shall enter into force as of the date of its publication on SAMA’s website.
Chapter VI. Appendices
Appendix (A)
Government Entities:
■ Public Prosecution ■ Control and Investigation Authority ■ General Auditing Bureau ■ Real Estate Development Fund (REDF) ■ General Authority of Zakat and Tax ■ King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center ■ Specialized central councils and committees ■ Gov. Universities and Colleges ■ King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology ■ National Cybersecurity Authority ■ Technical and Vocational Training Corporation ■ Any other similar government entities Appendix (B)
Legal Entities in Public Sector:
■ General Organization for Social Insurance (GOSI) ■ General Commission for the Guardianship of Trust Funds for Minors and their Counterparts (Wilayah) ■ Non-government universities and scientific institutes registered with the Ministry of Education ■ Public Investment Fund (PIF) ■ Saudi Arabian Airlines (Saudia) ■ Saudi Industrial Development Fund (SIDF) ■ Public Pension Agency ■ Saudi Arabian Oil Company (Saudi Aramco) ■ Any other similar legal entities Appendix (C)
Explanation of the Combination of the Ten-Digit Computer Number of the Ministry of Interior:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1. Digit number (1) on the left refers to the type of the computer number, and its value is as follows:
-The value is (1) for Saudi citizens. When a Saudi citizen is born, he/she is given a computer number (which is the number of his/her national ID). The computer number of an establishment of a Saudi natural person is the number of the owner’s ID.
-The value is (2) for foreign residents of all nationalities. The computer number for a resident is the same as that of his/her Iqama. Each foreign resident in Saudi Arabia has his/her own unique number regardless of him/her being a family head or a dependent. The computer number of an establishment of a foreign natural person permitted to own businesses is the number of his/her Iqama.
-The value is (3) or (5) for visitors coming to Saudi Arabia for the purpose of a temporary visit rather than residence, such as those coming for Umrah, on a special or business visit, etc. This value is also used for GCC citizens. The computer number is given to a GCC citizen coming to Saudi Arabia and is used in each visit to Saudi Arabia.
-The value is (6) for pilgrims. The number is given to a pilgrim upon his/her arrival in Saudi Arabia to perform Hajj.
-The value is (7) for government entities, joint-stock companies, privet entities, or any other entities, such as military missions, charities, international schools, sports clubs, or diplomatic bodies, etc.
2. The value from digit number (2) to digit number (9) is a serial number ranging from 00000000 to 99999999.
3. Digit number (10) is a “verification" digit. Its value ranges from (0) to (9) and is derived from the values of the other nine digits. It is used to check the correctness of the computer number. Any entity wishing to receive the formula applied to derive this digit for programming purposes, may contact the National Information Center of the Ministry of Interior..
Rules Governing Bancassurance Activities
No: 188/441 Date(g): 6/5/2020 | Date(h): 14/9/1441 Status: In-Force The Saudi Central Bank* has issued this Rules according to the Governor’s Decision number (188/441) dated 14/09/1441H, based on the powers vested to SAMA by the Cooperative Insurance Companies Control Law promulgated by Royal Decree No. (M/32) dated 02/06/1424H (corresponding to 31/07/2003), and its Implementing Regulation issued by the Decision of the Minister of Finance No. (1/596) dated 01/03/1425H (corresponding to 20/04/2004). And based on the Banking Control Law promulgated by Royal Decree No. (M/5) dated 11/06/1966.
* The "Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency" was replaced By the "Saudi Central Bank" in accordance with The Saudi Central Bank Law No. (M/36), dated 11/04/1442H, corresponding in 26/11/2020G.
Article One
Definitions:
The following terms and phrases, wherever mentioned herein, shall have the meanings assigned thereto unless the context otherwise requires:
1.1 SAMA: The Saudi Central Bank*. 1.2 Rules: The Rules Governing Bancassurance Activities. 1.3 Company: The insurance company licensed to practice insurance business in accordance with the provisions of the Cooperative Insurance Companies Control Law. 1.4 Bank: Any bank licensed to carry out banking business in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in accordance with the provisions of the Banking Control Law. 1.5 Bancassurance Activities: Marketing and distribution of insurance products by the Bank to its Clients according to the signed Agreement between the Bank and the Company. 1.6 Agreement: A contract by which the Company and the Bank agree that the Bank will carry out the Bancassurance Activities. 1.7 Authorised Employee: The Bank employee(s) assigned by the agreement with the Company to carryout Bancassurance Activities. 1.8 Client: a natural person or juristic entity who deals with the Bank. * The Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency was replaced By the name of Saudi Central Bank accordance with The Saudi Central Bank Law No. (M/36), dated 11/04/1442H, corresponding in 26/11/2020AD.
Article Two Scope of Application
These Rules shall apply to all Bancassurance Activities. The Cooperative Insurance Companies Control Law, its Implementing Regulation, the Banking Control Law and SAMA’s relevant regulations, rules, and instructions, and relevant laws and regulations issued by other authorities shall govern whatever is not provided for therein and to the extent possible.
Article Three Objective
The objective of these Rules is to regulate Bancassurance Activities and practices in Saudi Arabia and the relationship between the Company and the Bank in this regard.
Article Four Requirements for Practicing Bancassurance Activities
- Bancassurance Activities shall be practiced directly through the Bank. By merely establishing a tool among other tools for marketing and distribution for the Company, the contractual relationship between the Company and the Bank- in the context of conducting Bancassurance Activities - shall not include insurance agency, insurance brokerage, insurance advisory, or any insurance related profession.
- The Company and the Bank shall sign the Agreement before the Bank starts practicing Bancassurance Activities.
- The Company and the Bank shall obtain SAMA’s prior approval before signing the Agreement.
The Agreement must include, at a minimum, the following:
a. Term of Agreement;
b. Agreement termination procedures;
c. List of the electronic and non electronic marketing and distribution channels; through which the Bancassurance Activities will be practiced.
d. Training plan for Authorised Employees;
e. Know Your Client (KYC) procedures;
f. Compliance procedures;
g. Insurance classes and products to be covered under the Bancassurance activities;
h. Marketing and distribution procedures;
i. Collection of premiums procedures;
j. Bank commission and its calculation mechanism, due date, and collection procedures;
k. Client care and complaints resolution procedures; and
l. Procedures of receiving and transferring the claims to the Company.
Article Five Bank Obligations
1. The Bank shall be fully responsible for the Authorised Employees’ practice of Bancassurance Activities. In order to ensure that the activities are carried out in line with SAMA's instructions and principles of transparency, the Bank shall: 1.1 Ensure compliance with the terms of the Agreement and the procedures contained therein in all marketing and distribution channels of the Bank, and set the appropriate internal controls and procedures to ensure compliance with the relevant laws, regulations and rules; 1.2 Maintain adequate records demonstrating the Bank's compliance with the provision (1.1); 1.3 Prepare compliance reports regarding the Bancassurance Activities as agreed with the Company; 1.4 Ensure compliance with the limits of insurance policies permitted to be marketed and distributed in accordance with the Agreement; 1.5 Maintain the confidentiality of data, records and information of the Company and its Clients; and 1.6 Allow the Company to view, review all Bank books and records related to Bancassurance Activities or obtain copies of them, and prepare the following records: 1- Communications record; 2- Internal records; and 3- Clients’ complaints record. 2. The Bank shall establish a Bancassurance unit to oversee the Bancassurance activities, and the Bank’s code of governance shall determine its operation procedures and shall include, at a minimum, the following responsibilities: A. Supervision of the Bank's electronic and non-electronic marketing and distribution channels. B. Holding training courses for Authorised Employees. C. Establish procedures to control and verify that the marketing and distribution of insurance products are carried out in an honest, transparent and fair manner. 3. The Bancassurance unit shall be under the management of an employee with sufficient experience who will be employed by the Bank to fill the position of director of the Bancassurance department, after obtaining SAMA’s non-objection. 4. Bancassurance Activities shall be practiced through the Bank’s marketing and distribution channels electronic and non electronic. 5. The Bank shall ensure that all Authorised Employees have the Insurance Foundations Professional Exam certificate (IFCE) and any other certificate specified by SAMA. 6. The Bank must obtain the Company’s approval to expand the marketing and distribution channels, electronic and non electronic; through which Bancassurance Activities are practiced, along with notifying SAMA's of such. 7. The Bank must not conduct Bancassurance Activities with other than his Clients. Article Six Company’s Obligations
The Company shall perform and not assign any of the following authorities to the Bank:
a. Make any amendments to the insurance policies or its annexes.
b. Settlement of claims.
c. Payment of compensation.
- Obtain SAMA’s approval before any material amendments to the Agreement between the Company and the Bank.
The Company shall provide SAMA with an annual training plan for the Authorised Employees, provided that it includes -at a minimum- the following:
a. Training on marketing and distribution techniques;
b. Workshops to introduce insurance products; and
c. Training on anti-money laundering and counterterrorist financing.
- Maintain the confidentiality of the data and information of the Bank and its Clients.
- The Company shall regularly review the Bank’s practice of Bancassurance Activities, whether through Bank’s electronic or non- electronic channels.
- The Company shall pay the Bank the marketing and distribution of insurance products’ commission as a result of carrying out Bancassurance Activities during the period specified in the Agreement, provided that the commission is in line with SAMA;s instruction.
Article Seven
The Bank is prohibited from requiring the Client to obtain banking products in order to get the insurance products or vice versa, unless the insurance coverage is binding by a competent authority.
Article Eight
The Company may sign an Agreement with one Bank or more, and the Bank may sign an Agreement with one Company or more.
Article Nine Rules of professional Conduct:
The Bank shall comply with the rules of professional conduct by fulfilling the following requirements:
Act in an honest, transparent and fair manner, and fulfill all of their obligations towards the Clients and the Company, as stipulated by Saudi Arabian laws and regulations.
Where these obligations have not been fully codified, internationally accepted best practices should be honored.
- Act within reasonable competence when dealing with Clients and the Company, which is acquired through training, experience, and consulting with experts when needed.
- Continuously enhance the skills and knowledge of the Authorised Employees in charge, along with the continuous follow up of the products and services available in the market.
- Take reasonable care in maintaining adequate managerial, financial, operational, and human resources to carry out their business and serve the Clients.
- Communicate all relevant information including coverage details, conditions, exceptions and restrictions of the insurance policy to the Clients in a timely manner, and ensure that the Clients are aware of the commitment they are about to make to enable them to make a suitable decision.
- Take reasonable measures to ensure the accuracy and clarity of the information provided to and from the Clients and make such information available in writing.
Treat all data and information acquired about the Company and the Clients with utmost confidentiality, and take appropriate measures to maintain the secrecy of confidential documents in their possession, along with taking the following actions:
- Obtain and use of data only for activities specified under these Rules and not to be used in a manner that is incompatible with those purposes.
- Keep the data secure and up-to date.
- Provide data about insurance coverage to the Clients upon their written request.
- Not to disclose the data to any third party without prior authorization from SAMA, with the exception of the Bank or the Company’s external auditors, or the authorised companies to collect insurance and credit data.
- Banks must not motivate the Clients to revoke a valid insurance policy, and must not motivate the Clients to refuse a quotation given by a competitor using false or unfair evaluation in order to merely increase commissions.
- Ensure that the Clients fully understand the Bancassurance services provided by the Banks and the nature of the relationship between the Bank and the Company.
- Notify the Company of all the insurance information or documents related to Clients which may affect the decision of the Company to provide the coverage and the rates and conditions which the insurance policy will be built upon.
- Immediately notify the Clients about the acceptance or rejection of the coverage by the Company.
- Explain to the Clients the mechanism of paying the insurance premiums and any other additional due to the Company.
- Clarifying to the Clients that the contractual relationship will be with the Company.
Article Ten Banks Dealing with Clients Requirements
1. Pre-marketing and distribution Communication with Clients:
1.1 Advertising:
a) Ensure that advertisements are not misleading, over-stated or offensive ; b) Ensure that advertisements does not breach the laws or omit any regulatory requirement; c) Ensure that advertisements does not damage Clients’ faith or exploit their lack of experience or knowledge. d) Obtain the approval from the Company if the Company is mentioned in the advertisement. 1.2 providing Advice:
Banks shall provide advice on matters within their field of expertise and seek or recommend the help of experts when necessary. 1.3 Client Service:
a. Understand all the terms and conditions of all policies offered to the Clients ; and b. Understand the Clients’ profile, coverage needs, and appetite for risk. 1.4 Regulatory Requirements:
a. The Bank shall ensure that all documents issued are consistent with the regulatory and supervisory requirements; 1.5 Documentation:
a. Ensure that all written terms and conditions are fair in substance and that the Clients' rights and responsibilities are set out, clearly and inplain understandable language.; b. Send policy documentation to the Clients without avoidable delay; c. Send a written advice along with the policy documentation stressing on the importance of reading it carefully ; and d. Ensure that instruction letters, policies and renewal documents contain details of complaints handling procedures. 2. Marketing and distribution of Insurance Products and Services
2.1 Marketing and distribution Practices:
a. Ensure that the Clients understand the type of service being offered. b. Ensure that the policy proposed is suitable for the Client’s needs; c. Provide the Clients with comparisons in terms of price, coverage and services offered when offering several products. d. Notify the Clients promptly if unable to obtain the requested insurance. e. State the validity period for quotation if the proposed contract was not signed immediately; and f. Explain to the Clients their obligations to file claims immediately and to disclose all material facts relevant to the insurance coverage. 2.2 Providing of Information:
a. Request the Clients to make true, fair and complete disclosure and ensure that the consequences of nondisclosure of information and inaccuracies are pointed out to clients. ; b. Avoid influencing and pressuring the Clients along with emphasizing that all acknowledges or statements given are his/her own responsibility. c. Require the Clients to carefully check the information given in the documents. ; d. Explain to the Clients the importance of disclosing all subsequent changes that might affect the coverage throughout the duration of the policy. ; and e. Disclose of all information required for the purpose of insurance on behalf of the Clients with the Client's written consent and provide aclear presentation to the Company about the Client's risk description. 2.3 Interpretation of Contracts:
a. Explain all the essential provisions of the coverage provided by the policy to Clients. ; b. Notify the Clients with the Company’s quotation exactly as provided; and c. Notify the Clients of any significant or unusual restrictions or exclusions in the insurance policy, and explain the termination procedures. 2.4 Charges:
a. Disclose to the Clients the amount with the profits and commissions they are receiving upon selling the policy. b. Inform the Clients in writing of any additional fees or charges for any related services. 3 Post marketing and distribution Client Service
3.1 Confidentiality of Information:
a. Ensure that Clients data and confidential documents are stored safely with restricted access. ; and b. Ensure that only relevant parties can obtain the Clients’ data such as the Company and external auditors of the Bank and the Company. 3.2 Clients Notification:
The Banks hall promptly communicate any notifications received from the Company to the Client related to his insurance policy, along with obtaining a receipt of acknowledgments. 3.3 Renewal of Insurance Policy:
a. Ensure that renewal notifications include Clients’ duties to disclose changes affecting the policy, which have occurred since the policy inception or the last renewal date ; b. Ensure that renewal notification contains a requirement for keeping records, including copies of letters, of all information supplied to the Company for the purpose of renewal of the contract ; c. Ensure that the Clients are aware of the expiry date of the policy even if the Company has no intention to renew. d. Ensure that the Clients receive the renewal notice of the policy issued by the Company before its expiration. 3.4 Claims handling :
The Bank shall not approve or settle claims. However, the Bank shall:
a. Immediately acknowledge filed claims; b. Provide claim forms along with clarifying the information or procedures needed to be done the Client to file the claim; c. Provide adequate instructions to the Clients on filing claims and information on claim handling; d. Provide the Clients with an acknowledgement of receipt or a notification of any missing information or documents, within seven days of receiving the claim; e. Notify the Clients of any development regarding the claim at least once every 15 working days; f. Notify the Clients in writing of claim acceptance or rejection; and g. Explain the method of filing complaints and procedures of dispute resolution if the Client is not satisfied with the settlement reached. 3.5 Client Complaints:
a. Receive complaints, by phone or in writing such as letters, e-mail or fax; b. Explain complaint filing procedures; c. Provide the Clients with the contact information of the Company to follow up on their complaints; d. Notify the Clients of the developments in their complaints; e. Respond to the complaints within (15) days of filing; and f. Maintain an electronic system to record and follow up on complaints. Article Eleven Agreement Termination Procedures
- The Company or the Bank shall submit to SAMA a request to terminate the Agreement along with the reasons of termination.
After obtaining SAMA’s approval, the Company and the Bank shall:
a) Sign a financial clearance between them;
b) Announce the termination of the Agreement on their official websites; and
c) Take all actions that indicate the termination of the Agreement, including removal of all advertisements and returning the usernames and passwords of the Company’s electronic systems
Article Twelve Control and Inspection
- SAMA shall supervise and conduct a periodic or surprise inspection of the Bank and the Company to ensure compliance to the Agreement and SAMA’s Bancassurance Rules, and investigate any violations detected by the inspection or from the complaints received by SAMA.
- SAMA may request all relevant information and documents to ensure the Bank and the Company’s compliance with the provisions of the Agreement and SAMA’s applicable instructions on conducting Bancassurance Activities.
Article Thirteen Consequences of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with the requirements of these Rules shall be deemed a violation of the Cooperative Insurance Companies Control Law, its Implementing Regulation and the Banking Control Law, and may subject the Bank or the Company to legal penalties.
Profit Sharing Investment Accounts Rules
No: 44012303 Date(g): 11/9/2022 | Date(h): 15/2/1444 Status: In-Force Based on the powers granted to the Central Bank under its Law issued by the Royal Decree M/36, dated 11/04/1442 H, and related regulations. And in reference to the ongoing work to establish a supervisory framework for banks practicing Islamic banking, and in order to enhance the environment of compliance with the provisions and principles of Shariah.
Attached are the Rules on Profit Sharing Investment Accounts (PSIA) for banks practicing Islamic banking. These rules aim to establish minimum set of regulatory requirements that must be adhered to by banks offering such accounts, in addition to enhancing customer protection and increasing transparency in the banking sector.
For your information and action accordingly as of 1 March 2023 G.
1. Introduction
In exercise of the powers vested upon the Central Bank under the charter issued by the Royal Decree M/36 on 11-04-1442 H corresponding to 26 November 2020 G and the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree no. M/5 dated 22/2/1386AH corresponding to 11 June 1966 G and the rules for Enforcing its Provisions issued by Ministerial Decision no.3/2149 on 14-10-1406A H, SAMA is hereby issuing the enclosed Rules on Profit Sharing Investment Accounts (PSIA) aimed to develop the practices followed by banks operating PSIAs. These rules should be read in conjunction with the wider SAMA regulatory framework.
2. Objectives
The objectives of these rules are to provide the minimum requirements to be met by banks in Saudi Arabia that offer PSIA products. The rules aims to enhance consumer protection, transparency and financial stability in the banking sector whilst also ensuring compliance with Shari’ah principles in the operation of PSIAs.
3. Scope of Application
These rules are applicable for all local Saudi banks that conduct Shari'ah compliant banking and are licensed by SAMA under the Banking Control Law.
4. Definitions
The following words and phrases, wherever mentioned in these Rules will have the meanings assigned to them unless the context implies otherwise:
SAMA: Saudi Central Bank
Bank: Any local bank that is licensed to carry out banking business in Saudi Arabia in accordance with the provisions of the Banking Control Law and that conducts Shari'ah compliant banking.
Board: The Board of Directors appointed by the shareholders in line with applicable laws and regulations.
Executive Management (Senior Management): Persons entrusted with managing the daily activities of the bank, and proposing and implementing strategic decisions.
Shari’ah Committee: a Shari’ah Committee responsible for supervising compliance with Shari’ah principles and rules and their application in the bank.
Shari’ah Compliant: Compliance with Shari’ah decisions issued by the bank’s Shari’ah Committee.
Islamic Window: That part of a conventional bank (which may be a branch or a dedicated unit of that bank) that conducts Shari’ah compliant banking, finance and investment activities.
Investment Account Holders (or IAH): Bank clients who have Shari’ah compliant investment accounts.
A Profit Sharing Investment Account (or PSIA): an account that satisfies the following conditions:
a. It is managed by a bank in accordance with Shari’ah principles and is held as being Shari’ah compliant;
b. Under a management agreement with the bank, where the Investment Account Holder (IAH) concerned and the bank agree to share any profits generated from PSIAs assets in a specified ratio and the IAH agrees to bear any loss not caused by the bank’s negligence, misconduct, fraud or breach of contract.
Mudarabah: a partnership contract between the capital provider and a partner whereby the capital provider would contribute capital to an investment that is to be managed by the partner. Profits generated by the investment are shared in accordance with the agreement specified in the contract, while losses are borne by the capital provider unless the losses are due to misconduct, negligence or breach of contracted terms.
Musharakah: a partnership contract in which the partners agree to contribute capital to an enterprise, whether existing or new. Profits generated by that enterprise are shared in accordance with the agreement specified in the Musharakah contract, while losses are shared in proportion to each partner's share of capital.
Wakalah: an agency contract where the customer (principal) appoints an institution as agent (wakil) to carry out the business on his behalf. The contract can be for a fee or without a fee.
Unrestricted PSIA: is a PSIA for which the IAHs authorize the PSIA manager to invest the IAHs’ funds in a way that the manager considers appropriate, without any restriction as to where, how or for what purpose the funds may be invested. In an unrestricted PSIA, the bank can comingle the IAHs funds with its own funds or with other funds that the bank has the right to use.
Restricted PSIA: is a PSIA where the IAHs authorize the bank to invest the IAHs’ funds, with specified restrictions as to where, how and for what purpose the funds may be invested.
Profit Equalization Reserve (or PER): The amount appropriated out of the muḍarabah profits, in order to maintain a certain level of return on investment for the muḍarib and unrestricted investment account holders.
Investment Risk Reserve (or IRR): The amount appropriated out of the profit of investment account holders, after allocating the muḍarib’s share of profit, in order to cushion against future investment losses for investment account holders.
5. Operation of Profit Sharing Investment Accounts
Banks may raise funding through Profit Sharing Investment Accounts (PSIA) using, for example, Mudarabah and Wakalah contracts. In a Mudarabah arrangement, the bank acts as the Mudarib and the fund providers as the Rabb-ul-Mal, otherwise called Investment Account Holders (IAH). In a Wakalah arrangement, the bank acts as a Wakeel for the IAH.
Mudarabah contracts entail the sharing of profits between the contracting parties using a pre-agreed profit sharing ratio. IAHs are liable to bear losses arising from the investments managed by the bank except in case of proven fraud, negligence, misconduct or breach of contract.
Being an equity-based contract, IAH are expected to bear the credit risk of any counterparty to whom the funds are invested with as well as the market risk of the assets in which the funds were invested.
Banks may also in practice use profit smoothing techniques to mitigate against withdrawal risks associated with PSIAs. Profit smoothing can include the creation of reserve accounts such as the Profit Equalization Reserve (PER) and the Investment Risk Reserve (IRR) as per the discretion of the bank.
6. Responsibilities of the Board of Directors
A bank’s Board of Directors (or the delegated committee of the Board) must ensure that it approves policies that enable a prudent management of assets and risks associated with PSIAs.
The Board (or the delegated committee of the Board) is responsible to provide effective oversight and monitoring to ensure that PSIAs are managed in the best interests of the IAHs, in line with these Rules. In particular the Board must ensure there is effective oversight of:
a. Financing and investment activities undertaken on behalf of IAHs;
b. A sound risk management framework that adequately identifies, measures, monitors and controls risks that are funded by assets funded by PSIAs
c. The fiduciary duties performed by the bank to ensure that they are in accordance with the terms and conditions of the contracts between the bank and its IAHs
d. The level of reserves (PER/IRR), to ensure that the level is appropriate and as fair as possible to existing and new IAHs; and
e. The disclosure of relevant information to IAHs on a periodic basis
7. Responsibilities of the Senior Management
A bank's Senior Management must ensure it formulates policies which approved by the Board of Directors governing PSIAs which ensure their effective and prudent management, including the following:
a. Governance requirements including setting controls, responsibilities, and delegation of authority.
b. Guidelines to ensure PSIA funds are invested in accordance with the relevant terms and conditions of the PSIA contract
c. Guidelines to safeguarding the interests and rights of the IAHs
d. The basis for allocating expenses and profits or losses to IAHs
e. Guidelines on PER and IRR management, and to whom those reserves would revert in the event of a write-off or recovery
f. Monitoring liquidity mismatches
g. Valuation and monitoring of PSIA assets
h. Dealing with any losses incurred as a result of negligence, misconduct, fraud or breach of contract on the part of the bank
i. An acknowledgement of the right of the IAHs to monitor the performance of their investments and the associated risks, and how IAHs can exercise that right
8. Prudential Requirements
Banks must follow SAMA's prudential requirements pertaining to regulatory capital for the calculation of risk weights for assets funded by PSIAs and also ensure appropriate calculation of PSIA funds in their Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) and Net Stable Funding Ratio (NSFR) as per SAMA’s liquidity requirements.
PSIA funds and any associated reserve accounts (PER and IRR) are prohibited from being included in the calculation of a bank’s regulatory capital.
Banks must ensure that they manage concentration risks arising from PSIAs in line with SAMA's Large Exposure Rules.
If the management of IAH funds is outsourced to a 3rd party, Banks must ensure that such an arrangement is in compliance with all applicable outsourcing rules and regulations issued by SAMA.
SAMA may, by way of prudential assessment, direct a bank to treat, or not to treat, an arrangement between the bank and a client (for example by way of mudarabah, musharakah or wakalah) to be a PSIA.
9. Product Awareness
A bank must ensure prospective IAH are made aware, in writing, as part of the investor agreement that:
a. The IAH bears the risk of loss to the extent of the IAHs investment; and
b. The IAH would not be able to recover that loss from the bank, except in the case of negligence, misconduct, fraud or breach of contract on the part of the bank
10. Product Governance
SAMA emphasises that banks ensure compliance with relevant regulations and instructions pertaining to new products and services when considering PSIAs.
10.1 Terms & Conditions
The terms and conditions of a contract for a PSIA must be clear, concise and easily understandable by an IAH. The contract must state the type, purpose, terms and period of the contract and the profit-sharing ratio agreed at the time of the opening of the account. A bank must ensure that the following information is included in the terms and conditions given to an IAH:
a. How the funds of the IAH will be managed and invested;
b. The PSIA’s investment objectives;
c. The basis for allocating profits and losses;
d. A summary of the policies for valuing the PSIAs assets
e. If the bank uses PER/IRR reserves as a smoothing technique, a summary of the policies for transferring funds to and from the reserve
10.2 Contract Form
The following must be stated in the contract:
a. the rights and liabilities of both parties—in particular, the circumstances where losses are to be borne by the IAH;
b. the implications on the IAH’s contractual rights with regard to the early withdrawal, early redemption or other exit;
c. the duty of the bank to disclose accurate, relevant and timely information to the IAH on the investment of funds, including its performance, investment strategies, valuation, and frequency of valuation of the PSIA’s assets;
d. how any losses incurred as a result of negligence, misconduct, fraud or breach of contract on the part of the bank will be dealt with;
e. how any subsequent changes in the profit-sharing ratio will be disclosed;
f. any smoothing techniques that the bank uses
g. whether or not zakat is paid on behalf of the IAH by the bank
11. Disclosure Requirements
11.1 Financial Statements
A bank must ensure that its financial statements contain at minimum the following disclosures with regards to PSIA:
a. an analysis of its income according to types of investments and their financing;
b. the basis for calculating and allocating profits between the bank and the IAHs;
c. the equity of the IAHs at the end of the reporting period;
d. the basis for determining any PER or IRR;
e. the changes that have occurred in any of those reserves during the reporting period;
f. to whom any remaining balances of any of those reserves is attributable in the event of liquidation of the bank
11.2 IAH Disclosures
A bank must provide each IAH of a PSIA a periodic statement (through SMS, e-mail or website) about the PSIA at intervals stated in the contract or terms of business. The interval must not be longer than 6 months
The bank must ensure that the periodic statement contains the following information as at the end of the period covered by the statement:
a. the number, description and value of investments held by the IAH;
b. the amount of cash held by the IAH;
c. details of applicable charges (including any deductions of fees that the bank is allowed to deduct from the profits of the PSIA) and the basis on which the charges are calculated;
d. the total of any dividends and other benefits received by the bank for the PSIA;
e. the total amount, and particulars, of all investments transferred into or out of the PSIA;
f. details of the performance of the IAH’s investment and the historical performance on PSIA investment returns;
g. the allocation of profit between the bank and the IAH;
h. any changes to the investment strategies that could affect the IAH's investment.
12. Separation of PSIA Types
A bank must keep its accounts for unrestricted IAHs separate from the accounts for restricted IAHs. The bank must record all its transactions in investments for those accounts separately.
13. Effective Date
These Rules shall come into force with effect from the 1st March 2023.
Regulation of Agent Banking in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
No: 37541/67 Date(g): 20/2/2019 | Date(h): 15/6/1440 Status: In-Force Section One: Definitions and General Provisions
The Regulation is issued pursuant to powers granted to SAMA under the following laws and regulations:
a. Charter of the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority, issued by Royal Decree No. 23 dated 23/05/1377H; and
b. Banking Control Law, issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/02/1386H.
Banking Agents shall comply with this Regulation in addition to relative laws, regulations, and instructions, including the following:
- Banking Control Law and its instructions;
- Anti-Money Laundering Law and its Implementing Regulations;
- Law on Terrorism Crimes and Financing and its Implementing Regulations;
- SAMA Rules on Outsourcing, and Outsourcing Controls for Foreign Banks’ Branches Operating in Saudi Arabia; and
- Rules Governing Anti-Money Laundering and Combating Terrorist Financing issued to banks, money changers, and foreign banks’ branches operating in Saudi Arabia.
Article 1: Definitions
The following terms and phrases, wherever mentioned herein, shall have the meanings assigned thereto unless the context otherwise requires:
SAMA: Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority*.
Bank: any bank licensed to carry out banking business in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in accordance with the provisions of the Banking Control Law.
Regulation: Regulation of Agent Banking.
Agent(s): a legal entity contracted by a licensed commercial Bank and approved by SAMA to engage in Agent Banking activity.
Agent Banking: the provision of banking services and/or products by an Agent on behalf of a Bank in accordance with the provisions of this Regulation.
Know Your Customer (KYC): the processes that the Agent needs to carry out in order to identify its Customers and beneficiaries and verify their identities.
Conflict of Interest: a situation involving achieving a material or moral interest that contradicts job duties.
Exclusive Agent: an Agent that entered into an agency agreement with one Bank to exclusively provide banking services and/or products on behalf of the contracting Bank.
Multiple Agent: an Agent that entered into a non-exclusive agency agreement with a Bank or into agency agreements with multiple Banks to provide banking services on its/their behalf.
Customer: any natural or legal person obtaining banking services or products or to whom such services or products are offered.
* The Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency was replaced by the name of Saudi Central Bank in accordance with The Saudi Central Bank Law No. (M/36), dated 11/04/1442H, corresponding 26/11/2020AD.
Article 2: Purpose and Scope
1. The objectives of this Regulation are as follows:
a. Increasing banking services outreach and promoting financial inclusion to the unbanked and under-banked population while maintaining the safety, soundness and stability of the banking sector;
b. Encouraging Banks to use Agents in the provision of banking services to reduce the cost of banking services and to foster financial inclusion, reach and depth;
c. Setting a regulatory and supervisory framework for Agent Banking, in compliance with which banking services are offered whilst ensuring full compliance with the Banking Control Law and the implementation of its provisions in addition to SAMA instructions;
d. Providing the minimum standards and requirements for Agent Banking to organize business;
e. Outlining the permissible activities that can be carried out by a banking Agent after receiving SAMA’s non- objection; and
f. Providing minimum standards of data and network security, consumer protection and risk management to be adhered to in the conduct of Agent Banking activity.
2. This Regulation shall apply to all Banks desiring to contract with an Agent.
Article 3: Responsibility
1. It is the responsibility of the board of directors of each Bank to ensure compliance with this Regulation. Banks shall be solely responsible for the selection of Agents. Without prejudice to the provisions hereof, the relationship between the Bank and its Agent shall be direct and governed by a contract.
2. The Bank is responsible for all actions or omissions of its Agent(s) in the matter of providing the permissible banking products and services on behalf of the Bank.
3. The board of directors of each Bank shall be responsible for approving policies, procedures and processes which ensure the following:
a. Credible Agents are identified and selected.
b. Risks associated with Agent Banking are identified, documented and addressed. Adequate risk management policies are developed and implemented, in a way consistent with relevant rules and instructions issued by SAMA.
c. Agent Banking activities are constantly monitored to ensure compliance with the provisions hereof and other relevant laws and rules.
d. All necessary controls are in place and complied with to ensure that the contracted Agent fully complies with all legal and supervisory requirements, including SAMA requirements related to AML/CFT, combating embezzlement and financial fraud, and information security.
Section Two: Applying for Agent Banking
Article 4: Application Requirements
1. Banks wishing to contract with Agents shall apply for SAMA’s no-objection pursuant to the provisions hereof. The applications submitted by Banks shall be as follows:
a. One-time application for SAMA’s non-objection to the engagement of the Bank in Agent Banking activity; and
b. Prior to contracting with each Agent, a separate application for SAMA’s non-objection to each Agent to be contracted under an “Exclusive Agent” or “Multiple Agent” arrangement for the purposes of Agent Banking and in accordance with SAMA’s requirements.
c. Applications mentioned in Clause (1.a) and Clause (1.b) of Article 4 may be submitted at the same time. However, the application mentioned in Clause (1.b) may not be submitted alone unless the Bank has previously submitted SAMA’s non-objection application referred to in Clause (1.a).
2. When submitting the application mentioned in Clause (1.a) of Article 4, Banks must also submit, along with it, the following:
a. Approval of the Bank’s board and its commitment to complying with this Regulation and what SAMA issues in this regard;
b. Bank’s internal policy on Agent Banking that covers procedures related to Agent selection, management, monitoring, operations, compliance, conduct, service quality and business supervision;
c. A copy of the Bank’s branch expansion plan;
d. Proof of the Bank’s infrastructure that supports Agent Banking, including systems and technologies to be utilized;
e. The Bank’s qualifying criteria for engaging Agents, such as the following:
- Outreach
- Efficiency
- Integrity
- Security
- Proper IT Infrastructure
f. Description of permissible services that may be provided through the Bank’s Exclusive Agent or Multiple Agent arrangement;
g. Agent Banking contract template;
h. Description of processes for customer due diligence, including KYC and compliance with AML/CFT laws and instructions;
i. Description of procedures of information security and confidentiality protection;
j. Risk assessment report, including risk management, internal control and operational policies and procedures;
k. Description of consumer protection measures, including financial awareness and education strategies related to Agent Banking;
l. Description of controls and monitoring procedures to ensure compliance with relevant laws, regulations, instructions and regulatory requirements;
m. Business Continuity Plan (BCP) and contingency arrangements to ensure continuity of Agent Banking services in the event of disruption; and
n. Any other policies, procedures and/or requirements relevant to the management of Agent Banking business as SAMA may deem appropriate.
Article 5: Application to Contract with an Agent for Agent Banking
1. The Bank may use a super-agent to manage its other banking Agents, provided that the super-agent meets all the requirements of the Fit and Proper Assessment for Agent Banking stipulated in Article 13 hereof while retaining overall responsibility for the agency relationship.
2. The Agent company shall have a commercial register that permits the engagement in Agent Banking business.
3. The Agent shall apply for and receive necessary approval from the relevant supervisory and regulatory entity before the Bank applies for SAMA’s non-objection to the Agent to be contracted.
4. The Bank may appoint its direct employees to perform or supervise Agent Banking business on the Agent premises. In the event that the Bank and its Agent agree on assigning the Agent Banking business to Agent’s employees upon Agent Banking contract, provisions of Article 19 hereof shall be observed.
5. The Bank must provide a signed declaration by its Chief Executive Officer or a duly designated senior officer, confirming that the Bank has carried out the proper and fit assessment of the proposed Agent. The declaration must also indicate that the proposed Agent has met the minimum requirements of Agent Eligibility prescribed herein and has the competence to run Agent Banking business on behalf of the contracting Bank.
6. After reviewing the complete applications in accordance with the provisions hereof, SAMA will notify the Bank of the result of the application.
Article 6: Not Commencing Agent Banking Activity
SAMA’s non-objection to contracting with an Agent shall be deemed cancelled if the approved Agent does not commence business within a nine-month period from the date of issuing SAMA’s non-objection. SAMA may, at its discretion, extend this period.
Section Three: Agent Banking Contract
Article 7: Key Requirements
a. After obtaining SAMA’s non-objection, the Bank must enter into a written contract for a specified period with the Agent for the provision, on the Bank’s behalf, of any of the banking services for which SAMA’s non-objection was issued.
b. The Agent Banking contract must clearly specify the rights and responsibilities of all parties without prejudice to this Regulation and must be signed by the relevant parties prior to the commencement of Agent Banking services by the Agent.
Article 8: Contract
At a minimum, the Agent Banking contract must incorporate provisions that address the following:
1. The appointment of a third party as the Bank’s Agent to provide a clearly defined scope of banking services.
2. Capacity and nationality of the parties and the necessity of all parties having the authority to enter into this Agent Banking contract.
3. The Agent’s personal and business details, including the Agent’s business hours and any other important information.
4. The services provided by the Agent in detail, subject to the provisions of Article 20 hereof.
5. The Agent’s responsibilities, including, at a minimum, the following:
a. Dealing with Customers in a professional way and avoiding any prohibited activities as specified herein.
b. Exercising customer due diligence when conducting transactions, including:
1. Specifying a Customer authentication mechanism for transactions executed through the Agent; and
2. Using an ICT device with a screen of proper size for Customers to review and verify the details of transactions executed.
c. Taking consumer protection measures as follows:
1. Providing proof of transactions to Customers;
2. Facilitating channeling of complaints by Customers to the contracting Bank; and
3. Disclosing mandatory information as specified in SAMA regulations, instructions, and Consumer Protection Principles.
d. Compliance with all applicable laws, instructions and internal policies of the Bank, including the Bank’s codes of ethics and conduct.
e. Exercising due care in handling the Agent Banking systems and devices.
f. Maintaining records, documents, files and proof of transactions for a period not less than 10 years. The Agent must provide the Bank with these records regularly in previously determined periods. The Bank shall then maintain these records to facilitate supervision, control and verification as specified in Article 27 hereof.
g. Fulfilling reporting requirements necessary to enable the Bank to effectively monitor the performance of the Agent on a monthly basis and reporting incidents that may materially affect the efficiency of service delivery.
h. Allowing access upon receiving notification for the contracting Bank to carry out examination or on-site inspection and investigation on the Agent’s premises, and cooperating when the Bank requires information from the Agent as stipulated in Article 29 hereof.
i. Having a description of prohibited activities that the Agent cannot practice on behalf of the Bank, as indicated in Article 20 hereof.
j. Keeping confidential the Customers’ information and not disclosing any information obtained by virtue of work.
k. Conforming to legal and regulatory requirements.
6. Mechanisms for dispute resolution and indemnities, which cover disputes between Customer and Agent, disputes arising between the Agent and the Bank, and non-compliance of the Agent that is detrimental to the Bank. Such mechanisms shall also encompass recourse to other methods of compensation, procedures and period for resolution, indemnities, and obligations of the respective parties in the event of a dispute.
7. Terms of termination or expiration of the Agent Banking contract, which may include failure to meet obligations of the contract or comply with provisions hereof.
8. Measures to mitigate risks associated with Agent Banking services.
9. Compliance with AML/CFT and KYC requirements, including providing SAMA, by the Bank, with all requested documents and periodic reports on AML/CFT.
10. A statement that all information or data that the Agent collects in relation to Agent Banking services, whether from the Customers, the Bank or other sources, is the property of the Bank and that such information must be kept confidential and no unauthorized third party will have access to Customer information. The statement shall also indicate that the aforementioned provisions shall survive termination of the Agent Banking contract.
11. Changing the contract terms for default and contract termination.
12. A transition clause on the rights and obligations of the parties upon termination or cessation of the Agent Banking contract.
13. Stating that the banking services indicated are subject to regulatory review and that SAMA must be granted full authority to inspect and request information, data and documents at any time and full access to the internal systems, reports and records of the Bank and Agent. In addition, the Agent Banking contract must include a statement indicating that SAMA has the power to interrogate the Agent’s staff.
14. SAMA power to cancel or suspend its non-objection as it deems appropriate pursuant to this Regulation.
15. Stating that the Agent will not perform management functions, make management decisions, or act or appear to act in a capacity equivalent to that of a member of management or an employee of the Bank.
16. Any other terms or provisions that the Bank or the Agent considers necessary without prejudice to the provisions of laws, regulations, rules and instructions issued by SAMA.
Article 9: Agent Eligibility
1. The Agent must be licensed to practice its commercial activity before the Bank applies for SAMA’s non-objection to the Agent to be contracted as a banking Agent.
2. The following entities are eligible for appointment as Agents under this Regulation:
a. Companies, except for commercial banks and finance companies, without prejudice to Companies Law;
b. Post offices;
c. SME businesses, such as chain stores;
d. Mobile network operator agents;
e. Foreign licensed companies registered through SAGIA; and
f. Any other entities that SAMA may prescribe.
3. The entity must not have been classified as a non-performing borrower by any banks in the last 12 months preceding the date of signing the contract (such information having been obtained from a licensed credit bureau). The Agent must maintain this status for the whole period of engaging in Agent Banking business.
4. It is necessary to have appropriate physical infrastructure and human resources to provide the Agent Banking services required.
Article 10: Renewal of Agent Banking Contract
Banks wishing to extend Agent Banking contracts must renew their contracts with Agents, whether ‘Exclusive’ or ‘Multiple’, at least one month prior to the expiration date of the banking Agent contract, following a comprehensive assessment of outsourcing risks.
Article 11: Termination of Agent Banking Contract
1. SAMA may withdraw or suspend licenses granted to Banks to engage in Agent Banking business in any of the following cases:
a. Violating any provisions hereof as may, in the opinion of SAMA or the contracting Bank, warrant termination of the agency contract; or
b. Furnishing contracting Bank(s) with false or inaccurate information under this Regulation.
2. Subject to the provisions for termination of the agency contract set out in the contract, the Bank must terminate an agency contract in any of the following cases:
a. if the Agent is guilty of a criminal offense involving fraud, dishonesty or any other forms of financial impropriety;
b. if the Agent, where it is a legal person, is being dissolved or wound up through a court order or otherwise;
c. if the Agent, where it is a sole proprietor, dies or becomes mentally incapacitated;
d. if the Agent transfers, relocates or closes its place of agency business without the prior written consent of the contracting Bank;
e. if the Agent carries on Agent Banking business when the Agent’s principal commercial activity has ceased;
f. if the Agent sustains a financial loss or damage to such a degree that, in the opinion of the Bank, makes it impossible for the Agent to gain its financial soundness within three months from the date of the loss or damage; or
g. if the Agent fails to hold or renew its valid business license.
3. Where a dispute arises between a Bank and its Agent, the parties must exert every effort to settle the dispute within a period of 10 (ten) business days from the date of such dispute. If the dispute is not resolved within this stipulated period and the litigation is sought, then the Bank must begin preparations to terminate the agency within the timeframes mentioned herein before litigation starts.
4. Where an Agent Banking contract is terminated, the Bank must publish a notice of the termination in the locality where the Agent was operating or in any other manner, such as SMS messages, to adequately inform the general public of the cessation of the Agent Banking contract.
5. Upon termination of the Agent Banking contract, the Bank may not re-contract with the Agent, whose agency contract was cancelled, after changing its commercial name.
Article 12: Record Retention
The Agent shall maintain records and documents of its contracting Bank’s Customers for a period not less than ten (10) years. The Bank shall specify the mechanism for their retention and transfer to its possession.
Article 13: Fit & Proper Assessment
1. Prior to arranging a contract with a third party for Agent Banking, the Bank must carry out a ‘fit and proper’ assessment. The assessment is aimed at ensuring that the Agent, its proprietors, and persons involved in the management of the Agent Banking business are sufficiently competent, ‘fit and proper' and that the management structures and funding sources are adequate. The key components of Fit and Proper Assessment, at a minimum, must take into consideration the following:
a. The moral, business and professional suitability of the entities to be contracted as Agents;
b. Negative information obtained from a credit bureau or other credible sources;
c. Criminal records, especially in relation to issues of ML/TF, fraud, or integrity;
d. Business or work experience;
e. Sources of funds necessary to finance the establishment of the Agent Banking business; and
f. Any other information that may negatively or positively affect the prospective Agent.
2. Any Agent, its proprietors, partners, officers or any other individuals that has/have been vetted and approved by SAMA within the previous 12 months may be exempted from vetting under this Regulation.
Article 14: Agent Due Diligence
1. The Bank must establish clear agent due diligence policies. Minimum contents must include methods of identifying Agents, initial due diligence, regular due diligence checks to be performed at specified periods, check list of early warning signals, and corrective actions to ensure proactive agent management.
2. The Bank must clearly specify roles/responsibilities of functions/departments within the Bank with regard to agent management in the agent due diligence procedures.
3. The Bank must ensure that proper monitoring processes for AML/CFT and combating embezzlement and financial fraud in the area of Agent Banking are in place. The necessary actions to be taken by Agents in this regard must be communicated to the Agents, and the Agents’ compliance must be monitored regularly.
4. Due Diligence must, at a minimum, cover the following:
a. Verification of legal status of the Agent;
b. Verification of address and location of all prospective Agents;
c. Establishing that there is no conflict of interest between the Bank and the Agent;
d. Verification of the adequacy of the prospective Agents’ resources for Agent Banking business, including financial and infrastructure resources (especially information security, technology and personnel);
e. Agent’s trustworthiness and likelihood of good behavior;
f. Clear credit history of Agent with a licensed credit bureau;
g. The Bank’ approval for the Agent’s procedures to ensure compliance with security risk management processes; and
h. Any other measures deemed necessary by the Bank.
Article 15: Customer Due Diligence
1. Each Bank engaging in Agent Banking must develop a ‘Customer Due Diligence (CDD)’ program that is tailored to its individual circumstances, type of Agents and risk level. The CDD program should include policies and procedures for the following, as a minimum:
a. Know Your Customer (KYC);
b. Information security; and
c. Data privacy and confidentiality.
2. The Bank must be responsible for ensuring compliance of its Agents with its CDD program and the CDD requirements provided herein.
3. Agents must establish the identity of their Customers as deemed appropriate by the Bank, including through ID, fingerprint, etc., and must verify the purpose and nature of making any banking activities or any banking relationship through Agents.
4. If an Agent has reasons to doubt the credibility of information provided by the Customer, it has to use all the possible reliable means to validate such information. In such cases, the Agent must stop dealing with the Customer and report findings to the Bank’s Money Laundering Reporting Officer (MLRO).
Section Four: Agent Banking Operations
Article 16: Obligations and Responsibilities of the Bank
1. The Bank must make a clear, informed and documented decision on the use of Agents for rendering banking services to its Customers.
2. The Bank must be wholly responsible and liable for all actions or omissions of its Agent(s). This responsibility must extend to actions of the Agent(s) even if not authorized in the contract so long as they relate to Agent Banking services or other matters connected therewith. Such responsibilities include the following:
a. Maintaining effective oversight of the Agent’s activities and ensuring that appropriate controls, including remote transaction monitoring to identify and report suspicious and fraudulent transactions, are incorporated into the Bank’s procedures on Agent Banking, in order to assure compliance with relevant laws, regulations and instructions.
b. Assessing the adequacy of controls of Agent Banking activities through regular audits.
c. Formulating and implementing policies and procedures to safeguard the information, communication and technology systems and data from threats.
d. Providing Agents with this Regulation, operational manuals and risk management policy documents as must be needed for rendering services to Customers efficiently.
e. Conducting risk-based review of critical Agent Banking processes to ensure that relevant laws, rules, policies and instructions are adhered to.
f. Selecting credible Agents with suitable/convenient retail outlets.
g. Managing and mitigating risks associated with the engagement of Agents to provide banking services on behalf of the Bank.
h. Providing basic financial education for Customers and Agents. Such education should cover, at a minimum, the importance of protecting the bank card PIN and not disclosing the confidential information of bank accounts to Agents and the confidential information of banking products and services provided. The Bank must periodically train its Agents as set out in Article 18 hereof.
i. Assigning one of its branches or establishing a central administration to be responsible for supervising its Agent(s) operating in a designated area and recruiting experts necessary to effectively supervise its Agent(s).
j. Enabling Agents when executing Customers’ transactions to use ICT devices that are integrated into the technological systems of the Bank. The figures of the transactions must be reflected in ‘Core Banking Solution’ (CBS) of the Bank. The Customer must get instant confirmation of the transaction through paper-based receipt (debit or credit slip), as well as SMS confirming the transaction.
k. Branding Agent banking business in such a clear manner so that the Customer can realize that the Agent is providing services on behalf of the Bank.
l. Taking steps to update and modify, where necessary, its existing risk management policies and practices to cover current or planned Agent Banking services, and to ensure the integration of Agent Banking applications with the main banking systems so as to achieve an integrated risk management approach for all banking activities. The Bank must also seek to perform regular, dependent test by an internal/external auditor or by the Bank’s concerned department to assess the Agent’s AML/CFT program.
m. Preparing and publishing an updated list of all its Agents, by type of Agent, on its website and annual reports. In addition to this, the Bank may publish a comprehensive list of Agents on flyers, corporate gifts and such other publications, as it deems appropriate.
n. Developing a written policy on conflict of interest and ensuring that this policy helps detect potential conflicts of interest. When the possibility of a conflict of interest arises between the Bank and the Agent, this should be disclosed to SAMA.
Article 17: Cash Services
If the Agent Banking contract allows for providing banking services that involve cash, the Bank shall establish, subject to prior non-objection of SAMA, an appropriate daily cash withdrawal and deposit limit for Customers.
Article 18: Training of Banking Agents’ Employees
Banks must train their Agents’ employees to enhance their competency before any Agent Banking activities are conducted. Training must continue for the whole period of the Agent Banking contract to equip Agents’ employees with any updates. At a minimum, training must encompass the following:
a. Products and services offered by the Agent on behalf of the Bank;
b. Know Your Customer (KYC) processes;
c. Protection of Customer information and complaints handling;
d. Fraud detection mechanisms, including identification of counterfeit money;
e. Procedures of anti-money laundering and counter terrorist financing (AML/CFT);
f. Equipment operation and troubleshooting;
g. Claims processing and reconciliation;
h. Obtaining the Retail Banking Professional Foundation Certificate (RBPFC);
i. Agents that handle loan or credit processing must have fulfilled the requirements set by SAMA;
j. Codes of ethics and conduct; and
k. Procedures and mechanisms of reporting fraudulent and suspicious transactions to the Bank.
Article 19: Permissible Activities
1. The Bank may contract with its Agent to provide some or all of the banking services prescribed under this Article. The services provided by the Agent must be stated in detail in its contract with the Bank and must be prominently displayed on the Agent’s business premises and on the website of the Bank, where a full list of all of the Bank’s Agents and their services can be found.
2. Banks shall be responsible for determining, based on agent risk assessment, the services a particular Agent may provide.
3. Permissible services for Agents, after the Bank obtains SAMA’s non-objection, are as follows:
a. Bank accounts opening;
b. Preparation and submission of loan applications and other related documentation;
c. Preparation and submission of applications for credit cards, domestic worker salary cards and other cards, as well as other related documentation;
d. Preparation and submission of bank letters of guarantee and other related documentation;
e. Cash deposits and withdrawals through ATMs;
f. Check deposits through ATMs;
g. Check book request and collection;
h. Payment of electronic bills, fees and fines for utility services;
i. Generation and issuance of account statements;
j. Activation of accounts after obtaining the final approval of the Bank;
k. Funds transfers, local and international;
l. Currency exchange;
m. Issuance of bank debit and credit cards and checks after obtaining the final approval of the Bank;
n. Encashment of checks;
o. Provision of Banking services for SMEs;
p. Reception and submission of POS terminals’ applications;
q. Sales and marketing services; and
r. Any other activities as may be determined from time to time by SAMA.
Article 20: Prohibited Activities
The Bank shall not permit the Agent to perform any of the following activities:
a. Operating or carrying out any transactions when there is communication failure with the Bank and operating in an offline mode or on a manual basis;
b. Carrying out a transaction where a receipt or acknowledgement cannot be generated;
c. Charging the Customer any fees that are not approved by SAMA or included in the Agent Banking contract;
d. Providing, rendering or holding itself out to be providing or rendering a banking service that is not specifically permitted in the contract;
e. Conducting non-electronic transactions outside of the business premises;
f. Soliciting personal information from Customers, including account details and Personal Identification Number (PIN) of Customers;
g. Providing any form of manual cash services unless a written official non objection letter is obtained in this regard from SAMA;
h. Carrying out any Agent Banking transactions or activities other than those approved in SAMA’s non-objection to the Agent contracted;
i. Conducting any payment system services outside of SAMA’s payment system infrastructure;
j. Accessing credit reports at a licensed credit bureau, as part of the loan application process;
k. Disclosing any information obtained by virtue of work;
l. Violating the Bank’s codes of ethics and conduct; or
m. Any other prohibited activities specified herein or as may be determined from time to time by SAMA.
Article 21: Relocation, Transfer and Closure of Agent Premises
The Bank must ensure the following:
a. that its Agent does not transfer, relocate or close its Agent Banking premises without serving a written notice of intention on the Bank at least sixty (60) business days in advance. In these cases, the Bank must apply for SAMA’s non-objection to the measure intended not less than thirty (30) business days prior to transfer, relocation or closure of Agent Banking premises. The Bank must also forward the details and reason(s) for relocation, transfer or closure of premises to SAMA.
b. that the Agent posts a notice of the relocation, transfer or closure on the Agent’s premises so as to be clearly visible to the general public at all times. Further, the Agent must advise Customers by an effective channel of its intention to relocate, transfer or close the Agent Banking business.
Article 22: Settlement of Transactions
To ensure quality of services provided for the beneficiaries and to earn their trust, the Bank must perform the following:
a. Ensure that all transactions carried out through the banking Agent are posted on a real time basis for ‘in bank’ account transactions;
b. Complete transactions that credit or debit accounts in other banks in accordance with SAMA clearing instructions;
c. Conduct a daily reconciliation to ensure settlement is done properly; and
d. Clarify responsibilities of both the Bank and the Agent towards transaction settlement risks.
Article 23: Information Technology (IT) and Operational Requirements
The technology implemented by the Bank for Agent Banking must comply with the industry standard technology in terms of hardware and software. At a minimum, the Bank must ensure that:
a. The Bank has an automatic system that is suitable for Agent Banking and that provides services stipulated in the contract with the required quality, security and speed.
b. The technology deployed comprises a set of interoperable infrastructure modules that work seamlessly and harmoniously. There must be an end- to-end connection from the Bank to the banking Agent.
c. Payment orders are instantly executed. In the event of failure of communication during a transaction, the transaction must be reversed.
d. An audit trail is maintained and made available on request.
e. All settlement information details are preserved.
f. The Bank puts in place adequate measures to mitigate all the risks that could arise from the deployment and use of its Agent Banking IT infrastructure.
g. The Agent Banking IT infrastructure must be, at a minimum, as follows:
1. Be able to support real time, electronic processing of transactions executed;
2. Be able to provide a secured network, including end-to-end encryption;
3. Be able to support Agent Banking services; and
4. At the end point, devices should not store sensitive Customer information, e.g. PIN, passwords, fingerprints, etc.
h. At a minimum, two-factor authentication is required for Agent and Customer registration.
i. Transaction information is transmitted in a secure manner.
j. There is an advanced and secure technological infrastructure.
k. A secured network, including end-to-end encryption, is provided.
Section Five: Consumer Protection
Article 24: Consumer Protection Requirements
Banks must put in place an appropriate consumer protection framework that ensures implementation of all requirements set out in the Banking Consumer Protection Principles (BCPP) and SAMA instructions to protect beneficiaries from risks involved in Agent Banking services, such as fraud, loss of privacy, loss of service, etc.
The Bank must ensure that the following requirements, at a minimum, are complied with at all times:
a. The Agent must have signs that are clearly visible to the public, indicating that it is a provider of services of the Bank with which it has an Agent Banking contract. The Agent must not represent to the public that it is a Bank.
b. The Agents must issue receipts for all transactions undertaken directly through them. Banks must provide their Agents with necessary tools that enable generation of receipts or acknowledgements for direct transactions carried out through Agents.
c. Where the Agent acts as a receiver or deliverer of documents, the Agent must provide an acknowledgement for all documents received from or delivered to the Customer. Such acknowledgement should include all relevant details.
d. Customer complaints must be resolved in accordance with SAMA requirements on customer complaints. The Bank must keep record of all customer complaints and how such complaints were redressed.
e. The Customer must be made aware of the fact that he/she must not carelessly store PIN and other critical information or share such information with other parties, including Banks and their Agents.
f. The Bank must take necessary steps to promote awareness among Customers about its Agent(s). Such awareness should cover, at a minimum, the responsibilities of the Bank and the Agent, rights of Customers, safety measures to make transactions with Agents, services that can or cannot be provided by the Agent, commissions, and fees.
g. Banks must publish and update the details of their Agents (e.g. name, address, and communication channels) on their websites, including existing Agents, terminated Agents, Agent relocations and/or transfers.
h. Protection measures of Customer information must be developed. Banks and Agents must ensure that such information is not disclosed to unauthorized third parties without prior non-objection of SAMA. Non-Compliance with this provision is considered a crime punishable by law as per the Banking Control Law.
i. A client manual of Agent Banking services must be established. The manual should address the commitment of the Bank and the Agent to security, privacy policy and confidentiality of data, reliability and quality of services, transparency of products and services, and prompt response to enquiries and complaints.
j. The Agent must adequately disclose and display other information on its business premises, which includes, but not limited to, the following:
1. Its appointment as an Agent of a Bank and the duration of the appointment;
2. The list of services, client manual, fees and charges, and daily transaction limits for Customers;
3. The dedicated single toll-free number(s) through which Customers can contact the Bank or the responsible branch; and
4. The current license for the commercial activity being undertaken by the Agent (prominently displayed on its business premises).
Section Six: Supervision of Banking Agents
Article 25: Key Inspection and Supervision Procedures
a. Banks shall be held fully liable for the actions and compliance of their Agents. In addition, Banks must, at least, have in place adequate technological systems for risk management, consumer protection, AML/CFT, and combating embezzlement and financial fraud. It is the responsibility of the Bank’s board of directors to ensure the following:
1. Bank’s policies and procedures are comprehensive and reflect all of SAMA regulatory requirements;
2. Mechanisms are established to ensure that relevant departments of the Bank implement all the necessary provisions of SAMA instructions; and
3. Monitoring of Agents’ activities matches any risks posed to the Bank.
b. Banks must take all other measures, including onsite visits undertaken by their staff or authorized persons to ensure that Agents operate strictly within the requirements of the law, guidelines and Agent Banking contract.
c. Banks must formulate internal audit policy to monitor and control their Agents and must conduct monitoring visits to the Agent’s outlets at regular intervals to ensure that the Agents are working in accordance with the terms and conditions of the contract, rules, regulations, and instructions issued by SAMA. A report of each visit must be prepared and submitted to SAMA upon its request or with the overall annual report prescribed in Article 30.
d. SAMA will monitor the Bank-Agent relationship and its compliance with laid down instructions. SAMA has the right to carry out monitoring visits at any time to any of the Agent’s outlets.
e. SAMA shall have free, full, and unfettered access to the internal systems, documents, reports, records, staff and premises of the Agent at any time as far as the Agent Banking business is concerned. SAMA shall exercise such powers as it may deem necessary.
f. Notwithstanding Banks' responsibility to monitor and supervise their Agents, as set forth in Clause (a) of Article 25, SAMA may, at any time and as it may deem necessary, perform the following:
1. Requesting information and data directly from Agents;
2. Carrying out full-scope or thematic inspection, with regard to Agent Banking, of the records and premises of the Agent;
3. Directing an Agent to take specific actions or desist from specific practices;
4. Ordering the termination of the Agent Banking contract;
5. Directing the Bank to take specific actions against the Agent;
6. Directing the Bank to take remedial actions as a result of the conduct of an Agent; and
7. Any other guidelines, procedures and/or requirements as SAMA may deem appropriate.
Article 26: Off-site Inspection
SAMA, based on reports submitted to it, will carry out off-site monitoring of banking Agents’ business to assess and monitor risks (particularly material risks) and compliance with laws, regulations and instructions that SAMA supervises their implementation.
Article 27: On-Site Inspection
1. SAMA may conduct onsite inspections, as it may deem appropriate and at any time, carried out by its staff or appointed individuals.
2. The Bank and the Agent shall submit documents requested by SAMA staff or appointed individuals in the form and at the time they determine.
Article 28: Random Inspection
SAMA may make both random and targeted visits to Agent’s premises as it may deem necessary at any time (based on a standard sampling method or on reports identifying Agents that have been the subject of multiple complaints). The visits are aimed at examining the compliance of the Agent with all requirements prescribed herein, including those related to consumer protection.
Section Seven: Agent Registration
Article 29: Agent Registry
1. SAMA will establish an electronic agent registry to which Banks are required to submit information on every Agent operating on their behalf. The agent registry must include, as a minimum, the following:
a. Start date of business relationship as set out in the contract;
b. Agent name and business name;
c. Business address;
d. Geographic coordinates of business location;
e. Contact numbers;
f. Agent’s core business and number of years in operation; and
g. Agent banking contract.
2. Banks may not engage in Agent Banking unless they have registered the required information in the agent registry. Any Banks or Agents engaging in Agent Banking without registering in the agent registry will be subject to any actions or penalties that SAMA may take or impose in this regard.
3. Banks must be responsible for keeping the registry up-to-date.
4. In case of any changes in the Agent’s information (e.g. telephone number), Banks must update data in the registry within ten (10) business days of the date of such change made by the Agent.
Article 30: Annual Reporting
The Bank shall submit an overall report on its Agent Banking business annually to its board. The Bank’s board shall, in its turn, submit to SAMA an approved report that includes, as a minimum, the following information:
a. Nature, value, volume and geographical distribution of operations or transactions;
b. Cases of money laundering and terrorism financing;
c. Incidents of fraud, theft or robbery;
d. Results of the monitoring visits carried out by the Bank; and
e. Customer complaints, their nature and number, and the remedial measures taken to address them.
Article 31: Timely and Accurate Reporting
1. Upon request, Banks shall submit timely and accurate reports to SAMA. Banks will be held liable for any false or late reporting and will be subject to actions and penalties that SAMA may take or impose.
2. Banks shall submit, and be willing to submit in the manner required, any information on the volume and value of transactions carried out for each type of services provided by each Agent, or any other information requested by SAMA at any time as it may deem necessary.
Section Nine: Violations
Article 32: Measures and Penalties
SAMA will take measures and/or impose penalties set forth in related laws against any Banks violating any provisions hereof.
Section Ten: Enforcement
Article 33: Enforcement
This Regulation enters into force as of the date of its publication on SAMA’s website.
Guide to Rules Governing Banks’ Remittance Centers
No: 381000063572 Date(g): 12/3/2017 | Date(h): 14/6/1438 Status: In-Force Based on the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/2/1386H, and the Ministerial Resolution No. 2149/3 dated 14/10/1406H regarding the Implementation Rules for Banking Control Law, and in continuation of the efforts of SAMA to support Remittance Centers by addressing the various technical, operational, and procedural challenges.
Attached is the first edition of the "Guide to Rules Governing Banks’ Remittance Centers". SAMA confirms that all banks operating in the Kingdom must adhere to the implementation of what is stated in this guide, starting from 15/10/1438H, corresponding to 9/7/2017G.
1. Introduction
Remittance services are among the most important services provided by the banking sector in the Kingdom. This service is provided through banks’ remittance centers and licensed remittance companies.
In light of the growing numbers and amounts of transfer transactions and the noticeable increase in the numbers of remittance centers and their branches in the Kingdom, they face various challenges—particularly in technical, operational and procedural aspects—in order to be able to interact professionally with developments in local and international legislations, regulations and rules related to money transfer procedures.
In order for remittance centers to be able to maintain their competitive capabilities, achieve maximum customer satisfaction and provide distinctive services, these centers need modern development strategies through a clear vision; application of a well thought-out methodology; and utilization of modern banking technologies in this field.
In an effort to advance and elevate this sector to a more developed, competitive and organized environment, SAMA has developed the Guide to Rules Governing Banks’ Remittance Centers which includes a set of objectives, regulations, and various developmental features.
Subsequently, this Guide will be developed in line with developmental and organizational changes and procedures.
1.1: Scope
The regulations of this Guide shall apply to all operations of banks’ remittance centers and licensed remittance companies. SAMA is the supervisory authority authorized to implement and take necessary measures as it deems appropriate in regard to any violations of the regulations of this Guide, including imposing penal fees and/or implementation procedures in accordance with the provisions in force under the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/02/1386H, and the implementation rules of the provisions of the Banking Control Law issued by Ministerial Resolution No. 3/2149 dated 14/10/1406H.
1.2: Purpose
By developing this Guide, SAMA aims to lay down the basic procedures and requirements to govern the work of these centers and ensure the quality of their customer services.
2. Relevant Laws, Rules and Regulations
* The Anti-Forgery Law, issued by royal decree No. (M/114), dated 26/11/1380H, has been replaced by the Penal Code for Forgery Offenses, issued by royal decree No. (M/11), dated 18/02/1435H.
3. Definitions
The following terms and phrases – wherever mentioned in this Guide – shall have the meanings assigned thereto unless the context requires otherwise:
SAMA:
Saudi Central Bank*.
Saudi Arabia Financial Investigation Unit (SAFIU):
The authority authorized to receive and analyze reports of activities suspected of being related to money laundering and terrorist financing from all financial and non-financial institutions.
Financial Action Task Force (FATF):
An inter-governmental body that sets standards and promotes effective implementation of legal, regulatory and operational measures to combat money laundering terrorism financing, proliferation financing and other threats related to the integrity of the international financial system.
Centers:
Banks’ remittance centers and licensed remittance companies.
Bank:
The bank to which the remittance center belongs.
Remittance Membership / Membership:
A register with a bank’s remittance center established by virtue of a contract called "Remittance Membership Opening Agreement" signed by the center and the membership holder (the customer) that includes all of said customer's information. This agreement constitutes rights and obligations for both parties in accordance with the relevant regulations and instructions.
* The "Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency" was replaced By the "Saudi Central Bank" in accordance with The Saudi Central Bank Law No. (M/36), dated 11/04/1442H, corresponding in 26/11/2020G.
4. Working Hours of Banks’ Remittance Centers*
- The official business days are from Sunday to Thursday.
- Saturday is an optional additional business day after obtaining SAMA's no-objection for each branch.
- Friday is an official weekly day off for all remittance centers.
- The working hours of the centers' branches will be from 9:30 a.m. to 5:30 p.m.
* This paragraph has been amended in accordance with SAMA circular No. (41/2304), Dated 09/09/1439H.
5. General Provisions
1) All instructions issued in all SAMA circulars regarding outbound and inbound remittances of all types shall be complied with, for example but not limited to: Anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing circulars.
2) Compliance and implementation of the provisions of the Rules Governing the Opening of Bank Accounts and General Operational Guidelines in Saudi Arabia (4th Update) and any previous or subsequent new updates.
3) Reject remittances for any of the countries with whom dealings are prohibited.
6. Disclosure and Transparency
1) Remittance centers must clarify the rights and responsibilities of each party and details of prices, commissions and fees charged by the center, displaying such details on a prominent place in a clear, concise and none-misleading manner.
2) Remittance centers should provide a free paper copy of the Banking Consumer Protection Principles in all branches.
7. Complaints
An appropriate, clear and effective mechanism for customer complaints must be set based on the Regulations for Complaint Handling and Establishment of Complaint Units at Banks and the Banking Consumer Protection Principles—the centers’ complaint mechanism and the period for handling complaints shall be clarified.
8. Services Provided within Remittance Centers
1) Point-of-sale terminals must be made sufficiently available to accept the Saudi Network "mada" cards at all branches of remittance centers.
2) Set up a separate queue dedicated for women in each branch in case of the absence of a ladies section.
3) The centers should verify that all electronic services meet the needs of customers and facilitate the completion of remittances according to state-of-the-art methods.
4) Emphasize on employees to perform their duties efficiently and professionally, ensuring their ability to provide the required services to customers; and provide appropriate and continuous training for employees.
5) Commit to good behavior and professionalism when providing customer service.
6) Work on raising the level of service quality within the branch, such as placing Queuing Machines.
7) Prioritize the service of people with special needs and provide appropriate tools to facilitate their entry into the branches.
9. Customer Acceptance Policies and Procedures
Customer acceptance policies and procedures include all factors relevant to a customer as the person performing a financial transaction through remittance centers; procedures to verify customer’s identity, address and business, and the amount of income and sources of funds; determining the purpose of establishing the relationship (remittances membership) between the remittance center and its customers, while not dealing with unknown or fictitious names and taking into account the full compliance with regulations and instructions issued by SAMA, AML/CFT-related instructions, ‘Know Your Customer (KYC)’ requirements, and Customer Due Diligence (CDD) procedures for customers of various types and categories; and setting classifications and prerequisites to establish relationships with customers.
9.1: Membership
Customers of remittance centers fill in their personal details in the individual membership opening form to benefit from the services provided by the center. The center then issues a membership card to the customer that contains his/her personal number which is linked to an automated system and on which his/her personal details, photo ID, and signature proving the presence of the person himself/herself and the validity of details filled in the form and the details of the beneficiary of the transfer at the center authorized by SAMA to practice this activity. The customer must present their membership number when carrying out any financial transaction in addition to the original ID card to ensure that they are the original party in the relationship and that the ID card is valid.
Membership is subject to regulatory procedures in terms of updating details and freezing, in addition to setting permissible financial limits according to customers' status, log in frequency and so on.
9.2: Membership Opening Conditions
All requirements set forth in the Rules Governing the Opening of Bank Accounts and General Operational Guidelines shall be adhered to, and membership must meet the prerequisites for verification requirements for identities and real users (the beneficiary) of such memberships, including the following:
1) The membership must be opened by the customer themselves, requiring their presence in person while taking into account cases in which the customer is required to visit to establish the relationship as provided for in the Rules Governing the Opening of Bank Accounts and General Operational Guidelines in Saudi Arabia.
2) Fill in all details and information related to ‘KYC’ principle in the Membership Opening Form and confirm its validity by signing it.
3) Provide an original copy of valid national IDs for citizens or resident ID for expatriates, to be included within the customer’s file.
4) Remittance centers shall be responsible for matching and verifying the validity of details with the original documents submitted by the customer; and placing the stamp and date on each document and storing them in the automated system.
5) It is necessary to have an identifier for women who cover their faces.
6) Minors (under the age of 18 Hijri years) will not be eligible for membership except with the approval of the guardian or curator (not an identifier).
7) Legal persons are not permitted to open remittance memberships. They are required to open a bank account through which they carry out all financial transactions.
8) An expatriate who has a temporary residence permit in the passport -granted thereto by the Kingdom's embassies under a work visa only in preparation for obtaining a resident ID - can be granted membership based on such permit (for a period of 3 months), to be frozen following expiry of that period until a valid resident ID card is issued.
9) Follow the instructions of persons with whom dealing is prohibited in accordance with the decisions of the Security Council and the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority.
10) Determine the full information of the beneficiaries of the remittance outside the Kingdom, such as the name and ID number, if available, or an account number and address.
11) Membership may not be shared by more than one person.
12) Membership may not be treated as a checking account or used for purposes inconsistent with the primary purpose for which it was opened.
13) An item that contains confirmation from customers that they are the real beneficiaries from the membership and have a direct relationship with the beneficiaries of the remittance shall be added in the membership opening form.
14) Determine the amounts and numbers of expected monthly/yearly remittances (outbound and inbound), and evaluate whether they are adequately commensurate with customers’ monthly incomes.
9.3: Updating Details
Remittance centers shall update customers’ details regarding their membership in the following cases:
1) Upon the expiry of the identity validity period or after the lapse of a maximum of 5 years, whichever is earlier.
2) When customers’ personal identification documents and details, or the nature of their financial operations, are suspected.
3) When their financial transactions do not conform with the information provided to the remittance center or when the pattern and behavior of the customer’s financial operations change.
It is also possible to benefit from the service (Yaqeen) as an the additional option for verifying the identity of customers electronically according to SAMA circular No. (371000018071) dated 12/2/1437H.
9.4: General Instructions Regarding Customers
1) Remittance centers shall identify the customer through valid identification documents in all cases in which it deals with customers.
2) The nature of customers' business and activities shall be consistent with the volume, purpose and category of the executed financial transactions, in addition to the importance of identifying the real beneficiaries of such transactions and taking necessary measures to verify customers.
3) The validity period of the resident ID/visa/temporary resident permit shall be taken into consideration when dealing with expatriates, pilgrims, Umrah performers and visitors.
4) Secure information from official certifications such as the national ID, resident ID or passport and obtain a copy of such, as well as ensuring their conformity to the original ones carried by the customer and employee upon creating the membership.
5) Reject any dealings with fictitious, digital or anonymous names.
6) Membership numbers shall be linked with names and ID numbers, and shall be considered an automatic reference to the transactions carried out when creating the relationship (creating a membership number for the customer).
7) The requirements of KYC, AML/CFT rules issued by SAMA and other relevant regulations and instructions shall be applied.
8) The relationship with the customer shall be terminated when the remittance center is unable to verify the sources of transactions or doubts the validity or adequacy of the customer’s identification details, or when the customer continues to use the remittance membership for purposes other than that for which the membership was created.
9) The customer's name and the national/resident ID number shall be entered in both Arabic and English, and shall be considered mandatory fields for opening the membership.
10) The opening of membership shall be approved by the manager of the remittance center after verifying all the customer information and their conformity with the volume and nature of his/her activities and transactions.
11) The necessary approvals shall be applied when opening remittance memberships for high-risk customers or for which enhanced heightened due diligence is required based on the FATF recommendations and AML/CFT rules.
9.5: ‘Know Your Customer’ Principle
The purpose of applying ‘KYC’ principle is to enable remittance centers to form a clearer picture by ascertaining the true identity of each customer with an appropriate degree of confidence and identifying the types of business and transactions that the customer is likely to carry out with a remittance center. Moreover, for achieving this purpose, remittance centers procedures shall include the following measures:
1) Identify and verify the identity of all permanent and temporary customers on a continuous basis.
2) Identify the identity of the real beneficiaries for all transactions carried out by customers at the level that achieves complete understanding and knowledge thereof.
3) The risk-based approach shall be applied to assess the risks associated with various types of customers and take appropriate measures to enhance the requirements for identifying and verifying the identity of customers or real beneficiaries of their transactions.
4) Take the measures that would update the requirements for identifying and verifying the identity of all customers on a continuous basis.
5) Track changes in the identity of customers and take necessary action regarding their impact on the requirements of control and supervision.
6) Make available identification records of customers/real beneficiaries to the competent officials responsible for compliance with the AML/CFT standards and relevant concerned officials.
7) Verify the identity of customers and real beneficiaries through reliable and independent sources.
9.6: Customer Due Diligence (CDD) Measures
The application of due diligence procedures entails that remittance centers monitor, and make sure that they understand, the financial transactions of customers and their real beneficiaries; and that they verify all business activities in which they engage, as well as information related to membership creation while satisfying themselves that such information is reliable and clear. The instructions require that remittance centers apply the essential due diligence procedures to all permanent and temporary customers, including real beneficiaries, and that these procedures be continuous and consistent with the degree of risks associated with the business and transactions carried out by customers as follows:
1) Track the activities of financial transactions and their consistency with the information provided by customers.
2) Due diligence procedures are required upon creating and strengthening the relationship when carrying out sporadic transactions whose value, individually or collectively, exceeds the declared limits. They are also required in the event of cases suspected to involve ML/TF, regardless of exemptions or transaction amount limits, or in case of doubts about the accuracy or adequacy of the information previously obtained when identifying customers.
3) Check whether any person is acting on behalf of the customer and ensuring the legality of such practice.
4) Determine the persons who hold ownership or control over the customer.
5) Due diligence procedures shall be strengthened for high-risk customers possibly due to the volume or types of anticipated or actual transactions, including those that involve jurisdictions classified as high risk or those mentioned on the FATF website as being jurisdictions that do not adequately implement the recommendations related to AML/CFT, or transactions that are defined by law or applicable instructions as being a high-risk source, such as correspondent banking relationships and politically exposed persons.
6) Simple due diligence procedures and measures shall not be acceptable in case of suspicion of ML/TF transactions.
7) Ability to mitigate the due diligence requirements on relationships that have been classified into low risk categories according to the risk assessment carried out by the remittance center.
8) To not permit the termination or absolute restriction of relationships with entire categories of customers aiming to avoid risk management or due to limited financial returns (profits) and without considering other risk mitigation measures for individual customers within a specific sector and dealing with risks on a case-by-case basis.
10. Outbound and Inbound Domestic and International Remittances
Domestic/international remittance activities (sending and receiving) shall be carried out through modern money transfer systems, such as SWIFT and the Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express System (SARIE), and instantaneous money transfer systems, or through contractual agreements with reliable money transfer service providers under the following conditions:
1) The execution of money transfer transactions for customers shall be accepted through membership only.
2) Domestic money remittances shall be carried out through SARIE only.
3) Money transfers (receiving) may be received for temporary customers (who are not entitled to create a membership relationship) of visitors who hold a visa/temporary residence permit as well as pilgrims and Umrah performers, provided that the amount of a single financial transaction does not exceed SAR 5,000 or its equivalent with a total not exceeding SAR 50,000 or its equivalent during one year, and that the requirements for dealing with temporary customers are fulfilled. A copy of the passport, including the page showing the entry visa, shall be obtained when carrying out permissible transactions. Other money transfer requirements, including the availability of other details such as home country address, contact number or the point of contact in Saudi Arabia and the signature, shall be taken into consideration, and the relationship of the recipient of the transfer with the transferor shall be clarified.
4) The consistency of the nature of the customer’s business and activities – whether as the owner of the membership or a temporary customer – the sources of funds and his/her annual income will be considered against the volume of his/her financial transactions and the purpose and type of the executed financial transactions.
5) Identify the real beneficiary who is in full or partial control of the membership or the financial transactions executed by customers; take necessary measures to achieve customer identification procedures; and fulfil CDD requirements.
6) Record all money transfers made by customers in the membership record of customers, provided that they include detailed information about such remittances.
7) Strengthen implementation requirements of the ‘KYC’ principle, and take necessary steps to meet heightened CDD requirements for high-risk customers.
8) Document, and record in the registers, all outbound and inbound money transfers that have been made for customers, including names of transferors and beneficiaries, and transfer amounts with their dates—such transfers shall be automatically linked to the customer’s ID number.
9) Furnish SAMA, in coordination with Banking Supervision Department, with a monthly statement that includes all money transfers that have been carried out with internal and external financial institutions (banks and money changers).
10) Take into consideration money transfer requirements set forth in the AML/CFT rules issued by SAMA.
11) Obtain complete and accurate information about the transfer originator (the customer) for outbound remittances, and shall be kept complete in the transfer message, or shall include the following:
a. Required and accurate information about the transfer originator:
- The name of the transfer originator.
- The membership number of the transfer originator when the transaction was carried out.
- The address of the transfer originator which can be left blank if it is not available and replaced with the official ID number (the national ID for citizens, the resident ID for expatriates) or the date and place of birth together.
- The purpose of the transfer shall be specified in detail, confirming full knowledge about the beneficiary.
b. Information required about the real beneficiary:
- The beneficiary's name and address in his/her home country.
- The date of birth, if available.
- The type of relationship with the beneficiary.
- The beneficiary’s account number when this account is used to carry out the transaction or, in case there was no account, use a distinct identification number for the transaction so that it could be monitored.
12) In the event of inbound remittances, and given the importance of considering common procedures followed by countries and financial institutions operating therein, complete information about the transfer originator shall be obtained and attached fully to the transfer message as provided in the abovementioned Paragraph 11.
13) In the event that a number of external wire transfers are sent from one originator within a bulk transfer to beneficiaries in another country, all information related to the originator accompanying the wire transfer with that transfer should be included for each external wire transfer, provided that the bulk transfer file (in which individual wire transfers are collated) contains the full information of the originator which can be tracked easily.
14) In the case where wire transfers are not accompanied with complete information about the originator, remittance centers operating in the Kingdom must put in place effective procedures and deal with them as follows:
- Obtain complete information from the correspondent financial institution or from the transfer service provider— this applies to all domestic and international banks.
- Reject the transaction and return the transfer if the correspondent financial institution does not respond.
- In case a transaction was suspicious and the financial institution did not respond, it is necessary to report this to SAFIU.
- Document the decisions that were taken in writing along with their reasons, and keep these documentary and electronic records for a period of ten years based on AML/CFT rules issued by SAMA.
- Inbound remittances must include the name of the financial institution, the country of origin for the transfer, the name of the correspondent financial institution and the country, and the correspondent financial institution must adhere thereof. In the event of a change in the transfer originator information, the remittance center must inform the beneficiary of such change.
15) Strengthen due diligence measures when implementing remittances related to politically exposed persons such as job holders, leadership incumbents and diplomats.
16) Reject any outbound/inbound remittances from/to Saudi Arabia for any charitable or non-profit organizations, except for bodies authorized to do so according to the Rules Governing the Opening of Bank Accounts and General Operational Guidelines in Saudi Arabia.
17) When implementing any new electronic money transfer and payments systems, it must be ensured that they have the ability to prevent and detect ML/TF operations.
18) Comply with transparency standards and ensure that money transfer messages (accompanying outbound/inbound transfers) contain full information of the originator and the beneficiary.
19) Perform continuous CDD measures towards customers sending/receiving remittances and audit the operations executed throughout the period of that relationship to ensure the completeness and conformity of operations carried out with the volume of customers activity, including the source of income, noting that the task of implementing the measures of ‘KYC’ and due diligence for the transferring person rests with the party, whether foreigner or domestic, transferring the funds.
20) In cases where technical restrictions prevent the transmission of complete information of the originator that is associated with an external wire transfer along with a local wire transfer (during the period necessary for harmonizing payment systems), the intermediate remittance center - the recipient of the transfer - must keep a record of all the information received from the financial institution that issued the transfer for a period of 10 years based on the AML/CFT rules issued by SAMA, taking into account the commitment to a period not exceeding (72 working hours) to respond to any inquiries received from the correspondent bank or concerned authorities.
21) In the event of repeated cases of lack of information, and lack of cooperation of the correspondent financial institutions (banks, money changers originating the transfer, transfer services providers); transfer centers operating in Saudi Arabia should assess the relationship with such banks, money changers, or transfer services providers, and consider restricting or terminating the relationship therewith.
22) In the case of suspicion of the transactions of, or the relationship with, a correspondent financial institution or a transfer services provider from a ML/TF perspective, such cases must be reported to SAFIU immediately and documented.
23) Remittance centers operating in Saudi Arabia contracting with money transfer services providers must obtain full information of the parties of the transfer transactions that such providers execute on their behalf.
24) Remittance centers operating in Saudi Arabia must put in place, for all their transactions, effective procedures to verify that ‘KYC’ requirements and due diligence measures are met and based on the risk rate and materiality treatment; and to tighten due diligence for funds transferred from or to countries against which FATF warnings have been issued.
25) Monitor all transactions (outbound/inbound transfers) to detect abnormal patterns in activities that do not have a clear economic or legal purpose, and examine the background and purpose of those transactions to the maximum extent possible, with the results being documented in writing.
26) When there are reasonable grounds to suspect that customers’ funds, operations and transactions represent proceeds of criminal activity or is related to or associated with ML/TF operations, they must be reported to SAFIU.
27) As for domestic transfers (inside the Kingdom) that are performed exclusively through SARIE, it is necessary to ensure that the name of the transferor and his/her account number are mentioned and that they are registered and stored in the remittance center’s system for the purpose of fast retrieval of information when requested by competent authorities. It is also necessary to verify the identity of the beneficiary from the internal (inbound) transfer in accordance with the Rules Governing the Opening of Bank Accounts and General Operational Guidelines.
28) Examine the names of individuals, entities and banks originating wire transfers and their beneficiaries against lists of individuals and entities whose assets must be stopped, rejected or frozen based on local instructions issued by supervisory authorities, as well as international lists such as the United Nations lists; and take necessary action thereof.
29) Examine the names of individuals, entities and banks that are the originators of transfers or intermediaries or beneficiaries thereof against international lists, such as those of the Security Council, the United Nations, FATF, etc.. and take necessary action accordingly.
11. Money Transfer Services Providers
The guidelines for contracting such transfer services providers must be observed, provided they include the following:
1) Transfer services providers to be contracted with is internationally recognized and licensed by supervisory authorities in the country of domicile of such providers.
2) Banks should submit a prior non-objection request from SAMA in accordance with SAMA Rules on Outsourcing for contracting with money transfer services providers, attached therewith a file that includes the final contract draft to be signed with the services provider, as well as its company brief and a certificate of compliance with AML/CFT.
3) The business of contracted money transfer services providers related to transactions executed through remittance centers operating in the kingdom should be subject to the supervision and control of the remittance center through which those transfer services providers operate.
4) Transferring money should fall under the core business of transfer services providers.
5) Transfer services providers must have in place adequate policies and measures for AML/CFT and combating embezzlement and financial fraud.
6) The contract to be concluded with the money transfer services provider shall include the following:
a. Compliance with the Kingdom's local laws and instructions, rules and circulars issued by SAMA.
b. Taking into account domestic, regional and international requirements, including compliance with international resolutions and the United Nations lists, as well as warning notices issued by international organizations, for example the warning notices issued by FATF.
c. Holding that the information they receive are subject to banking confidentiality clauses and is only used for authorized purposes.
d. Ensuring that all necessary prudential measures are applied when providing these services; and their effectiveness in the early detection of suspicious transactions.
e. The importance of adhering to the application of ‘KYC’ principle and fulfilling due diligence requirement on a continuous basis towards customers and sources and uses of transferred funds.
f. Commitment to provide SAMA with any requested information.
7- Linking the systems of money transfer services providers contracted by banks with said banks’ systems so as to reflect all transactions executed through the transfer services provider within the banks’ system.
12. Security Safety Laws and Systems
Remittance centers shall abide with the instructions provided in the Law of Private Security Services and its Implementing Regulations issued by Royal Decree No. M/24 dated 8/7/1426H; the Law of Transport of Money, Precious Metals and Negotiable Instruments issued by Royal Decree No. M/81 dated 18/10/1428H; and the Security Safety Guide issued by SAMA, No. 485/M A/36 dated 7/1/1416H, as well as any current or subsequent updates while considering the provisions of such instructions as the minimum of security and safety laws that must be adhered to.
13. Employment
Remittance centers (banks) shall comply with the instructions of SAMA, the Ministry of Labor and Social Development and other relevant supervisory and regulatory authorities regarding all laws, instructions and regulations issued for private sector employees as follows:
1) Compliance with the requirements for employment of citizens and for contracting employment services companies contained in SAMA Circular No. 341000068320 dated 3/6/1434H, and emphasizing on the commitment to the nationalization of jobs in compliance and anti-money laundering departments, remittances, cash advance and security guards pursuant with the instructions issued in this regard by His Majesty the King, as well as the instructions of concerned authorities such as the Ministry of Interior, Ministry of Labor and Social Development, and the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority.
2) Instructions for working hours and times, vacations and official holidays, including the provisions hereunder.
3) Instructions issued by the Ministry of Labor and Social Development regarding the Labor Law and employee-specific regulations.
4) Instructions issued by SAMA regarding appointment requirements for leadership positions and employment standards.
5) Providing both an administrative and functional structures that encompass all departments and jobs, including senior positions, in which departments' functions and individuals’ duties and responsibilities are specified.
6) Appointing a manager for remittance centers with subject matter and practical qualification who has experience in banking business; an appropriate degree of financial and administrative expertise; and a history of good conduct, and who has not been previously convicted of any crime violating honor or morals.
7) Providing SAMA (in coordination with Banking Supervision Department) a granular semi-annual report on the number of Saudi employees and percentage of jobs nationalization with its relevant plan.
Regulation on Branch Network
No: 43089486 Date(g): 24/5/2022 | Date(h): 23/10/1443 Status: In-Force Based on Saudi Central Bank Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/36) dated 11/04/1442 H and the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/5) dated 02/22/1386 H, and based on SAMA's supervisory and regulatory role and its keenness to promote the principle of financial inclusion, increase the access of financial services to priority areas and geographical diversification of the bank branch network, and to ensure that banks develop an integrated internal framework to regulate the opening, closing and transfer mechanism of branches, self-service centers and affiliated remittance centers.
The branch network instructions are attached and replace the Annual Branch Expansion Plan (ABEP) issued under Circular No. (351000126713) dated 11/10/1435 H.
1. Preamble
This Regulation is issued by the Saudi Central Bank (SAMA) in exercise of the powers vested upon it under its Law issued vide Royal Decree No. (M/36) on 11-04-1442H and the Banking Control Law issued by the Royal Decree No. M/5 on 22-02-1386H (11 June 1966G).
The Regulation lay down the regulatory processes for banks in planning for the opening, closure and relocation of their Branch Network.
The Regulation will become effective from the date of its issuance and supersede the existing SAMA Circular No. 351000126713 issued on 11-10-1435 H (7 August 2014 G).
2. Definitions
2.1 SAMA: The Saudi Central Bank established under the Law issued vide Royal Decree No. (M/36) on 11-04-1442H;
2.2 Regulation: The Regulation on Branch Network;
2.3 Bank: means any bank licensed to carry out banking business in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in accordance with the provisions of the Banking Control Law;
2.4 Branch Network: includes branches, service centers, and remittance centers;
2.5 Branches: means full-fledged branches providing full range of banking services as well as more efficient branch models (mini / light branches) offering basic banking services including, inter-alia, the opening of accounts, cash deposits, cash withdrawals, fund transfers, issuance and encashment of pay orders/demand drafts, etc.
2.6 Service Centers: means outlets established for providing customer facilitation, marketing and sales services, and similar other activities.
2.7 Remittance Centers: means financial service providers engaged in domestic/international remittance activities (sending and receiving money) in accordance with the SAMA Rules Governing Banks' Remittance Centers.
2.8 ATM: means automated teller machine. ATM includes Automated Teller Machines (ATMs), Cash Deposit Machines(CDMs), Interactive Teller Machines (ITMs), Kiosk and Self-Service Machines offering cash deposits and withdrawals;
2.9 Zones: Branch Network will be categorized into following zones for the purpose of this Regulation (based on the latest publicly available population data of the General Authority for Statistics):
a) Zone 1 (Large cities): to include all cities with population of 1.0 million and above;
b) Zone 2 (Medium Cities): to include all cities with population of 0.5 to 1.0 million;
c) Zone 3 (Small Cities): to include all cities with population of 0.1 to 0.5 million;
d) Zone 4 (Rural Areas): to include villages and small towns with population of less than 0.1 million.
2.10 Priority Areas: includes Zone 3 (Small Cities) and Zone 4 (Rural Areas)
2.11 Digital Modes: means channels used to execute transactions through electronic mediums or using technology enabled/virtual/online modes. These modes includes, inter-alia, the use of debit/credit/prepaid cards, internet banking, mobile banking, mobile wallets, digital payment apps, etc.;
2.12 Customer: means any natural or legal person obtaining banking services or products or to whom such services or products are offered by a bank;
2.13 Inactive License: means a license previously issued by SAMA for the opening of a branch but the concerned branch is currently inoperative due to either delay in commencement of operations or suspension of its operations for whatever reasons.
3. Objectives of the Regulation
The Regulation is aimed at achieving the following key regulatory objectives:
a) Promoting financial inclusion and increasing outreach of financial services to the priority areas;
b) Setting a regulatory and supervisory framework for the branch network;
c) Encouraging geographic diversification of the branch network;
d) Ensuring consumer protection; and
e) Facilitating banks in streamlining their branch networks.
4. Scope of Application
The Regulation will be applicable to all locally incorporated banks as well as the branches of foreign banks licensed and operating in the Kingdom. The branches of foreign banks shall comply with this Regulation only if they plan to expand beyond three branches and to the extent, the Regulation becomes relevant to them.
5. Branch Network Policy
5.1 Banks are required to prepare a Branch Network Policy for opening, closing and relocating of branches, service centers, and remittance centers. Branch Network Policy of the Bank will cover, inter-alia, the following points:
a) Bank's overall strategy to serve customers (including the elderly and disabled customers) and deploy service channels (including the digital platforms);
b) Defining market niche / target market of the Bank;
c) Bank's approach towards promoting financial inclusion and increasing outreach of financial services;
d) Key channels to be deployed for the delivery of financial services;
e) Broad parameters/criteria for opening, closing and relocating of branches, service centers, and remittance centers;
f) Plans for promoting the use of digital modes;
g) Plans for offering any other financial services through branches (e.g. bancassurance) or engaging agent banks to undertake permissible banking activities;
h) Plans for serving customers in priority areas as a part of corporate social responsibility (CSR).
5.2 The Branch Network Policy will not cover ATMs, which will continue to be dealt with separately under the existing SAMA rules/instructions.
5.3 Banks will submit the draft Branch Network Policy to their Board of Directors (or the delegated committee of the Board) for review and approval. However, the Branch Network Policy of the branches of foreign banks can be approved by the Chief Executive or a duly authorized senior executive at Head Office instead of the Board of Directors.
5.4 Banks to submit the Branch Network Policy to SAMA after its approval by their Board of Directors (or the delegated Board committee) within four months from the issuance of this Regulation along with the following information:
a) Details and annual volume of financial services offered through digital modes during each of the last three years;
b) Number of branches, service centers, and remittance centers opened, closed or relocated (Zone-wise) during each of the last three years;
c) Number of new ATMs (including portable/temporary ATMs) deployed during each of the last three years;
d) Results of any customer survey conducted and/or Mystery Shopping done to assess the customer satisfaction and quality of banking services;
e) Any other measures taken to increase the outreach of financial services and offering basic banking services to public.
5.5 SAMA will review the Branch Network Policy to grant it's no objection. While evaluating the Branch Network Policy of a Bank, SAMA will review, inter alia, the following:
a) Bank's plan for offering financial services through digital modes and timeline for their roll out;
b) Results of any customer feedback survey conducted and/or Mystery Shopping done to assess the customer satisfaction and quality of banking services; and
c) Any other measures taken to increase the outreach of financial services and offering basic banking services in priority areas.
5.6 Banks will review (and update, if required) the approved Branch Network Policy every three years (or more frequently, if so required) to ensure its consistency with the relevant regulatory processes and prevailing market dynamics. The revised Policy after review and approval by the Board of Directors or the delegated committee of the Board (in the case of branches of foreign banks, by the Chief Executive or a duly authorized senior executive at Head Office) will be submitted to SAMA within 30 calendar days of its approval.
6. Licensing of Branches
6.1 Banks are required to obtain approval for license from SAMA for a new branch, service center or remittance center (both within the Kingdom and overseas). SAMA's prior approval for opening of a branch abroad will be required before approaching the concerned host supervisor/regulatory authority for any such approval.
6.2 Banks will submit the proposal for obtaining license of a new branch, service or remittance center to SAMA as per their approved Branch Network Policy. The proposal should contain all relevant information on the proposed branch/center including name of the city, tentative location, zone of location, brief justification for choice of the city/location, and feasibility study (including projected business/financial impact).
6.3 Banks are required to use inactive licenses for branches/service centers/remittance centers before approaching SAMA for the new licenses.
6.4 SAMA's prior approval for a new branch, service or remittance center will not be required if such branch/center is being opened within the same zone by using the inactive licenses for branches/service centers/remittance centers. Furthermore, SAMA's prior approval will also not be required if a new branch, service or remittance center is being opened in any of the smaller zones by using the inactive license of a branch/service center/remittance center of a larger zone. However, in such cases, banks will approach SAMA at-least two months in advance for amendment of the inactive license for opening the proposed branch or center at the new location.
6.5 Banks will not be required to submit Annual Branch Expansion Plan (ABEP) to SAMA once their Branch Network Policy is approved.
6.6 Banks are expected to play their role in increasing outreach of financial services to the priority areas as a part of their corporate social responsibility.
7. Opening of Branches
7.1 After receiving approval for a new branch license from SAMA, banks shall finalize the branch location, seek necessary approvals from the concerned government authorities, construct the branch and make all other arrangements to open the branch.
7.2 Once a branch is ready to commence operations, banks shall obtain a formal license from SAMA for opening of the approved branch. The request for obtaining such a license will contain all relevant information about the readiness of the bank to open the branch and will be submitted only after all necessary arrangements (as detailed in Point 7.3 below) for opening of the branch are in place.
7.3 All applications for obtaining a license for opening new branches shall be submitted along with relevant information including, inter alia:
a) The exact location of the branch;
b) The safety and security arrangements for the branch and the customers (including arrangements for the elderly and disabled customers);
c) The status of IT infrastructure/connectivity;
d) The proposed staffing arrangements;
e) The status of approvals from relevant government authorities;
f) Certificate of compliance with the municipality regulations, etc.;
g) A certificate from the internal audit department of the bank confirming that the new branch complies with all relevant requirements of the government authorities and SAMA.
7.4 Once SAMA issues a formal license for opening a branch, the bank will take all necessary measures to make the branch operational within six months of the date of issuance of the license and ensure compliance of all conditions of the branch license.
7.5 Banks shall inform SAMA in writing within 14 calendar days of commencement of operations by a new branch.
8. Closure of Branches
8.1 Banks will seek prior approval of SAMA for the closure or relocation of a branch or service center. Furthermore, in case of any forced closure/relocation of a branch, service or remittance center due to circumstances beyond their control, banks will notify all such cases to SAMA along with the reasons thereof.
8.2 Banks will have the flexibility to plan for closure or relocation of branches and service centers or convert a branch to a service center in Zone 1 and 2. However, any such request for closure or relocation will be allowed by SAMA subject to the condition that the bank has taken necessary measures to promote the use of digital modes.
8.3 Closure of branches or service centers in Zones 3 and 4 (priority areas) will not be allowed but their relocation within the same city/governorate will be permissible.
8.4 Banks will be allowed to merge two nearby branches in case of merger of two banks or in other justifiable cases subject to the condition that there remains a branch of the same bank within the distance of 10 kilometers.
8.5 Banks will not terminate the services of any employee merely due to the closure or relocation of a branch or service center.
8.6 Banks will be free to close and/or relocate remittance centers as per their approved Branch Network Policy. However, they will be required to notify SAMA at-least 30 calendar days before any such closure or relocation of a remittance center.
9. Communication to Customers
9.1 Banks will be required to inform customers through SMS and Email at-least two months before closure or relocation of any branch, service center or remittance center.
9.2 Banks will place a notification on the bank's website as well as on the branch site/entrance with contact numbers for seeking further information;
9.3 The communication from bank shall guide the customers about alternate options for them for availing the banking services. This will, inter alia, include information about the nearest branch of the bank, service center or other available channels.
10. Submission of Returns
Banks will submit the following returns to SAMA on quarterly basis within 30 calendar days of the end of each calendar quarter:
10.1 Data on opening, closing and relocation of branches, service and remittance centers (as per format attached as Annexure-I).
10.2 Data on delivery channels used to serve the customers (as per format attached as Annexure-ll).
10.3 Data on customers served in-person/physically in branches/centers, ATMs and Agent banks (as per format attached as Annexure-lll).
Annexure-I
Name of the Bank: --------------------------
Data on opening, closing and relocation of branches, service and remittance centers for the quarter ended-------------
Data of Branches Sr. No. Zones Branches Opened during Quarter Branches closed during Quarter Branches relocated during Quarter Total active Branches at Quarter end Total inactive Branch licenses 1 Zone 1 2 Zone 2 3 Zone 3 4 Zone 4 5 Outside KSA 6 Total Data of Service Centers Sr. No. Zones Centers Opened during Quarter Centers closed during Quarter Centers relocated during Quarter Total active Service
Centers at Quarter endTotal inactive Service
Center licenses1 Zone 1 2 Zone 2 3 Zone 3 4 Zone 4 5 Outside KSA 6 Total Data of Remittance Centers Sr. No. Zones Centers Opened during Quarter Centers closed during Quarter Centers relocated during Quarter Total active Remittance Centers at Quarter end Total inactive Remittance
Center licenses1 Zone 1 2 Zone 2 3 Zone 3 4 Zone 4 5 Outside KSA 6 Total Annexure-II
Name of the Bank: ---------------------------
Data on delivery channels used to serve customers, for quarter ended----------------
Sr. No. Zones Total No. of active customers of the Bank at beginning of the Quarter Total No. of customers served during the Quarter No. of Customers served in person/physically in branch/service center during
QuarterNo. of Customers served through digital modes during the quarter No. of
Customers served through self-service machines during the quarterNumber of
Customers served through any other mode during the quarter1 Zone 1 2 Zone 2 3 Zone 3 4 Zone 4 5 Outside KSA 6 Total Note: In the last column, provide the number of customers served through any mode other than in-person/physically served, digital modes or through self-service machines).Annexure-III
Name of the Bank: ---------------------------
Data on customers served in-person/physically in branches/centers/ ATMs/Agents for the quarter ended------------
Sr. No. Buckets of Customers (Average No. of customers served per day, during the quarter No. of Branches No. of Service Centers No. of Remittance centers No. of self-service machines No. of ATMs No. of branches of agent banks Total 1 0-10 2 11-20 3 21-30 4 31-50 5 51-70 6 71-100 7 101-200 8 201-300 9 301-400 10 401-500 11 Above 500 12 Total Governing Rules for Electronic Issuance and Authenticity Verification of Banking Documents
No: 43049648 Date(g): 5/1/2022 | Date(h): 2/6/1443 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Further to SAMA's instructions issued under Circular No. (41071604) dated 28/12/1441 H, which aim to encourage banks in providing the service of issuing banking documents and verifying their authenticity electronically, and as a continuation of SAMA's efforts to develop the financial sector and align with the latest digital technologies to facilitate banking transactions.
Enclosed are the regulations for the issuance and electronic verification of banking documents, aimed at enhancing the electronic services provided to banking sector customers and ensuring the reliability of electronically issued documents according to best practices.
For your information and adherence to these regulations starting from April 1, 2022G.
Chapter One: Introduction and Definitions
First/Introduction
These regulations aim to enhance the electronic services provided to banking sector customers, improving their quality and effectiveness according to best practices. They are designed to facilitate financial transactions by saving time and effort in obtaining banking documents and certificates, and to ensure the reliability of electronically issued documents.
Second/Definitions
The following terms -wherever they appear in these regulations- shall have the meanings specified next to each, unless the context requires otherwise:
Central Bank: Saudi Central Bank (SAMA)
Regulations: Regulations for the issuance and electronic verification of banking documents.
Bank: Banks licensed to conduct banking activities in accordance with the provisions of the Banking Control Law.
Banking Documents: Documents or certificates issued by banks at the customer's request for various purposes. Chapter Two: Issuance and Verification
First/Issuance of Banking Documents
1. The bank should utilize technological systems to process all customer requests for the issuance of banking documents.
2. The bank must provide the option to issue banking documents electronically in Arabic, and in English if requested by the customer.
3. The bank’s mechanism for providing electronic issuance of banking documents should ensure the following: 3.1 Compliance with technical requirements and regulations outlined in relevant systems and instructions, including but not limited to: the Personal Data Protection Law, the Electronic Transactions Law, the Cyber Security Framework, the Business Continuity management Framework, and any directives issued by SAMA or relevant authorities.
3.2 Inclusion in the banking documents of assurances regarding the protection and confidentiality of the information contained, and the responsibility of the bearer to maintain it.
3.3 Ensuring that the banking document meets the internal policies of each bank regarding its official status, such as stamps, signatures, and any measures that ensure the electronic document is considered equivalent to a paper document.
4. The bank should use clear and descriptive titles for banking documents that reflect their actual purpose.
5. The bank must include the date of issuance in all banking documents. Second/Electronic Verification of the Accuracy of Banking Documents
- The bank must provide an electronic verification service for all banking documents issued by it, whether (electronically or in paper form).
- The bank must include a clear explanation in the issued banking documents on how to perform the electronic verification.
- The bank must provide an electronic verification service for all banking documents issued by it, whether (electronically or in paper form).
Chapter Three: Banking Documents
8. The documents listed in this chapter represent the minimum required for issuance by the bank. The purpose indicated for each document should be considered in case of differences in their titles, as follows:
Document
Description
Bank Certificate: A document that confirms the existing relationship between the bank and the customer, including the account number, the date of account opening, and the total balance as requested by the customer.
Debt Confirmation: A document that details an outstanding debt of the customer to the bank, including the amount and the remaining debt.
Account Statement: A statement showing the account balance and transactions conducted during a period specified by the customer.
Clearance Certificate: A document in which the bank acknowledges that there are no outstanding financial obligations of the customer to the bank.
International Bank Account Number (IBAN) Certificate: A document confirming the client's International Bank Account Number (IBAN). Chapter Four: Final Provisions
- These guidelines do not invalidate the provisions outlined in related instructions and any subsequent updates.
- The bank must adhere to issuing banking documents within the timeframes specified by the relevant SAMA's instructions, and must inform the customer of the time required to issue the banking document upon request.
- The bank must implement procedures and measures to ensure compliance with these guidelines.
- The bank must educate customers on the process for issuing banking documents and verifying their authenticity electronically.
- The bank must periodically review the banking documents most frequently requested by customers to prioritize the provision of electronic issuance services for these documents.
- These guidelines do not invalidate the provisions outlined in related instructions and any subsequent updates.
Saudi Arabian Benchmark (SAIBOR/SAIBID)
No: 430418800000 Date(g): 13/12/2021 | Date(h): 9/5/1443 Status: In-Force Further to SAMA Circular No. 67/30986 dated 17/05/1440H concerning the Interbank Offered Rate (SAIBOR).
we would like to inform you that, based on the Saudi Central Bank Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/36 dated 11/04/1442H, and the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/02/1386H. And in line with international principles, recommendations, and best practices, and to maintain the quality and integrity of the Benchmark Rate. The instructions in the aforementioned circular have been updated to include improvements to the calculation mechanism for SAIBOR and SAIBID. Banks are required to:
- Adopt the updated mechanism and attached instructions for calculating the Benchmark Rate.
- Compliance with the updated code of conduct agreed upon between the entity responsible for calculating the Benchmark Rate and the banks contributing to its calculation.
- Carry out all necessary regulatory and contractual arrangements and treatments, including those related to existing contracts and financial, legal, regulatory, tax, and accounting matters, to implement the updated definitions and mechanism for calculating the Benchmark Rate.
- Review and update contract and agreement models as necessary to incorporate more flexible terms and provisions.
SAMA emphasizes that this circular does not exempt banks from the responsibility of conducting a regulatory and legal review, and taking necessary measures to address the status of relevant contracts and agreements. It is also the responsibility of the concerned bank to handle any failure to achieve the necessary treatments or settlements concerning these contracts and agreements.
The updated Benchmark Rate Instructions (SAIBOR/SAIBID) are attached, to replace the previous instructions issued under the aforementioned circular.
For your information and action accordingly as of 26 December2021G, noting that the transition process will take place gradually in accordance with the directions of SAMA.
1. Introduction
To maintain the quality and soundness of the Saudi Arabian Benchmark "SAIBOR/SAIBID", banks were instructed in 2017 to form a SAIBOR technical working group (TWG) under the supervision of SAMA. The TWG includes representatives from Saudi Banks, the benchmark administrator and the Saudi Central Bank. The members were tasked to review the integrity and robustness of the current Saudi Arabian Interbank Offered Rate (SAIBOR) and identify areas for enhancement.
The enhancements to SAIBOR/SAIBID below are compatible with International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) principles for financial benchmarks. These enhancements were the results of the TWG assessment of the existing methodology and the results of the contributor banks surveys, feedback from a public market consultation performed by the benchmark administrator on the key changes being made to the methodology and the results of the benchmark administrator testing phase to demonstrate how the enhanced methodology would perform as compared to existing SAIBOR.
The enhancement issued by SAMA in exercise of the authority vested under the Saudi Central Bank Law issued via Royal Decree No. M/36 dated 11/04/1442H, and the Banking Control Law issued 22/02/1386H.
These requirements supersedes the previous requirements provided in Circular No. 30986/67 issued in 17/05/1440H.
2. Definition of SAIBOR/SAIBID
SAIBOR - The Saudi Arabian Interbank Offered Rate ("SAIBOR") benchmark is an indicative offer rate at which contributor panel banks would be able to borrow unsecured interbank funds in Saudi Riyals, anchored in transactions where possible together with a historical spread adjustment. A waterfall methodology is applied to enable a rate to be published in a wide range of market circumstances.
SAIBID - SAIBID is a benchmark representing the realized cost of contributor panel banks' wholesale unsecured funding in Saudi Riyals, anchored in transactions where possible. A waterfall methodology is applied to enable a rate to be published in a wide range of market circumstances.
3. Bank Calculation Methodology
3.1 SAIBOR and SAIBID will be based on contributor bank submissions, determined using a standardized waterfall methodology, as summarized below.
SAIBID Submission SAIBOR Submission Level 1
Where a SAIBOR contributor bank has sufficient eligible transactionsVolume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) only VWAP plus Spread Percentage Level 2
Where a SAIBOR contributor bank has insufficient eligible transactions to make a Level 1 submissionVWAP (including credit spread adjustment) VWAP (including credit spread adjustment) plus Spread Percentage Level 3
The SAIBOR contributor banks may only provide a Level 3 submission if there are insufficient eligible transactions to make a submission at Level 1 or Level 2. If there are transactions that would be eligible for Level 1 or Level 2, except that they took place prior to a move in policy rates, then the process described below under SAMA Policy Rate Moves shall be followed for the purpose of Level 3.Subject to process described SAMA Policy Rate Moves below, expert judgment will estimate the VWAP that would have been calculated had unsecured eligible transactions occurred in the last business day. Subject to process described in SAMA Policy Rate Moves below, expert judgment will estimate the VWAP that would have been calculated had unsecured eligible transactions occurred in the last business day and will include the Spread Percentage
3.2
The key terms set out in the above table and subsequently in this document will be defined as following:
■ Spread Percentage: As of the date of this Circular, the Spread Percentage is 16 per cent and represents the difference between SAIBOR and SAIBID across all relevant tenors for the most recent five years of publicly available data. The Spread Percentage will be applied to each submission in order to create the SAIBOR submission. The appropriateness of the level of Spread Percentage will be reviewed regularly on at least an annual basis and more frequently if required by market conditions. Under the review process, the benchmark administrator will consult with the panel of contributing banks and will amend the Spread Percentage subject to approval by SAMA.
■ Spread Cap: the Spread Percentage may be subject to a cap to be introduced and specified at the discretion of SAMA should market conditions require it. Following any such introduction of a Spread Cap, it shall be reviewed regularly on at least an annual basis and more frequently if required by market conditions. Under the review process, the benchmark administrator will consult with the contributing banks and will introduce or amend (as relevant) the Spread Cap subject to approval by SAMA.
■ Credit Spread Adjustment (Level 2): Saudi Riyal repo transactions used in Level 2 may be collateralized with any type of Saudi Riyal fixed income security. Such a secured transaction will typically be priced at a lower rate than an equivalent unsecured transaction. In order to maintain consistency with Level 1 submissions and the objective of SAIBOR, a contributor bank will use expert judgment to include a suitable credit premium in the VWAP created from the secured repo transaction(s) before making the Level 2 submission. Expert judgment may not be used for any other purpose for a Level 2 submission and is subject to the submission procedures and recording keeping requirements described under "Expert Judgment" below. The credit premium should reflect the nature and credit quality of the collateral used in the repo transaction(s) and result in a submission rate that is equivalent to an unsecured transaction rate.
■ Business Day: A "business day" for the purposes of a SAIBOR submission is defined as the 24 hour period from the start of the submission window on the previous business day until the start of the submission window on the current day of the submission.
■ Expert Judgment:
- Where expert judgment is used, the panel banks have the flexibility to determine its own expert judgment approach.
- Expert judgment approach must be properly documented in the SAIBOR internal submission procedures developed by each SAIBOR contributor bank. These submission procedures are subject to appropriate internal governance processes1. Each contributor bank will notify SAMA and the benchmark administrator of its submission procedures by no later than 31 December 2021 and at least annually thereafter. In addition, each contributor bank will notify SAMA and the benchmark administrator following any significant change to its submission procedures. In each case, notice will be provided by a contributor bank by submitting a copy of its submission procedures to SAMA and the benchmark administrator2. When submitting such submission procedures to SAMA and the benchmark administrator each contributor bank shall include a statement stating that the version of the submission procedures provided has been approved by its Board or its Board delegated authority.
- The SAIBOR internal submission procedures and records detailing the factors and judgment used in each daily submission must be available at all times to be shared with SAMA and/or the administrator upon request.
3.3 Contributor banks are required to implement a process whereby the Head of Asset and Liability Management (ALM) or similar position in the bank (without any role in proprietary trading) takes the responsibility for submission of the SAIBOR/SAIBID rates on a daily basis to the benchmark administrator independently without any influence from the bank's Treasurer or the Deputy Treasurer. Banks are required to obtain SAMA's approval for individuals in these roles as per SAMA circulated requirements for Appointments to Senior Positions in Financial Institutions Supervised by the Saudi Central Bank using SAMA standard fit and proper application.
3.4 Contributor banks must develop and implement reasonable submission procedures based on the applicable SAIBOR/SAIBID methodologies. The overall submission procedures should at a minimum include the following:
■ Eligible transaction and other data inputs in calculating submissions
■ Record the level of the waterfall used to calculate the submission;
■ Procedures to detect and evaluate the bona-fide nature of such transactions and inputs;
■ Policies guiding and detailing the use of expert judgment, including documentation;
■ Maintaining reports, records and underlying documentation supporting submissions;
■ Procedures for pre-submission validation of eligible inputs and procedures for review by senior staff to check inputs before submission.
3.5 The submission procedures should be approved by the Board or Board delegated authority and should be consistently applied. Each contributor bank should ensure that its Internal Audit Department undertakes an annual review of the process and of the methodologies and report to the relevant contributor bank's Senior Management, Audit Committee and the Board on the compliance with the established policies and procedures.
1 For the avoidance of doubt, each contributor bank's submission procedures shall property document its SAIBOR and SAIBID submission procedures in respect of the SAIBOR and SAIBID contributions to the benchmark administrator as detailed further in paragraph 2.4 below, including (but not limited to) eligible transaction and other data inputs in calculating submissions for Level 1, 2, and 3 submissions and policies guiding and detailing its expert judgment approach.
2 Copies of each contributor bank's submission procedures should be provided to: (1) SAMA at the following email address: BankingDataSection@SAMA.GOV.SA; and (2) the benchmark administrator at the following email address: FRCompliance@lseg.com.4. Minimum Eligible Transaction Size
A minimum size for each individual eligible transaction of SAR 10mm for the O/N, 1 week, 1 month and 3 month SAIBOR tenors. For 6 month and 12 month SAIBOR tenors, there is no minimum size for individual transactions to be eligible but the aggregate transaction size (that is, the combined size of all transactions used in the VWAP calculation for Level 1 or Level 2) must be equal to or greater than SAR 50mm in order for the VWAP to qualify for a SAIBOR submission.
5. Transaction Tenor Criteria
Benchmark submissions are currently computed for 6 tenors
Tenor Permitted maturity range Overnight 1 business day, and must be an overnight transaction 1 week 5 business days 1 month From 25 to 35 calendar days inclusive 3 month From 80 to 100 calendar days inclusive 6 month From 150 to 210 calendar days inclusive 12 month From 330 to 390 calendar days inclusive The qualifying ranges can be progressively tightened as the market deepens.
6. Transaction Window and Publication
SAIBOR will be published at 12:00pm KSA time. The transaction window for data collection will be as of 11:00am of the previous business day up and until 11:00am of the current business day. Subsequently, contributor banks will be able to submit their contributions to the benchmark administrator from 11:00am up until 11:50am.
7. Final Calculations and Averaging
Under the enhanced methodology, the following Minimum Contribution Criteria shall apply.
Contributions Received Number of High
Contributions
TrimmedNumber of Low
Contributions
Trimmed5 or more 2 2 4 or fewer N/A N/A
■
Where 5 or more contributions are received, the contributions will be applied with a trimming methodology where the 2 highest and lowest contributions, per tenor, are excluded from the calculation, once the trimming methodology has been applied, the SAIBOR rates will be calculated as an average of the remaining rate and published to 5 decimal places.
■ If fewer than 5 contributions are received by the time that SAIBOR is due to be published, the fallback arrangement described below will apply.
Fallback Arrangement
■ If the minimum 5 contributions are not received by 11:50am KSA time, a fallback arrangement is triggered. Triggering the fallback arrangement extends the contribution window by 30 minutes from 12:00pm to 12:30pm KSA time to accept additional contributions from contributor banks who have not contributed.
■ If the minimum contributions are reached by 12:30pm KSA time, the benchmark will be released. If not, the previous day's SAIBOR value will be republished together with a flag indicating a republication.
8. Contributor Banks Standards for Submission and Data Keeping
Banks expected to:
■ Submit SAIBOR/ SAIBID will reflect the true price of unsecured wholesale liquidity in the KSA Market.3
■ Maintain records and evidence to substantiate the rates submitted to the benchmark administrator.
■ In case of significant perceived credit deterioration of a SAIBOR and SAIBID contributing bank, Saudi Central Bank and the benchmark administrator will review the eligibility of the bank concerned.
3 Wholesale liquidity is defined as unsecured SAR funding from all sources for the banks with maturities of less than one year excluding retail deposits less than SAR 10million and equity.
9. Reporting to SAMA
Contributor banks are required to provide a monthly report on their interbank transactions using the SAMA SAIBOR/SAIBID monthly return (attached) within five (5) working days after the end of each month to BankingDataSection@SAMA.GOV.SA.
Annex 1: Eligibility Detailed Criteria
Waterfall Level Eligible Transaction Types Eligible Counterparty Minimum Transaction Size Minimum No. of Transactions Level 1 ■ Unsecured wholesale Saudi Riyal deposits received or raised by the SAIBOR contributor bank from an eligible counterparty.
■ Domestic primary and secondary market transactions by a SAIBOR contributor bank where it raises funds via unsecured certificates of deposit (CDs) and commercial paper (CPs) where such instruments are:- Denominated in Saudi Riyals;
- The transactions take place in the domestic KSA market; and
- Issued by the relevant SAIBOR contributor bank itself.
Exclusions:- Structured deposits- Internal transactions such as transactions with a subsidiary (including a subsidiary that is a fund and including transactions between contributor bank branches and its head office).- Unsecured deposits made by SAMA unless expressly advised otherwise by SAMA and where transacted at market prices.- Transactions which have been Entered into outside of the applicable lookback period. See Lookback Period below.- Transactions that occurs before a move in the repo or reverse repo policy rates by SAMA. See SAMA Policy Rate Moves below.
■ Banks■ AH central banks4■ Government Related Entities (GREs)■ Non-bank Financial Institutions■ Corporates and all retail segments (that meet the required minimum threshold amount)■ O/N, 1 week, 1 month and 3 month SAIBOR tenors - minimum size for individual transactions of SAR 10mm■ 6 month and 12 month SAIBOR tenors:■ no minimum size for individual transactions.■ -aggregate transaction size of all transactions used in the VWAP calculation must be equal to or greater than SAR 50mm.■ Transactions with a minimum of 2 different counterparties, provided if only one eligible transaction has taken place following a move in policy rates by SAMA during the Lookback Period, that single transaction shall be used to make a Level 1 submission.Level 2 ■ Saudi Riyal repo transactions (excluding those with SAMA) which have the economic effect of the contributing bank being the receiver (i.e. borrower) of Saudi Riyals. All types of Saudi Riyal fixed income securities are permitted collateral for an eligible repo transaction.Exclusions:- Internal transactions such as with a subsidiary (including a subsidiary that is a fund and including transactions between contributor banks between contributor banks branches and its head office).- Repo transactions with SAMA.- Transactions that occurs before a move in the repo or reverse repo policy rates by SAMA. See SAMA Policy Rate Moves below.As per Level 1 As per Level 1 A Level 2 submission may be made using a single eligible repo transaction. Level 3 Subject to the "Sama Policy Rate Moves", acceptable Level 3 inputs that may be used to form the expert judgment used to determine a Level 3 submission are5:■ Transactions that are outside the specified tenor buckets;■ Interpolation/extrapolation (from transactions in the markets underlying Level 1 and Level 2);■ Other market instruments: interest rate swaps, money market operation rates, forward rate agreement/single period swaps, overnight-indexed swaps, SAMA bills;■ Macro-economic factors (monetary policy change, policy rate change in major economies & significant economic data);■ Credit standing i.e. a published and verifiable change in the credit standing of the bank; and■ Other factors: those that can be evidenced and verified, as agreed with a contributor panel bank's internal compliance and risk.The key terms set out in the above table be defined as following:
■ Lookback Period: When identifying eligible transactions for Level 1 or Level 2, a SAIBOR contributor bank must first use transactions executed during the last business day. If there are insufficient eligible transactions in the last business day, the SAIBOR contributor bank may extend the period to the last two business days. This process may be repeated, extending the period by one business day at a time, until either sufficient eligible transactions have been obtained or until a maximum of five business days has been reached.
For the avoidance of doubt, the process of looking back by one extra day at a time (up to a maximum of 5 business days and subject to any moves in policy rates by SAMA) must be completed for Level 1 before the contributor bank moves to Level 2. If sufficient eligible transactions are found in the Lookback Period for Level 1, these will be used to create a submission even if more recent transactions exist that would be eligible for Level 2.
Banks are allowed to use Level 3 inputs without any restriction on maximum number of business days.
■ SAMA Policy Rate Moves: No transaction that occurs before a move in the repo or reverse repo policy rates by SAMA will be an eligible transaction for Level 1 or Level 2. This also applies intraday: any transaction that occurs before a policy rate during a business day will not be an eligible transaction. The following process shall apply following a policy rate move by SAMA:
1. Eligible transactions that take place after the policy rate move will be used to make a Level 1 submission. If there are insufficient eligible transactions (see Level 1 eligibility criteria above) following such a move during the maximum five day look back period, Level 2 will be used.
2. Eligible transactions that take place after the policy rate move will be used to make a Level 2 submission. If there are insufficient eligible transactions (see Level 2 eligibility criteria above) following such a move during the maximum five day look back period, Level 3 will be used.
3. Where Level 3 is used following a policy rate move by SAMA, both Level 1 eligible transactions and also Level 1 transactions that would have been eligible except for the fact that they took place before the move in policy rates by SAMA will be used, when exercising expert judgment, to create a VWAP, subject to the process described under Lookback Period above. The VWAP will then be adjusted by the SAIBOR contributor bank to adjust for the effect of the move in policy rates. Such adjustment will be in accordance with the contributor bank's documented internal submission procedures. Submissions for SAIBOR will include the Spread Percentage adjustment to the final VWAP and submissions for SAIBID will exclude the Spread Percentage adjustment to the final VWAP.
4. Where Level 3 is used following a policy rate move by SAMA and there are insufficient Level 1 eligible transactions (see Level 1 eligibility criteria above) to create a submission even when including Level 1 transactions that took place before the move in policy rates, then both Level 2 eligible transactions and also Level 2 transactions that would have been eligible except for the fact that they took place before the move in policy rates by SAMA will be used to create a VWAP, subject to the process described under Lookback Period above and including the adjustment for the credit premium detailed above under "Credit Spread Adjustment (Level 2)". For the purposes of exercising expert judgment, the VWAP will then be adjusted by the SAIBOR contributor bank to adjust for the effect of the move in policy rates. Such adjustment will be in accordance with the contributor bank's documented internal submission procedures. Submissions for SAIBOR will include the Spread Percentage adjustment to the final VWAP and submissions for SAIBID will exclude the Spread Percentage adjustment to the final VWAP.
5. If there are insufficient transactions for both Level 1 and Level 2 including transactions that took place prior to a policy move by SAMA, expert judgment alone will be used by a SAIBOR contributor bank to make a submission.
6. Where a VWAP is adjusted at Level 3 as described above, the size of the adjustment should not exceed the size of the move in policy rates by SAMA except where the SAIBOR contributor bank has strong reasons to believe that a larger adjustment is required to ensure that the submission is representative of current market conditions. In all cases where expert judgment is used including such VWAP adjustments, a contributor bank must record all the factors used in determining the submission it makes as detailed under "Expert Judgment" above.
4 Including SAMA deposits but only where transacted at market prices and are specified for inclusion by SAMA
5 Level 3 should represent the Bid-side of the market but SAIBOR submissions determined using Level 3 should include the Spread Percentage (see table in Section 2.2)SAMA SAIBOR/SAIBID Monthly Return
Instruction guidelines
How to report the data
Scope of consolidation
The information is asked at the solo domestic level of each bank.
Reference date
The reference date should be 30/31 of each month.
Completeness of the analysis
Please provide your responses on the relevant cells in the excel file without modifying the format of the templates.
Quantitative information
The quantitative responses should be amounts in SAR '000. The Bank's input for SAIBOR/SAIBID rate each day should be included in all tabs 'SAIBOR', 'SAIBID' and 'Other info’
Qualitative information
Please provide specific responses to the qualitative questions at a sufficient level of detail to achieve the objectives of the return.
Sample data
We have taken a sample example to demostrate how the return should be filled.
Contact persons
Kindly refer to SAMA's SAIBOR/SAIBID circular for report submission details which can be found under "Reporting to SAMA"
Deadline for submission
5 working days
Name of the Bank Reporting period
SAR Interbank Lending Transactions (SAIBOR)
Trade Date Transaction rate Name of the counterparty (kindly use official name) Maturity date Duration in number of days Bank's input for SAIBOR rate If transaction rate is different from input rate, state reasons 29/05/21 100,000 1.10 ABC Bank 30/05/21 1 1.25 Name of the Bank Reporting period
SAR Interbank Borrowing Transactions (SAIBID)
Trade Date Transaction rate Name of the counterparty (kindly use official name) Maturity date Duration in number of days Bank's input for SAIBOR rate If transaction rate is different from input rate, state reasons 29/05/21 100,000 0.75 ABC Bank 30/05/21 1 0.80 Name of the Bank Reporting period
List all bid/offer transactions undertaken at the bank's offered/bid rates
Date Bank's input for SAIBOR rate Number of transactions not undertaken at offered rates Number of transactions Name of customers (kindly use Official name) Rate offered Tenor (no. of days) Reasons for not undertaking 29/05/21 1.25 1 ABC Bank 1.30 100,000 30 Customers negotiating a lower rate 29/05/21 1.25 2 CBA Bank 1.45 50,000 90 No interest in 90 days 29/05/21 1.25 4 DEF Bank 1.25 50,000 7 Customers demanding a lower rate than SAIBOR Date Bank's input for SAIBOR rate Number of transactions not undertaken at offered rates Number of transactions Name of customers (kindly use Official name) Rate offered Tenor (no. of days) Reasons for not undertaking 29/05/21 0.90 1 ABC Bank 0.90 75,000 60 Banks not willing to offer at SAIBOR rate
Charging Policy for Cross Currency Payments Using "AFAQ" Service
No: 43038107 Date(g): 2/12/2021 | Date(h): 27/4/1443 Status: In-Force
Further to SAMA Circular No. (42068309), dated 24/9/1442H, regarding the Operating Rules for Cross Currency Payments using "AFAQ" Service for the local banking sector.Please find attached the Charging Policy for Cross Currency Payments using AFAQ Service.
For your information and action accordingly as of 8/5/1443 H corresponding to 12/12/2021 G.
1. Definitions
In this document, the following terms will have the following meanings except as the context may otherwise require:
Term Definition SAMA Saudi Central Bank. GPC Gulf Payments Company. AFAQ Arabian Gulf System for Financial Automated Quick Payment Transfer Cross-Currency
PaymentPayment from the bank of one country to a bank from another country through the GCC RTGS Central Component. The Paying Bank sends funds in its country domestic currency, and the Receiving bank receives funds in its country domestic currency. Operating Rules Operating Rules for Cross Currency Payments using AFAQ Service Pilot Phase The period of time commencing upon April 19, 2021 until close of business on July 17, 2021 2. Introduction
2.1 General
The ''Arabian Gulf System for Financial Automated Quick Payment Transfer" (AFAQ) is the Real Time Gross Settlement service for cross-currency cross-border payments between Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Countries; that is owned and managed by the National Central Banks (NCBs) of the six GCC countries (Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Kingdom of Bahrain, Sultanate of Oman, Qatar and Kuwait).
AFAQ Service is in line with the Charter of the Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf, which aims at achieving closer convergence and stronger links among the GCC countries, reaching advanced economic and financial integration, promoting collaboration, integration, interconnectedness and all aspects of cooperation among the GCC member states and their people at all levels.
AFAQ service has been designed to effectively mitigate frictions associated with conventional cross border payments; namely cost, speed and transparency. This innovative service would serve to bring down the cost of executing cross border payments incurred by relevant stakeholders within the ecosystem.
2.2 Purpose
With the aim of Facilitating cross-border payments in the region, providing essential infrastructure to enable the on-going integration of financial markets across the GCC region, utilizing the advantages of real-time gross settlement, Encouraging closer financial and economic integration between the GCC countries; SAMA has implemented a Specific Model in which functions of the Domestic RTGS system for both Sending and Receiving cross-border payments will be performed at the AFAQ Service's Central Component hosted technically by the Gulf Payments Company (GPC); While controlled, supervised & operated by SAMA according to the operating Rules.
2.3 Statuary Authority
Without prejudice to Saudi Central Bank "SAMA" rights under applicable laws and regulations, this Charging Policy is constituted by SAMA in exercise of the powers stipulated in the Saudi Central Bank Law dated 11/04/1442H (26.11.2020); Designating SAMA as the competent authority to Establish, Develop & Operate national infrastructures for Payment, Clearing & Settlement systems; Issue rules, guidelines, and licenses; Control and Oversee Payment, Clearing & Settlement systems within its sphere of competence.
2.4 Scope
Fees are levied by SAMA on the Participants for the use of the Service. Fees are levied under the following headings:
• Service & Transaction Fees charged to the Sending Participant according to the volume of messages sent by that Participant.
• Exceptional and Penalty fees aimed at encouraging best practice to ensure the smooth functioning of the overall service for the benefit of all Participants and their customers.
2.5 Amendment
SAMA may amend, replace or supplement the contents of this Charging Policy as it deems fit; in consultation with Participants. Such amendment will be duly notified to Participants.
2.6 Compliance
Each Participant will comply with this Charging Policy.
3. Service & Transaction Fees
3.1 Participant Membership Fee
SAMA will charge an annual charge of SAR 50,000.00 to cover the expenses incurred in regards to operating & maintaining the Service.
3.2 Discounted Participant Membership Fee
Participants joining AFAQ within the first 6 months after completion of the Pilot Phase will receive a 50% reduction on the Participant Membership Fee.
During the discount period of 6 months, the amount of the Participant Membership Fee will be calculated as 1/12th of the annual fee for each month or part thereof from the date of joining.
From the start of the seventh month after completion of the Pilot Phase, Participant Membership Fee will revert to the full annual charge of SAR 50,000.00
3.3 Transaction Fees
A fee of SAR 12.00 will be charged for each payment message sent by the Participant.
3.4 Discounted Transaction Fees
No transaction fees will be charged during the Pilot Phase.
For a period of 6 months from the completion of the Pilot Phase, a discount on the transaction fees will apply resulting in a fee of SAR 10.00 to be charged for each payment message sent by the Participant.
From the start of the seventh month after completion of the Pilot Phase, transaction fees will revert to SAR 12.00 for each payment message sent by the Participant.
4. Exceptional and Penalty Fees
Penalty fees and charges intended to encourage best practices and to ensure the smooth operation of the Service will be charged to Participants who fail to meet the required standards.
These Exceptional and Penalty fees aren't expected to yield any significant income to SAMA, as Participants can avoid such charges by adopting the best practices, which this type of fee is intended to promote.
4.1 Cut-off time extension
When a Participant wishes to have the cut-off time on any day extended, a formal request must be submitted to SAMA by whatever communication facility is agreed with SAMA at the time. Such requests should be sent to SAMA as early as possible.
If the request is approved by SAMA, a penalty fee will be charged to the Participant requesting or causing the cut-off time extension. The amount of the fee payable will be SAR 25,000.00 for each period of 30 minutes by which the cut-off time is to be extended.
4.2 Late Return of Payments
The Operating Rules specify latest times governing the return of payments by a Receiving Participant. If the payment is returned after the specified time, a penalty fee of SAR 100.00 will be charged for the late return of payment.
SAMA may levy an additional charge based on the amount of the payment returned.
Any Participant that receives a Return Payment later than that set out in the operating Rules shall forward the details to SAMA.
5. Payment of Invoices
Invoices will be issued by SAMA to Participants in respect of AFAQ as follows:
• Transaction Fees will be invoiced to Participants on a monthly basis.
• Participant Membership Fees will be issued to Participants yearly in advance. During the 6 month discount period set out in Section 3.2 above, invoices for Participant Membership Fees will be issued at the time of joining.
• Exceptional & Penalty Fees will be charged to Participants on a case-by-case basis.
All fees are payable within 10 business days of receipt of the relevant invoice by the Participant.
If the designated fee is not paid within 10 business days, A penalty fee of SAR 1,000.00 will be charged for late payment.
6. FX Margin
Given the fact that the FX Rate is guaranteed by the respective central banks during the daily operations of AFAQ & taking into consideration that Participants wouldn't incur FX rate risk, cost of funding foreign currencies or other costs associated with the conventional correspdent banking model, No FX margin may be applied.
7. Fees charged to Customers
Whilst a Participant opting for charging fees to remitters is urged to set discounted & competitive fees with the aim of encouraging the use of the Service & in alignment with the Banking Tariff communicated by SAMA, the tariff which may be charged to a Customer by a Participant for sending a cross currency payment using AFAQ Service must not exceed the allowable maximum fee for cross border transfers as illustrated in the Banking Tariff; as amended from time to time.
8. Other Exceptional and Penalty fees
SAMA may charge additional appropriate penalty fees where there is,
• A breach of the Operating Rules,
• Non-compliance with any of the timings set by SAMA in the Daily Business Cycle,
• Contravention of any of the conditions stated in this Charging Policy, or,
• Any other circumstances that SAMA deems to be not in the best interest of the smooth functioning of the Service.
Appendix 1
Service Fees
Fee Type Fee Scale Pilot
PhaseDiscount Period of 6
MonthsAfter The Discount Period And Subsequent Years * Participant Membership fees OSAR SAR 25,000.00
(1/12th for each month or part thereof) = 12,500.00 SAR
SAR 50,000.00 Transaction Fees
Fee Type Fee Scale Pilot
PhaseDiscount Period of 6
MonthsAfter The Discount Period And Subsequent Years *Transaction fees OSAR SAR 10.00
per payment message
SAR 12.00
per payment message
Appendix 2
Exceptional & Penalty Fees
Penalty Type Fees Scale Participant who returned the payment ,late 100.00 SAR
per payment message
Participant requests to have the cut-off time on any day extended 25,000.00 SAR
for each 30 minutes extension
A breach of the Operating Rules. Penalty amount will be determined by SAMA Non-compliance with any of the timings set in the Business Day Timetable. Contravention of any of the conditions set out in the Charging Policy. Any other circumstances that SAMA deems to be not in the best interests of the smooth functioning of the Service. Initial Public Offering (IPO) Rules for Receiving and Lending Banks
No: 43060832 Date(g): 9/2/2022 | Date(h): 8/7/1443 Status: In-Force Based on the powers granted to the central bank for the supervision and oversight of the banking sector in the Kingdom, and in reference to the SAMA's circulars regarding the role and participation of banks in Initial Public Offering (IPO), Circular No. 38399/MAF/588, dated 12/11/1426H, Circular No. MAF/337, dated 8/11/1425H, and Circular No. 333/MAF/200, dated 22/8/1413H, and the General Rules for Regulating underwriting transactions by Saudi joint stock companies.
We would like to inform you that SAMA has introduced new Initial Public Offering (IPO) Rules for Receiving and Lending Banks. These rules aim to ensure that banks participating as receiving or lending banks in IPOs in the financial market effectively manage the potential risks they may be exposed to.
For your information and action accordingly as of this date.
1. Introduction
These Rules are issued by Saudi Central Bank (SAMA) in exercise of the powers vested upon it under its Law issued by the Royal Decree No. M/36 dated 11/04/1442H, and the Banking Control Law issued by the Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/02/1386H and the Rules for enforcing its Provisions issued by Ministerial Decision No. 3/2149 dated 14/10/1406H.
These Rules shall supersede the previous instructions issued by SAMA related to the role and participation of banks in IPOs in connection to Circular No. 38399/MAF/588 dated 12/11/1426H and No. MAF/337 dated 8/11/1425H and 333/MA/200 dated 22/8/1413H, and the circular on the general rules regulating underwriting transactions by Saudi joint stock companies, with an emphasis on compliance with these rules in line with the rules, instructions and other regulatory requirements issued whether by SAMA or other legislative authorities, where applicable.
2. Definitions
1. The following terms and phrases, wherever mentioned herein, shall have the meanings assigned to them unless the context otherwise requires:
Term Definition SAMA Saudi Central Bank Receiving Bank A receiving bank that collects and processes application forms and subscription amounts from retail subscribers within an IPO. For an IPO with more than one receiving bank, the term “receiving bank” includes the main receiving bank or a sub-receiving bank. Lending Bank A bank that extends credit facilities to its clients for the purpose of facilitating their subscription for securities in an IPO. Issuer A person who issues or intends to issue securities. Securities A security is a document that shows a person’s legal ownership of a share in a joint stock company and reflects a financial value. Offering Period It includes the period of registration of subscription applications, the process of book building, the payment of the subscription value, and the final allocation of offered shares. Related Parties The parties outlined in Article 2, Paragraph 6 of the first update to SAMA Related Parties Rules for Banks vide SAMA’s Circular No. 41045379 dated 01/07/1441H. Exposures The Exposures outlined in Article 3.1, Paragraph 4 of the Large Exposure Rules for Banks vide SAMA’s Circular No. 67/1651 dated 09/01/1441H. Retail Subscribers A natural person who is not a legal entity nor of high net worth. High-Net-Worth Subscribers Natural persons with high solvency who are classified according to the limits and criteria of the bank, provided that their assets under the bank’s management are not less than SAR 5 million. Legal Entities A legal entity such as commercial institutions, companies, government and semi-government sectors, and financial institutions or a group of persons and/or entities that come together for a specific purpose and form a legal entity. Government Offering The IPO of a company’s Securities in which the Saudi government, or any entity directly or indirectly affiliated with it, owns 51% or more. 3. Objective
2. These Rules aim to assist a Receiving Banks or a Lending Bank Involved in an IPO of Securities in setting the minimum policies and procedures to reduce the potential risks to which they may be exposed.
4. Scope
3. These Rules apply to all banks that take part in an IPO of Securities, whether inside or outside Saudi Arabia, in the capacity of:
a. Lending Bank and/or;
b. Receiving Bank.
5. Governance
4. Banks shall incorporate the provisions of the Rules into its policies and procedures, and take the necessary measures to ensure compliance with them. Banks shall also apply, at a minimum, the following governance procedures:
a. Banks’ board of directors, or their authorized delegate, shall be responsible for setting the criteria for participation as a Lending Bank or a Receiving Bank.
b. Banks shall prove its ability to take part in an IPO and undertake its role prudently and efficiently, by possessing the financial and operational capacity that includes the resources, systems and procedures necessary to manage the associated risks.
c. Banks shall set procedures to monitor IPO-related activities, and comply with the requirements contained in these Rules.
5. Banks may not contravene its internal policies related to financing programs or other programs without obtaining the approval of the bank’s board of directors or its authorized delegate.
6. Banks shall ensure the effectiveness of all relevant systems before commencing an IPO.
6. Risk Management and Operational Capabilities
6.1 Lending Bank
7. A bank that wishes to participate in an IPO as a Lending Bank shall apply, as a minimum, the following:
a. The policy and procedures related to the financing of Securities shall be documented and adequately cover all the main risks that the bank may be exposed to.
b. Adhere to credit policies approved by the bank, and limit the total Exposures in each IPO within an amount that does not exceed the bank's ability to meet its obligations on the settlement date.
c. Follow the internal policies of guarantees, or any other related policies.
d. Conduct a comprehensive analysis, prior to financing the purchase of Securities, that at least includes the potential impact on the Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR), Loan-to-Deposit Ratio (LDR), SAMA Liquidity Ratio, Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR), the Net Stable Funding Ratio (NSFR), Leverage Ratio, Large Exposure limits, and Exposures limits to Related Parties, taking into account the relevant instructions issued by SAMA.
6.1.1 Lending Limits
8. The Leverage Ratio for retail subscriptions shall not exceed 50% of the amount to be subscribed for each Retail Subscriber, with a maximum financing limit not exceeding 2 million Saudi Riyal.
9. Both High-Net-Worth Subscribers and Legal Entities are excluded from Paragraph 8 above. However, the bank shall follow its approved credit standards, and limit the total Exposures to an amount within the risk appetite of the subscriber (credit lines).
10. Banks shall not exceed the Exposures limits stipulated in the relevant instructions issued by SAMA.
6.2 Receiving Bank
11. A bank that wishes to participate in an IPO as a Receiving Bank shall apply, as a minimum, the following:
a. Have a clear understanding of the respective role and responsibilities of the Receiving Bank and the Issuer of an IPO. This shall be clearly defined in the Receiving Bank agreement.
b. Only undertake the role commensurate with its financial and operational capacity, and to conduct a thorough analysis in advance of the potential financial impact arising from an IPO.
6.2.1 Operational Capabilities
12. If a bank has not previously acted as a Receiving Bank in an IPO, or is wishing to act as a Receiving Bank in a large-scale IPO or a government offering, the bank shall notify SAMA in advance and, in particular, prove its financial and operational capacity to process the share applications in accordance with Paragraph 11-b above. It shall also prove its ability to manage the subscription amounts and recycle the application monies in the money market when needed.
13. If a bank intends to act as a Receiving Bank in a large-scale IPO or Government Offering, it shall have sufficient experience and a track record in acting as a Receiving Bank.
14. Banks shall give proper consideration to the number and readiness of branches or any other channels to be designated as channels for receiving subscription applications, and ensure the adequacy of arrangements to meet the expected demand of subscribers.
15. The bank shall ensure that it is fully qualified and conversant with IPO process, while ensuring concentrating its resources and effecting its relevant policies. For large-scale IPOs or government offerings, the bank shall establish a temporary internal committee to coordinate the receipt of information on the subscription and escalate to senior management if necessary.
16. In determining whether an IPO is of a large scale for the bank for the purposes of paragraphs 12, 13 and 15 above, the bank shall benchmark the scale of the IPO against its own financial capacity (capital base) by multiplying the expected share price by the number of shares to be issued and dividing the result by the bank’s Tier 1 regulatory capital. If the resulting percentage is equal to or greater than 100%, the IPO will be considered of large scale. Factors to be considered include the estimated value of subscription monies to be recycled, the general trends in the stock market during the IPO, and the expected level of demand from subscribers.
17. The Receiving Bank shall agree in advance with the Issuer and approve a plan to deal with the high levels of demand for purchasing Securities in the IPO process. The plan must include - at least - the following considerations:
a. Possibility of adding branches to receive subscription applications if needed, including making relevant announcements.
b. Possibility of using another Receiving Bank to assist in receiving or processing applications.
c. Possibility of extending working hours to receive applications, if possible.
d. Arrangements for printing and distributing additional copies of subscription application forms and prospectuses, if needed.
e. Arrangements to hire additional staff, if necessary.
18. The Receiving Bank shall work closely with the Issuer during the IPO process to determine the need for contingency measures in accordance with the approved plan, as required.
6.2.2 Liquidity Requirements
19. Banks shall effectively manage its balance sheet and plan well in advance to ensure continuous compliance with the LDR, SAMA Liquidity Ratio, LCR, NSFR, and any other liquidity requirements required by SAMA.
20. Banks shall review the collateral pledged with SAMA and their daytime limits to ensure they have sufficient collateral to cover large intraday transfers and liquidity needs during the IPO process.
21. Banks shall take due diligence when recycling application monies in the money market, if needed. A Receiving Bank is encouraged to participate in the interbank lending, as needed.
7. Cybersecurity
22. Banks shall establish appropriate precautionary cybersecurity controls to protect the information assets and data of banks and subscribers from cyberattacks, taking into account compliance with the regulatory requirements related to cybersecurity.
23. Banks shall ensure that controls related to cybersecurity monitoring are applied to all systems and applications used in the IPO process. The monitoring incident response capabilities shall be governed by the cybersecurity incident response policy, and ensuring the readiness of incident response teams.
24. Banks shall conduct a comprehensive testing program to ensure cyber resiliency and controls effectiveness of the systems and applications used in the IPO process, including - but not limited to - the following:
a. Vulnerability assessment and penetration testing.
b. Cybersecurity compromise assessment.
25. Banks shall ensure operational resiliency by testing a range of potential disruptive scenarios, in line with regulatory requirements related to business continuity management.
26. Banks shall implement preventive measures to reduce the risks arising from the third-party and service providers dependencies and should also ensure the readiness of third-party arrangements to support the systems and applications involved in the IPO process.
8. Subscription Surplus Refund
27. Banks shall establish documented procedures to refund the value of the subscription surplus, if any, after share allocation.
28. Banks shall inform subscribers of the subscription surplus refund process and timeline. The surplus amount shall be refunded to the subscriber's account via electronic means only.
29. In the event of IPO cancellation or incompleteness, banks shall return the entire subscription amounts to the subscriber’s account via electronic means only, according to the respective timetable.
30. Banks shall exercise due diligence in handling subscription amounts refunds and, at minimum, shall verify the identity of the subscriber before refunding the amount.
9. Reporting
31. Banks shall submit to SAMA an IPO data report based on the following:
a. End of Offering Period report.
b. In the event that an IPO falls under the definition of a large-scale IPO or a Government Offering, reports shall be submitted on daily basis during the Offering Period.
32. Reports shall be submitted to SAMA within a maximum of one working day based on abovementioned instructions.
33. Reports shall be submitted to SAMA via e-mail: BankingDataSection@SAMA.GOV.SA
34. SAMA, at its sole discretion, may apply Article 31-b to subscriptions that do not fall under the definition of a large-scale IPO or Government Offering.
10. Implementation and Effective Date
35. These Rules shall come into force from issuing date.
Instructions on Periods of Issuing the Clearance Letter and Executing Requests for Account Transfer and Debt Transfer
No: 43023350 Date(g): 21/10/2021 | Date(h): 15/3/1443 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Based on the authorities vested to SAMA under its law issued by Royal Decree No. M/36 dated 11/4/1442H, the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/2/1386H, and the Finance Companies Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/51 dated 13/8/1433H, and in reference to the timeframes for issuing clearance letters, account transfers, and debt transfers outlined in various related instructions of SAMA
Attached are the instructions on timeframes for issuing clearance letters, account transfers, and debt transfers, which supersede the time-frames specified in various related instructions of SAMA. Exceptions to these instructions include cases subject to judicial decisions and ongoing cases before the competent authorities.
To take note and act accordingly within thirty working days from its date.
Chapter One: Definitions and General Provisions
1. Definitions
The following words and phrases, wherever they appear in these instructions, shall have the meanings set forth below, unless the context requires otherwise:
Central Bank: The Saudi Central Bank.
Instructions: Instructions on timeframes for issuing clearance letters, account transfers, and debt transfers.
Financial Institutions: Banks and finance companies under the supervision and regulation of SAMA.
Banks: Banks licensed to conduct banking activities in accordance with the provisions of the Banking Control Law.
Customer: An individual benefiting from the products or services of financial institutions.
Account Transfer: The process of transferring a customer's account balance from one bank to another, with the closure of the original account.
2. General Provisions
2.1 These instructions aim to specify the timeframes that financial institutions must adhere to when receiving a customer's request for issuing a clearance letter, transferring an account, or transferring debt. This is intended to protect customers, ensure fairness in transactions, and promote competition.
2.2 These instructions do not affect the provisions outlined in related instructions or any subsequent updates, including, but not limited to, the following:
- Banking Consumer Protection Principles as communicated by SAMA Circular No. (341000095960) dated 3/8/1434H.
- Regulations For Consumer Financing as per SAMA Circular No. (351000116619) dated 10/9/1435H.
- SAMA Circular No. (361000083199) dated 11/6/1436H concerning Consumer Financing Buyout.
- Regulations of Issuance and Operating of Credit and Monthly charge Cards as communicated by SAMA Circular No. (361000090389) dated 26/6/1436H.
- Finance Consumer Protection Principles as communicated by SAMA Circular No. (361000110320) dated 14/8/1436 H.
- SAMA Circular No. (39100028242) dated 10/3/1439H regarding the Transfer of the Real Estate Financing Debts.
- SAMA Circular No. (391000086876) dated 9/8/1439H concerning the Transfer of Mortgage Loans.
Chapter Two: Timeframes for Processing Customer Requests
3. Clearance Letter
Financial institutions must process the customer's request for issuing a clearance letter - regardless of its purpose, including salary transfers - provided there are no outstanding financial obligations from the customer, within a timeframe not exceeding one business day from the date of receiving the request. For customers with a credit card and/or monthly debit card, this timeframe extends to seven business days.
4. Account Transfer
Banks must process the customer's request to transfer an account within a timeframe not exceeding one business day from the date of receiving the request.
5. Debt Transfer
5.1 Consumer Finance:
Financial institutions (debt sellers) must process the customer's request to transfer debt by completing the necessary consumer finance debt transfer forms within a timeframe not exceeding one business day from the date of receiving the request.
5.2 Real Estate Finance:
A-Financial institutions (debt sellers) must process the customer's request to transfer real estate financing debt by completing the necessary real estate financing debt transfer forms within a timeframe not exceeding three business days from the date of receiving the request.
B- Financial institutions (debt sellers) must complete the processing of the customer's request within a timeframe not exceeding five business days from the date of receiving the approval of the financing entity (the institution wishing to purchase the debt) for the debt transfer.
Chapter Three: Final Provisions
- Exceptions to these instructions include cases subject to judicial decisions and ongoing cases before the competent authorities.
- Financing entities must take all necessary measures to ensure compliance with the timeframes specified in these instructions. They should utilize technological systems and electronic services to process customer requests, including the issuance and electronic verification of documents.
- The timeframes outlined in these instructions replace those specified in other related SAMA instructions.
- Exceptions to these instructions include cases subject to judicial decisions and ongoing cases before the competent authorities.
Operating Rules for Cross Currency Payments using AFAQ Service
No: 42068309 Date(g): 5/5/2021 | Date(h): 24/9/1442 Status: In-Force In reference to the Gulf Instant Payment Settlement System "AFAQ", which aims to provide a unified environment for financial transactions between the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries and offer financial services to customers of all categories by enabling and facilitating cross-border transfers in a fast, secure, and efficient manner. This system serves as a tool to ensure the flow of payments in the local banking sector and supports bilateral and multilateral trade activities, contributing to enhancing economic cooperation and integration among the GCC member states.
Attached is the document regarding the "Operating Rules for Cross Currency Payments using AFAQ Service for the local banking sector".
For your information and implementation as of the current date.
1. Definitions
In this Operating Rules, the following terms will have the following meanings except as the context may otherwise require:
Term Definition SAMA Saudi Central Bank. NCB National Central Bank (NCB) or Monetary Authority of each of the six GCC countries. GPC Gulf Payments Company. AFAQ Arabian Gulf System for Financial Automated Quick Payment Transfer Confirmed
Exchange RateThe exchange rate to be used for conversion between a pair of GCC currencies. This rate is confirmed and guaranteed by the relevant NCBs on every Business Day for use throughout that Business Day. Cross-currency payment Payment from the bank of one country to a bank from another country through the GCC RTGS Central Component. The Paying Bank sends funds in its country domestic currency, and the Receiving bank receives funds in its country domestic currency. CSM Country Specific Model. Domestic RTGS The RTGS system operated by each NCB for processing domestic and eligible cross-currency cross-border payments.
The Domestic RTGS systems act in both Sending and Receiving mode. For clarity purposes in this OR references to the "Receiving Domestic RTGS" and "Sending Domestic RTGS" are used to illustrate various actions performed by these systems while they are acting in either Receiving or Sending mode.
AFAQ CC The Central Component (CC) of the AFAQ Service. OR Operating Rules. RPG Regional Payment Gateway. The RPG acts in both Sending and Receiving mode. Arbitrage The simultaneous buying and selling of securities, currency, or commodities in different markets or in derivative forms in order to take advantage of differing prices for the same currency or asset. 2. Introduction
2.1. General
The "Arabian Gulf System for Financial Automated Quick Payment Transfer" (AFAQ) is the Real Time Gross Settlement service for cross-currency cross-border payments between Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Countries; that is owned and managed by the National Central Banks (NCBs) of the six GCC countries (Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Kingdom of Bahrain, Sultanate of Oman, Qatar and Kuwait).
AFAQ Service is in line with the Charter of the Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf, which aims at achieving closer convergence and stronger links among the GCC countries, reaching advanced economic and financial integration, promoting collaboration, integration, interconnectedness and all aspects of cooperation among the GCC member states and their people at all levels.
2.2. Purpose
With the aim of Facilitating cross-border payments in the region, providing essential infrastructure to enable the on-going integration of financial markets across the GCC region, utilizing the advantages of real- time gross settlement, Encouraging closer financial and economic integration between the GCC countries; SAMA has implemented a Specific Model in which functions of the Domestic RTGS system for both Sending & Receiving cross-border payments will be performed at the AFAQ Service ‘s Central Component hosted technically by the Gulf Payments Company (GPC); While controlled, supervised & operated by SAMA according to the operating Rules.
2.3. Statuary Authority
Without prejudice to Saudi Central Bank "SAMA" rights under applicable laws and regulations, these Operating Rules are constituted by SAMA in exercise of the powers stipulated in the Saudi Central Bank Law dated 11/04/1442H (26/11/2020G); Designating SAMA as the competent authority to Establish, Develop & Operate national infrastructures for Payment, Clearing & Settlement systems; Issue rules, guidelines, and licenses; Control and Oversee Payment, Clearing & Settlement systems within its sphere of competence.
2.4. Scope
These Operating Rules will cover the following areas:
a) Key operational activities across cross currency payments using AFAQ Service; hereinafter referred to as "the Service",
b) Business Rules for access and eligibility of Direct Participants, suspension, termination and withdrawal of Direct Participants,
c) Payment Rules for eligible payments,
d) Business day timetable and calendar,
e) Claims and dispute management
f) Business continuity and contingency arrangements.
2.5. Amendment
SAMA may amend, replace or supplement the contents of these Operating Rules as it deems fit; in consultation with Participants. Such amendment will be duly notified to Direct Participants.
2.6. Compliance
Each Direct Participant will comply with these Operating Rules.
2.7. Charges
The Direct Participants will pay SAMA's charges for the use of the Service in accordance with the Service Charging Policy issued by SAMA, as amended by SAMA from time to time.
2.8. Controlled Documents
A list of controlled documents which delineates operations of the Service is included in APPX (1). The controlled documents set out the detailed system operations.
3. Direct Participants
3.1. Direct Participants Admission
SAMA may admit Direct Participants as members of the Service if in the opinion of SAMA they meet the qualifying criteria as defined by SAMA from time to time. A Direct Participant in the Service must be:
• Participating in the Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express System (RTGS).
• Maintaining a current AFAQ's account in accordance with SAMA's banking conditions.
• Complying with legal, supervisory, technical & operational requirements communicated by SAMA.
• Signatory to the Agreement of Participation in the Service.
3.2. Suspension or Termination of Direct Participants
On notice to a Direct Participant, SAMA may in its discretion suspend a Direct Participant temporarily or terminate a Direct Participant permanently (in each case with immediate effect or as otherwise prescribed in the notice) if the Direct Participant fails to comply with the qualifying criteria defined by SAMA from time to time or if the Direct Participant is, or states that it is, or SAMA reasonably suspects that it may be insolvent or if Direct Participant's relevant licence is revoked or if the Direct Participant fails to comply with these Operating Rules or if, in the good faith opinion of SAMA, the continued membership of the Direct Participant may prejudice the Service or the other Direct Participants or is undesirable.
3.3. Withdrawal of Direct Participants
Subject to receiving a prior written consent of SAMA, Direct Participant may withdraw from the Service upon serving written notice to SAMA within a period not falling less than thirty 30 days prior to the proposed withdrawal date.
3.4. Obligations on Cessation
In case of cessation, the Direct Participant will remain liable for all its accrued and accruing obligations under these Operating Rules. SAMA may give directions as it sees fit to give effect to the suspension, termination or withdrawal of the Direct Participant, including without limitation the surrender of its rights, software and materials in respect of the Service and the continued use or non-use of the Service.
3.5. Notice
SAMA will as soon as practicable give the other Direct Participants notice of changes to or suspensions of a Direct Participant.
4. Systems & Operations
4.1. Overview of AFAQ Service's Architecture
The AFAQ Service is made up of the following components:
• Sending Domestic RTGS system,
• Sending Regional Payment Gateway (RPG),,
• Central Component,
• Receiving Regional Payment Gateway (RPG),
• Receiving Domestic RTGS system,
• Communications network linking all of the other components of the full system,
• In the case of the countries using the CSM, the functions of the Domestic RTGS system, for both Sending & Receiving cross-border payments, will be performed at the AFAQ Service CC. The service is technically hosted by GPC. The service is managed by the NCB of the country using the CSM as part of their Domestic RTGS services.
4.1.1 Sending Domestic RTGS
The Sending Domestic RTGS system, operated by that country's NCB, handles all communications with the Direct Participants in the sending country. It also deals with all aspects of the processing of outward cross- border payments in accordance with the OR of that country's Domestic RTGS system, including, message validation, accounting, verification of availability of funds on the account of the Sending Participant, debiting the account of the Sending Participant, crediting the account of the Receiving NCB and translation of the messages, if necessary, to the format required by the Sending RPG.
4.1.2 RPG
RPG’s main functions are to validate, transform and route the cross-border payment messages.
• Message routing and validation,
• Message queuing in any event causing the AFAQ Service or RPG to queue messages until they can be delivered,
• Handling of Payment Completion Confirmations,
• Exception handling and return of payments,
• Systems management and access control,
• Synchronization of static data with the AFAQ Service cc.
• Holding of the current Participant Directory for message validation purposes.
• Holding of the current FX Translation Rates table for message validation purposes.
• Holding of the current Calendar for message validation purposes.
• Conversion of message formats MX from/to MT.
• Rejection of cross-border cross-currency payments where validation fails.
4.1.3 Sending RPG
The Sending RPG, operated by that country's NCB, receives individual payment messages from the Sending Domestic RTGS system, validates the message format, encrypts all the sensitive data, adds the summary data required for settlement and prepares the full message for transmission to the AFAQ Service CC. The Sending RPG also processes Payment Completion Confirmation messages from the AFAQ Service CC and matches them with the previously sent payment messages.
4.1.4 Receiving RPG
The Receiving RPG, operated by that country's NCB, receives payment messages from the AFAQ Service CC, decrypts the sensitive data, translates the messages into the format required by the Receiving Domestic RTGS system and forwards the messages to the Receiving Domestic RTGS.
Any data not included in the message from the Receiving RPG to the Receiving Domestic RTGS system is retained and available in the Receiving RPG. Receiving Direct Participants and Receiving NCBs have access to this data.
The Receiving RPG also processes Payment Completion Confirmation messages from the Receiving Domestic RTGS, matches them with the previously sent payment messages and transmits the Completion Confirmation to the AFAQ Service CC.
4.1.5 AFAQ Service CC
The AFAQ Service CC will perform the following main functions:
• Receive payment messages from the Sending RPG,
• Validate the message format and content,
• Perform the accounting entries over the shadow accounts of sending and receiving NCBs, and the Primary Accounts of Direct Participants in the case of countries using the CSM,
• Transmit the payment message to the Receiving RPG, or, to the Direct Participants in the case of countries using the CSM,
• Process Payment Completion Confirmation messages from the Receiving RPG, match them with the previously sent payment messages and transmit the Completion Confirmation to the Sending RsPG, or, to the Direct Participants in the case of countries using the CSM,
• Process payment rejections and returns,
• Maintain the Direct Participants directory,
• Maintain FX Exchange Rates for cross-currency conversion and end-of-day Settlement,
• Maintain the Business Day Timetable and Calendar,
• Provide enquiry services to NCBs, and to the Direct Participants in the case of countries using the CSM,
• Produce and transmit MT950 Shadow Account statements at end-of-day, and
• Perform end-of day Settlement activities.
4.1.6 Receiving Domestic RTGS
The Receiving Domestic RTGS system, operated by that country's NCB, handles all communications with the Direct Participants in the receiving country. It also deals with all aspects of the processing of Inward cross-border payments in accordance with the rulebook of that country's RTGS system, including, debiting the account of the Sending NCB, crediting of the account of the Receiving Participant, sending of the Payment Completion Confirmation to the Receiving RPG and transmission of the inward payment message to the Receiving Participant.
4.1.7 Country Specific Model (CSM)
The architecture for the CSM is the same as for the standard RPG configuration except that there is no automated communication with the country's Domestic RTGS system that processes domestic transactions.
4.2. Service's Architecture
As SAMA has adopted the CSM for carrying out SAMA and Direct Participants operations in AFAQ's Service, the functions of a Domestic RTGS system in respect of both inward and outward cross-border payment processing and bookkeeping of Direct Participants' mirror accounts and the relevant NCB shadow accounts are performed in the AFAQ Service CC.
4.3. SAMA's Systems
SAMA controls the installation, maintenance, operation, security, and contingency of the Service and has the right to regulate, administer and monitor the Service using the facilities afforded.
4.4. Direct Participants' Systems
Each Direct Participant is responsible at its own cost for the development, maintenance, security and reliability (including back-up and contingency) of its host system connected to the Service and any links from or to the Service.
4.5. Certification
No Direct Participant may use the Service until it and its systems used in relation to the Service have been certified by SAMA.
4.6. Monitoring
SAMA has the right to monitor relevant Direct Participant's activities for the sake of ensuring that the Service is operated properly, exercising responsibility for central risk management and mitigating pertinent risks.
4.7. Responsibility for Liquidity
SAMA has no responsibility to monitor Direct Participant’s liquidity. It is the responsibility of each Direct Participant to manage its own Liquidity.
4.8. Information
The Service provides reporting and enquiry facilities operating in near real-time; giving each Direct Participant immediate visibility of respective position & enabling it to manage its Liquidity.
4.9. Enhancements to Systems
SAMA may arrange for enhancements and changes to the Service and advise the Direct Participants accordingly, giving such notice before the changes are to be implemented as SAMA considers reasonable. SAMA may give directions for the safe, accurate and timely implementation of changes, updates and distributions. The changes will be binding on the Direct Participants and each Direct Participant will at its own cost carry out all necessary tests & modifications to its own systems linked to the Service and to its pertinent procedures to give effect to these measures.
4.10. Service Levels
SAMA may from time to time specify the service levels to be provided by the Service and by the Direct Participants systems used in connection with the Service.
4.11. Reporting
Each Direct Participant must inform SAMA Immediately of any event which may affect its role or function as a Direct Participant in the Service, including any known or planned disconnection from the Service, or any significant changes to Its host system interface to the Service, its organisation, or environment.
4.12. Operating Procedures
Each Direct Participant must maintain their own internal operating procedures that comply with these Operating Rules.
4.13. Contingencies
Each Direct Participant must ensure that their back-up and contingency procedures are such that the Service is capable of completing their daily processing requirements, without compromising the integrity, security, or performance of the Service. Each Direct Participant will ensure that it has access to adequate contingency facilities to enable It to send and receive its Payment Messages at least during the Operational Phase of the Business Cycle. Each Direct Participant shall ensure that their contingency procedures allow the resumption of operations at the contingency site when required, with the minimum loss of operational time in accordance with the Business Continuity Management Framework published by SAMA, as amended from time to time.
4.14. Tests
Each Direct Participant will comply with the Business Continuity Management Framework issued by SAMA & conduct realistic tests of contingency facilities at least twice annually to ensure the readiness and capability of operations. Signed records of the conduct of such tests must be retained.
4.15. Back-ups
Each Direct Participant is responsible for backing up data and programs for its own the Service operations.
4.16. Confidentiality
Unless advised otherwise by SAMA, The Direct Participant agrees to keep confidential all information concerning SAMA's business or its ideas, intellectual properties, products, customers or services that are of confidential, proprietary or trade secret nature.
4.17. Security
The Direct Participants will abide by applicable rules, regulations, policies and frameworks issued by SAMA; including the Service Security Policy as amended by SAMA from time to time. The Direct Participant must ensure the security and soundness of (SAMA - AFAQ) operations and inform SAMA in case of any security incidents.
4.18. Fraudulent Activities
The Direct Participant must take necessary actions & implement adequate measures to prevent, detect and respond in a timely manner to fraudulent activities involving the Service & report such activities to SAMA and the Direct Participants concerned in accordance with relevant fraud prevention guidelines.
4.19. Accounts at SAMA
Each Direct Participant must maintain a current the Service account at SAMA. Relevant Direct Participant's account must be held in accordance with SAMA's banking conditions from time to time.
5. Business Day Timetable and Calendar
5.1. Timetable
The timetable will allow all Direct Participants to provide high level of service to their customers. The Business Day Timetable will be impacted by providing adequate time for the completion of start-of-day and end-of-day business processes and to allow reasonable time for extending the period required for "pre end- of-day activities" in the event of problems or delays.
Some of the Business Day times are controlled by the system(s) while others are intended as times that all parties must adhere to.
The following key events occur during the course of the business day (Business Day Period):
1. System start.
2. FX Translation Rate adjustment - NCBs can send messages with FX Translation Rates; the official rate for their currency against the USD.
3. FX Translation Rate authorization - at the beginning of the period AFAQ Service cc calculates the cross- rates for all currency pairs and delivers them to NCBs for approval. NCBs send authorization messages: either approval or decline. In case no approval or decline is received, the FX rate is considered as unconfirmed. The system will prohibit cross-border payments for unconfirmed pairs of currencies.
4. System Housekeeping - at the beginning of the period, the system sends FX Translation rates notifications to the NCBs for all approved currency pairs. This period is also used for other housekeeping e.g. Business Day Calendar changes and Participant Directory updates.
5. Start of Day Funding: In accordance with SAMA's banking conditions the Direct Participant wishing to transact through AFAQ on a specific day shall prefund their respective account with SAMA through the Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express "RTGS" on a daily basis to ensure that available balance in AFAQ is sufficient to cover all payment messages of all types as they fall due for payment. The Start of Day Funding message must be supplemented as per the following criteria:
• Be for credit to SAMA.
• Be an Interbank Payment Message.
• Quoting the Routing Code /AFAQSD100/ in Account with institution Field.
• Stating the nature & date of the funding in the Sender to Receiver Information Field.
6. Exchange period for all types of payments - exchange window for any type of operations including returns initiated by Direct Participants.
7. Exchange period for Interbank payments - only interbank payments will be accepted during this period.
8. End-of-day operations - automated return of cross-currency payments by Central Component which cannot be delivered to the RPGs of the receiving countries. RPGs do not automatically return the payments which cannot be delivered to the Domestic RTGS systems - as this should be only RPG operator's decision.
9. Reporting - generation of statements and Net Position reports, reconciliations and confirmations by NCBs & Direct Participants.
10. End-of-day Settlement window - end of day settlement operations through the Settlement Agent.
11. End-of-day reconciliation with NCBs - NCBs can monitor today's activity and send inquiries to the system to reconcile their activities during the day in case of any inconsistencies.
12. End of Day reconciliation With Direct Participants: On a successful completion of End of Day Settlement Window with NCBs, SAMA will reconcile respective accounts held & issue a "Zeroizing" transaction to sweep the available balance maintained by the Direct Participant within the Service to the current account of the Direct Participant in RTGS.
13. Archiving - data archiving
14. System stop.
5.2. Business Days
SAMA will specify and advise the Direct Participants of the days deemed Business Days for the purposes of the Service. SAMA may declare Business Days to be non-Business Days and vice versa for the purposes of the Service.
5.3. Calendar
The Business Day Calendar is maintained as a table in the AFAQ Service cc. The table contains a calendar of working days and holidays for cross-currency payments per country. Cross-currency payments are processed only if there is a working day in both the Sending and Receiving countries. Any updates to the calendar will be made within the AFAQ Service CC.
5.4. Cut-off
SAMA has the right to manage the orderly cut-off of the Service.
5.5. Limits on Transactions
SAMA may limit the categories of transactions allowed during times of the Business Cycle under advice to the Direct Participants.
5.6. Closures
SAMA may close the Service for the purposes of maintenance, correction of technical problems، or installation of systems, or other reason, which in SAMA's opinion makes a closure desirable.
5.7. Availability
Each Direct Participant will ensure that it is in a position to receive and send Payment Messages during the Operational Phase advised by SAMA.
6. FX Rates and Currency Conversion
Prior to the start of the "open for business" phase, confirmed exchange rates will be set in the central system and the RPGs. These rates will be used throughout that business day for the transformation of payment messages. The Sending Direct Participant must include the currency code and amount in the currency of the sending country as well as the exchange rate and the currency code and amount in the currency of the receiving country in the appropriate fields of payment messages. The exchange rate must be the correct confirmed exchange rate for the pair of currencies for that business day. The exchange rate and the converted amount will be validated by the RPG and AFAQ Service cc. Payment messages with an incorrect exchange rate and/or converted amount will be rejected.
7. Payment Messages
7.1. Eligible AFAQ Transactions
7.1.1 The Direct Participant must ensure that AFAQ Transactions shall be effected solely for Genuine Client Needs. For the purposes of these Rules, Genuine Client Needs means bona fide financial and payment needs of non-banking clients of financial institutions participating in the AFAQ system, including (but not limited to) payments arising from bilateral commercial trade activities, remittances and consumer payments.
7.1.2 The Direct Participant shall place adequate measures to ensure that the Service is utilized in a manner consistent with clause 7.1.1.
7.1.3 The Direct Participant shall not, nor shall it permit any of its clients to engage in or be part of Arbitrage or Speculative Activities to profit from any price differences that may exist from time to time between the Foreign Exchange Rates used within the Service and any rates used in other foreign exchange markets.
7.2. Qualified Payment Messages
Payment messages transmitted for processing by the Service must meet the following criteria:
a) Single Payment Messages only,
b) Customer or Interbank payments in the format specified by SAMA,
c) Same day value only - must be a working day in both the Sending and Receiving countries,
d) Must include the currency code and amount in the currency of the Sending country as well as the exchange rate for that business day and the currency code and amount in the currency of the Receiving country in the appropriate fields.
e) Follow message specifications set out in respective Message Format Guidelines.
f) Be for credit to:
• The Receiving Direct Participant itself (interbank payment),
• A Financial Institution holding an account with the Receiving Direct Participant (Interbank payment), or,
• A non-financial institution or person holding an account with the Receiving Direct Participant (Customer payment).
7.3. Payments Processing
The payment for the Receiving Country, when transformed by the AFAQ Service, contains the opposite exchange rate and the two currency amounts in the opposite order. The Receiving Direct Participant, for checking of correct calculation of amounts, should use the original exchange rate used by the Sending Direct Participant (or Sending Domestic RTGS system).
The AFAQ Service cc will process the transaction as per the following:
1) Payments from countries using the CSM
a. Payment Message in the Sending Currency of countries using the CSM:
i. DR: Settlement Account of the Sending Direct Participant;
ii. CR: Shadow Account of the NCB of the Receiving Country;
b. Payment Message in the Receiving Currency:
i. DR: Shadow Account of the NCB of countries using the CSM,
ii. CR: Control (Technical) Account of the NCB of the Receiving Country
2) Payment to countries using the CSM
a. Payment Message in the Sending Currency:
i. DR: Control (Technical) Account of the NCB of the Sending Country,
ii. CR: Shadow Account of the NCB of the countries using the CSM.
b. Payment Message in the Receiving Currency of countries using the CSM:
i. DR: Shadow Account of the NCB of the sending country,
ii. CR: Settlement Account of the Receiving Direct Participant (in the countries using the CSM).
In all cases the entries of both payment messages are posted simultaneously.
If the payment cannot be processed by the AFAQ Service cc for any of the reasons listed under Reasons for Rejection in APPX (2), a rejection message will be sent back to the Sending RPG. The Sending RPG will generate a return payment and send it to the Sending the Direct Participant stating the reason for rejection.
A returned payment message must not be resent with the same Unique Message Reference as the original one. It may, after correction of the reason(s) for rejection, be sent as a new payment by the Sending Direct Participant with a different Unique Message Reference, but UETR can be the same.
7.4. Completion of a Payment
A payment is deemed to be completed, for the purpose of sending the Payment Completion Confirmation, once it has been validated and accepted by the Receiving Domestic RTGS system for onward transmission to the receiving Direct Participant.
The final stage of processing of a payment within the receiving country is subject to the rules, regulations and processing procedures that govern the Receiving Domestic RTGS system.
7.5. Confirmation of Completion
The Receiving Domestic RTGS system, after it has validated the incoming payment and accepted it for onward transmission to the Receiving Direct Participant, will generate and send a Payment Completion Confirmation through the Receiving RPG to the AFAQ Service CC quoting the Unique Message Reference of the payment message.
The AFAQ SERVICE cc will match the Payment Completion Confirmation with the Sent Payment with the same Unique Message Reference and forward the Payment Completion Confirmation through the Sending RPG to the Sending Domestic RTGS system.
The Sending NCB will monitor all payments sent to ensure that matching Payment Completion Confirmations have been received. If the relevant Payment Completion Confirmation has not been received after an interval of 10 minutes from the time the payment was sent by the Sending RPG, and the payment in question was not returned or rejected, the Sending NCB will commence enquiries with GPC as to the cause of the missing confirmation. The Sending NCB is required to monitor receipt of all Payment Completion Confirmations. All payments must be confirmed as completed before the end-of-day process is started.
7.6. Crediting Beneficiary's Account
In accordance with applicable laws, rules & regulations, The Receiving Direct Participant, where the Beneficiary's account number quoted in the Payment Message is the correct account number for the Beneficiary stated in "Beneficiary Customer" field (Field 59), must credit the Beneficiary with same day value as soon as possible but not later than the end of the same Business Cycle.
7.7. Value to Correct Beneficiary
The Receiving Direct Participant will ensure that the value of the payment is given to the correct Beneficiary as per the details in the relevant Payment Message.
7.8. Returns by the Receiving Direct Participant
In case a Payment Message couldn't be credited to the Beneficiary Customer, The Receiving Direct Participant - unless advised otherwise by SAMA - should return to the Sending Direct Participant as soon as possible, preferably within the same business day. If the payment cannot be returned on the same business day, it should be returned before the cut-off time for that type of payment on the next business day or within 2 business days at the latest without liability for use of funds compensation; abiding by the return rules prescribed in 7.8 & using the same exchange rate and currency amounts as in the original received payment with no deductions.
7.9 Return Payment Rules
The receiving Direct Participants shall perform the following validation checks, for returned cross-currency payment messages:
• Any Payment being returned must be returned as a single message,
• The Payment Reference in field 72 is the same as the Reference in the original payment,
• Only one successful return payment is allowed for each received payment message,
• The payment must be returned within a maximum of 2 business days from the date of receiving the original payment message when both countries (sending and receiving) have business day simultaneously,
• The payment currency code and amount in the return payment must be the same as those in the original payment message,
• The exchange rate in the return payment must be the same as the exchange rate in the original payment message received by the return message creator's party,
• The instructed currency code and amount in the return payment must be the same as those in the original payment message received by the return message creator's party,
• The presence of original direct payment reference is checked in Central Component database and Return is rejected if
o The original direct credit reference is not found, or,
o The return is greater than two business days
o A successful Return has already been accepted by the Central Component
o Either of the currency amounts, currency code or exchange rate do not match the original payment
7.10 Reasons for Return or Rejection
A list of valid return and rejection codes is included in APPX (2).
7.11 Payments to the UAE
All payments sent to UAE must contain the correct Purpose of Payment Code according to the list of such codes as communicated by SAMA.
7.12 IBAN
All Customer Payments sent to those countries that use the International Bank Account Number (IBAN) standard - as advised by SAMA from time to time - must quote the IBAN in the Beneficiary Customer's account number field in the payment message in the format and following the rules published for the receiving country. Failure to include valid IBAN may be a valid reason for rejecting/returning the payment.
7.13 Finality Provisions
A payment is deemed to be Final & Irrevocable once the account of the Sending Direct Participant has been debited.
7.14 Cancellation
A Payment Message, once it has been debited to the account of the Sending Direct Participant, cannot be cancelled or recalled.
7.15 Anti-Money Laundering and Combating Terrorist Financing
Each Direct Participant must comply with Anti Money Laundering and Combating Terrorist Financing laws and the Implementing Regulations.
8 Miscellaneous
8.1 Liabilities of SAMA
Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in these Operating Rules or in any document or electronic communication referred to in these Operating Rules, neither SAMA nor any of its officers, employees or agents ("a Specified Party") shall be liable for any losses, or damages or expenses of any kind, whether direct or consequential ("Losses") suffered by a Direct Participant or any other person arising directly or indirectly from:
a) any delays caused by or malfunctions or breakdowns or any inadequacy of the Service,
b) any interruption or loss of the Service or of any of the services contemplated by the Service,
c) any liability for Losses attributable to those parts of the Service which are the responsibility of a Direct Participant or to a Direct Participants fault or systems, or
d) (without limitation) any acts or omissions of a Specified Party in connection with the Service or these Operating Rules;
8.2 Force Majeure
A specified Party shall not be liable for any Losses or any non-performance of the Operating Rules or of Payment Messages or of any obligation in relation to the Service arising directly or indirectly from circumstances beyond reasonable control.
8.3 Emergencies
If any malfunction, breakdown, or interruption or any emergency affects the Service or its operations, transactions will be handled in accordance with the directions of SAMA. Without limiting the discretion of SAMA, SAMA may extend the hours of operation of the Service, direct the use of contingency facilities or close down the Service in whole or in part.
8.4 Direct Participants Act as Principals Only
Each Direct Participant shall be liable as principal in respect of its Payment Messages.
8.5 Assignments
No Direct Participant may assign all or any of its rights or obligations under these Operating Rules. The Service Operating Rules bind the successors of each Direct Participant.
8.6 Dispute Settlement
In the case of any unresolved disputes or claims arising between any persons in relation to these Operating Rules or any rules, regulations or directives issued pursuant to them, the complainant may submit the dispute or claim to SAMA.
8.7 Severability
In case any provision in this Operating Rules shall be invalid, illegal or unenforceable, the validity, legality and enforceability of the remaining provisions shall not in any way be affected or impaired thereby.
8.8 Governing Law
These Operating Rules are governed by the Laws of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Appendix 1 - Controlled Documents
This table contains the list of documents that have been shared with the pilot banks.
AFAQ Documentation Version Document SAMA-l 3095 DS 509 001 GCC RTGS SAMA Design specification Participants edition 2019-11-01 SAMA-l 3095 MF 502 001 GCC SAMA-LQ-Message Formats-2019-11-01 SAMA-l 3095 MF 502 001 GCC SAMA-MT-Message Formats-2019-11-01 SAMA-l 3095 TD 501 008 GCC RTGS REST API specification 2019-09-06 SAMA-l 3095 DS 506 018 GCC RPG Design SAMA Specifics Participants updated 2020-07-02 SAMA-l 3095 DS 506 002 GCC RPG SAMA Design Specification Participants Edition 2020-09-16 Version 001 GCC RTGS MX Message Formats for Participants 2020-09-16 Version 001 SAMA RPG Participant User Guide revision Version 001 GCC RTGS Security Requirement Version 1.0 GPC Circular No.003- Explanatory Note for AFAQ Currency Conversion 2020- 11-17 Version 1.1 Final GPC PKI Commercial CP Version 1.0 GCC RTGS Cross Currency Service - Integration Test and Market Rehearsal Plan version for Pilot Banks Version 1.0 GPC Market Rehearsal Kick-Off Presentation - KSA & BAH 30.N0V-2020 Appendix 2 - Return and Rejection Codes
This table contains the list of Return and Rejection codes that can be used in status messages. The codes can be interpreted as having the meanings shown for each code.
Return reason codes based on payments Rejected by the RPG or Central Component Code Explanation RJ00 System error. Contact support. RJ01 Incorrect FX Rate RJ02 Incorrect Receiving Currency amount RJ03 Invalid Value Date RJ04 Currency code wrong for Receiving country RJ05 A non working day in the Receiving Country RJ06 A non working day in the Sending Country RJ07 Invalid business day period RJ08 Invalid Receiving Direct Participant RJ09 Participant is not active RJ10 Non delivery to Receiving Domestic RTGS RJ11 FX rate is not authorized RJ12 BIC is invalid RJ13 Returned at cut-off time as not delivered RJ14 Approved FX rate not found RJ15 FX rate is absent RJ16 Payments are not allowed RJ17 No active business day found RJ18 Invalid account RJ19 Lack of funds RJ20 No direct credit found RJ21 Return period expired RJ22 Incorrect return amount RJ23 Return payment duplication RJ24 Payment was cancelled RJ25 Payment was rejected RJ90 Access rights check failed Payments Returned
Will be registered in AFAQ CC dictionary (which may be updated from time to time).
System will validate during return processing.
Code Explanation AC01 Format of the account number specified is not correct AC03 Wrong IBAN in SCT AC04 Account number specified has been closed on the bank of account's books AC06 Account specified is blocked prohibiting posting of transactions against it. AC13 Debtor account type is missing or invalid AC14 An agent in the payment chain is invalid AC15 Account details have changed AC16 Account is in sequestration AC17 Account is in liquidation ADRM Beneficiary account is dormant AG01 Transaction forbidden on this type of account (formerly No Agreement) AG02 Bank Operation code specified in the message is not valid for receiver AM01 Specified message amount is equal to zero AM02 Specific transaction/message amount is greater than allowed maximum AM03 Specified message amount is a non processable currency outside of existing agreement AM04 Amount of funds available to cover specified message amount is insufficient. AM05 Duplication AM06 Specified transaction amount is less than agreed minimum. AM07 Amount of funds available to cover specified message amount is insufficient. AM09 Amount received is not the amount agreed or expected AM10 Sum of instructed amounts does not equal the control sum. ARDT Already returned original SCT BACL Beneficiary account closed BALC Beneficiary account blocked BADE Beneficiary account does not exist BADC Beneficiary account is in a different currency BDIN Beneficiary Name does not match Beneficiary account number BE01 Identification of end customer is not consistent with associated account number (formerly Creditor Consistency). BE04 Specification of creditor's address, which is required for payment, is missing/not correct (formerly Incorrect Creditor Address). BE05 Party who initiated the message is not recognized by the end customer BE06 End customer specified is not known at associated Sort/National Bank Code or does no longer exist in the books BE07 Specification of debtor's address, which is required for payment, is missing/not correct. BE08 Returned as a result of a bank error. CN01 Authorization is cancelled. CURR Currency of the payment is incorrect CUST Cancellation requested by the Debtor DS28 Return following technical problems resulting in erroneous transaction. DT01 Invalid date (eg, wrong settlement date) ED01 Correspondent bank not possible. ED03 Balance of payments complementary info is requested ED05 Settlement of the transaction has failed. ERIN The Extended Remittance Information (ERI) option is not supported. FF05 Local Instrument code is missing or invalid FOCR Return following a cancellation request FR01 Returned as a result of fraud. FRTR Final response/tracking is recalled as mandate is cancelled. IBAN Invalid Beneficiary account number IBIC Invalid Beneficiary BIC MD06 Return of funds requested by end customer MD07 End customer is deceased. MS02 Reason has not been specified by end customer MS03 Reason has not been specified by agent. NARR Reason is provided as narrative information in the additional reason information. NOAS No response from Beneficiary NOCM Customer account is not compliant with regulatory requirements, for example FICA (in South Africa) or any other regulatory requirements which render an account inactive for certain processing. NOOR Original SCT never received PPCI Purpose of Payment Code incorrect or invalid RC01 Bank Identifier code specified in the message has an incorrect format (formerly Incorrect Format For Routing Code). RC07 Incorrect BIC of the beneficiary Bank in the SCTR RF01 Transaction reference is not unique within the message. RR01 Specification of the debtor's account or unique identification needed for reasons of regulatory requirements is insufficient or missing RR02 Specification of the debtor's name and/or address needed for regulatory requirements is Insufficient or missing. RR03 Specification of the creditor's name and/or address needed for regulatory requirements is insufficient or missing. RR04 Regulatory Reason RUTA Return following investigation request and no remediation possible. SL01 Due to specific service offered by the Debtor Agent SL02 Due to specific service offered by the Creditor Agent SL11 Whitelisting service offered by the Debtor Agent; Debtor has not included the Creditor on its "Whitelist'' (yet), In the Whitelist the Debtor may list all allowed Creditors to debit Debtor bank account. SL12 Blacklisting service offered by the Debtor Agent; Debtor included the Creditor on his "Blacklist". In the Blacklist the Debtor may list all Creditors not allowed to debit Debtor bank account. SL13 Due to Maximum allowed Direct Debit Transactions per period service offered by the Debtor Agent. SL14 Due to Maximum allowed Direct Debit Transaction amount service offered by the Debtor Agent. SP01 Payment is stopped by account holder. SP02 Previously stopped by means of a stop payment advise. TMO1 Associated message was received after agreed processing cut-off time. TRAC Return following direct debit being removed from tracking process. ULBA Unable to locate Beneficiary account UPAY Payment is not justified. XX00 Unknown reason (system replaces when receives a reason not registered in the CC dictionary) Instructions for Banking Obligations and Transactions in Accordance with the Bankruptcy Law and Its Implementing Regulations
No: 42066419 Date(g): 1/5/2021 | Date(h): 20/9/1442 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Referring to the Bankruptcy Law, issued by Royal Decree No. (M/50) dated 28/05/1439 H, and its Implementing Regulations, issued by Council of Ministers Resolution No. (622) dated 24/12/1439 H, and acknowledging the important role of banks in implementing the bankruptcy law.
To clarify the obligations of banks according to the Bankruptcy Law and its Implementing Regulations, as well as to facilitate banking transactions related to bankruptcy procedures, please find attached the instructions detailing banking obligations and transactions in light of the Bankruptcy Law and its Implementing Regulations. These instructions supersede SAMA instructions communicated by Circular No. (41039914) dated 08/06/1441 H.
For your information, and to act in accordance with the instructions effective from this date.
Chapter One: Definitions and General Provisions
1. Definitions
1.1 The words and phrases used in these instructions shall have the meanings defined in Article (1) of the Bankruptcy Law, issued by Royal Decree No. (M/50) dated 28/05/1439 H, and Article (1) of its Implementing Regulations, issued by Council of Ministers Resolution No. (622) dated 24/12/1439 H. 1.2 The following words and phrases -wherever they appear in these instructions- shall have the meanings set forth below, unless the context requires otherwise: Central Bank: The Saudi Central Bank.
The Law : The Bankruptcy Law.
The Regulation:: The Implementing Regulations of the Bankruptcy Law.
Competent Court: The court where the request to commence bankruptcy proceedings is filed.
The Committee: The Bankruptcy Committee.
2. General Provisions
2.1 These instructions aim to clarify the obligations of banks and financial institutions according to the provisions of the Law and Regulation, as well as to facilitate banking transactions related to bankruptcy procedures. 2.2 These instructions do not affect the provisions of the Law and Regulation, as well as other related regulations and instructions, including- For example but not limited to- the following: Rules on Management of Problem Loans, issued by SAMA Circular No. (41033343) dated 11/05/1441 H. Rules for Bank Accounts, issued by SAMA Circular No. (65681/67) dated 01/11/1440 H. Regulations for Bankruptcy Procedures in Commercial Courts, issued by Minister of Justice Decision No. (6421) dated 21/03/1441 H. SAMA Circular No. (42025830) dated 21/04/1442 H, concerning the affirmation not to refuse to confiscate a bank guarantee letter due to the commencement of bankruptcy proceedings and the suspension of claims against the client who issued the guarantee letter. SAMA Circular No. (42016471) dated 16/03/1442 H, concerning the importance of adhering to the regulations related to the commercial environment and credit transactions. Chapter Two: Obligations of Banks and Financial Institutions
3. Banks and Financial Institutions, as operators of banking activities or creditors of the debtor, must adhere to the following:
3.1 Facilitate the provision of any information or procedures related to the debtor’s transactions subject to financial reorganization, liquidation, financial reorganization for small debtors, liquidation for small debtors, or administrative liquidation to the trustee or committee, as applicable, through various channels, in accordance with the provisions of Chapter Three of these instructions. 3.2 Adhere to the suspension of claims against the debtor immediately upon receiving proof of a court order from the competent court suspending claims. This should be done through official notification channels, the trustee, or the debtor—whichever is applicable— including debit and transfer orders from bank accounts in accordance with the judgments and decisions issued by the competent courts after the suspension of claims, with the following considerations: Adhere to the suspension of claims according to the timeframes specified for each procedure in the Law, or until the bank receives confirmation of the cancellation of the suspension, considering any extensions that may be granted by the competent court.
The suspension of claims does not extend to attachment and debit orders from bank accounts and prohibitions on transactions based on judgments and decisions issued before the suspension of claims, unless otherwise directed by the competent court.
Ensure compliance with relevant legal provisions regarding the enforcement on guarantees during the suspension of claims.
3.3 Submit the bank's claims to the trustee or committee—whichever is applicable—within the specified timeframe, detailing their nature and attaching supporting documentation. 3.4 Verify the powers and duties of the trustee, and each trustee individually if there are multiple, based on the competent court's ruling. 3.5 Ensure that employees in the relevant departments and branches are familiar with these instructions. Chapter Three: Banking Transactions That May Be Required by the Trustee or Committee
4. Bank Accounts
4.1. A bank account must be opened for the debtor subject to one of the bankruptcy procedures outlined in Section (3.1) according to the following requirements: 1. A request from the trustee or committee, as applicable, to open the account, specifying its purpose. 2. A decision from the competent court including any of the following: A. The initiation of liquidation or liquidation for small debtors for the natural or legal person, and the appointment of a single trustee. B. The initiation of liquidation or liquidation for small debtors and the appointment of multiple trustees, specifying their duties and powers, including the opening and management of bank accounts. C. The initiation of administrative liquidation and the appointment of the Bankruptcy Committee to manage the procedure. D. The suspension of the debtor’s authority and the appointment of the trustee to manage the operations during financial reorganization proceedings. 3. A copy of the trustee's national ID, or a letter from the committee containing the details of the person authorized to manage the account in administrative liquidation proceedings, along with a copy of their national ID. 4. A copy of the commercial register, the founding contract, and its appendices for the legal entity subject to bankruptcy proceedings, or the national ID/residence permit for the natural person. 4.2 The trustee or committee must be enabled to continue managing the debtor's accounts subject to one of the bankruptcy procedures outlined in Section (3.1) according to the following requirements: 1. A decision from the competent court including any of the following: A. The initiation of liquidation or liquidation for small debtors for the natural or legal person, and the appointment of a single trustee. B. The initiation of liquidation or liquidation for small debtors and the appointment of multiple trustees, specifying their duties and powers, including the management of bank accounts. C. The initiation of administrative liquidation and the appointment of the Bankruptcy Committee to manage the procedure. D. The suspension of the debtor’s authority and the appointment of the trustee to manage operations during financial reorganization proceedings. 2. A copy of the trustee’s national ID, or a letter from the committee detailing the person authorized to manage the account in administrative liquidation proceedings, along with a copy of their national ID. 4.3 A bank account must be opened for the purpose of depositing the proceeds from the sale of the bankruptcy assets securing the debtor’s debt subject to financial reorganization or financial reorganization for small debtors, according to the following requirements: 1. A request from the trustee to open the account, specifying the purpose and the account’s validity period, which should not exceed the date of issuance of the competent court’s judgment to conclude the proceedings. 2. A decision from the competent court initiating the financial reorganization or financial reorganization for small debtors for the natural or legal person and appointing the trustee. 3. A copy of the trustee’s national ID. 4. The trustee’s acknowledgment to notify the bank immediately upon the court’s decision regarding their dismissal or acceptance of their resignation, and to enable the new trustee to continue managing the account, following the court's decision appointing the new trustee in place of the current trustee, along with a copy of their national ID. 5. Bank Account Statements for a Period of Ten Years
5.1 The trustee or the committee—depending on the circumstances—shall be provided with the bank account statements of the debtor subject to one of the bankruptcy procedures specified in paragraph (3.1), after fulfilling the decision of the competent court containing any of the following: A. The initiation of liquidation or liquidation for small debtors for the natural or legal person and the appointment of a single trustee. B. The initiation of liquidation or liquidation for small debtors and the appointment of multiple trustees, specifying their duties and powers, including the request for bank account statements. C. The initiation of administrative liquidation and the appointment of the Bankruptcy Committee to manage the procedure. D. The suspension of the debtor’s authority and the appointment of the trustee to manage operations during financial reorganization proceedings. 6. The Execution or Submission of the Transactions Outlined in Sections (4) and (5) Should not Exceed the Timeframes Specified in the Following Table
Section
Timeframe
Section (4.1) One business day from the completion of requirements. Section (4.2) Immediately upon completion of requirements. Section (4.3) One business day from the completion of requirements (for opening the account), and immediately upon completion of requirements (for continuing account management). Section (5.1) Seven business days from the completion of requirements. The requirements and Information Needed for Customers’ Bank Account Statements
No: 42059442 Date(g): 4/4/2021 | Date(h): 22/8/1442 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Based on the powers granted to SAMA under the provisions of the Banking Control Law and its implementing regulations, and in line with SAMA’s supervisory and regulatory role over financial institutions under its jurisdiction, and in an effort to standardize the minimum operations, information, and details that should be included in bank account statements for customers according to unified standards across all banks. Given that the information contained in a bank account statement serves as a source and reference for legal evidence in matters that benefit the public interest, it simultaneously assists customers in understanding the sources of funds deposited into their accounts, the amounts withdrawn and transferred from them, as well as the types, nature, and dates of the transactions carried out. This ensures clarity and precision in understanding, leaving no room for ambiguity. Furthermore, this enables customers to determine their responsibility for verifying the sources and uses of their funds and the authorities for managing these transactions. This information also benefits banks by providing clear responses to customer inquiries regarding transactions on their accounts.
Attached is the updated version of the required information for bank account statements for customers. Banks are also reminded of the option to provide customers with a simplified bank account statement as an alternative, which includes at a minimum: (The type of transaction, its date, and the amount).
Please take note and ensure compliance with these specified requirements by the end of the second quarter of 2021G.
Transaction Type and Criteria for Statement Details: Cash Deposit (Bank Branch). (1/1)
Type of Transaction and Standards for Account Statement Details
Cash Deposit (Bank Branch). (1/1)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A
Creation of the Service Delivery Channel
1
Name of Service Delivery Channel/Code (Bank Name + Branch Name where the deposit is made)
√
√
-
2
Location of the Service Delivery Channel (City where the branch is located)
√
√
-
3
Transaction Reference Number (Generated by the system)
√
√
-
4
Type of Transaction (Cash Deposit - Bank)
√
√
-
5
Transaction Date
√
√
-
6
Transaction Time (Mandatory for ATM and online transactions, optional for other transactions)
√
√
Statements arranged by date and time
7
Due Date (Creditor)
√
√
-
B
Credit Information
1
Amount
√
√
-
2
Currency
√
√
-
3
Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4
Purpose / Payment Details / Source of Funds
-
-
-
5
Depositor's Name
-
-
-
6
Depositor's ID Number
-
-
To be recorded on the cash deposit form
Transaction Type and Criteria for Statement Details
Cash Deposit (ATM) - (1/2)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Name of the Service Delivery Channel/Code (Bank Name + ATM Code for cash deposit)
√
√
-
2 Location of Service Delivery Channel (City where the ATM is located)
√
√
-
3 The transaction reference number (generated by the ATM)
√
√
-
4 Transaction type (Cash Deposit - ATM)
√
√
-
5 Transaction start date
√
√
-
6 Transaction start time (mandatory for ATMs and electronic banking transactions, optional for other regular transactions)
√
√
Mandatory for ATMs and electronic banking transactions
7 Due date (creditor)
√
√
-
B Creditor information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied exchange rate
-
-
-
4 Purpose / Payment details / Source of funds
-
-
-
5 Depositor's name
-
-
-
6 Depositor's ID number
-
-
-
7 Fees
-
-
-
Cash Withdrawal (Check) – (2/1)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Name of Service Delivery Channel/Code (Bank Name + Branch Name from which the cash is withdrawn)
√
√
-
2 Location of Service Delivery (City where the branch is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (generated by the system)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Cash Withdrawal - Within Bank)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Creation Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Creation Time
√
√
-
7 Due Date (Debtor)
√
√
-
B Debit Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Fees
√
√
If withdrawal is in a foreign currency
5 Check Number
√
√
-
6 Beneficiary Name
-
-
-
7 Beneficiary ID Number
-
-
Recorded by the cashier on the check
Cash Withdrawal (Form) – (2/2)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Name of Service Delivery Channel/Code (Bank Name + Branch Name where the cash is withdrawn)
√
√
-
2 Location of Service Delivery channel (City where the branch is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (generated by the system)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type(Cash Withdrawal - Receipt)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Creation Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Creation Time
√
√
-
7 Due Date (Debit)
√
√
-
B Debit Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Fees
√
√
If withdrawal is in a foreign currency
5 Beneficiary Name
-
-
-
6 Beneficiary ID Number
-
-
Recorded on the form
Cash Withdrawal (ATM) – (2/3)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Name of Service Delivery / Code (Bank Name + ATM Code where the cash is withdrawn)
√
√
-
2 Location of Service (Country and City where ATM is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference (Name and Code of the Bank that issued the ATM/Visa card + Transaction Reference Number generated by the ATM)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Cash Withdrawal "Mada Card / Credit Card" – ATM)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Creation Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Creation Time (Mandatory for ATMs and electronic banking transactions; optional for other regular transactions)
√
√
Mandatory for ATMs and electronic banking transactions.
7 Due date (debtor)
√
√
-
B Debit Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Fees
√
√
If the amount is withdrawn in a foreign currency
Deposit of Checks (Clearing – External) (3/1)
No
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A
Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1
Name of the Service Delivery Channel / Code (Bank name and Branch/Department conducting the transaction)
√
√
-
2
Location of the Service Delivery Channel (City name where the branch/department is located)
√
√
-
3
Reference number for the transaction (generated by the system)
√
√
-
4
Transaction Type (Cash Deposit - Bank)
√
√
-
5
Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6
Transaction Start Time
√
√
-
7
Due Date (Creditor)
√
√
-
B
Creditor Information
1
Amount
√
√
-
2
Currency
√
√
-
3
Check Number
-
-
-
4
Drawn on the Bank Name
-
-
-
5
Name of the Depositor
-
-
If not the account holder
6
Depositor ID Number
-
-
To be recorded on the check deposit form
7
Name of the Drawer
-
-
-
8
Country of the Bank Issuing the Check
-
-
-
Check Deposit (Collection) – (3/2)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Name / Code of the Service Delivery Channel (Bank Name and Branch/Department where the transaction occurs)
√
√
ATM Information (if the check was deposited via an ATM)
2 Service Delivery Channel Location (City where the branch/department is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (generated by system)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Check Collection)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Start Time
√
√
-
7 (Credit) Due Date
√
√
-
8 (Debit) Due Date
√
√
-
B Debtor information
1 Amount
√
√
Collection fees
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Cheque number
√
√
-
5 Drawn on the bank name and city
-
-
-
6 Fees (collection fees + correspondent banks)
-
-
-
C Creditor Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Cheque number
√
√
-
5 Drawn on the bank name and city
-
-
-
6 Depositor's name
-
-
If not the check holder
7 Depositor's ID number
-
-
And it is recorded on the check deposit form
8 Drawer's name
-
-
-
Check Deposit (Same Bank- Internal) – (3/3)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Name / Code of the Service Delivery Channel (Bank Name and Branch/Department where the transaction is conducted)
√
√
ATM Information (if the check was deposited via an ATM)
2 Service Delivery Channel Location (City where the branch/department is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (generated by system)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Internal Check Deposit)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Start Time
√
√
-
7 Due Date (Debit)
√
√
-
8 Due Date (Credit)
√
√
-
B Debtor information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Cheque number
√
√
-
5 Beneficiary's name
√
√
-
C Creditor Ledger Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Cheque number
√
√
-
5 Drawn on the bank's name
-
-
-
6 Depositor's name
-
-
If not the cheques holder
7 Depositor's ID number
-
-
And it is recorded on the check deposit form
8 Check issuer's name
-
-
And it is recorded on the check deposit form
9 Check issuer's ID number
-
-
And it is recorded on the check deposit form
Check Cashing (Clearing/Internal Collection) – (4)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Delivery Channel Name/Code (Bank Name and Branch/Department where transaction takes place)
√
√
-
2 Location of the Service Delivery Channel (Name of the city where the branch/department is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (Generated by the system)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Clearing/Internal Collection)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Start Time
√
√
-
7 Due Date (Debtor)
-
-
-
8 Due Date (Creditor)
-
-
-
B Debtor ledger information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Cheque number
√
√
-
5 Beneficiary's name
-
-
-
6 Beneficiary's ID number
-
-
-
7 Presenting bank / Collecting bank's name
-
-
-
Outbound Money Transfer (Fast System) – (5/1)
No
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A
Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1
Name / Code of the Service Delivery Channel (Bank Name and Branch where the transaction is conducted)
√
√
-
2
Location of the Service Delivery Channel (Name of the City for the Branch)
√
√
-
3
Transaction Reference Number (Outbound Transfer Number generated by the system) + Local System Transaction ID Number
√
√
Local System Transaction ID Number
4
Transaction Type (Outbound Transfer – Local System)
√
√
-
5
Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6
Start Time of the Transaction (Mandatory for ATM/Electronic Banking Transactions, Optional for Other Transactions)
√
√
Mandatory for ATM Transactions
/ Electronic Banking
7
Due Date (Debit)
√
√
-
B
Debit Entry Information
1
Amount
√
√
-
2
Currency
√
√
-
3
Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4
Fees
√
√
-
5
Beneficiary Name
-
-
-
6
Beneficiary Bank Name/Code
-
-
-
7
Beneficiary Account Number
-
-
Credit Card Number if to a Credit Card Account
8
Beneficiary Address
-
-
To be noted on the form
9
Purpose/Details of the Transaction
-
-
To be noted on the form
10
Number and Date of Reference at SAMA / Judicial Order if Issued by SAMA
-
-
-
Outbound Money Transfer (SWIFT) – (5/2)
No
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A
Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1
Name / Code of the Service Delivery Channel (Bank Name and Branch where the transaction is conducted)
√
√
-
2
Location of the Service Delivery Channel (Name of the City where the Branch conducting the transaction is located)
√
√
-
3
Transaction Reference Number (Outbound Transfer Number Generated by the System)
√
√
-
4
Transaction Type (Outbound Transfer – SWIFT)
√
√
-
5
Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6
Start Time of the Transaction (Mandatory for ATM/Electronic Banking Transactions, Optional for Other Transactions)
√
√
Mandatory for ATM/Electronic Banking Transactions
7
Due Date (Credit)
√
√
-
B
Credit Entry Information
1
Amount
√
√
-
2
Currency
√
√
-
3
Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4
Fees
√
√
SWIFT Fees
5
Commission
√
√
Commission on Transfer
6
Beneficiary Name
-
-
-
7
Beneficiary Bank Name
-
-
-
8
Beneficiary Account Number
-
-
-
9
Beneficiary Address
-
-
To be noted on the form
10
Country of Transfer
-
-
-
11
Purpose / Details of the Transaction
-
-
To be noted on the form
Outbound Transfer (Salaries) – (5/3)
No
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A
Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1
Name / Code of the Service Delivery Channel (Bank Name and Branch where the transaction is conducted)
√
√
-
2
Location of the Service Delivery Channel (Branch City Name)
√
√
-
3
Transaction Reference Number (MT 102 - Outbound Transfer Number generated by the system) + Local System Transaction ID Number
√
√
Local System Transaction ID Number
4
Transaction Type (Salaries – Total Customer Payments)
√
√
-
5
Start Date of the Transaction
√
√
-
6
Transaction Start Time (Mandatory for ATM/Electronic Banking Transactions, Optional for Other Transactions)
√
√
Mandatory for ATM/Electronic Banking Transactions
7
Due Date (Debit)
√
√
-
B
Debit Entry Information
1
Amount
√
√
Total Amount
2
Currency
√
√
-
3
Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4
Fees
√
√
Total Customer Payments Fees
5
Payment Details (Salaries)
√
√
-
Outbound Transfer (Profit Shares) – (5/4)
No
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Name/Code of service delivery Channel(Bank Name and Branch where the transaction takes place)
√
√
-
2 Channel Location (Branch City Name)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (MT 102 - Outbound Transfer Number Generated by the System)
√
√
Local System Transaction Identifier Number
4 Transaction Type (Profit Shares – Total Customer Payments)
√
√
-
5 Start Date of the Transaction
√
√
-
6 Start Time of the Transaction
√
√
-
7 Maturity Date (Debit)
√
√
-
B Debit Entry Information
1 Amount
√
√
Total Amount
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Exchange Rate Applied
-
-
-
4 Fees
√
√
Customer Payments Total Message
5 Field 70: Payment Details (Profit Shares + Period) Example: Profit Shares / First Half of 2010G
√
√
-
Inbound Transfer (Rapid System) – (6/1)
No
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Channel Name/Code (Bank Name and Branch/Department where the transaction takes place)
√
√
-
2 Channel Location (City Name where the Branch/Department is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (Inbound Transfer Number) + Local System Transaction Identifier Number
√
√
Local System Transaction Identifier Number
4 Transaction Type (Inbound Transfer – Local System)
√
√
-
5 Start Date of the Transaction
√
√
-
6 Start Time of the Transaction (Mandatory for ATM/Electronic Banking Transactions, Optional for Other Transactions)
√
√
-
7 Maturity Date (Credit)
√
√
-
B Credit Entry Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Sender Name
-
-
-
4 Sender Account Number
-
-
Credit Card Number if from a Credit Card Account
5 City Name of Sender
-
-
-
6 Name/Code of the transferring bank
√
√
-
7 Purpose/Payment Details
-
-
-
8 Reference number and date at SAMA / judicial decision in case it is mandated by SAMA
-
-
-
Inbound Transfer (SWIFT System) – (6/2)
No
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Channel Name/Code (Bank Name and Branch/Department where the transaction takes place)
√
√
-
2 Channel Location (City Name where the Branch/Department is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (Inbound Transfer Number)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Inbound Transfer – SWIFT)
√
√
-
5 Start Date of the Transaction
√
√
-
6 Start Time of the Transaction
√
√
-
7 Maturity Date (Credit)
√
√
-
B Credit Entry Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Sender Name
-
-
-
5 Sender Account Number
-
-
-
6 Sender's Country Name
-
-
-
7 Bank Name of Sender
-
-
-
8 Purpose/Payment Details
-
-
-
Incoming Transfer (Salaries) – (6/3)
No Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Name / Code of Service Channel (Bank and Branch / Department where the transaction takes place)
√
√
-
2 Location of the Service Channel (City name where the branch/department is located)
√
√
-
3 Reference number for the transaction (MT 102 - Incoming Transfer Number) + Local System Unique Identifier for the transaction
√
√
Unique Identifier for Local System Transactions
4 Type of Transaction (MT 102 - Local Incoming Transfer - Salaries)
√
√
-
5 Date of Transaction Start
√
√
-
6 Time of Transaction Start
√
√
Mandatory for ATM / electronic banking transactions
7 Due Date (Creditor)
√
√
-
B Creditor Transaction Details
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Name of the Customer Order (Transferrer)
√
√
-
4 Name / Code of the Transfer Bank
√
√
-
5 Purpose / Payment Details (Salaries)
-
-
-
Incoming transfer (profit share)- (6/4)
No Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel 1 Name / Code of the service delivery channel (name of the bank and branch / department where the transaction is conducted)
√
√
-
2 Location of the service delivery channel (name of the city where the branch/department is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction reference number (MT 102 – incoming transfer number) + local system transaction identification number
√
√
Local system transaction identification number
4 Transaction type (Profit Share)
√
√
-
5 Transaction start date
√
√
-
6 Transaction start time
√
√
-
7 Due date (credit entries)
√
√
-
B Creditor ledger information
1 Amount √ √ - 2 Currency √ √ - 3 Field 50: Name of the ordering customer (remitter). Example: Saudi Telecom Company, SABIC, etc √ √ The company that declared the profit share 4 Name / Code of the remitting bank - - - 5 Name of the entity / company - - - 6 Account number of the entity / company - - - 7 Name of the remitting bank - - - 8 Field 70: Purpose/Payment details (Profit share + period) Example: Profit share / First half of 2010 - - - C Debtor ledger information 1 Amount √ √ - 2 Currency √ √ - 3 Field 50: Name of the ordering customer (remitter) Example: Saudi Telecom Company, SABIC, etc √ √ The company that declared the profit share 4 Name/Code of the remitting bank - - - 5 Beneficiary's name - - - 6 Beneficiary's account number - - - 7 Beneficiary's bank - - - 8 Field 70: Purpose/Payment details (Profit share + period) Example: Profit share / First half of 2010 - - - Internal Transfer (Account to Account – Same Bank) – (7)
No
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Name / Code of Service Channel (Bank and Branch / Department where the transaction takes place)
√
√
-
2 Location of the Service Channel (City name where the branch is located)
√
√
-
3 Reference number for the transaction (generated by the system)
√
√
4 Type of Transaction (Transfer from Account to Account)
√
√
-
5 Date of Transaction Start
√
√
-
6 Time of Transaction Start
√
√
-
7 Due Date (Creditor)
√
√
-
8 Due date (creditor)
√
√
-
B Debtor ledger information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Exchange Rate Applied
√
√
-
4 Beneficiary's name
-
-
-
5 Beneficiary's ID number
-
-
-
6 Beneficiary's account number
-
-
-
7 Purpose of the transfer
-
-
-
8 Reference number and date in SAMA / court order in case it is mandated by SAMA
-
-
-
C Creditor ledger information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Exchange Rate Applied
-
-
-
4 Name of the remitter
-
-
-
5 ID number
-
-
-
6 Account number
-
-
-
7 Purpose / Payment details
-
-
-
8 Reference number and date in SAMA / court order in case it is mandated by SAMA
-
-
-
Cashier Request (in Saudi Riyals) – Version (8)
No.
Information Standards
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Channel Name/Code (Bank and Branch Name)
√
√
-
2 Service Channel Location (Branch City Name)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (Generated by System)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Cashier Request)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Start Time
√
√
-
7 Due Date (Credit)
√
√
-
B Debit Entry Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Commission
√
√
-
5 Bank application number
-
-
-
6 Beneficiary's name
-
-
-
Demand Draft Under Collection – Version (9)
No.
Information Standards
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Channel Name/Code (Bank and Branch Name)
√
√
-
2 Service Channel Location (Branch City Name)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (Generated by System)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Demand Promissory Note)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Start Time
√
√
-
7 Due Date (Debit)
√
√
-
B Debtor Ledger Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Commission
√
√
-
5 Demand promissory note number
-
-
-
6 Beneficiary's name
-
-
-
SADAD Payments System – (10)
No.
Information Standards
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Channel Name (Bank/Branch/Management/Electronic Banking Channel)
√
√
-
2 Service Channel Location (City Name for Branch/Management/Electronic Banking Channel)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (Generated by SADAD system - 9 digits)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (SADAD Payments)
√
√
-
5 Transaction start date
√
√
6 Transaction start time (mandatory for ATM transactions, optional for regular transactions)
√
√
Mandatory for ATM transactions. Optional for regular transactions
7 Due date (debtor)
√
√
-
B Debtor Ledger Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Biller name (company name) Example: Saudi Telecom Company, Saudi Electricity Company, Mobily, Ministry of Interior - Traffic Violations, Ministry of Interior - Driver’s License, Ministry of Interior - Vehicles, Ministry of Interior - Saudi Passports, and others
-
-
-
4 Invoice number or biller subscription number (for Saudi Telecom Company and Saudi Electricity Company) / or beneficiary ID number (for the Ministry of Interior)
-
-
-
C Creditor Ledger Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Biller name (company name) Example: Saudi Telecom Company, Saudi Electricity Company, Mobily, Ministry of Interior - Traffic Violations, Ministry of Interior - Driver’s License, Ministry of Interior - Vehicles, Ministry of Interior - Saudi Passports, and others
-
-
-
4 Invoice number or biller subscription number (for Saudi Telecom Company and Saudi Electricity Company) / or beneficiary ID number (for the Ministry of Interior)
-
-
-
Direct Debit Payments - (11)
No
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Channel Name (Bank Name and Branch/Department where the transaction occurs)
√
√
-
2 Service Channel Location (City Name where the Branch/Department is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (System-generated unique reference number) + Local System Transaction ID
√
√
Local System Transaction ID
4 Transaction Type (Direct Debit Payments)
√
√
-
5 Start Date of the Transaction
√
√
-
6 Start Time of the Transaction
√
√
-
7 Maturity Date (Debtor)
√
√
-
B Debit Ledger Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Beneficiary Name (Originator's Name)
-
-
-
5 Beneficiary Bank (Guaranteeing Bank Name)
-
-
-
6 Direct Debit Authorization Number
-
-
-
Foreign Currency Purchase (Cash) - (12)
No
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Channel Name (Bank Name and Branch where the transaction occurs)
√
√
-
2 Service Channel Location (City Name where the Branch is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (System-generated unique reference number)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Foreign Currency Sale)
√
√
-
5 Start Date of the Transaction
√
√
-
6 Start Time of the Transaction
√
√
-
7 Maturity Date (Creditor)
√
√
-
B Creditor Ledger Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Currency Purchased from the Customer
-
-
US Dollar, Euro, AED + Amount
Foreign Currency Sale (Cash) - (13)
No
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Channel Name (Bank Name and Branch where the transaction occurs)
√
√
-
2 Service Channel Location (City Name where the Branch is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number # (System-generated unique reference number)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Foreign Currency Purchase)
√
√
-
5 Start Date of the Transaction
√
√
-
6 Start Time of the Transaction
√
√
-
7 Maturity Date (Debtor)
√
√
-
B Debit Ledger Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Costs
-
-
-
5 Commissions
√
√
-
6 Currency Sold
-
-
US Dollar, Euro, AED + Amount
7 Depositor Name
-
-
-
8 Depositor ID Number
-
-
-
9 Source of Funds
-
-
-
10 Purpose of Deposit
-
-
-
Credit Card Settlements - Transactions - (14)
No
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1
Service Channel Name (Bank Name and Branch/Department where the transaction occurs)
√
√
-
2
Service Channel Location (City Name where the Branch/Department is located)
√
√
-
3
Transaction Reference Number (System-generated unique reference number)
√
√
-
4
Transaction Type (Credit Card Settlement)
√
√
-
5
Start Date of the Transaction
√
√
-
6
Start Time of the Transaction (Mandatory for ATM/online banking transactions, optional for other regular transactions)
√
√
Mandatory for ATM/online banking transactions.
7
Maturity Date (Debtor)
√
√
-
8
Maturity Date (Creditor)
-
-
-
B Information on debit entries (entry for a demand deposit for the customer's current account). Credit card balance settlements are executed for the outstanding limit of the Visa credit card (Visa credit limit) at the beginning or end of each month, according to the arrangements agreed upon with the customer.
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Account Number (Credit Card) of the Beneficiary Creditor
-
-
-
Point of Sale Operations – ATMs/Visa Card - (15)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Channel Name (POS Number + Bank Name + Store Name)
√
√
-
2 Service Channel Location (Country or City Name of the POS)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (ATM Number/Visa Card Number + Bank Name)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Purchase via POS/Visa Card/Mada Card/Mada Pay/Apple Pay)
√
√
-
5 Credit Card Company
√
√
-
6 Transaction Start Time (Mandatory for ATM/Online Banking Transactions; Optional for Other Transactions)
√
√
Mandatory for ATM/Online Banking; Optional for Regular Transactions
7 Due Date (Debtor)
√
√
-
8 Due Date (Creditor)
-
-
-
B Debit Ledger Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Fees
√
√
Purchase via Visa Card / Cash Withdrawal
C Credit Ledger Information
1 POS Number
√
√
-
2 Bank Name of the POS
√
√
-
3 Store Name of the Transaction
√
√
-
4 Service Channel Location (City Name of the POS)
√
√
-
5 Country Name
√
√
-
6 Issuing Bank Name of the Card
√
√
-
7 Transaction Type (Purchase via POS/Visa Card/Mada Card/Mada Pay/Apple Pay)
√
√
-
8 Credit Card Company (Visa, MasterCard, American Express)
√
√
-
Public Offering of Shares - Subscription - (16)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Delivery Name/Code (Bank Name + Branch Name where the operation is executed)
√
√
-
2 Delivery Location (City Name where the branch is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (Generated by the system)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Initial Public Offering – Subscription)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Start Time
√
√
Mandatory for ATM/Online Banking Transactions
7 Due Date (Debtor)
√
√
-
B Debit Entry Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Request Number for the Initial Public Offering
-
-
-
5 Entity/Company Name
-
-
-
6 Entity/Company Account Number
-
-
-
C Credit Ledger Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Request Number for the Initial Public Offering
-
-
-
5 Number of Shares Subscribed
-
-
-
6 Entity/Company Name
-
-
-
7 Entity/Company Account Number
-
-
-
8 Transfer Bank Name
-
-
-
Pending Orders - (17)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Channel Name/Code (Name of Bank/Branch where the operation is executed)
√
√
-
2 Service Location (City Name of the branch executing the operation)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (System generates a reference number) + The unique identifier number for the transaction concerning local system operations
√
√
Reference number specific to the local system transactions
4 Transaction Type (Standing Order)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Start Time
√
√
Mandatory for ATM/Online Banking Transactions
7 Due Date (Debtor)
√
√
-
B Debtor Ledger Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Fees
√
√
-
5 Funded (Current order)
√
√
-
6 Beneficiary's Name
-
-
-
7 Beneficiary's account number
-
-
-
8 Beneficiary's address
-
-
-
9 Beneficiary's bank name
-
-
-
10 Transaction details (type of current order and its reference number)
-
-
-
C Creditor Ledger Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Fees
√
√
-
5 Funded (Standing order)
√
√
-
6 Remitter's name
-
-
-
7 Account Number
-
-
-
8 Remitting bank's name
-
-
-
9 Purpose of the transfer
-
-
-
10 Transaction details (type of current order and its reference number)
-
-
-
Costs / Fees – Operations - (18)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Channel Name / Code (Name of the department / branch of the bank where the transaction is executed)
√
√
-
2 Service Channel Location (Name of the city where the branch executing the transaction is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (The system generates a reference number for the transaction)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Costs / Fees)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Start Time
√
√
-
7 Due Date (Debtor)
√
√
-
B Debtor Ledger Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applicable Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Transaction Details (Details of Costs / Fees)
-
-
-
5 Name of Entity / Company
-
-
-
C Creditor Ledger Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applicable Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Transaction details (costs/fees details)
-
-
-
5 Name of the entity / company
-
-
-
Term Deposits - (19)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Channel Name (Name of the department / branch of the bank where the transaction is executed)
√
√
-
2 Service Channel Location (Name of the city where the branch/department executing the transaction is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (Transaction Number)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Term Deposit)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Start Time
√
√
-
7 Due Date (Debtor)
√
√
-
8 Due Date (Creditor)
√
√
-
9 Type / Details of the deposit
-
-
-
B Debtor Ledger Information (Funds are deposited as term deposits and a confirmation of the term deposits is issued to the customer)
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applicable Exchange Rate
-
-
-
C Creditor Ledger Information (Upon maturity, the principal + interest is deposited as mentioned in the confirmation of the term deposits sent to the customer)
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applicable Exchange Rate
-
-
-
Term Loan Transactions - (20)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Channel Name (Name of the department / branch of the bank where the transaction is executed)
√
√
-
2 Service Channel Location (Name of the city where the branch/department executing the transaction is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (Transaction Number)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Term Loan)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Start Time
√
√
-
7 Due Date (Debtor)
√
√
-
8 Due Date (Creditor)
√
√
-
B Debtor Ledger Information (Loan Installment Payment) (Installment schedule as per the agreement signed by the customer)
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applicable Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Type of financing
-
-
-
5 Payment details
-
-
-
C Creditor Ledger Information (Loan Payment) (A confirmation of the loan detailing the loan specifics is sent to the customer)
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applicable Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Type of financing
5 Financing details
-
-
-
Murabaha Deposits - (21)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Channel Name (Name of the department / branch of the bank where the Murabaha deposit is made)
√
√
-
2 Service Channel Location (Name of the city where the branch/department executing the transaction is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (Transaction Number)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Murabaha Deposit)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Start Time
√
√
-
7 Due Date (Debtor)
√
√
-
8 Due Date (Creditor)
√
√
-
B Information for Debits (Payment) (An investment confirmation of Murabaha containing investment details is sent to the customer)
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applicable Exchange Rate
-
-
-
C Creditor ledger information (on the payment date) (a credit entry is made for the sale price, including the purchase amount + the profit mentioned in the Murabaha investment confirmation)
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applicable Exchange Rate
-
-
-
Tawarruq Financing - (22)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Channel Name (Name of the department/branch where the operation is executed)
√
√
-
2 Service Location (City where the branch/department is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (Murabaha transaction number)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Murabaha Financing)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Start Time
√
√
-
7 Due Date (Debtor)
√
√
-
8 Due Date (Creditor)
√
√
-
B Debit Entry Information (Payment of installment) (A Tawarruq financing confirmation containing the transaction number and details of the purchase and sale of the commodity is sent to the customer.)
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
C Creditor Ledger Information (Tawarruq Repayment) (Confirmation of Tawarruq containing transaction number and details of goods purchase and sale is sent to the customer)
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
SAMA Orders - (23)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Service Delivery Channel Name (Name of the department/branch where the operation is executed)
√
√
-
2 Service Location (City where the branch is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (The system generates a reference number for the transaction) + Unique Identifier Number for Rapid System Transactions
√
√
Unique identifier number for Rapid System Transactions
4 Transaction Type (Standing Order)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Start Time
√
√
-
7 Due Date (Debtor)
√
√
-
B Debtor Ledger Information
1
Amount
√
√
-
2
Currency
√
√
-
3
Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4
Fees
√
√
-
5
Commission (Standing Order)
√
√
-
6
Name of Beneficiary
-
-
-
7
Beneficiary Account Number
-
-
-
8
Beneficiary Address
-
-
-
9
Name / Code of Beneficiary Bank
-
-
-
10
Reference Number at SAMA
-
-
-
11
Purpose of Transfer if specified in SAMA Order
-
-
-
12
Transaction Details (Type of standing order and reference number)
-
-
-
C Creditor Ledger Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Fees
√
√
-
5 Commission (Standing Order)
√
√
-
6 Name of Remitter
-
-
-
7 Account Number
-
-
-
8 Name of Remitter Bank
-
-
-
9 Purpose of Transfer if specified in SAMA Order
-
-
-
10 Transaction Details (Type of standing order and reference number)
-
-
-
Issuing a Bank Check - (24)
No.
Information Criteria
Arabic
English
Notes
A Establishing a Service Delivery Channel
1 Name / Code of the Service Delivery Channel (Name of the bank and the branch/department where the transaction is executed)
√
√
-
2 Location of the Service Delivery Channel (Name of the city where the branch/department is located)
√
√
-
3 Transaction Reference Number (Generated by the system)
√
√
-
4 Transaction Type (Issuing a Bank Check)
√
√
-
5 Transaction Start Date
√
√
-
6 Transaction Start Time
√
√
-
7 Due Date (Debtor)
-
-
-
8 Due Date (Creditor)
-
-
-
B Debtor Ledger Information
1 Amount
√
√
-
2 Currency
√
√
-
3 Applied Exchange Rate
-
-
-
4 Check Number
√
√
-
5 Name of Beneficiary - for Order
-
-
-
6 Name of Beneficiary
-
-
-
Instructions on the Working Hours of Bank Branches, Self-Service Centers, and Remittance Centers in Shopping Centers
No: 41049329 Date(g): 11/3/2020 | Date(h): 16/7/1441 Status: In-Force Translated Document
In accordance with Article Sixteen of the Banking Control Law and in reference to SAMA circular No. 35487/BCS/586 dated 09/10/1427H concerning the working hours of bank branches for the public.
Instructions for the operating hours of bank branches, banks, self-service centers, and remittance centers in shopping malls, aimed at extending the operating hours of these branches and centers according to specific regulations in compliance with relevant laws and instructions.
For your information and action accordingly as of 15/3/2020G. All banks are required to review the status of their existing branches and remittance centers within shopping malls and specify the services provided during these hours in accordance with these instructions.
First: Definitions
The following terms and phrases - wherever mentioned herein- shall have the meanings assigned thereto, unless the context requires otherwise:
Shopping malls: Large, enclosed markets, typically consisting of multiple floors and containing various businesses, entertainment venues, and food outlets.
Independent Branch: A fully integrated, standalone bank branch located in the same building as the shopping mall, accessible solely through an external entrance.
Non-Independent Branch: A fully integrated bank branch located within the shopping mall.
Independent Self-Service Center Branch: A standalone self-service center within the mall building, accessible solely through an external entrance.
Non-Independent Self-Service Center Branch: A self-service center located inside the mall, or in a rented space in the mall’s lobby.
Independent Remittance Center Branch: An independent fully integrated remittance center branch within the mall. The branch entrance is external only.
Non-Independent Remittance Center Branch: A fully integrated remittance center branch located within the shopping mall.
Cash Transactions: Transactions that involve the exchange of cash through deposits, cash withdrawals, or the deposit, withdrawal, or issuance of cheques through tellers.
Customer Services: Opening accounts, updating information, printing "MADA" cards and credit cards, and receiving inquiries, requests, and complaints.
Marketing and Sales Services: Offering consumer loan products, real estate loans, and credit cards.
Second: General Provisions
- The working hours of independent bank branches and independent remittance center branches shall remain the same in accordance with the instructions issued by SAMA in this regard.
- The application of the provisions of these instructions shall not result in any violation of the provisions of the Labor Law and its implementing regulations.
- SAMA must be informed about any branches with extended working hours, and any changes that occur in this regard later.
Third: Instructions
A. Non-Independent Branches.
Non-independent bank branches are allowed to operate for extended working hours in line with the mall's working hours throughout the week, following these controls:
- Operations after 4:30 PM from Sunday to Thursday shall be limited to customer service, marketing and sales services without providing cash transactions.
- Cash transactions shall not be provided on Fridays and Saturdays, with operations limited to customer service, marketing and sales services only.
B. Independent and Non-Independent Self-Service Center Branches.
Independent and non-independent self-service center branches are allowed to operate for extended working hours in line with the mall's working hours throughout the week, following these controls:
- The cash withdrawal or cheque cashing service shall not exceed an amount of (5,000) SAR through Interactive Teller Machines (ITM) after 4:30 PM from Sunday to Thursday.
- The cash withdrawal or cheque cashing service shall not exceed an amount of (5,000) SAR through Interactive Teller Machines (ITM) on Fridays and Saturdays.
C. Non-Independent Remittance Centers.
Non-independent remittance center branches are allowed to operate extended working hours in line with the mall's working hours throughout the week, provided that operations after 5:30 PM are limited to membership opening services, data updates, beneficiary additions, card printing, and providing cash transfer services only through self-service machines (KIOSK) or point-of-sale devices.
Rules of Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express Indirect Participation
No: 43046288 Date(g): 27/12/2021 | Date(h): 23/5/1443 Status: In-Force Based on the powers vested to the Saudi Central Bank under its law issued by Royal Decree No. M/36 dated 11/04/1442 H, the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/02/1386 H, and the implementing the provisions of the Banking Control Law issued by Ministerial Resolution No. 3/2149 dated 14/10/1406 H.
Attached are the rules for indirect participation of banks in the Saudi Rapid Financial Transfer System, which aims to set eligibility criteria for indirect participation in the system, and to determine the requirements of the service level agreement between the bank participating directly and indirectly in the system.
1. Introduction
1.1 Background
These rules are issued by SAMA in exercise of the powers vested upon it under Saudi Central Bank Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/36 on 11/4/1442 H (26/11/2020 G), the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 on 22/02/1386 H (11/6/1966 G) and Council Minister Resolution #226 dated 2/5/1440 H.
This document set out respective rules regulating Indirect Participation within the Real Time Gross Settlement System.
Based on SAMA's own discretion, SAMA can direct a Bank to change its status from Indirect Participant to Participant or vice versa giving sufficient notice period. Similarly, SAMA can also hold, limit, suspend or revoke Settlement Agent status of a Bank giving sufficient notice period.
1.2 Definitions
Bank As defined in Article 1(a) of the Banking Control Law and licensed by its provisions. National Bank As defined in Article 1(c) of the Banking Control Law. Foreign Bank As defined in Article 1(d) of the Banking Control Law. Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express System, the Kingdom's Inter-Bank Electronic Funds Transfer Systems i.e. the Central System at SAMA, the Participants’ Gateways, the security sub-system, the Contingency Central System and Gateways, the communications links between these systems, and all other systems used by SAMA in connection with Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express. Participant As defined by Rule 2.1.1. of SARIE Operating Rules and Regulations - Version 3.0. Settlement Agent A Participant who is authorized by SAMA to clear, settle and record transactions for Indirect Participants. Indirect Participant A Non-Participant Bank, whose transactions are cleared, settled and recorded by a Settlement Agent through Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express. 1.3 Scope
1. These rules are only applicable to Banks.
2. Any Financial Institutions, supervised by SAMA or any other regulatory authority, are out of scope in relation to the applicability of these rules.
3. For the avoidance of any doubt, these rules are not applicable to International Corresponding Banking Business.
2. Criteria
2.1 Participant
4. As stipulated in SARIE Operating Rules and Regulations.
2.2 Indirect Participant
5. Subject to SAMA’s approval, a bank may opt to apply to register itself as Indirect Participant.
6. A Bank can be a Participant or an Indirect Participant therefore cannot hold both participation statuses at one time.
7. Upon receiving information as per Article 19 of these Rules, SAMA will assess overall risk before approving Tiered Participation Participant arrangement.
8. SAMA may define and impose risk exposure thresholds on case-by-case basis, which Indirect Participant has to monitor on a period basis.
9. Indirect Participant must notify SAMA its expectation on a bi-annual basis to when it is likely to breach thresholds as and if communicated by SAMA.
10. Indirect Participant must provide an updated information as required by Article 22 of these Rules whenever there is a significant change to risk exposures.
11. An existing Participant may apply to de-register itself to be Participant and register itself to Indirect Participant subject to SAMA’s approval.
12. An Indirect Participant may appoint only one Settlement Agent in Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express and shall notify the identity of the Settlement Agent to SAMA in writing at least three (3) months before such service come into effect in Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express.
2.3 Settlement Agent
13. Only National Banks having Participant status can be Settlement Agents.
14. Participants must follow SAMA New Banking Products and Services Regulation before offering Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express Clearing Service to Banks.
15. SAMA may define and impose risk exposure thresholds on case-by-case basis, which Settlement Agent has to monitor on a periodic basis.
16. Settlement Agents must notify SAMA its expectation at least on an annual basis to when it is likely to breach thresholds.
17. Participants, through its own current account with SAMA (as Indirect Participant will not maintain current account with SAMA) must be able to clear all types of SAR transactions on the behalf of their indirect participants without any encumbrance.
18. Participants must have ability and capacity to execute SAMA’s monetary operations (Overnight Repurchase Agreement (Repo), Overnight Reverse Repurchase Agreement (Reverse Repo), USD sales etc.) and SAMA’s open market operations (SAMA Bills and term Repo etc.) on the behalf of their indirect participants without any encumbrance.
3. Indirect Participant Registration
3.1 Application Letter
19. A bank wish to register itself as Indirect Participant must send application letter to SAMA along with following documents:
i) Appointment Letter from Chief Executive Officer (CEO) or equivalent of the Indirect Participant proposing the appointment of Settlement Agent;
ii) A letter from the Bank to SAMA explaining to why it is in the Bank’s interest to operate as Indirect Participant;
iii) Draft Service Level Agreement between Settlement Agent and the Bank wishing to register itself as Indirect Participant; and
iv) Current Year plus 3 year SAR Payment Instructions Volumes and Values forecast (Incoming and Outgoing) of the Indirect Participant.
20. Based on review of the application letter and documents / information stated in article 19, SAMA will approve Bank’s registration as indirect participant to the Bank. SAMA may require additional information or may apply additional criteria on a case-by-case basis.
21. SAMA may reject the request if SAMA is of the view that Bank does not satisfy the Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express Indirect Participation Rules. SAMA can also reject the request if it is of the view that it would be best interest of Financial Sector for the Bank to be Participant.
3.2 Appointment of Settlement Agent
22. As a part of appointing Settlement Agent, Indirect Participant must ensure that:
i) the Settlement Agent is authorized to clear, settle and record transactions for Indirect Participants;
ii) the Settlement Agent has operational, technical, financial and organizational capacity to support the needs of the Indirect Participant;
iii) it has identified all material dependencies on its Settlement Agent and must satisfy itself on the arrangements Settlement Agent has in response to those dependencies;
iv) it has performed detailed risk assessment on the Settlement Agent; and
v) all arrangements are in place with Settlement Agent to satisfy Indirect Participant's own clearing liabilities such for e.g. Intraday and / or Overnight Liquidity Facilities.
3.3 Onboarding of Indirect Participant
23. As a part of its onboarding process, Settlement Agent should ensure that:
i) it has identify, assess and document the risk associated with its provision of Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express clearing and settlement services to the Indirect Participant including the impact of its own additional capital requirement due to increase in risks.
ii) it has ability and capacity to clear Indirect Participant’s liabilities (whether prefunded or not) i.e. Settlement Agent must ensure that it maintain adequate liquidity with SAMA to ensure its and its indirect participant’s liabilities are cleared on a timely manner. It establishes and operates such controls, policies and arrangements as are necessary to ensure that it has appropriately mitigated to an acceptable level the risks associated with providing Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express clearing and settlement services to its Indirect Participant.
iii) it has taken reasonable steps to ensure that the Indirect Participant to whom it will provide do not jeopardize the safety, integrity or reputation of the Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express.
iv) it has performed detailed risk assessment on its portfolio of Indirect Participants once additional Indirect Participant will be on-boarded.
3.4 Service Level Agreement
24. Both parties ("Indirect Participants and Settlement Agents") must ensure that they have a legally enforceable service level agreement in place under jurisdiction of Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
25. Scope of services, roles and Responsibilities of both parties must be clearly defined.
26. Effective and expiry dates of the agreement, mechanism of renewal and requirement of periodic review of the agreement must be clearly defined.
27. All key performance indicators and its related attributes such as (but not limited to) definitions, calculation methods, threshold levels, frequency of measurements, reporting mechanism etc. must be clearly defined.
28. All applicable Information Security and Business Continuity Requirements pertaining to both parties in case of Incidents and Disasters must be clearly documented.
29. Both parties must ensure that dispute resolution arrangements are clearly documented including details of the charges payable in case of error, back value etc.
30. Both parties shall establish a process regularly to monitor and document (at a minimum annually) the performance of each other against their contractual obligations in respect of the service level agreement.
4. Risk Management
4.1 Material Dependencies
31. As part of appointment process of Settlement Agent, Indirect Participant should assess and document all its material dependencies on the Settlement Agent. Indirect Participant must ensure that they have adequate arrangements to manage these dependencies, as Settlement Agent will clear all types of SAR transactions of Indirect Participant.
32. Similarly, as part of Indirect Participant On-boarding process, Settlement Agent should assess and document all its material dependencies on Indirect Participant and review adequacy of the arrangements Indirect Participant have to manage these dependencies.
33. Both parties must re-assess and document review of the dependencies identified in Article 31 and 32 above and their arrangements to manage those dependencies at least on an annual basis. As a part of annual review process, both parties should receive/provide updates from/to each other on the arrangements in place to manage material dependencies both parties have on each other.
34. As a part of annual or subsequent review process, both parties should consider whether there are any new material dependencies identified since the last review or appointment date.
35. Both parties should review the effects of all incidents (operational, technical or others) incurred on the service since the last review. Both parties must satisfy themselves that all the remedial action taken to mitigate risk(s) are designed, implemented and operating effectively.
36. Both parties must ensure that similar process is carried to all newly identified dependencies as stated in Article 33 above.
37. Both parties must maintain an up to date log of all incidents that caused disruption to the services with sufficient detail i.e. nature of the incident, detail of its root cause and disruption created, any losses incurred, details of remedial action and status of the remedial action.
4.2 Prudential Requirements
38. Settlement Agent must incorporate all credit lines (utilized, unutilized, committed and uncommitted) assigned to indirect participants as part of the SAMA’s requirements for measuring Counterparty credit risk at the time of on-boarding and on an on-going basis.
39. Indirect Participant must incorporate, manage and measure Settlement Agent Counterparty credit risk especially the cash balance and collateral held by Settlement Agent.
40. Both parties must measure and incorporate all associated risks with Tiered Participation arrangement as part of the Prudential Risk Requirements at the time of inception and on an on-going basis.
5. Other Provisions
5.1 Reporting Requirements
41. Settlement Agent must file statistical report return relating to its Indirect Participants within 5 working days of the month end as prescribed in Appendix 1.
42. Settlement Agent must report all operational incidents and/or credit events relating to services provided to its Indirect Participants within 24 hours of the incident / event occurrence followed by a full report within 7 working days of occurrence detailing the cause(s) of event along with remedial action taken to avoid repetition.
43. Similarly, Indirect Participant must report all operational incidents and/or credit events relating to services provided by its Settlement Agent within 24 hours of the incident / event occurrence followed by a full report within 7 working days of occurrence detailing the cause(s) of event along with remedial action taken to avoid repetition.
44. In case of an operational incident and / or credit event, SAMA encourages both parties to work closely with each other to remediate the effect(s) of incident / event effectively and efficiently. SAMA also encourages both parties to submit joint report instead of submitting separate reports as prescribed in article 42 and 43 of these rules. In case, either Settlement Agent or Indirect Participant submits a joint report, then both parties will be no longer required to submit separate reports as prescribed in articles 42 and 43 of these rules.
45. Banks are required to submit a copy of the report to SAMA via the following email address.
5.2 End User Terms
46. Settlement Agent shall ensure that the contract between the Indirect Participant and its End Users provides (in easily understandable language and in a clear and comprehensible form) all matters related to services relating to Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express.
Appendix 1 - Monthly Statistical Return
Part A: SAR Outgoing Instructions
Insert name of the Settlement Agent Monthly Indirect Participants SAR Outgoing Instructions Month, YYYY Date Indirect Participant’s Name 1 Indirect Participant’s Name 2 Total Indirect Participants Instructions Total Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express Instructions processed by Settlement Agent Percentage of Indirect Participant Instructions over Total Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express Instructions Volume Value Volume Value Volume Value Volume Value Volume (%) Value (%) a b c d e f = b + d g = c + e i j k = f/i x 100 l = g/j x 100 dd/mm/yyyy dd/mm/yyyy dd/mm/yyyy Total In case of a bulk instruction - take volume of individual instructions within the bulk instructionPart B: SAR Incoming Instructions
Insert name of the Settlement Agent Monthly Indirect Participants SAR Incoming Instructions Month, YYYY Date Indirect Participant’s Name 1 Indirect Participant’s Name 2 Total Indirect Participants Instructions Total Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express Instructions processed by Settlement Agent Percentage of Indirect Participant Instructions over Total Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express Instructions Volume Value Volume Value Volume Value Volume Value Volume (%) Value (%) a b c d e f = b + d g = c + e i j k = f/i x 100 l = g/j x 100 dd/mm/yyyy dd/mm/yyyy dd/mm/yyyy Total In case of a bulk instruction - take volume of individual instructions within the bulk instructionPart C: Credit Lines and Collateral
Insert name of the Settlement Agent Credit Lines and Collateral Held As of DD/MM/YYYY SAR' mn Indirect Participant’s Name Credit Lines Value of Collateral Held Total Unutilized Utilized Committed Uncommitted Total Cash Non- Cash a** b c d e ***g h i Indirect Participant’s Name 1 Indirect Participant’s Name 2 Indirect Participant’s Name 3 Total ** a = b + c = d + e
*** g = h + 1Financial Sector Safety and Security Guidelines CCTV Specifications Summary
No: 694270000149 Date(g): 22/7/2019 | Date(h): 20/11/1440 Status: In-Force Reference to the telegram from His Royal Highness, the Minister of Interior, No. 68733 dated 27/03/1440H, regarding the Royal Decree No. 59766 dated 20/11/1439H, which directs the Ministry of Interior to prepare a regulatory framework mandating all government, commercial, and public places, as well as any other locations deemed necessary by the Ministry, to install security surveillance cameras connected to the National Information Center. Also, in reference to the telegram from the Deputy Minister for Security Capabilities, No. 8692 dated 03/09/1440H, which includes instructions for the relevant authorities to require banks and financial institutions, to implement the agreed-upon technical specifications for security systems and to provide the agency with a timeline for implementation.
Attached herewith is the final version of the technical specifications for the security systems in the financial sector. We kindly request that you expedite their implementation from the date of this notice for all your new or under-construction locations. For existing premises, you are required to provide SAMA within two weeks of this notice with an upgrade and modification plan that includes the site name, number of cameras, and the timeline. Should you have any inquiries regarding this matter, please coordinate with the advisor to the Deputy Governor for the Development of the Financial Sector or contact via email at (BankingSafetySecurity@SAMA.GOV.SA).
Security Surveillance Systems
The Security Surveillance Systems specified in this document are based on the following standards:
• BS EN 62676-4 2015, Application Guidelines, including Operational Requirements.
• Centre for Applied Science and Technology CAST (UK Government).
• ANSI/ASIS PAP-1:2012 Physical Asset Protection.
Note:
• The minimum recording retention for all bank facilities (Head Office, Branches, Cash Centres and ATMs) security surveillance systems shall be 90 days.
• In the event of any claims or complaints from customers, financial organisations need to create a copy of the CCTV footage of the incident and store it for a period of 1 year from the date of receiving the complaint
• In the event of any rejected claims or complaints from the customer, banks need to take a copy of the CCTV footage of that incident and store for a period of 5 years from the date of the complaint.
The following specifications shall be used to define surveillance objectives for CCTV equipment at branches:
CCTV system surveillance objectives Ser Surveillance objective Body representation Appropriate linear resolution Face width Camera type required for coverage 1 Identification 120% 250 Pixels/m 40 Pixels Full HD with WDR above 120db 2 Recognition 50% 100 Pixels/m 17 Pixels Full HD camera 3 Detection 10% 20 Pixels/m 3 Pixels Full HD Camera The following table defines how specific areas within branches/facilities shall be considered with reference to the surveillance objectives defined above.Surveillance objectives by branch/facility areaBranch/facility area Surveillance objective All entrances and exits; indoor and outdoor Identification Full coverage of parking areas Detection Full coverage of cash counters Identification Full coverage of perimeter area Detection Full coverage of reception and customer waiting area Identification Full coverage of service area Recognition Full coverage of locker/safe rooms Identification Emergency doors and exits Identification Entrances to utility/communication/HVAC/electrical rooms Identification Full coverage of IT rooms and data centres Identification Full coverage of ATMs Identification Cull coverage of customer face at ATM/CCDM Identification The following table specifies the branch surveillance objectives by functional area and the technology required to achieve these objectives.Surveillance objectives by branch (Customer side) functional area and technological requirementsFunctional area Surveillance objective Technology required Main branch entrance Identification Wide Dynamic Range (WDR) and IR camera Waiting area Identification Normal dome camera with 2.8 - 12mm VF lens Reception Identification Normal dome camera with 2.8 - 12mm VF lens Corridors Detection Normal dome camera with 2.8 - 12mm VF lens Lobbies Identification Normal dome camera with 2.8 - 12mm VF lens Tellers Identification WDR Box camera with 20mm VF lens Operations area Recognition Indoor IR camera with VF lens Elevators - outside of elevator Recognition Normal dome camera with 2.8 - 12mm VF lens Customer Parking Recognition Outdoor IR/PTZ IR camera Perimeter Recognition Outdoor IR/PTZ IR camera ATM Identification Inbuilt pin-hole camera The following table specifies the office surveillance objectives by functional area and the technology required to achieve these objectives.Surveillance objectives by office (Staff /Employee side) functional area and technological requirementsFunctional area Surveillance objective Technology required Main entrance door Identification WDR camera Reception Identification Normal dome camera with 2.8 - 12mm VF lens Lobby Identification Normal dome camera with 2.8 - 12mm VF lens Corridors Detection Normal dome camera with 2.8 - 12mm VF lens Elevators Detection Normal dome camera with 2.8mm VF lens Emergency exits Identification Normal dome camera with 2.8 - 12mm VF lens Storage areas Recognition Normal dome camera with 2.8 - 12mm VF lens IT / IDF room Identification Indoor IR camera with VF lens Security Control Room / IT room Identification Indoor IR camera with VF lens SWIFT/dealing/treasury room Recognition IR camera with VF lens File and Passport office Recognition IR camera with VF lens Data centre Identification Indoor IR camera with VF lens Vault - outside Identification Indoor IR camera with VF lens Vault - inside Identification Indoor IR camera with VF lens Office entrance Recognition Normal dome camera with 2.8 - 12mm VF lens Vehicle entry Identification Indoor IR camera with VF lens and number plate recognition Access points to the building Detection Indoor IR camera with VF lens Utility rooms Recognition Indoor IR camera with VF lens Perimeter Detection PTZ camera/Outdoor IR camera Parking - indoor Detection Indoor IR camera with VF lens Parking - outdoor Detection PTZ camera/Outdoor IR camera CCTV System Installation Requirements
The CCTV system design shall enable monitoring of buildings and facilities from a security control room; furthermore, the system must be able to integrate with third party systems including but not limited to the Building Management System (BMS), Access Control Systems (ACS) and the Intruder Detection System (IDS).
The system must be designed, engineered, furnished, delivered, installed and tested prior to handover, with appropriate handover documentation signed by the receiving authority and the installation engineers. The system must be supported by an Uninterruptable Power Supply (UPS) as well as being connected to a generator to ensure for long term continuity in the event of power loss.
The security surveillance system must support the following recording types: • Motion Detection
• Continuous Recording
• Video Analytics
Each branch/facility shall maintain a register which records all security equipment failures, including details regarding time and date of failure; type of failure; action taken; date of rectification. All failures and intentional stoppages of the system shall be recorded in the log.
All cameras shall be installed in protective enclosures at locations and heights which are not easily accessible. These enclosures shall be rated to prevent the ingress of dust, dirt and moisture that might affect the operation of the camera. Vandal proof housings shall be used for cameras installed at a height which is accessible to people. Outdoor camera enclosures shall be rated to a minimum of IP66, with a sun-shield.
All siting of cameras should appropriately consider factors such as lighting ambient conditions.
Supporting CCTV equipment shall be installed in lockable racks or cabinets in secure rooms, in accordance with the branch security zoning policy.
General CCTV Camera Specifications
CCTV cameras shall be compliant with the following specifications:
• IP cameras shall be compliant with the H.264 baseline encoding profile
• IP cameras shall be capable of multi-stream with its native resolution and FPS
• Live stream of IP cameras shall be a minimum resolution of 720p at a minimum of 12 FPS
• Recording streams of IP cameras shall be in accordance with storage requirements in this document
• Each camera shall be configurable with a single IP address
• IP cameras shall support security features including HTTPS standards
• IP cameras shall be able to automatically start streaming according to the last known configuration when it is restarted/reset/rebooted
• Cameras must support 4CIF through full HD resolutions
• Full HD quality day and night cameras with wide dynamic range (WDR) above 120dbs and with backlight compensation shall be required for the main areas as per surveillance objectives
• The FPS software should be capable of being scalable between 12 - 30 FPS
• IP cameras shall be synchronised to the NTP server or similar time server
• All cameras shall be configured with a unique name based on the location and coverage; camera names shall not be repeated.
• The system must have a time and date display on the image.
• The system must be capable of searching by time, date and the camera for real time view.
• The system must be an integral part of a private network with an IP-based infrastructure.
• The network infrastructure should be able to afford high quality images and video during display and recording.
• A firewall and security system should be provided for the CCTV network in case of connecting to other networks.
• The system should give warnings when the communication is interrupted or lost.
Specifications for CCTV Cameras and NVR Server
The following tables define the exact specifications for each specific camera type employed at branches/facilities and the NVR server.
PTZ IP cameras
PTZ IP cameras specification table
Ser Specification description 1. The image sensor shall be ⅓or ½ CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) 2. Shall be true Day and Night and automatically switches between colour and black/white depending on the illumination 3. Minimum of 20x optical zoom and 12x digital zoom, minimum 2 Megapixel Full HD resolution cameras. Min of 20x optical zoom in HD cameras 4. Optical zoom control shall provide a scaling function that automatically adjusts the speed of the pan and tilt movement dependent on the field of view 5. Shall be a true IP camera with a high-level connection to the other components in the system; camera shall communicate internal errors and support built-in functions like motion detection through a TCP/IP 6. Auto focus and iris with manual override 7. Shall support a minimum illumination for colour 0.2 lux 80% scene reflectance and 0.02 lux 80% scene reflectance for B/W 8. Shall have back-light compensation; multiple users; privacy zone masking; auto and manual tour; remote set-up and automatic image flip 9. Gain control should be automatic; manually 'on' or 'off' 10. Shall be capable of utilising encrypted password transmission (HTTPS) 11. Panning range shall be 360° continuous and tilting range shall be 180°. In-built geared pan/tilt is preferred 12. Pan/tiIt speed shall be minimum of 0.5%/s to 100%/s 13. Minimum 100 pre-sets and shall have accuracy of +/- 0.1° 14. Operating temperature shall be -10°C to +60°C. Relative humidity shall be 0 - 95% non- condensing 15. Shall have built-in compression algorithms such as MJPEG and H.264 16. Vandal- and dust-proof housing construction with polycarbonate dome and cast aluminium body 17. Shall be ONVIF (open network video interface forum) compliant 18. Outdoor cameras shall be in an IP66 rated enclosure with sun-shroud 19. Cameras must contain open API and support multi streaming External fixed IP cameras
External fixed IP cameras specification table
Ser Specification description 1 The image sensor shall be ⅓ or ½ CMOS. CCD chips used in less than 0.5 lux illumination with 20mm vari-focal lens, minimum 2-megapixel camera. Lux should be 0.2lux colour, 0.01 lux B/W 2 Shall be D/N automatically, switching between colour and B/W mode and vice versa 3 Auto focus and iris with manual over-ride 4 Shall have upgradable internal storage minimum 32GB SD card 5 Shall be ONVIF (open network video interface forum) compliant 6 Outdoor cameras shall be in an IP66 rated enclosure with sun-shroud 7 Shall support 12VDC, 24VDC and POE (power over Ethernet) 8 Automatic tracking white balance 9 Operating temperature should be -10 to +60 10 Cameras must contain open API and support multi streaming Dome IP cameras
Dome IP cameras specification table
Ser Specification description 1 The image sensor shall be ⅓ or ½ CMOS. CCD chips used in less than 0.5 lux illumination with 20mm vari-focal lens, minimum 2-Megapixel camera. Lux should be 0.2lux colour, 0.01 lux B/W 2 Auto focus and iris with manual over-ride 3 Shall have tri-axis 4 Shall have upgradable internal storage minimum 32GB SD card 5 Shall be ONVIF (open network video interface forum) compliant 6 Shall support 12VDC, 24VDC and POE (power over Ethernet) 7 Automatic tracking white balance 8 Shall have built-in compression algorithms such as MJPEG and H.264 9 Cameras must contain open API and support multi streaming Indoor IR IP cameras
Indoor IR IP cameras specification table
Ser Specification description 1 The image sensor shall be ⅓ or ½ CMOS. CCD chips used in less than 0.5 lux illumination with 20mm vari-focal lens, minimum 2-megapixel camera. Lux should be 0.2lux colour, 0.01 lux B/W 2 High power infrared LED's 3 Auto focus and iris with manual over-ride 4 Shall support 12VDC, 24VDC and POE (power over Ethernet) 5 Shall have built-in compression algorithms such as MJPEG and H.264 6 Shall be ONVIF (open network video interface forum) compliant 7 Automatic tracking white balance 8 Cameras must contain open API and support multi streaming Indoor IP Box cameras
Indoor IP Box cameras specification table
Ser Specification description 1 The image sensor shall be ⅓ or ½ CMOS. CCD chips used in less than 0.5 lux illumination with 20mm vari-focal lens, minimum 2-Megapixel camera. Lux should be 0.2lux colour, 0.01 lux B/W 2 Dual encoding stream support 3 Support up to 32GB SD card capable to record in motion in case of NVR failure 4 Automatic tracking white balance 5 Shall have built-in compression algorithms such as MJPEG and H.264 6 Shall be ONVIF (open network video interface forum) compliant 7 Shall support 12VDC, 24VDC and POE (power over Ethernet) 8 Cameras must contain open API and support multi streaming Outdoor IR IP cameras
Outdoor IR IP cameras specification table
Ser Specification description 1 The image sensor shall be ⅓ or ½ CMOS. CCD chips used in less than 0.5 lux illumination with 20mm vari-focal lens, minimum 2-Megapixel camera. Lux should be 0.2lux colour, 0.01 lux B/W 2 Auto focus and iris with manual override 3 Shall support a minimum illumination for colour 0.2 lux 80% scene reflectance and 0.02 lux 80% scene reflectance for B/W 4 High power infrared LEDs 5 Shall have built-in compression algorithms such as MJPEG and H.264 6 Shall be ONVIF (open network video interface forum) compliant 7 Outdoor cameras shall be in an IP66 rated enclosure with sun-shroud 8 Operating temperature shall be -10°C to +60°C. Relative humidity shall be 0 - 95% non- condensing 9 Cameras must contain open API and support multi streaming Pinhole IP cameras
Pinhole IP cameras specification table
Ser Specification Description 1. The image sensor shall be ⅓ or ½ CMOS. CCD chips used in less than 0.5 lux illumination with 20mm vari-focal lens, minimum 2-Megapixel camera. Lux should be 0.2lux colour, 0.01 lux B/W 2. Super wide dynamic range 3. Shall have built-in compression algorithms such as MJPEG and H.264 4. Shall be ONVIF (open network video interface forum) compliant 5. Operating temperature shall be -10°C to +60°C. Relative humidity shall be 0 - 95% non-condensing 6. Cameras must contain open API and support multi streaming NVR server
NVR specification table
Ser Specification description 1 When viewing recorded footage the server shall be capable of providing 90 to 180 days of continuous recorded footage at a minimum of 12 FPS with the resolution of 5MP with RAID 5 on hot swappable hard disk arrangement; the RAID 5 shall be hardware controlled. External NAS/SAN storage shall be considered for any branch installation with more than 32 cameras 2 Shall be capable of full operation under a Physical Security Information Management (PSIM) system with full integration capability for video analytics 3 Shall be client-server based NVR 4 Shall support simultaneous recording, playback, exporting video and searching 5 Shall support recording of a minimum of 12 FPS with 5MP resolution for each video channel individually 6 Shall have extra 25% provision in video inputs and storage capacity for future expansion 7 Shall support H.264/MPEG4/MJPEG compression 8 Shall have twin gigabit Ethernet ports 9 Shall have a USB ports and HDMI ports and VGA ports 10 Shall be based on Linux or Windows server (at least 2008) standard platform or above 11 The NVR and storage shall be equipped with dual processor, dual power supplies and a minimum of 10/1 gigabit per second dual communication uplinks to network with any single point of failure. 12 The CPU load of server and storage must not exceed 70% 13 Shall support plug and play configuration 14 Shall support individual camera schedule with different frame rates and resolution 15 Shall support continuous, motion based, alarm and events based recording 16 Shall be synchronised automatically with time server or NTP server 17 Shall support ONVIF communication protocol 18 Shall support multiple users with different privileges 19 Shall be protected with passwords 20 Shall be capable of sending an email in the event of a loss of video or NVR failure 21 Shall be in a secure location, which limits access to those with access rights and fixed in an IT rack CCTV Operational Deployment Requirements
The following operational deployment requirements for CCTV will be maintained for all branches/facilities
Security Surveillance operational deployment requirements
Ser Operational deployment requirement 1 Each branches/facilities entrance and exit (whether from outside or from inside a building) shall be provided with a dedicated CCTV camera, deployed to provide identification of an unknown person, e.g. 120% of screen height. Cameras looking towards the outside of the building from an internal mounting position will need a wide dynamic range in order to capture the intended target 2 All internal public circulation and assembly areas shall be provided with a camera with general views which allow the individual target to be tracked throughout the branch. This requires recognition of a known person e.g. 50% of screen height 3 Each entrance to the private (staff) domain (whether from the exterior or from the public domain) shall be provided with a dedicated CCTV camera, deployed to provide identification of an unknown person, e.g. 120% of screen height. Cameras looking towards the outside from an internal mounting position will need a wide dynamic range in order to capture the intended target 4 Provided the entrance to the private (staff) domain are sufficiently covered by CCTV there should be no need to track through the common staff areas, unless required by each individual bank policy 5 As well as a general view of the teller area, each individual teller station should have its own dedicated camera. The dedicated camera should be able to capture all transactions as well as identifying an unknown customer e.g. 120% of screen height. The dedicated camera should ideally be positioned above the teller station, looking towards the customer, but capturing the whole workstation. It is required to cover cash drawers and activity of the same area 6 Highly restricted access areas (operations room, IT servers, data centres, safety deposit rooms, tellers, operations area and any other cash dealing areas) require fixed cameras with general views which allow an individual target to be tracked throughout the area while monitoring their activities. This requires identification of a known person, e.g. 1200% of screen height. If the area is too large to be covered by an individual camera, additional cameras shall be deployed as necessary to comply with this guidance 7 The entrance to the vault/strong room/safety deposit box room shall be provided with a dedicated CCTV camera on the inside in addition to the vault entrance from the outside, deployed to provide identification of an unknown person, e.g. 120% of screen height. Additionally, the area should be provided with general views which allow an individual target to be tracked throughout the area while monitoring their activities, requiring recognition of a known person, e.g. 50% of screen height. Users of safety deposit boxes shall be provided a private area where items can be deposited and removed out of sight of the cameras 8 The entire cash and valuables in transit (CVIT) route shall be monitored by CCTV. The route should be provided with a general view which allows an individual target to be tracked along the entire path and their activities monitored, requiring recognition of a known person, e.g. 50% of screen height 9 All ATM's shall have a wide dynamic range camera within the body of the machine to identify the user, e.g. 120% of screen height. Additionally, all ATM shall have a general view camera covering the area around the machine which provides recognition of a known person, e.g. 50% of screen height 10 All branch external facades shall be monitored by CCTV. The cameras shall be able to observe the activities around the entire branch perimeter, e.g. 25% of screen height. Additionally, any external areas owned by the branch, such as customer and staff parking, should also have observation coverage. 11 It is mandatory for fixed CCTV cameras to be deployed in the following areas: Teller areas/teller counters focussing to teller and customer's face as well as teller counter for cash demonstration (using one camera for each teller and another camera for the drawer) Teller door entrance/teller counters field area Customer services and waiting areas Operations areas, back office and cash loading area All corridors leading to the vault, where applicable Branch vault room, focussing on the whole vault entrance/exit Branch vault room, focussing on the cash cabinet and the entrance Safety deposit box room entrance ITD server; SWIFT/dealing and security room: CPD; Cad file office; HR filing; passport office; IDF room On-site and off-site ATMs (a minimum of two cameras, one focussing on the customer's face and the other on the withdrawal of cash; with an additional camera used for perimeter/rear entry of the service cabinet, where applicable) Staff entrance door Bank main entrance Bank premises and parking area Lift lobbies, office entrances and emergency exit Customer service, counter coverage and reception area Any other risk area as per requirements To cover the security items Entry to high security areas, subject to prior approval from authorised staff Design and fixing of cameras shall be in proper sequence with the recording device Specification and viewing angles shall comply with SAMA policy Recording capacity shall be in accordance with SAMA policy NVR recorder must be secured in accordance with this document CCTV system shall be supported by a UPS in accordance with SAMA requirements There shall be separate power supply for all devices and cameras No cables shall be exposed without conduits CCTV room temperatures shall be maintained as per system requirements Spot monitor for branch manager and security officer Sufficient lighting shall be provided for all monitoring and recording areas Security system drawings must be received from the supplier prior to the installation of the systems, and once the systems have been installed 12 CCTV room shall be covered by a camera and the entrance shall be via an access control system reader. Only designated and authorised bank personnel shall handle the CCTV system and equipment 13 Deployment of CCTV cameras shall be at an appropriate angle, in which maximum areas can be viewed. In the event that a camera's location needs to be changed approval shall be sought from the respective branch manager or department head in consultation with the security department 14 Branch staff shall be assigned to ensure the correct temperature is maintained in the CCTV room 15 A CCTV system viewing monitor shall be installed in the office of the respective branch manager 16 Authorisation for access to the security system control room shall be restricted to the designated staff only. In the event of a requirement for system vendor/maintenance technician attendance, this should only be authorised by the designated responsible staff and designated security department personnel. Technician attendance should be logged alongside the purpose for the visit 17 Entry to the CCTV/IT room is restricted and all entry shall be documented in the security log-book alongside a reason and relevant justification 18 Support to law enforcement authorities will follow the bank procedures after approval by the bank's security department 19 Video data overwriting or missing recordings shall be reported immediately to the branch/facility management and the security department 20 To ensure optimum system performance the branch manager/delegated staff shall check the CCTV system on a daily basis; the Head of branch operations/delegated staff shall ensure that the security personnel are checking the system on a daily basis and that there is no interruption to the system. Checks should include whether standard time is applied to the security system. Any interruption in recording or fault in the security system shall be reported immediately to the security department who will coordinate with the vendor maintenance team 21 Security systems maintenance records shall be maintained in a separate file for future record and maintenance. All visits of contractors/system vendors shall be recorded in the log, and shall be at the prior approval of relevant branch/facility manager in consultation with the bank security department 22 The CCTV checking form used in branches and bank facilities shall be maintained daily and submitted at the end of the month by security to the security department; it shall be signed by the designated staff alongside the signature of the security guard 23 In compliance with system maintenance requirements, the CCTV system shall be regularly maintained by the vendor to ensure it is working optimally 24 Each branch/facility must ensure that the system is in operational condition at all times and recordings are stored for the duration dictated by SAMA regulations 25 All cameras on the NVR shall be coded with a unique identification number 26 All equipment requiring users to log on using a password shall be configured with user/site-specific password/passwords. No system/product default passwords shall be allowed 27 The CCTV system at all branches/facilities shall be inspected annually by the security department CCTV Surveillance Specifications
1. General
The ATM will have a pin-hole camera located above the client facing screen to record the client's face, this will be supported by an overhead camera to record the transaction and whether cash was deposited and withdrawn. Additionally, in the case of an off-site ATM and additional camera is to be located to observe and cover rear entrance to the cash service room as well as an internal camera to observe the custodians/financial organisation employees during their activities inside the service room. Supporting CCTV equipment shall be installed in lockable racks or cabinets in secure rooms, in accordance with the branch security zoning policy.
Note: This section must be read along with Security Surveillance Systems, from pages 2-16, as the primary resource and means to support and clarify the surveillance requirements.
Camera Description
1. The specified unit shall be of manufacturer's official product line, designed for commercial and/or industrial 24/7/365 use.
2. The specified unit shall be based upon standard components and proven technology using open and published protocols
3. The specified unit shall be manufactured in accordance with ISO 14001.
Certifications and Standards
General abbreviations and acronyms:
1. AGC: Automatic gain control
2. AES: Advanced Encryption Standard
3. API: Application Programming Interface
4. Aspect ratio: A ratio of width to height in images
5. Bit Rate: The number of bits/time unit sent over a network
6. Bonjour: Enables automatic discovery of computers, devices, and services on IP networks.
7. DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
8. DNS: Domain Name System
9. EIS: Electronic Image Stabilization
10. FPS: Frames per Second
11. FTP: File Transfer Protocol
12. H.264 (Video Compression Format)
13. IEEE 802.1x: Authentication framework for network devices
14. IP: Internet Protocol
15. IR light: Infrared light
16. ISO: International Standards Organization
17. JPEG: Joint Photographic Experts Group (image format)
18. LAN: Local Area Network
19. LED: Light Emitting Diode
20. LPR: License Plate Recognition
21. Lux: A standard unit of illumination measurement
22. MBR: Maximum Bit Rate
23. MPEG: Moving Picture Experts Group
24. Multicast: Communication between a single sender and multiple receivers on a network
25. NTP: Network Time Protocol
26. NTSC: National Television System Committee - a colour encoding system based on 60Hz
27. ONVIF: Global standard for the interface of IP-based physical security products
28. PACS: Physical Access Control System
29. PAL: Phase Alternating Line - a colour encoding system based on 50Hz
30. PoE: Power over Ethernet (IEEE 802.3af/at) standard for providing power over network cable
31. Progressive scan: An image scanning technology which scans the entire picture
32. PTZ: Pan/Tilt/Zoom
33. QoS: Quality of Service
34. RAID: Redundant Array of Independent Disks
35. SaaS: Software as a Service
36. SIP: Session Initiation Protocol
37. SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
38. SMPTE: Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers
39. SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol
40. SSL: Secure Sockets Layer
41. TCP: Transmission Control Protocol
42. TLS: Transport Layer Security
43. Unicast: Communication between a single sender and single receiver on a network
44. UPnP: Universal Plug and Play
45. UPS: Uninterruptible Power Supply
46. VBR: Variable Bit Rate
47. VMS: Video Management System
48. WDR: Wide dynamic range
The specified unit shall carry the following EMC approvals:
1. EN 55032 Class A, EN 55024, EN 61000-6-1, EN 61000-6-2
2. FCC Part 15 - Subpart B Class A
3. VCCI Class A
4. RCM AS/NZS CISPR 32 Class A
5. ICES-003 Class A
6. KCC KN32 Class A, KN35
The specified unit shall meet the following product safety standards:
1. IEC/EN/UL 60950-1
2. G. The specified unit shall meet relevant parts of the following video standards:
3. SMPTE 296M (HDTV 720p)
4. SMPTE 274M (HDTV 1080p)
5. SMPTE ST 2036-1 (UHDTV)
The specified unit shall meet the following standards
1. MPEG-4:
a. ISO/IEC 14496-10 Advanced Video Coding (H.264)
2. Networking:
a. IEEE 802.3at (Power over Ethernet Plus)
b. IEEE 802.1X (Authentication)
c. IPv4 (RFC 791)
d. IPv6 (RFC 2460)
e. QoS - DiffServ (RFC 2475)
Quality Assurance
A. All installation, configuration, setup, program and related work shall be performed by electronic technicians thoroughly trained by the manufacturer in the installation and service of the equipment provided.
B. The contractor or designated sub-contractor shall submit credentials of completed manufacturer certification, verified by a third-party organization, as proof of the knowledge.
C. The Contractor shall provide four (4) current references from clients with systems of similar scope and complexity that became operational in the past three (3) years. At least three (3) of the references shall be utilizing the same system components, in a similar configuration as the proposed system
D. The specified unit shall be manufactured in accordance with ISO 9001.
Warranty
A. All security system components and labour furnished by the contractor including wiring, software, hardware and custom parts shall be fully warranted for parts, materials, labour and travel expenses for a minimum of three (3) years from date of the final acceptance of the Video Surveillance System.
B. The manufacturer shall provide warranty and optional extended warranty for the camera for a total period of maximum five years. If enacted as part of the contract, the contractor will repair or replace parts and/or labour per the warranty for the length of this warranty at no cost to the client.
2. Products
General
A. Cameras shall be Full HD IP-based and comply with established network and video standards.
B. Cameras shall be powered by the switch utilizing the network cable. Power injectors (midspans) shall be provided by the contractor when required for proper operation.
C. Cameras shall be fully supported by an open and published API (Application Programmers Interface), which shall provide necessary information for integration of functionality into third party applications.
D. Cameras shall comply with relevant ONVIF profile as defined by the ONVIF Organization.
Video Surveillance Schedule
A. Camera types listed below describing various resolutions, form-factor and features shall be supplied by a single camera manufacturer for the video surveillance system.
Video Surveillance Cameras
A. Fixed 2 MP camera for IP
1. The fixed network camera shall meet or exceed the following design specifications:
a) The camera shall operate on an open source; Linux-based platform and including a built-in web server.
b) The camera shall be equipped with an IR-sensitive progressive scan megapixel sensor.
c) The camera shall provide a removable IR-cut filter, providing day/night functionality.
d) The camera shall provide remote focus functionality.
e) The camera shall provide local video storage utilizing a microSD/microSDHC/microSDXC memory card expansion.
f) The camera shall be manufactured with an aluminium casing.
g) The camera shall be equipped with a SFP slot for fibre network connectivity.
h) The camera shall incorporate network redundancy functionality.
i) The camera shall be designed to be compatible with different lenses from the manufacturer, including:
1. 24 mm fixed lens, f/2.8
2. 35 mm fixed lens, f/2
3. 50 mm fixed lens, f/1.4
4. 85 mm fixed lens, f/1.2
5. 100 mm fixed lens, f/2.8
6. 10-22 mm varifocal lens, f/3.5-4.5
7. 55-250 mm varifocal lens, f4-5.6
8. 70-200 mm varifocal lens, f/2.8
2. The fixed camera shall meet or exceed the following performance specifications:
a) Illumination. The camera shall meet or exceed the following illumination specifications:
• Colour: 0.2 lux F1.2
• B/W: 0.001 lux F1.2
b) Resolution
• The camera shall be designed to provide video streams in resolutions up to 1280x720 (HD 720p) at a minimum of 12 frames per second using H.264 or Motion JPEG.
• The camera shall be designed to provide up to 4 individually cropped out view areas
• The camera shall support video resolutions including:
i. 1280x720 (HDTV 720p) or better
c) Encoding
• The camera shall support the following video encoding algorithms:
i. Support H.264 with automatic scene adaptive bitrate control
ii. MPEG 4
• The camera shall provide independently configured simultaneous H.264 and Motion JPEG streams.
• The camera shall in H.264 support Variable Bit Rate (VBR) for video quality adapted to scene content. To protect the network from unexpected bit rate spikes the camera shall support Constant Bit Rate (CBR) or Maximum Bit Rate (MBR).
• The camera shall provide configurable compression levels.
• Support standard baseline profile H.264 with motion estimation.
• Support motion estimation in H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10/AVC.
• The camera shall for its H.264 implementation support scene adaptive bitrate control with automatic dynamic Region of Interest (ROI) to reduce bitrate in unprioritized regions in order to lowering bandwidth and storage requirements.
d) Transmission
• The camera shall allow for video to be transported over:
i. HTTP (Unicast)
ii. HTTPS (Unicast)
iii. RTP (Unicast & Multicast)
iv. RTP over RTSP (Unicast)
v. RTP over RTSP over HTTP (Unicast)
• The camera shall support Quality of Service (QoS) to be able to prioritize traffic
• Cameras must contain open API and support multi streaming
e) Image
• The camera shall incorporate Automatic and Manual White Balance.
• The camera shall incorporate an electronic shutter operating in the range of 1/8000 to 1 s.
• The camera shall support manually defined values for:
o Colour level
o Brightness
o Sharpness
o Contrast
• The camera shall incorporate a function for optimization of low light behaviour.
• The camera shall allow for rotation of the image.
f) User Interface
• Web server
i. The camera shall contain a built-in web server making video and configuration available to multiple clients in a standard operating system and browser environment using HTTP, without the need for additional software.
ii. Optional components downloaded from the camera for specific tasks, e.g. Active X, shall be signed by an organization providing digital trust services, such as Verisign, Inc.
• Language Specification
i. The camera shall provide a function for altering the language of the user interface and shall include support for at least 10 different languages.
• IP addresses
i. The camera shall support both fixed IP addresses and dynamically assigned IP addresses provided by a Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) server.
ii. The camera shall allow for automatic detection of the camera based on UPnP and Bonjour when using a PC with an operating system supporting this feature.
iii. The camera shall provide support for both IPv4 and IPv6.
g) Event functionality
• The camera shall be equipped with an integrated event functionality, which can be trigged by:
i. Video Motion Detection
ii. Audio Detection
iii. Live Stream Accessed
iv. Camera tampering
v. Manual Trigger/Virtual Inputs
vi. PTZ functionality
vii. External input
viii. Embedded third party applications
ix. Edge storage disruption detection
• Response to triggers shall include:
i. Send notification, using HTTP, HTTPS, TCP, SNMP trap or email
ii. Send images, using FTP, HTTP, HTTPS, network share or email
iii. Send video clip, using FTP, HTTP, HTTPS, network share or email
iv. iv. Send SNMP trap message
v. Recording to local storage and/or network attached storage
vi. Activating external output
vii. Play audio clip
viii. PTZ control functionality
ix. Day/Night vision mode
x. Text Overlay
• The camera shall provide memory for pre-& post alarm recordings.
h) Edge storage
• The camera shall support continuous and event-controlled recording to:
i. Local memory added to the cameras microSD-card slot
ii. Network attached storage, located on the local network
• The camera shall be able to detect and notify Edge storage disruptions.
i) Protocol
• The camera shall incorporate support for at least the following: IPv4/v6, HTTP, HTTPS, SSL/TLS, QoS Layer 3 DiffServ, TCP, ICMP, SNMPv1/v2c/v3 (MIB-II), RTSP, RTP, UDP, IGMP, RTCP, SMTP, FTP, DHCP, UPnP, ARP, DNS, DynDNS, SOCKS, SSH, NTP, CIFS/SMB, Bonjour.
• The Simple Mail Transport Protocol (SMTP) implementation shall include support for SMTP authentication.
j) Text overlay
• The camera shall:
i. Provide embedded on-screen text with support for date & time, and a customer-specific text, camera name, of at least 45 ASCII characters.
ii. Provide the ability to apply privacy masks to the image.
iii. Allow for the overlay of a graphical image, such as a logotype, into the image.
k) Security
• The camera shall support the use of HTTPS and SSL/TLS, providing the ability to upload signed certificates to encrypt and secure authentication and communication of both administration data and video streams.
• The camera shall provide centralized certificate management, with both pre-installed CA certificates and the ability to upload additional CA certificates. The certificates shall be signed by an organization providing digital trust services.
• The camera shall support IEEE 802.1X authentication.
• The camera shall provide support for restricting access to pre-defined IP addresses only, so-called IP address filtering.
• The camera shall restrict access to the built-in web server by usernames and passwords at three different levels.
l) API support
• The camera shall be fully supported by an open and published Application Programmers Interface (APi), which shall provide necessary information for integration of functionality into third party applications.
• The camera shall conform to ONVIF profile G as defined by the ONVIF Organization.
• The camera shall conform to ONVIF profile S as defined by the ONVIF Organization.
m) Embedded applications
• The camera shall provide a platform allowing the upload of third party applications into the camera.
n) Installation and maintenance
• The camera shall be supported with Windows-based management software which allows the assignment of IP addresses, upgrade of firmware and backup of the cameras' configuration.
• The camera shall support the use of Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)-based management tools according to SNMP v1, 2c & 3 / MIB-II.
• The camera shall allow updates of the software (firmware) over the network, using FTP or HTTP.
• The camera shall provide the ability to perform remote focus adjustment.
• The camera shall provide the ability to apply a rectangle of customer-defined number of pixels to the image, which can be used as a pixel counter identifying the size of objects in number of pixels.
• The camera shall accept external time synchronization from an NTP (Network Time Protocol) server.
• The camera shall store all customer-specific settings in a non-volatile memory that shall not be lost during power cuts or soft reset.
• The camera shall incorporate a software-controlled functionality for network redundancy.
o) Access log
• The camera shall provide a log file, containing information about the 250 most recent connections and access attempts since the unit's latest restart. The file shall include information about the connecting IP addresses and the time of connecting.
• Provide a connection list of all currently connected viewers. The file shall include information about connecting IP address, time of connecting and the type of stream accessed.
p) Camera diagnostics
• The camera shall be equipped with LEDs, capable of providing visible status information. LEDs shall indicate the camera's operational status and provide information about power, communication with receiver, the network status and the camera status.
• The camera shall be monitored by an overwatch functionality, which shall automatically re-initiate processes or ultimately attempt to restart the unit if a malfunction is detected.
• The camera shall send a notification when the unit has been re-booted, and all services are initialized.
q) Hardware interfaces
• Network interface
i. The camera shall be equipped with one 100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T PoE Fast Ethernet-port, using a standard RJ45 connector and shall support auto negotiation of network speed and transfer mode (full and half duplex).
ii. b. The camera shall be equipped with one SFP connector for SFP fibre module (100/1000 Mbps).
• Serial interface
i. The camera shall be equipped with one RS-485/422 serial port.
• Inputs/Outputs
i. The camera shall be equipped with two configurable I/O ports, accessible via a removable terminal block. These inputs/outputs shall be configurable to respond to normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC) dry contacts. The output shall be able to provide 12 V DC, 50 mA.
• Power
i. The camera shall be equipped with a removable terminal block providing connectivity for external power.
r) Enclosure
• The camera shall be manufactured with an aluminium casing.
s) Power
• Power over Ethernet Plus IEEE 802.3at Type 2 Class 4
i. Max: 25.5 W
ii. Typical: 13.1 W
• 20- 28 V DC
i. Max: 18.6 W
t) Environmental
• The camera shall operate in a temperature range of -10 °C to +60°C & in a humidity range of 10-95% RH (non-condensing). Execution
Installation
A. Outdoor cameras shall be in an IP66 rated enclosure with sun-shroud.
B. The Contractors or subcontractor's main resources within the project shall carry proper professional certification issued by the manufacturer and verified by a third-party organization to confirm sufficient product and technology knowledge.
C. The Contractor shall carefully follow instructions in documentation provided by the manufacturer to ensure all steps have been taken to provide a reliable, easy-to-operate system.
D. All equipment shall be tested and configured in accordance with instructions provided by the manufacturer prior to installation.
E. All firmware found in products shall be the latest and most up-to-date provided by the manufacturer, or of a version as specified by the provider of the Video Management System (VMS) or the Network Video Recorder (NVR) alternatively the DVR manufacturer.
F. All equipment requiring users to log on using a password shall be configured with user/site-specific password/passwords. No system/product default passwords shall be allowed.
NVR server
The NVR must, in the event of any alert/alarm, automatically stream the CCTV footage to the SCR for storage. This will allow and support any follow up actions by the SCR operators or MOI investigations. This is especially important in the event that the ATM unit is intentionally damaged or rammed with the aim of toppling or removing it from site. As such a final snapshot of the illegal activity will be available and safely stored.
Maintenance
A programme of preventative maintenance must be undertaken in line with the manufactures' guidelines; periods between maintenance checks must not exceed six months (except where contractually agreed). Additionally, regular testing of the system must be undertaken to ensure key components are functioning to full specification. Details of the tests should be recorded in the site record for the IDS and retained as well as updates/copies forwarded to the security department.
Bandwidth Requirements for Security Systems
This guideline is applicable for all existing and future deployment and installation of security systems. This encompasses all systems inclusive of the Surveillance System, Access Control System and Intrusion Detection Systems.
The hard-wired direct network interface bandwidth for all security devices shall be sized to cater for the local bandwidth of the accumulated video and alarm feeds as a minimum capacity. All switches and routers used on the security network shall be rated for gigabit speeds (minimum 1 GB) throughout the supporting infrastructure.
When hard wired direct network connectivity is not available directly to the command centre (indirect via telco or wireless / G3 /G4 / G5 networks), connectivity bandwidth shall be sized in the same way as the hard-wired network.
In all cases, the bandwidth for the WAN connectivity between all bank facilities must allow for on the spot streaming and retrieving of the CCTV footage, with a minimum of 15 FPS and 2MP resolution.
Depositors Protection Fund(DPF) Rules
No: 361000089524 Date(g): 14/4/2015 | Date(h): 25/6/1436 Status: In-Force In order to provide a formal mechanism for the protection of small depositors and to further strengthen the existing safety nets, SAMA has decided to establish a Depositors Protection Fund (DPF). The main objective of the DPF is to maintain financial stability by protecting small depositors.
SAMA has prepared the enclosed DPF Rules to provide for the establishment of the DPF and for matters connected therewith. These Rules are being issued by SAMA under Article 3(d) of its Charter issued by Royal Decree No. 23 dated 23-5-1377H (15 December 1957G) and Article 16(3) of the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22-2-13.86H (11 June 1966 G). AU banks including the branches of foreign banks licensed under the Banking Control Law that conduct banking business in Saudi Arabia shall be members of the DPF and liable to pay the prescribed premium. These Rules shall come into force with effect from 1st January 2016.
In order to provide a formal mechanism for the protection of Eligible Depositors and to further strengthen existing safety nets, SAMA has decided to establish a Depositors Protection Fund (DPF) in Saudi Arabia. These rules (DPF Rules) for the establishment of the DPF are being issued by SAMA in exercise of the powers vested upon it under Article 3(d) of its Charter issued by Royal Decree No. 23 dated 23-5-1377 H (15 December 1957 G) and Article 16(3) of the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22-2-1386 H (11 June 1966 G).
The main objective of the DPF is to maintain financial stability by protecting depositors up to certain limits.
These Rules are meant to provide for the establishment of the DPF and for matters connected therewith:
1. Definitions
The following terms and phrases, where used in these Rules, shall have the corresponding meanings, unless the context requires otherwise:
i. SAMA: The Saudi Central Bank*. ii. Rules: Depositors Protection Fund (DPF) Rules. iii. Bank: means any Person practicing any banking business as such term is defined in the Banking Control Law of the Kingdom issued under Royal Decree No. M/5 on 22/2/1386H (11/6/1966). iv. Subsidiary: means any legal entity in which a Bank owns or controls more than 50% of the shares or voting rights. v. Deposit: means the unpaid balance of the aggregate of moneys received or held by a Bank from or on behalf of a person in the usual course of the business of deposit taking of the Bank and includes:
a) a bank draft, cheque or other similar instrument or instruction entered into a payment system notwithstanding any delay or failure or unsettlement by the Bank in crediting the account; b) all forms of deposits including current accounts, savings accounts, time deposits, inheritance accounts, unclaimed accounts, escrow accounts, client accounts, trust accounts, structured deposits, etc. by whatever name called; c) a foreign currency deposit; and/or d) any other deposit or financial instrument as may be specified by SAMA.
However, the term “Deposit” does not include the following, unless it is otherwise specified by SAMA:
a) a deposit that is not payable in Saudi Arabia; b) an inter-bank deposit; c) a negotiable instrument of deposit and any other bearer deposit; d) a repurchase agreement; and e) any other deposit or financial instrument as may be specified by SAMA.
vi. Eligible Depositor: means any depositor of a Bank, whether a natural or a legal Person, but excludes the following:
a) members of the board of directors and senior management of Bank (including its chief executive officer and Key Executives) as well as their Family Members; b) other Banks or financial institutions; c) shareholders holding in excess of 5% shares in the Bank d) Saudi government or quasi-government institutions; or e) Persons acting on behalf of any of the Persons mentioned in a) through c) above; f) any other Person(s) or institution(s) as may be specified by SAMA from time to time;
vii. Family Members: means first-degree relatives including father, mother, spouse and children. viii. Key Executive: means an officer of the Bank whose appointment is subject to prior non-objection of SAMA. ix. Person: means a natural or a legal person. x. Assessment Year: means a calendar year from 1st January to 31st December for determining the amount of annual premium payable by a Bank to the DPF;
* The Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency was replaced by the name of Saudi Central Bank in accordance with The Saudi Central Bank Law No. (M/36), dated 11/04/1442H, corresponding 26/11/2020G.
2. General Provisions
i. These Rules shall be called the Depositors Protection Fund Rules, 2015 (hereinafter called the DPF Rules); ii. The DPF Rules shall be applicable to all Banks, including all branches of foreign Banks licensed under the Banking Control Law that conduct banking business in Saudi Arabia. However, the provisions of these Rules shall not apply to the following:
a) branches of Saudi Banks operating outside the Kingdom; b) subsidiaries of Saudi Banks operating within or outside the Kingdom.
iii. All Banks, including all branches of foreign Banks, operating in Saudi Arabia shall be participants of the DPF and required to pay the prescribed premium; iv. The DPF Rules shall come into force with effect from 1st January 2016.
3. Establishment of the DPF
i. The DPF shall be established as an administrative unit in SAMA. The head of the DPF unit shall report to the Deputy Governor for Supervision; ii. The management and oversight of the DPF shall be provided by a governing committee appointed by the Governor of SAMA and its terms of reference will be approved by SAMA; iii. The governing committee may constitute one or more subcommittees and determine their terms of reference to ensure smooth functioning of the DPF.
4. Functions of the DPF
The DPF shall cany on all or any of the following functions:
i. Collect premiums and contributions; ii. Manage resources of the DPF and conduct its operations; iii. Evaluate the adequacy of the DPF’s funding from time to time; iv. Assess claims of Eligible Depositors for payments out of the DPF; v. Make payments of accepted claims to Eligible Depositors within applicable protection limits; vi. Perform all such other functions as may be incidental or related to the affairs of the DPF or required to achieve its objectives.
5. Resources of the DPF
i. The DPF’s resources shall consist of the following:
a) Initial and periodic premium payments from Banks; b) return on the investment of DPF’s resources; c) proceeds received from a Bank’s property in case of its sale or liquidation; d) Other sources of funding including loans and grants.
ii. If at any time, the resources of the DPF fall short of its liabilities, such shortfall may be covered in such manner as may be specified by SAMA and may include, inter alia, requiring Banks to make advance premium payments and/or increasing the rate and/or frequency of premium payments for which Banks will be notified in advance; iii. SAMA shall open and maintain a separate account in the name of DPF with itself and all premium payments and contributions shall be deposited in the said account.
6. Use of the DPF’s Resources
i. The DPF’s resources shall be used only for:
a) payments in relation to protected Deposits up to the applicable protection limits under the DPF Rules; b) repayment of principal and payment of commission/return on any loans obtained by the DPF; and c) meeting its operating expenses;
ii. The DPF’s resources shall be managed by the governing committee according to the guidelines approved by SAMA.
7. Protection of Deposits
i. The DPF shall insure the payment of Deposits held on an Eligible Depositor’s account(s) with a Bank up to the applicable protection limit as determined by SAMA from time to time. However, no financial liability shall be assumed by SAMA as a result of making any such determination; ii. The applicable protection limit shall be inclusive of any special commission/ return due or accrued on Deposits up to the cut-off date determined by SAMA.
8. Protection Limit
i. The protection limit for protection of Eligible Depositors shall be SAR 200,000 per Person per Bank. This means that the total amount payable by the DPF to any one Eligible Depositor in respect of his Deposit in a Bank shall not exceed SAR 200,000; ii. SAMA may, from time to time, having regard to the availability of funds with the DPF as also to the maintenance of financial system stability, raise the above protection limit as deemed appropriate.
9. Determining the Size of Protected Deposits
i. The total amount of a Bank’s liability to an Eligible Depositor shall be determined by adding up all such Eligible Depositor’s Deposits, including any return due or accrued thereon on or before the cut-off date set by SAMA. In establishing the Bank's total liability to an Eligible Depositor, foreign currency Deposits shall be converted into Saudi Riyals at the exchange rate determined by SAMA on the cut-off date; ii. Only one Deposit per Person per Bank shall be covered under the DPF. If an Eligible Depositor has more than one account with a Bank, all Deposits with that Bank shall be deemed to be one Deposit and be protected only up to the maximum limit of SAR 200,000. Where an Eligible Depositor is a joint owner of a Deposit with a Bank together with one or more other Persons, only his proportionate share of such joint Deposit(s) shall be taken into account, and, together with any other Deposits he may have with that Bank, be deemed to be one Deposit and be protected only up to the specified limit of SAR 200,000 per Person per Bank; iii. The Deposit of a legal Person shall not be aggregated with the personal Deposit of its owner(s) while determining the amount of protected Deposit; iv. Any Deposits which are subject to a regulatory freeze, or restrictions of any sort shall not be included while determining the amount of protected Deposits unless specifically allowed by SAMA; v. The amount of a protected Deposit shall be determined after deducting any sum of money which the Bank is legally entitled to deduct by way of set-off from the deposit held by a depositor with the Bank; vi. SAMA may provide further guidance on determining the size of Deposits as well as the procedure to be adopted for payment of the protected amount of Deposits.
10. Payment of Premium
i. Every Bank shall initially pay a flat rate premium to the DPF as may be specified by SAMA from time to time. However, SAMA may at any time change the basis for calculation of premium, and may in particular move from a flat rate to a risk-based method; ii. The annual premium owed by a Bank for an Assessment Year shall initially be 0.05% of the average amount of Deposits of Eligible Depositors held by the Bank. However, SAMA may review the premium rate from time to time and make changes therein as deemed appropriate after taking into account the relevant factors including size of the accumulated DPF. Any such change in premium rate shall be notified to Banks at least six months in advance; iii. The amount of premium shall be payable on a quarterly basis and calculated by Banks at the rate of one-fourth of 0.05% (i.e. 0.0125%) of the average amount of deposits of Eligible Depositors held by the Bank during the preceding calendar quarter. The quarterly average of deposits will be calculated by adding the opening and closing balance of deposits of Eligible Depositors during a calendar quarter and dividing it by 2. The payable premium must be paid by a Bank within thirty (30) days of the end of each calendar quarter. The first premium payment shall be for the quarter ending 31st March 2016 and shall be paid by 30 April 2016; iv. No premium contribution (or part thereof) shall be refundable to a Bank in any circumstance; v. The annual premium payable by a Bank shall be based on returns containing data of Deposits to be certified by its Managing Director or Chief Executive Officer and must be submitted in the form and within the deadlines determined by SAMA; vi. If a Bank fails to make a premium payment in full and on time, SAMA may impose a premium surcharge and take any other punitive action against the defaulting Bank as permitted under the Banking Control Law.
11. Submission of Return
i. Every Bank shall submit to SAMA a quarterly return containing information on the composition and amounts of its average Deposits for each calendar quarter. The return shall also set out in detail the calculation of the annual premium and shall be certified by the Managing Director or Chief Executive. The return shall be submitted to the DPF Unit within 30 days of the end of every calendar quarter; ii. If a Bank fails to submit the above return within the specified time or provides incorrect information, SAMA may take any action permitted under the Banking Control Law.
12. Responsibilities of Banks
i. A Bank shall pay the annual premium and any premium surcharge within such time and in such manner as specified by SAMA; ii. A Bank shall be liable to fully indemnify the DPF for any payments made to its Deposit holders, until its liquidation; iii. A Bank shall comply with and observe all relevant rules, regulations, directives/instructions, etc. issued by SAMA; iv. A Bank shall forthwith inform SAMA about any significant deterioration in its capital adequacy or liquidity position or any other major development which has a significant bearing on its safety and soundness.
13. Maintenance of Accounts
i. The DPF shall maintain separate accounts and other records and prepare annual financial statements including the profit and loss account and balance sheet; ii. The accounts of the DPF shall be audited by an external auditor to be appointed by SAMA for this purpose.
14. Miscellaneous Matters
i. SAMA may from time to time issue further instructions and guidance to the Banks to deal with any other related matters and to achieve the objectives of the DPF; ii. Any issues arising during the implementation of these rules shall be dealt with under the rules and regulations of SAMA and the applicable laws of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
*************
Depositors Protection Fund (DPF): Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q.1: What is the Depositors Protection Fund(DPF)
Ans.: The DPF is a fund established to protect eligible depositors. All banks including the branches of foreign banks licensed under the Banking Control Law that conduct banking business in Saudi Arabia are members of the DPF. The DPF will provide full protection to depositors having deposits of up to SAR 200,000, including principal and accrued commission/retum, with a member bank. For example, if a person had a deposit in a member bank with a principal balance of SAR 194,500 and accrued commission/return on this deposit of SAR 5,000 on the cut-off date, the full SAR 199,500 would be insured, since principal plus commission/return did not exceed the SAR200,000 protection limit for a single depositor.
Q.2: Why the coverage under DPF is restricted to SAR 200,000?
Ans.: The objective of the DPF is to provide adequate protection to eligible depositors. The protection limit of SAR 200,000 would fully insure more than 97% of depositors of banks. This is a high level of coverage and exceeds international norms of 80% to 90%.
Q.3: Why is the DPF established? I thought Saudi Arabia’s banking system is very safe?
Ans.: Yes, Saudi Arabia’s banking system is safe and sound. SAMA has a regulatory framework in place to ensure the safety and soundness of individual banks as well as the overall Banking System. SAMA also ensures that banks are well managed, well capitalized and have enough liquidity to meet their obligations to depositors. The DPF is a financial safety net and layer of protection for depositors. The objective is to build up a protection fund in good times rather wait for a crisis to happen.
Q.4: How does the DPF work?
Ans.: In the unlikely event of a member bank failure, SAMA premiums paid by member banks and other resources available with it.
Q.5: Who is covered under the DPF?
Ans.: Individuals and other non-bank depositors with accounts in member banks are covered. Non-bank depositors include sole proprietorships, partnerships, companies, unincorporated entities, etc. However, the following are not covered:
a) members of the board of directors and senior management of Bank (including its chief executive officer and Key Executives) as well as their Family Members; b) other Banks or financial institutions; c) shareholders holding in excess of 5% shares in the Bank d) Saudi government or quasi-government institutions; or e) Persons acting on behalf of any of the Persons mentioned in a) through c) above;
Q.6: What types of deposits are covered for protection under DPF?
Ans.: All types of deposits whether in local or foreign currency with member banks including current accounts, savings accounts, time deposits, inheritance accounts, unclaimed accounts, escrow accounts, client accounts, trust accounts, structured deposits, etc. are covered except the following:
a) a deposit that is not payable in Saudi Arabia; b) an inter-bank deposit; c) a negotiable instrument of deposit and any other bearer deposit; d) a repurchase agreement; and e) any other deposit or financial instrument as may be specified by SAMA.
Q.7: If I have deposits in several member banks, will all my deposits be added up for deposit protection purposes?
Ans.: No. Your deposits in different member banks are protected separately. The SAR200,000 deposit protection limit is applicable per depositor per member bank.
Q.8: If I have deposits in different branches of the same member bank, will all my deposits be protected separately?
Ans.: No. Deposits held in different branches of the same member bank will be consolidated for deposit protection purposes.
Q.9: As foreign currency deposits also enjoy protection under the DPF, are they separately protected from Saudi Riyal deposits?
Ans.: No. Saudi Riyal and foreign currency deposits are not separately protected if they are placed in the same member bank. Foreign currency deposits will be converted to Saudi Riyals and aggregated with local currency deposits for protection of up to SAR200,000.
Q.10: Do I need to sign up or pay a premium to be covered by the DPF?
Ans.: No action is needed from you as a depositor as all premiums and costs relating to coverage under the DPF are borne by member banks.
Q.11: In the event that a compensation is to be claimed from a failed bank, do I need to file a claim with the DPF or the bank?
Ans.: The DPF will provide details on how the compensation will be made. You do not need to file any claims. The DPF will make announcements for payment of compensation to eligible depositors through the public media and at the affected bank and its branches. If your deposit exceeds the compensation from the DPF, you can file a separate claim with the liquidator of the affected bank for the difference but you cannot claim what has already been compensated under the DPF.
Q.12: How the DPF will affect credit rating of a bank?
Ans.: The DPF is a regulatory financial safety net and should have a positive impact on credit ratings of member banks. The statement earlier issued by the Supreme Economic Council in October 2008 stating that the Saudi authorities continued to ensure the safety of local banks and bank deposits, has not been withdrawn. As the protection provided by the DPF is a designated layer of protection for the eligible depositors, it should provide additional comfort to the external rating agencies.
******************
Banking Products and Finance Activities
Responsible Lending Principles for Individual Customers
No: 46538/99 Date(g): 16/5/2018 | Date(h): 2/9/1439 Status: In-Force Responsible Lending Principles, issued by SAMA under Circular No. (46538/99) dated 02/09/1439H (17/05/2018), Amended by SAMA’s Circular No.( 40694/1) dated 09/09/1439H (24/05/2018).Note: This translation is provided for guidance. The governing text is the Arabic text.
Relevant Laws and Instructions
*These regulations have been replaced by the updated Debt Collection Regulations and Procedures for Individual Customers in accordance with circular No. (106889333), dated 06/09/1446H, corresponding to 05/03/2025G.
Chapter I Definitions
1. The following terms and phrases, wherever mentioned herein, shall have the meaning assigned thereto unless the context requires otherwise:
SAMA: Saudi Central Bank*.
Governor: Governor of Saudi Central Bank (SAMA).
Creditor: Banks and finance companies, supervised by SAMA and licensed to practice one or more activities of finance.
Principles: Responsible Lending Principles for Individual Customers.
Consumer: An individual who obtains or applies for a finance loan or at whom such finance is directed.
Finance Amount: The limit or the total amount made available to the consumer under a finance contract.
Term Cost: The term cost due by the consumer under a finance contract, which may be expressed as a fixed or changed annual percentage of the Finance Amount provided for the consumer.
Variable Term Cost: The term cost specified according to an index or a reference rate which must be explicitly stated in the finance contract; such a cost will change in accordance with the change in such an index.
Total Amount Payable by the Consumer: Finance amount plus all due costs that the consumer must pay as per provisions of finance contract, including term cost, fees, commissions, administrative costs, insurance and any expenses deemed necessary to obtain finance and excluding any expenses that the consumer can avoid, such as costs and fees customer must pay upon his/her violation of any obligations mentioned in the finance contract.
Monthly Credit Obligations: Total amount payable by the consumer, which is calculated on a monthly basis, as per the credit report issued by licensed credit bureaus and the consumer’s disclosure.
Gross Salary: The basic monthly salary (after deducting pension or GOSI contributions) plus all fixed allowances paid to the consumer by the employer on a monthly basis.
Total Monthly Income: The monthly average income of the consumer from any periodical income whether received on a monthly, annual or other periodic basis, including gross salary or any other income (allowances and compensation that are paid periodically, rental income, revenues of other investments, etc.) which can be reasonably verified, calculated as per provisions of Paragraph (17) hereof.
Monthly Disposable Income: The remaining amount of the consumer’s total monthly income for spending, investment or savings after deducting current or expected basic expenses and monthly credit obligations, calculated on a monthly basis.
Deductible Ratio: The ratio of consumer’s monthly credit obligations to total monthly income, calculated as per terms and conditions stated in Chapter IV on Quantitative Principles of Responsible Lending.
Deduction: The act of deducting an amount from the consumer’s gross salary or monthly pension.
* The "Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency" was replaced By the "Saudi Central Bank" in accordance with The Saudi Central Bank Law No. (M/36), dated 11/04/1442H, corresponding to 26/11/2020G.
Chapter II General Provisions
2. The principles herein aim to encourage responsible lending that meets the actual needs of consumers, especially those related to owning housing and assets rather than consumer purposes. The principles also aim to enhance financial inclusion by providing adequate financing for all segments of society, taking into account reasonable deductible ratios that the consumer can afford. In addition, the principles focus on ensuring fairness and competitiveness among creditors to make sure that their procedures and mechanisms are effective and efficient.
3. The principles apply to all creditors and finance activities directed at consumers. These activities encompass all credit products and programs designed for individuals, including, but not limited to, personal finance, vehicle finance, credit cards and real estate finance.
4. The creditor must set appropriate internal controls and procedures to ensure compliance with the principles herein, other relevant laws, regulations, and instructions. It must also pay special attention to documenting information and maintaining documents provided by consumers, thereby gaining an acceptable degree of reliability.
5. If the creditor assigns certain related work to another party or other parties, it must ensure that those parties act in compliance with the principles herein and that they do not contravene the provisions hereof, other relevant laws, regulations and instructions.
6. The creditor must take necessary measures to ensure that the principles herein are fully understood and adhered to by its staff and are shared with its consumers. It must not only focus on the number of financing agreements or the value of finance, but it must also take into account such principles when preparing its incentive programs for its staff. It must ensure that no programs are developed in a way that may lead to irresponsible finance.
7. The creditor must keep sufficient records that show its commitment to the principles herein, other related laws, regulations, and instructions.
Chapter III Qualitative Principles of Responsible Lending
8. The creditor must adopt a clear, transparent and documented scientific method, criteria and procedures to evaluate the creditworthiness of the consumer and his/her ability to repay. These methods, criteria, and procedures must be in accordance with the best practices in this area without prejudice to the principles herein. The board of directors of the creditor must adopt, revise annually, and update when necessary these criteria and procedures. The creditor must apply these procedures and document this application in the finance file before granting finance.
9. Upon the consumer’s consent, the creditor must examine the credit record of the consumer to verify his/her solvency, ability to meet the monthly credit obligations, and his/her credit behavior. The information obtained must be documented in the finance file. The creditor must ask the consumer to disclose, in writing, any other credit obligations he/she has, such as loans from his/her employer, friends or relatives, whether current or expected, and this must be documented in the finance file. Upon granting the finance, the creditor must, in accordance with the provisions of relevant laws, regulations and instructions, register all credit information relating to the finance granted to the consumer with licensed credit bureaus after obtaining his/her consent. The creditor must then update such information throughout the period of dealing with the consumer. The creditor must reject a finance request if it does not obtain the consumer’s consent to all matters stated in this paragraph.
10. The creditor must assess the ability of its consumers to meet monthly credit obligations, especially in cases where consumer's deductible ratios are close to the maximum deduction limits set out herein. The assessment of the ability to meet monthly credit obligations is primarily based on the assessment of the consumer’s monthly disposable income that can be used to meet his/her monthly credit obligations. Basic expenses that vary according to several factors, such as income levels, number of dependents, and residence place, whether the consumer owns such a place, rents it, or otherwise, must be taken into consideration, the creditor should develop appropriate rules in line with best practices to apply comprehensive factors to various categories of consumers. The finance is considered bearable if the consumer’s total monthly credit obligations, upon granting him/her finance, are less than the consumer’s monthly disposable income. This must also be consistent with the deductible ratios stated in Chapter IV on Quantitative Principles of Responsible Lending, Paragraphs (15, 16, and 17) hereof.
11. Based on a credit study and assessment of consumer’s monthly disposable income, the creditor must use financial models and tools to measure the consumer’s ability to meet monthly credit obligations and to what extent such finance suits his/her needs and circumstances. Such models depend on some basics, including identifying and classifying the regular basic expenses of various consumers. Basic expenses cover, as a minimum, the following groups:
a. Food expenses, which are affected by the number of dependents;
b. Housing (rent) and services’ expenses, which depend on whether the consumer is the owner or tenant of the house or otherwise;
c. Wages for domestic worker;
d. Education expenses, which are affected by the number of dependents;
e. Health care expenses, which are affected by the number of dependents;
f. Transportation and communications expenses;
g. Insurance expenses for individuals and their dependents, as the case may be; and
h. Any expected costs or expenses.
In addition to the above-mentioned expenses, existing monthly credit obligations, which can be verified through licensed credit bureaus; finance granted by the consumer’s employer, friends, or relatives; and any other finance that is repaid through installments on a monthly, semi-annual, or other basis must be considered.
12. The creditor must ensure both the efficiency and effectiveness of such financial models and tools, used to measure the consumer’s ability to repay finance. It should benefit from its information and data, as well as legally available general statistics sources. The methodology of such models and tools must include, as a minimum, the following:
a. A mechanism to calculate and analyze total monthly income;
b. A mechanism to calculate and analyze monthly credit obligations; and
c. A mechanism to calculate and analyze basic expenses, including the following:
o A list of basic expense indices compared to verified data;
o The ability of changing basic expenses according to income levels; and
o The ability of changing basic expenses according to the number of dependents.
Chapter IV Quantitative Principles of Responsible Lending
This article is amended in accordance to SAMA circular No. (40694/1) dated 09/09/1439.13. Terms for calculating the consumer’s monthly credit obligations must be observed as follows:
a. The monthly credit obligation of a credit card must be equal to the minimum repayment of the credit ceiling for each credit card issued to the consumer.
b. Monthly credit obligations include all credit obligations to creditors and specialized government lending institutions; any other credit obligations, such as loans from employers, friends, or relatives; and other types of finance.
c. Before granting finance with variable term cost and upon calculating the monthly credit obligations of such finance, the creditor must take into account including additional margin in the term cost. The term cost and the additional margin must be considered when documenting the monthly credit obligations for such finance in the consumer’s credit report in the credit bureau in order to avoid risks of changes to term cost.
d. Upon granting finance, the creditor must be responsible when the deductible ratio exceeds the permitted limit hereunder if it is due to a change in the term cost. If this happens, the creditor must reschedule the repayment periods of the finance and must not add a term cost that may lead to exceeding such limits.
e. Monthly credit obligations of finance where all installments are not equal must be calculated based on monthly installments that are fixed at the monthly average level for all installments regardless of whether such finance is payable by equal repayments or requires a final payment.
14. Terms for calculating the total monthly income of the consumer must be observed as follows:
a. Gross salary, as documented by any means by the employer, must be included in such calculation.
b. As for other income, half of the monthly average of the total amount earned by the consumer from any periodical income, whether monthly, annual or other, must be included in such calculation. The other income must include periodically-paid allowances and compensation, rental income, revenues of investments, dividends, etc., which can be reasonably verified via, at least, a two-year bank statement or official documents proving their continuity.
c. Government subsidies, such as those given through the Citizen Account Program or social security, must not be counted as part of the total monthly income of the consumer. However, government subsidies that are documented through contracts with a citizen and that are provided by the Ministry of Housing or the Real Estate Development Fund may be incorporated in the total monthly income of the consumer in real estate finance products.*
15. Deductible ratios for consumers whose total monthly income is SAR 15,000 and less must be subject to the following restrictions:
a. The monthly credit obligations of finance, which are linked only to the monthly deduction of the gross salary of consumer, must not exceed 33.33% of the gross salary for employees and 25% for retired consumers.
b. Monthly credit obligations, excluding monthly credit obligations for real estate finance, must not exceed 45% of the total monthly income of the consumer.
c. Monthly credit obligations of finance must not exceed 55% of the total monthly income of the consumer However, for the consumers who are benefiting from the Ministry of Housing or the Real Estate Development Fund for mortgage products, the monthly obligations of finance must not exceed 65% of the total monthly income.*
16. Deductible ratios for consumers whose total monthly income is more than SAR 15,000 and less than SAR 25,000 must be subject to the following restrictions:
a. The monthly credit obligations of finance, which are linked only to the monthly deduction of the gross salary, must not exceed 33.33% of the gross salary for employees and 25% for retired consumers.
b. Monthly credit obligations, excluding monthly credit obligations for real estate finance must not exceed 45% of the total monthly income of the consumer.
c. Monthly credit obligations of finance must not exceed 65% of the total monthly income of the consumer.
17. Deductible ratios for consumers whose total monthly income is SAR 25,000 and more must be subject to the following restrictions:
a. Monthly credit obligations of finance, which are linked only to the monthly deduction of the gross salary, must not exceed 33.33% of the gross salary for employees and 25% for retired consumers.
b. Credit obligations of finance are subject to the credit policies of the creditor. The creditor must assess the ability of its consumers to meet monthly credit obligations stated herein.
18. Finance term must not exceed (5) years or (60) months from granting such finance, except for real estate finance and credit cards.
19. SAMA may review and amend periodically the ratios in Paragraphs 15, 16, and 17 hereof, taking into account the soundness and stability of the financial system and the forecasts for economic growth.
*Amended in accordance to SAMA circular No. (40694/1) dated 09/09/1439.
Chapter V Publishing and Coming into Force
20. The Principles hereof are issued by a decision of SAMA Governor and published on SAMA website.
21. The provisions of Paragraphs 15, 16 and 17 hereof must be applicable as of the date of circulating such principles.
22. All provisions hereof must come into force as of 01/12/1439H (12/08/2018). The principles herein must be fully observed from that date.
23. The principles herein must supersede any provisions to the contrary.
Regulations for Consumer Financing
No: 351000116619 Date(g): 7/7/2014 | Date(h): 10/9/1435 Status: In-Force These Regulations shall be applicable to Financing Contracts and all related Guarantee Agreements executed by banks licensed and authorized by SAMA. SAMA is the sole authority empowered to apply these Regulations and to take necessary measures as it deems appropriate regarding any violations of these provisions, including imposing punitive charges and or enforcement actions as applicable under the Banking Control Law. These Regulations supersede and replace the Regulations for Consumer Credit of October 2005 issued as circular 33232-MASH/516 dated 23/9/1426 H and its subsequent updates. SAMA may update these Regulations as and when required.
SAMA may, at its discretion, impose a restriction on a Creditor under which its Consumer Financing portfolio may not exceed a specified percentage of its total Financing portfolio.
Definitions
Article 1: Definitions
Each of the following words and phrases, wherever it appears in this Regulation, shall have the meaning following it in this article unless the context indicates otherwise:
Adequate notice: a printed notice to a Borrower that sets forth clearly the pertinent facts so that the Borrower may reasonably be expected to have noticed it and understood its meaning. The notice may be given by Guaranteed Communication Means reasonably assuring receipt by the Borrower.
Advertisement: a commercial message in any medium that promotes, directly or indirectly, a Financing product.
Amount of Financing: the limit or the total amount made available to a Borrower under a Financing Contract.
Annual Percentage Rate or APR: the discount rate at which the present value of all payments and installments that are due from the Borrower, representing the Total Amount Payable by the Borrower, equals the present value of all payments of the Amount of Financing available to the Borrower on the date on which the Financing amount or the first payment thereof is available to the Borrower, calculated in accordance with Annex 1.
Authenticated Communication: Borrower instructions received through a recorded, verifiable and retrievable medium such as paper, electronic or verbal recording.
Borrower: a natural person who, in Financing transactions covered by this Regulation, obtains Financing for purposes outside his trade or profession.
Business Day: a day on which the banks are open for business to the general public.
Calendar Day: any day in a month, including weekends and holidays.
Change in Circumstance: death, disability (partial or total), retirement (mandatory or voluntary), loss of job or bankruptcy of a Borrower*.
Consumer Financing: a Financing granted to a Borrower as follows:
- The Financing is for purposes unconnected with the Borrower’s commercial or professional activity, generally including personal Financing, car Financing, home improvement Financing, and similar products as approved by SAMA.
- Such Financing is granted for the purchase of goods and services for consumption or other needs of the Borrower as identified above, e.g. for the purchase of furniture, consumer durables, automobiles, household items, education, etc.
- Real estate Financing and Finance Leasing are excluded.
- Financing against shares (Margin Lending) is also excluded.
Creditor: a bank licensed and authorized by the Saudi Central Bank.
Default: any breach of the terms and conditions of the Financing Contract and the nonpayment by a Borrower of their monthly installment for 90 Calendar Days from its due date.
Default Notice: a notice from a Creditor to a Borrower under a Financing Contract with the Creditor notifying that he/she is delinquent in payments.
Draw-down: an Amount of Financing drawn by the Borrower under a Financing Contract.
Financing: the right to incur new debt and defer payment, or the right to defer existing debt.
Financing Contract: an agreement by which a Creditor grants, or promises to grant, a Consumer Financing or similar financial accommodation to a Borrower.
Gross Salary basic monthly salary (less GOSI and pensions contributions) plus all fixed allowances paid to Borrower by the employer on a monthly basis.
Guarantee Agreement: an ancillary agreement concluded by a Guarantor and guaranteeing or promising to guarantee the fulfillment of any form of Financing granted to a Borrower.
Guaranteed Communication Means: registered mail, hand delivery, and any recorded, verifiable and retrievable electronic medium.
Guarantor: a natural person who guarantees or promises to guarantee the fulfillment of any Financing granted to a Borrower.
Initial Disclosure: the information required to be provided to the Borrower by a Creditor upon opening a Consumer Financing account in accordance with Section 5 of these Regulations.
Licensed Credit Bureau: a credit information company licensed by SAMA to collect and maintain credit information on consumers and provide the same to members upon request.
Optional Feature: features and services which are not part of the standard features or services of the Financing Contract product, requiring payment of additional fees and/or Term Cost by the Borrower.
Outsourcing: an arrangement under which a third party (i.e. a service provider) undertakes to provide a Creditor with a service previously carried out by the Creditor itself or a new service to be launched by the Creditor. Outsourcing can be to a service provider in Saudi Arabia or overseas and the service provider may be a unit of the same Creditor (e.g. head office or an overseas branch), an affiliated company of the Creditor's group or an independent third party, and is subject to the requirement to fully comply with SAMA Rules on Outsourcing issued vide 34720/BCS/424 dated 17/7/1429H Correspondent to 20/7/2008.
Refinancing: repayment of an existing Financing from the proceeds of a new Financing granted to the Borrower.
Repayments or Deductions: deductions from the Gross Salary or monthly pension entitlement of a Borrower towards repayment of Financing. Only deductions for Real Estate Financing repayments and divorce settlements are excluded.
SAMA: the Saudi Central bank**.
Satisfactorily Resolved: resolution of the dispute in accordance with the procedures and timeframes for resolving disputes.
Secured Financing: a Financing that is collateralized by assignment of rights to property including a security interest in personal property or real estate taken by the Creditor as collateral. A Financing may be secured by pledge of cash (deposits), tangible goods or other collateral.
Term Cost: the term cost due and payable by the Borrower under the Financing Contract; this must be expressed as a fixed annual percentage of the Amount of Financing obtained by the Borrower.
Term to Maturity: the period from initial disbursement to the date on which the final repayment of the relevant Financing is due.
Total Cost of Financing: all costs payable by the Borrower under a Financing Contract other than the Amount of Financing, including Term Cost, fees, commissions, administrative services fees, insurance, and any charges required to obtain Financing, but excluding any expenses the Borrower can avoid, such as costs or fees due and payable by the Borrower as a result of the Borrower's breach of any obligations contained in the Financing Contract.
Total Amount Payable by the Borrower: the Amount of Financing plus the Total Cost of Financing.
*The definition of "Change in Circumstance" has been amended in accordance with Circular No (381000095088) dated 10/09/1438H. The amended definition is currently available only in Arabic.
** The "Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency" was replaced By the "Saudi Central Bank" in accordance with The Saudi Central Bank Law No. (M/36), dated 11/04/1442H, corresponding in 26/11/2020G.
Section One Scope of Application
Article 2: Application of the Regulations
- These Regulations apply to all kinds of Consumer Financing.
- These Regulations do not apply to lease or real estate Financing or margin lending.
Article 3: Meaning of Consumer Financing and Amount of Financing
- For the purposes of these Regulations, Consumer Financing is granted under a Financing Contract in case of any of the following:
- The repayment of a debt owed by a person (the Borrower) to another (the Creditor) is deferred; or
- a person (Borrower) incurs a deferred debt to another (Creditor).
- For the purpose of complying with Article 14(1), the Creditor must calculate the Amount of Financing based on the Borrower's Gross Salary or monthly pension entitlement (as the case may be) when the application for Financing is submitted.
- For the purposes of these Regulations, Consumer Financing is granted under a Financing Contract in case of any of the following:
Section Two Financing Contracts and Guarantee Agreements
Article 4: Financing Contracts and Guarantee Agreements
- A Financing Contract or Guarantee Agreement must be in the form of-
- a written contract document signed by the Borrower or Guarantor and the Creditor; or
- a written contract document signed by the Creditor and constituting an offer to the Borrower that is accepted in writing by the Borrower.
- All Financing Contracts, application forms, Guarantee Agreements, repayment schedules, Borrower acknowledgement letter and other documentation related to Consumer Financing must be in Arabic and if the Borrower requests that documentation be prepared in English, the documentation shall be prepared in both languages. The Creditor must provide copies thereof to the Borrower. In the event of a divergence between the Arabic and the English text of any such document, the Arabic text prevails.
- Each contracting party must receive a copy of the Financing Contract or Guarantee Agreement (as the case may be).
- A Financing Contract or Guarantee Agreement must be in the form of-
Article 5: Necessary content of Financing Contracts or Guarantee Agreements
1- The Creditors must provide a synopsis for each Financing Contract to the Borrower that contains, in clear and succinct language, basic information about the Financing, including the Total Cost of Financing. The receipt of this synopsis by the Borrower must be documented and included in the Financing file.
2- The Financing Contract must include at least the following information:
(a) names of the parties to the Financing Contract, the national identity number or Iqama number of the Borrower as applicable, official addresses, means of contact including telephone and mobile numbers and e-mails, if available;
(b) type of Financing;
(c) Term to Maturity;
(d) Amount of Financing;
(e) conditions for drawing down the Amount of Financing, if any;
(f) description of the calculation method for determining Term Cost to enable the Borrower to understand the Term Cost and to distribute the cost over the Term to Maturity;
(g) Term Cost and the conditions governing the application of the Term Cost and any index or reference rate applicable to the Term Cost;
(h) Annual Percentage Rate (APR);
(i) Total Cost of Financing and the Total Amount Payable by the Borrower, calculated at the time of entering into the Financing Contract; stating the assumptions made in order to calculate that amount;
(j) instalment amounts payable by the Borrower, number of instalments, due dates of instalments, and method of distribution over the remaining amounts;
(k) charges, commissions and costs of administrative services;
(l) payment periods of charges or amount that must be paid without paying the Amount of Financing; and related payment conditions;
(m) consequences of delayed repayment of instalments;
(n) where applicable, notarial fees;
(o) collateral and required insurance;
(p) procedures for exercising the right of withdrawal, if any, its conditions and resulting financial obligations;
(q) procedures for early repayment and indemnifying the Creditor, if applicable, and the method for determining such indemnity;
(r) procedures for dealing with collateral if its value decreases, if applicable;
(s) procedures for exercising the right of termination of the Financing Contract;
(t) Borrower's consent to filing his/her information in credit bureau records; and
(u) any other data or information stipulated by the Agency.
Article 6: Amendment of the Financing Contract
Any amendment (including any addition to) of a Financing Contract by the Creditor after it has been signed by the Borrower is invalid unless the Borrower has agreed in writing.
Article 7: Copy of Financing Contract and Guarantee Agreement for Borrower and Guarantor as applicable
If a Financing Contract or Guarantee Agreement needed to be signed by the Borrower or Guarantor and returned to the Creditor, the Creditor must give each of the Borrower or Guarantor, as applicable, a signed copy they may keep, not later than 10 Calendar Days after the Financing Contract or Guarantee Agreement has been entered into.
Article 8: Annual Percentage Rate (APR)
- The APR must include all mandatory charges or costs under a Consumer Financing as shown in the relevant advertising notices or materials.
- The Financing Contract must stipulate the use of the declining balance method in distributing the Term Cost over the maturity period, which means that the Term Cost is allocated pro-rata to installments based on the remaining balance of the Amount of Financing at the beginning of the period for which an installment is due.
- The Term Cost is fixed.
Article 9: Fees and Charges
All fees, costs and administrative services charges to be recovered from the Borrower by the Creditor must not exceed the equivalent of (1%) of the Amount of Financing or (5,000) five thousand Saudi riyals, whichever is lower.
Article 10: Right of Termination or Withdrawal
- The Borrower may, by giving written notice to the Creditor within 10 Calendar Days from the date of execution of a Financing Contract, terminate the Financing Contract, unless
- Draw-down of any part of the Amount of Financing has occurred; or
- A credit card or other means of obtaining Financing provided to the Borrower by the Creditor has been used to acquire goods or services for which Financing is to be advanced under the Financing Contract.
- In the event of termination under Article 10(1), the Creditor may not charge or claim any Term Cost and or fees from the Borrower unless the conditions under Article 10(1)(a) or (b) above have been met.
Clarifications in accordance with Circular No. (381000095091) dated 10/09/1438H.This part is currently available only in Arabic. Please Click here to read the Arabic version.
- The Borrower may, by giving written notice to the Creditor within 10 Calendar Days from the date of execution of a Financing Contract, terminate the Financing Contract, unless
Article 11: Early payments
- A Creditor must accept any payment under a Financing Contract before its due date as partial payment if it is equivalent to one full installment or multiples thereof.
- A Creditor must credit each payment made under a Financing Contract to the Borrower's account promptly after receipt of such payment.
- The Borrower may prepay, at any time, the remaining Amount of Financing without incurring any Term Cost for the remaining period. The Creditor is entitled to compensation from the Borrower for the following:
- The cost of re-investment, which may not exceed the Term Cost for the three months following the payment, calculated on the basis of a declining balance; and
- The expenses the Creditor pays to a third party as a consequence of the Financing Contract for the remaining period of the Consumer Financing if such expenses are unrecoverable, and provided that such expenses are properly recorded in the Borrower's Financing file.
- The Creditor must notify the Borrower in writing of all such fees payable by the Borrower as referenced under Art. 11(3)(a)and (b) above. The Creditor must give that notification by Guaranteed Communication Means within 10 Business Days after the first to occur of:
- receipt by the Creditor of a notice from the Borrower of the intended prepayment; or
- receipt by the Creditor of the prepayment,
Article 12: Balance Transfer
- Creditors must quickly facilitate the transfer of balance(s) to other Creditors in the Consumer Financing accounts of their Borrowers. Creditors must not unreasonably withhold their consent to a balance transfer request they receive.
- Creditors may not unreasonably withhold the issuance of a balance statement or certificate of outstanding liabilities requested by the Borrower; these must be issued within 7 Business Days from the date of request.
Article 13: Assignment of Rights
- If the Creditor assigns rights under a Financing Contract or the Financing Contract itself to a third party or issues securities against rights under the Financing Contract, the Borrower may use against the assignee any defense that would have been available to him against the original Creditor.
- The Creditor must receive a no-objection letter from SAMA before he can assign a Consumer Financing or a portfolio of Consumer Financings to another party.
Article 14: Maximum Credit Limit and Maximum Term to Maturity
- Before granting a new Consumer Financing or increasing the limit of any Consumer Financing and without prejudice to the requirements of any applicable law or regulation, a Creditor must ensure that the total monthly Repayments or Deductions recovered from a Borrower under his Consumer Financing obligations to all Creditors do not exceed 33.33% of the Borrower's Gross Salary during the period in which those Repayments or Deductions are made. For retired Borrowers, the deduction limit is 25% of their monthly pension.
- The Creditor must first obtain the Borrower's prior approval and then obtain and examine the credit record of the Borrower from one or more of the Licensed Credit Bureaus, to confirm the Borrower's compliance with the requirement under Article 14(1), his solvency, repayment capacity and credit conduct. The confirmation of such prior approval by the Borrower must be documented in the Borrower's Financing file.
- The Creditor must, upon the approval of the Borrower, register the Borrower's credit information with one or more of the Licensed Credit Bureaus in accordance with the relevant laws, regulations and instructions. Such information shall be updated throughout the period of dealing with the Borrower.
- The Creditor must decline a Financing request if he does not obtain the approval of the Borrower as referred to in Article 14(2) and 14(3) above.
- Creditors must ensure that the maximum Term to Maturity of a Consumer Financing does not exceed 5 years from the date of initial disbursement.
- *In the event of a Change in Circumstance of the Borrower, Creditors may reschedule the repayment terms of the Consumer Financing (provided no new Financing is being granted and without any change to the Term Cost under the original Financing Contract) in accordance their credit policies. Creditors must provide SAMA with a half-yearly report of all Consumer Financings that have been rescheduled.
- In calculating the maximum deductions of one third (33.33%) for Borrowers and one fourth (25%) for pensioners, Creditors must include all Consumer Financing Repayments or Deductions, including the minimum monthly payment required for all credit cards issued to the Borrower.
*Article 14(6) has been amended in accordance to Circular No (381000095088) dated 10/09/1438H. The amended article is currently available only in Arabic.
Section Three Obligations and Accountability
Article 15: General Requirements and Obligations of Creditors and Borrowers
- Consumer Financing granted on the basis of any security other than the deduction of salary or pension payments (e.g. against lien of deposits or assignment of other regular earnings or pledge of collateral) is not subject to the provisions under Article 14(1).
- A Creditor must carry out proper risk management procedures such as the use of credit scoring models for the granting or renewal of all Consumer Financings and must assign appropriate credit limits to its Borrowers.
- Prior to granting a new Consumer Financing, a Creditor must have received a Borrower request through Authenticated Communication or the execution of a Financing Contract. A Creditor may not increase the Financing limit of its Borrower without receiving a request through Authenticated Communication from its Borrower seeking such an increase. Each such increase/amendment in the Financing Contract requires execution of a new Financing Contract.
- Creditors are required to obtain knowledge of the purpose of the Consumer Financing from the Borrower and document that. This confirmation must be a part of a written acknowledgment by the Borrower clearly stating that he has fully understood the terms and conditions and confirms the execution of the respective Financing Contract.
- Creditors are only allowed to refinance Consumer Financing accounts of those Borrowers who have repaid at least 20% of their original Amount of Financing under their Consumer Financing account.
- Creditors refinancing the Consumer Financing accounts of their Borrowers must fully comply with the disclosure requirements under Section 5, Additionally, the Borrower must be provided with a break-down of the refinanced amount, clearly identifying the refinanced amount that will credited to his/her account, net of all identified fees and charges and the settlement of the original outstanding balance prior to a Refinancing.
- Borrowers opting for early retirement are required to ensure that their pension payments continue to be routed to the Creditor in the event of outstanding balances under their Consumer Financing account. A Creditor may require a suitable undertaking from the Borrower affirming the foregoing arrangement.
- Additional features or services requiring additional payment of fees and charges which are optional to the primary product features of the Consumer Financing may not be added on or embedded into the Consumer Financing account and must be clearly represented as an Optional Feature. A Borrower must have indicated his/her desire to obtain such services by Authenticated Communication before their inclusion in the account. Creditors must also clearly disclose all fees and charges for these services to the Borrower within their offer for such Optional Features.
- A Creditor must promptly advise its Borrowers of the following amendments and or changes in their Financing Contract by giving them at least 30 Calendar Days prior written notice:
(a) any increase of the annual fees and/or handling fees charged to the Borrower;
(b) an increase in recurring fees or charges
(c) any new fees or charges.
(d) any other changes.
- The Borrower may terminate the relevant Financing Contract with the Creditor if he/she does not agree to such amendment, change or modification by notifying the Creditor of his/her desire to terminate the Financing Contract within ten (10) Calendar Days after his/her receipt through Authenticated Communication of the notification of the aforementioned changes, subject to full settlement of all outstanding balances on the Consumer Financing account. The aforementioned notice must advise Borrowers of the 10 Calendar Day termination period.
- A Creditor engaging in Outsourcing any component of its Consumer Financing Business must comply with the Rules on Outsourcing issued by SAMA.
- A Creditor is required to implement a clearly defined Code of Conduct for employees engaged in roles involving sales and marketing of Consumer Financing products and follow-up and collection of impaired and delinquent Consumer Financing Accounts. (Creditors are also required to be in compliance with SAMA circular MAT/8211 dated 1/4/1431H.) A Creditor must provide those employees with a copy of the Code of Conduct and obtain their acknowledgement of receipt. The Code of Conduct must prohibit the following:
(a) Any contact with neighbours, relatives, colleagues or friends of the defaulting Borrower for the purpose of requesting or conveying information on the solvency of the Borrower or Guarantor.
(b) Any communications (verbal or written) to the Borrower or Guarantor conveying incorrect information on the consequence of defaulting on their obligations to the Creditor.
(c) Unauthorized repossession of the pledged collateral without judicial proceedings or the specific consent of the Borrower.
(d) Communicating with the defaulting Borrower using envelopes tagged with inscriptions identifying contents as containing debt collection information.
(e) Any breach of confidentiality of Borrower information, conflict of interest and breach of ethical values.
- Creditors are required to have structured training programs for all new staff and Consumer Financing product knowledge programs for staff involved in marketing and sales and customer service for Consumer Financing products.
- A Creditor must issue procedural rules to handle Borrower complaints relating to Consumer Financings and to ensure that Borrowers are made aware of the procedure and contact details of the complaint handling unit/department.
- If a Borrowers' application for any Financing facility is declined, the Creditor must provide the Borrower with a written reason for the rejection through Guaranteed Communication Means.
- Upon full and final repayment of the Consumer Financing by the Borrower, the Creditor is required to issue a no liability or clearance letter within 7 Business Days from the date of full and final settlement und update his record with a Licensed Credit Bureau.
Article 16: Non Performance of Financing Contract and Guarantee Agreements
- A Creditor may only proceed to enforcement against a Guarantor if the Borrower is in Default and has failed to comply with a Default Notice for a period of not less than 30 Calendar Days from the date of receipt.
- Creditors, their representatives, and any other assignees of the Creditor's rights under the Financing Contract or Guarantee Agreement may not take disproportionate, excessive or unreasonable measures to recover amounts due to them in the event of non-performance of aforementioned agreements
- A Creditor may demand immediate repayment in the event of Default only through a Default Notice requesting the Borrower, or where applicable, the Guarantor to comply with his/her obligations under the Agreement within 30 Calendar Days from the date of the issuance of notice.
- A Default Notice is not required in the event of any of the following:
(a) Fraudulent activities by the Borrower or Guarantor, which must be proven by the Creditor;
(b) Steps taken by the Borrower to sell or attempt to sell financed goods to which the Creditor has retained title or pledged collateral without due authorization of the Creditor.
- A Creditor may suspend Draw-downs under a Financing Contract in the event of a failure by either the Borrower or the Guarantor to abide by its terms and conditions in a Default. However the Creditor is required to give notice of its intent to suspend Draw-downs to the Borrower and the Guarantor (if any) without delay.
- A Creditor is required to provide without delay and upon request of the Borrower, a detailed statement of account incorporating all applicable fees, Term Cost and charges including any administrative charges, free of charge in the event of a Default or prepayment of the Consumer Financing.
- A Creditor may not bring an action for the enforcement of security over goods pledged as collateral without first obtaining approval from the Committee for Settlement of Banking Disputes if:
(a) the Borrower has repaid 75% of the Amount of Financing; and
(b) the Borrower has not provided his/her consent to the Creditor (whether in the Finance documentation or otherwise) to enforce that security.
Section Four Advertising
Article 17: Advertising Consumer Financing Products
- The Creditor must indicate in all product advertisements its name, logo, any identifying representation and contact details.
- The advertisement must disclose, in a manner that is clear to the Borrower, the name and Annual Percentage Rate of the advertised product and shall not include other rates such as the Term Cost.
- The Creditor may not do any of the following:
(a) Provide an advertisement that includes a false offer or statement or claim expressed in terms that would directly or indirectly deceive or mislead the Borrower.
(b) Provide an advertisement that includes the unlawful use of a logo, a distinctive mark, or a counterfeit mark.
- SAMA may require any Creditor who does not abide by the provisions of this Article to withdraw the advertisement within one Business Day of notice SAMA from to that effect.
- Furthermore, SAMA may take other punitive actions as required.
Section Five Rules of Information Disclosure
Article 18: General disclosure
A Creditor is required to provide the Borrower in writing with the Initial Disclosure information stated in Article 21 below. The Initial Disclosure must be made in clear and easy-to-read language duly highlighting terms and conditions which may affect the Borrower's rights and obligations, and the Creditor must use any format specified by SAMA from time for that purpose. Furthermore, the specific terms contained under Article 21 (1) (b) and (c) and information on the Total Cost of Financing must be included in the Initial Disclosure statement.
Article 19: Manner of Disclosure
- For the purpose of these Regulations, a Creditor must provide the Borrower with a written disclosure statement that provides the information required by these Regulations to be disclosed.
- A disclosure statement may be part of a Financing Contract or an application for a Consumer Financing or may be an annex to the foregoing documents.
- The Creditor is required to obtain written acknowledgement from the Borrower confirming he/she has received and read the Initial Disclosure statement.
- Information disclosed in a disclosure statement may be based on a reasonable assumption or estimate and such information must be clearly identified to the Borrower as an assumption or estimate.
- A disclosure statement, or consent in relation to a disclosure statement, must be in plain, clear and concise language. It must be presented in a manner that is logical and likely to bring to the Borrower's attention the information required by these Regulations to be disclosed.
- If the Borrower consents by Authenticated Communication, the disclosure statement may be provided by electronic means in an electronic form that the Borrower can retrieve and retain.
- A disclosure statement is deemed to be provided to the Borrower:
(a) on the day recorded as the time of sending by the Creditor's server, if provided by electronic means, and the Borrower has consented to receive it by electronic means.
(b) on the day recorded as the time of sending by a fax machine, if provided by fax and the Borrower has consented to receive it by fax;
(c) ten Calendar Days after the postmark date, if provided by registered mail; or
(d) when it is received, in any other case.
Article 20: Timing of Initial Disclosure
A Creditor that proposes to enter into a Financing Contract with a Borrower must provide the Borrower with the Initial Disclosure statement required by these Regulations prior to or upon entering into the Financing Contract by the Borrower and the Creditor.
Article 21: Initial Disclosure – Content
- A Creditor that enters into a Financing Contract with a Borrower must provide the Borrower with an Initial Disclosure statement that includes the following information:
(a) The initial limit of the Financing, if it is known at the time the disclosure is made;
(b) The APR and the annual Term Cost;
(c) The nature and amounts of any recurring non-Term Cost charges;
(d) The minimum payment during each payment period and the method for determining it;
(e) Each period for which a statement of account is to be provided;
(f) The date on and after which Term Cost accrues;
(g) The particulars of all charges and administrative fees that may be imposed;
(h) information about any Optional Feature in relation to the Financing Contract that the Borrower accepts in writing, the charges for each Optional Feature and the conditions under which the Borrower may cancel that feature;
(i) the manner in which the Term Cost is calculated; and
(j) information on all applicable charges including reporting of Default cases to a Licensed Credit Bureau or appropriate Regulatory Authorities as per SAMA's approval.
- If the initial limit of the Financing is not known when the Initial Disclosure statement is made, the Creditor must disclose it in:
(a) The first statement of account provided to the Borrower; or
(b) In a separate statement that the Borrower receives on or before the date on which the Borrower receives that first statement of account.
- If a Financing Contract is amended, the Creditor must, in writing and within 30 Calendar Days or more before the amendment takes effect, disclose to the Borrower and Guarantor (if any), any changes to the agreement pertaining to items referred to under Article 21(1) except changes to the following:
(a) A decrease in charges other than Term Cost or Default charges;
(b) A change concerning information about any Optional Feature in relation to the Financing Contract.
- An amendment referred to in Article 21(3) must be disclosed in the first statement that is provided to the Borrower after the amendment is made.
- If a Creditor offers to defer or skip a payment or installment under a Financing Contract, the Creditor must, with the offer, disclose in a prominent manner whether Term Cost will continue to accrue during any period covered by the offer if the offer is accepted. Creditors must ensure compliance with Article 14(5), i.e. the maximum Term to Maturity may not exceed 5 years.
Section Six Dealing with Borrowers
Article 22: Rules for dealing with Borrowers
- A Creditor must deliver at least on a quarterly basis to each Borrower a statement of his/her Consumer Financing transaction amounts in writing or through electronic medium (such as e-statement) as agreed with the Borrower in advance. The account statement should fully disclose the following information:
(a) The dates on which the statement period begins and ends.
(b) The opening and closing balances (indicating the amount owed by the Borrower at the beginning and at the end of the statement period).
(c) Particulars of each Draw-down during the statement period.
(d) The amount of the Term Cost charge debited to the Borrowers account during the statement period and when the Term Cost was debited.
(e) Particulars of any fees and charges debited to the Borrower's account during the statement period.
(f) Payments to or from the account.
(g) Particulars of each amount paid by the Borrower to the Creditor, or credited to the Borrower, during the statement period.
(h) Particulars of any amount transferred to or from the account to which the statement relates or to or from any other account maintained under or for the purposes of the Financing Contract.
(i) If a minimum amount is payable by the Borrower under the Financing Contract, a statement of the amount and the date by which it is due.
- The address for notification of account statement errors: The address or telephone number to be used for notification of account statement errors or any other enquiries that a Borrower may have on the account statement.
- The time period allowed to the Borrower to verify the accuracy of transactions as annotated in the account statement after which the account statement is binding: This period shall not be less than 30 Calendar Days as of the date of sending the statement via Guaranteed Communication Means
- The Saudi Riyal shall be used as a basis for calculating all transactions and charges of Consumer Financing, and it shall be used in all disclosures of monetary values for Consumer Financing accounts denominated in Saudi Riyal. For Consumer Financing accounts denominated in currencies other than Saudi Riyal, the basis for calculation will be their respective currency of account.
- If the Creditor wants to change the charges related to the Consumer Financing account or the method of paying due amounts, it must notify the Borrower of such change within a period of at least 60 Calendar Days prior to its application. The notice shall be mailed or delivered by Guaranteed Communication Means to the address on record of the Borrower.
- The Borrower is required to keep the Creditor's records updated with his/her latest address and to immediately notify the Creditor of any change in his/her contact details in writing or by Authenticated Communication. Failure to provide this information will release the Creditor from any liabilities and obligations under Article 22.5 above.
Section Seven Dispute Resolution
Article 23: Rules for Dispute Resolution
- The term “account statement error/dispute” means any transaction posted to the Borrower's Consumer Financing account, resulting in an error in the overall balance. Account statement errors shall include the following:
(a) Failure by the Creditor to properly credit a payment or any other amount deposited in the Borrower's account.
(b) Accounting error made by the Creditor, so that a charge would be lower or higher than it should be including the imposition of fees or charges that are not in accordance with the terms and the agreement in force.
(c) The Creditor's failure to deliver, by Guaranteed Communication Means, an account statement to the Borrower’s address on record.
(d) Any other errors not covered above.
- The term “notice of account statement error”/dispute means a written notification given by a Borrower to the Creditor, using the contact information as included within the said account statement or other information supplied by the Creditor, and it must meet the following requirements:
(a) It must be received by the Creditor no later than 30 Calendar Days after the Creditor had mailed or delivered by Guaranteed Communication Means the first account statement which contains the alleged account statement error.
(b) The notice shall enable the Creditor to identify the Borrower's name and account number, and indicate, to the extent possible, the Borrower's reasons for believing that an account statement error exists, the nature of such error, the transaction details including posting date and amount related to the error.
- The Creditor must address account statement errors/disputes as follows:
(a) The Creditor must mail or deliver by Guaranteed Communication Means a written response to the Borrower within 30 Calendar Days of receiving the notice of account statement error/dispute advising the Borrower of the likely timeframe of resolution of the error/dispute and requesting any additional available information or documentation.
(b) The Creditor shall conduct the necessary investigation and comply with the appropriate dispute resolution procedures (as communicated to the Borrower) within 60 Calendar Days, but in no case later than 90 Calendar Days from the date of receipt of the notice of account statement error/dispute.
- If the account statement error/dispute has not been Satisfactorily Resolved, the Borrower shall not be obliged to pay the portion of the required payment that the Borrower believes is related to the disputed amount, including Term Cost or any other charges. The Creditor may not try to collect any amount, Term Cost or other charges related to the account statement error/dispute until the dispute is Satisfactorily Resolved.
- The Creditor must not make or threaten to make an improper report about the Borrower's credit standing, or report that an amount or account is delinquent prior to the error/dispute being Satisfactorily Resolved, because the Borrower did not pay the disputed amount or relevant Term Cost or other charges during the error/dispute resolution process in any event, not earlier than 90 Calendar Days from the date of the notice of account statement error/dispute.
- If the Creditor determines that an account statement error has occurred as stated by the Borrower, it must correct the error and pay back any disputed amount and relevant Term Cost and other charges debited on the Borrower's account and deliver by Guaranteed Communication means a correction notice to the Borrower.
- If the Creditor determines that a different account statement error other than the one identified in the Borrower’s notice has occurred, the Creditor must mail or deliver by Guaranteed Communication Means to the Borrower the Creditor's reasons for believing that a different account statement error has occurred and the reasons for the belief that the error alleged by the Borrower is incorrect. The Creditor shall correct the error and credit the Borrower’s account with the correct amount in accordance with procedures in force.
- If the Creditor determines that no account statement error has occurred, it must mail or deliver by Guaranteed Communication Means to the Borrower an explanation of the reasons of believing that the error alleged by the Borrower is incorrect and provide the Borrower with copies of any documented evidence if he/she so requests.
- If the Creditor believes that a Borrower is liable for all or part of the disputed amount and relevant Term Cost and other charges, it must:
(a) Notify the Borrower in writing of the date when payment is due and the portion of the disputed amount and relevant Term Cost and other charges for which the Borrower is liable.
(b) Report to a Licensed Credit Bureau that an account or amount is delinquent because the amount due has remained unpaid after the due date provided for in the terms and conditions of the relevant Financing Contract.
- Without prejudice to applicable law and regulation, a Creditor that has fully complied with the requirements of this section shall not have further responsibilities under this section if the Borrower insists on his/her claim.
- The Committee for Settlement of Banking Disputes is the final authority in resolving any unresolved disputes between the Borrower and the Creditor.
- These Regulations are issued in Arabic and English. In the event of a conflict between the two versions of these Regulations, the Arabic version prevails.
Annex 1 Calculation of the Annual Percentage Rate
This annex has been updated by circular No (45025707) dated 17/04/1445H (corresponding to 01/11/2023). Please refer to Rules Governing Calculation of Annual Percentage Rate (APR) to read the updated version.The Annual Percentage Rate (APR) is the discount rate at which the present value of all payments and installments that are due from the Borrower, representing the Total Amount Payable by the Borrower, equals the present value of all payments of the Amount of Financing available to the Borrower on the date on which the Financing amount or the first payment thereof is available to the Borrower, in accordance with the following equation:
where:
m is the number of the last payment to be received by the Borrower
d is the number of a payment to be received by the Borrower
Cd is the amount of payment (d) to be received by the Borrower
Sd is the period between the date of the first payment to be received by the Borrower and the date of each subsequent payment to the Borrower, expressed in years and fractions of year, therefore S1=0.
n is the number of the last repayment or payment of charges due on the Borrower
p is the number of a repayment or a payment of charges due on the Borrower
Bp is the amount of repayment or payment of charges (p) due on the Borrower
tp is the period between the date of the first payment to be received by the Borrower and the date of each repayment or payment of charges due on the Borrower, expressed in years and fractions of year
X is the Annual Percentage Rate (APR)
- For the purpose of calculating APR, periods between dates shall be based on a year of 12 equal months.
- For the purpose of calculating APR, the Total Amount Payable by the Borrower shall be determined, including all unavoidable costs and fees with the exception of charges and fees payable by the Borrower as a result of non-compliance with any of his commitments laid down in the Financing Contract.
- The calculation of the APR must be based on the assumption that the Financing Contract will remain valid for the agreed period and that the Creditor and the Borrower will fulfil their obligations under the terms specified in the Financing Contract.
- If the Financing Contract contains clauses allowing variations in the charges contained in the APR but unquantifiable at the time of calculation, the APR shall be calculated on the assumption that the charges will remain fixed at the initial level and will remain applicable until the end of the Financing Contract.
- The Annual Percentage Rate must be calculated and expressed in percentage points with minimum two basis points and the portion of a basis point being rounded to one full point.
Rules Governing Calculation of Annual Percentage Rate (APR)
No: 45025707 Date(g): 31/10/2023 | Date(h): 17/4/1445 Status: In-Force Chapter I: General Provisions
Article 1: Definitions
The following terms and phrases, where used in these Rules, shall have the corresponding meanings unless the context requires otherwise:
Central Bank: The Saudi Central Bank.
Rules: Rules Governing the Calculation of the Annual Percentage Rate (APR).
Finance Providers: Banks, and Finance Companies Licensed to engage in retail lending.
Borrower: a person receiving finance.
Financing Agreement: an agreement whereby financing is granted for the activities listed in the Laws and Regulations.
Amount of Finance: the ceiling or the total amounts made available to the borrower under a finance agreement.
Annual Percentage Rate (APR): The discount rate at which the present value of payments and installments that are due from the borrower representing the total amount payable by the borrower equals the present value of all payments of the amount of financing available to the borrower on the date on which the financing amount or the first payment thereof is available to the borrower.
Total Amount Payable by the Borrower: the sum of principal loan amount and the total cost of finance.
Total Cost of Finance: All the costs to be paid by the borrower under a financing agreement other than the amount of Finance, including term cost, fees, commissions, administrative services fees, insurance, and any charges required to obtain finance excluding any expenses the borrower can avoid such as costs or fees payable by the borrower due to his breach of any of his obligations contained in the financing agreement.
Article 2: Scope of Implementation
1. These Rules shall be applicable on all finance providers engaging in retail lending 2. The Rules shall be read in conjunction with the related Laws and Regulations, including but not limited to the following: - Finance Companies Control Law and its Implementing Regulation. - Rules Regulating Consumer Microfinance Companies. - The Rules on Disclosure of Interest Rates on Financing and Saving Products. - The Regulations for Consumer Financing. - SAMA's Circular No. 381000095091 issued on 10/9/1438H to clarify Article (10) and Article (21) and the APR Calculation Mechanism in the Regulation for Consumer Financing. Article 3: General Provisions
1. The objective of these Rules is to standardize the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) calculation for different types of retail lending, ensuring transparency in the finance offers and comparability to enable retail consumers to make informed decisions.
2. The APR for financing transactions shall be determined in accordance with the instructions and APR Calculator implemented through these Rules for the following:
a. Advertising and promotional materials.
b. Finance offering stage.
c. Financing contract.
d. Periodic statements provided to customers.
e. Any other disclosure of APR.
Chapter II: APR Calculator
Article 4: SAMA APR Calculator
Finance providers shall utilize the Excel based calculator issued by SAMA for the purpose of implementing the Rules.
Article 5: Implementation and Update of the APR Calculator
- Finance providers shall update the relevant policies and procedures to comply with the requirements included in the Rules.
- Finance providers are responsible for implementing adequate internal controls and audit mechanisms to safeguard the integrity of the APR Calculator deployed. In case where the APR Calculator is automated, finance providers should verify the results obtained using the automated tool by comparing those results to the figures obtained by using Excel based APR Calculator provided by SAMA.
- Finance providers shall also ensure that the APR Calculator made available to customers through their websites is updated to align with the Rules requirements and the enclosed Calculator.
Chapter III: APR Calculation Requirements
Article 6: APR Calculation Method
The APR should be calculated based on the net present value method using the following formula:
Where:
- m is the last payment of the amount of finance to be received by the borrower. - d is the payment to be received by the borrower from the amount of finance. - Cd is the payment value of (d) to be received by the borrower from the amount of finance. - Sd is the period between the date on which the amount of finance or the first payment is available to the borrower and the date of payment (d), calculated in years and parts of the year, and so that this period of first payment received by the borrower from the amount of finance is zero (s1=0) - n is the last payment payable by the borrower. - p is the payment payable by the borrower. - Bp is the payment value (p) payable by the borrower - Tp the period between the date on which the amount of finance or the first payment is available to the borrower and the date of the payment (p) to be received from the borrower, calculated in years and parts of the year. - X is the Annual Percentage Rate. Article 7: Cost of Finance
1. For calculating the APR, finance providers shall specify the total amount payable by the borrower.
2. Finance providers shall include the cost elements in the total cost of finance as specified below:
a. All types of costs that the borrower has to pay in order to access the credit.
b. All costs shall be accounted for regardless of whether they are payable to the finance provider or a third party or payable directly or indirectly by the borrower or whether they give access to financial or non-financial services.
c. Term cost, commissions arising from the credit agreement, credit brokerage fees payable by the borrower, administrative fees / or loan processing fee, insurance related costs, valuation costs, cost of ancillary services, and taxes including VAT, etc.
d. Cost of ancillary services or supplementary services to the financing agreement, shall be included in the total cost of finance where the ancillary service is mandatory to obtain the finance or to obtain the finance on the terms and conditions marketed by the finance provider.
Article 8: Costs Excluded from APR Calculations
The total cost of finance shall not include:
a. Any amount charged in lieu of early repayment or settlement and changes in the terms and conditions of the financing agreement. b. Fees and charges incurred as a result of failure to comply with the terms of the agreement i.e., late payment charges in the form of penalties, charges for collection, etc. c. Other costs not paid in connection with the financing agreement (e.g. vehicle registration fees). Article 9: General Requirements
Finance providers must consider the following while calculating the APR:
- The periods between the date on which the amount of finance or the first payment is available to the borrower and the date of each payment received or payable by the borrower shall be calculated on the basis of 365 days a year.
- The APR shall be calculated on the assumption that the amount of finance is valid for the term agreed upon and the parties’ adherence to their obligations according to the conditions stipulated in the financing agreement.
- The APR must be calculated and expressed in percentage points with a minimum of two basis points, rounding half basis points to the nearest full basis points.
- In case the finance agreement contains a clause allowing variations in term cost and fees contained in the APR (e.g. floating) which is not quantifiable at the time of financing, the APR must be calculated on the assumption that the term cost and other charges remain fixed in relation to the initial term cost applied and will remain applicable until the end of the financing agreement.
Article 10: Specific Requirements for Credit Cards Products
Finance providers while calculating the APR for credit cards shall assume the following:
- The amount of finance is provided for a period of 1 year starting from the date of the initial drawdown or card allotment/approval date, and that the final payment made by the borrower clears the principal payment, term cost and other charges, if any.
- The principal payments and term cost are repaid by the borrower in 12 equal monthly payments, commencing 1 month after the date of the initial drawdown.
- If the ceiling of the credit card has not been determined, that ceiling shall assumed to be SAR 10,000 when calculating the advertised APR.
- At the pre-contractual stage, the amount of finance shall be equal to the financing limit or credit card limit requested by the customer or offered to the customer.
- At the contractual stage, the amount of finance shall be equal to the financing limit or credit card limit based on the agreement concluded with the borrower.
Chapter IV: Concluding Provisions
Article 11
The internal audit function shall review the APR calculation process at least annually. Any control deficiencies highlighted by the internal auditor shall be addressed by management in a timely and effective manner.
Article 12
These Rules shall enter into force (90) days after the date of their publication on SAMA’s official Website.
New Banking Products and Services Regulation
No: 45032226 Date(g): 30/11/2023 | Date(h): 16/5/1445 Status: In-Force This regulation was issued under circular No. (391000006163), dated 18/01/1439H, corresponding to 08/10/2017G, and updated by Circular No. (45032226), dated 16/05/1445H, corresponding to 30/11/2023G.Based on the powers granted to SAMA according to Saudi Central Bank Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/36) dated 11/04/1442 H and related regulations. And referring to SAMA Circular No. (391000006163) dated 18/01/1439 H regarding SAMA's New Banking Products and Services Guidelines, and in continuation of what SAMA issued in this regard.
Attached is the first update of the above-mentioned guidelines, which seeks to achieve several objectives, most notably promoting sound practices in managing the risks associated with products and services, clarifying the roles and responsibilities of the board of directors and senior management in the governance, development and oversight of banking products and services. In addition to improving the mechanism for receiving and processing bank notifications to introduce new banking products and services, clarifying the products and services that require no written objection or notification to SAMA (provided that the requirements in the instructions are met), and creating a unified model for introducing new banking products and services. These instructions will replace the previous instructions.
For your information and action accordingly as of March 1, 2024 G.
1. Introduction
Banks frequently introduce new products and services and/or modify existing products and services in normal course of business. These new or modified products and services could expose the banks or the financial system as a whole to new risks or could amplify existing risks. Therefore, the risks posed by the introduction and/or modification of products and services must be identified, assessed, monitored and managed appropriately by the banks.
New Banking Products and Services Guidelines were issued by SAMA in 2017; due to changes in the financial system and regulatory framework, SAMA decided to update these guidelines. The key objectives of this regulation is to promote sound risk management practices and/or manage risks associated with banking products and services. The banks must adhere to this regulation as minimum set of regulatory requirements.
2. Objective
This Regulation sets out SAMA’s requirements with regard to banks’ offering of new products and services and regulatory requirements of notifying SAMA prior offering a new product or service, and the required supporting documents to be submitted. In addition, the regulation aim to improve the time-to-market for banks to introduce new product and service, and promoting sound risk management practices in managing and controlling risks associated with banking products and services.
3. Scope of Application
This Regulation shall be applicable to all licensed banks in Saudi Arabia under the Banking Control Law.
4. Definitions
4.1 Product or Service
A product or service are what the banks offer to their customers within the scope of banking business as defined in the Banking Control Law.
4.2 New Product or Service
A new product or service is one that a bank offers for the first time in Saudi Arabia notwithstanding the fact that a bank, its parent bank, branches or subsidiaries in a foreign jurisdiction may have offered similar product and service outside of Saudi Arabia, or a variation to an existing product offered by bank in Saudi Arabia or a combination of product or service with another existing or new product or service, that results in a material change(1) to the structure, features or risk profile of the existing product or service.
(1) Material changes or modifications may include, for example, significant changes to key terms related to payout, rights and obligations of the counterparties/customers, the changes in nature of assets underlying the product or service, changes result in new or additional risk exposure to the bank or the customer.
4.3 Existing Product or Service
An existing product or service, which a bank had offered, and continue to offer, until the bank decides to discontinue or make material modifications to the product or service.
5. Board of Directors and Senior Management Responsibilities
5.1 Board of Directors (The Board)
5.1.1 The Board has an oversight responsibility (2) to ensure that senior management develop and implement the detailed internal policies and procedures for offering of new products and services.
5.1.2 The Board is responsible for ensuring that product and service risks are well managed, and the needs and rights of consumers are appropriately addressed.
5.1.3 The Board must review whether the offering of products and services by the bank remains consistent with the risk appetite approved by the board and internal policies and procedures for offering of new products and services.
5.1.4 The Board must review and revise the bank’s risk appetite when the offering of products and services by the bank is no longer consistent with the approved risk appetite. Any changes to the risk appetite must be justified and documented with detailed risk assessment, taking into consideration the risk management capabilities and risk bearing capacity of the bank. The Board must also ensure that internal policies and procedures are updated by senior management accordingly following changes in risk appetite.
(2) The management function responsible for overseeing the operations of Foreign Bank Branch (FBB) are to ensure that policies an d procedures for new products and services are consistent with the requirement of this regulation, and effectively implemented in its operations.
5.2 Senior Management
5.2.1 Senior management are responsible for the design, implementation, and compliance of the bank’s new products and services with the Board approved internal policies and procedures for offering of new products and services.
5.2.2 Senior management must ensure that offering of any new or existing products and services must fall within the scope of banking business as defined in the Banking Control Law.
5.2.3 Senior management must ensure that that risks arising from new products and services are well understood and aligned to the bank’s risk appetite and tolerance level.
5.2.4 Senior management has to determine whether the change to any product or service is considered to be a material change (3).
5.2.5 Senior management must periodically review the appropriateness of the products and services internal policies and procedures and whether they continue to meet the objectives as set out in this regulation, and must propose to the Board that the policies and procedures be amended if this is no longer the case.
5.2.6 Senior management must identify and mitigate potential negative effects on the bank's reputation either actual or perceived.
5.2.7 Senior management must ensure that there are full operational readiness to support new products and services, including processes, controls and systems infrastructure and approvals from other authorities are obtained prior to offering new products and services, where relevant.
(3) Chief Risk Officer (CRO) and Chief Compliance Officer (CCO), in coordination with the product or service developer, are responsible for determining whether the change to any product or service is considered to be a material change.
6. Products and Services Policy Requirements
6.1 General Requirements
Banks are required to have in place an internal policies and procedures that set out the oversight and governance arrangements for the offering of new products and services. These internal policies and procedures must at minimum satisfy the following:
6.1.1 To be integrated as part of the bank’s governance, risk management and internal control framework.
6.1.2 Defining the roles and responsibilities of all stakeholders including the Board and all control functions involved in developing and launching new products and services.
6.1.3 Defining parameters for the authority which approves new products and services including the circumstances under which such authority may be delegated.
6.1.4 Defining the requirements to have a pilot or testing phase for new products and services. A bank is required to assess the effect of a product and service on target market before its commercial launch and take appropriate changes where scenario analysis shows adverse results for the target market.
6.1.5 Consumer protection requirements including the bank’s standards for management of customer suitability and mis-selling risks along with a requirement to conduct annual assessment of all products and services against such established standards.
6.1.6 The internal policies and procedures must be reviewed and updated on a regular basis or when it’s needed, ideally on an annual basis, and at least once every (3) years.
6.1.7 The policies and procedures must be communicated by the bank in a timely manner to all relevant parts and levels within the organization, and to ensure that the new product and service offering are fully integrated throughout a bank’s line functions.
6.2 Considerations
When developing products and services internal policies and procedures, banks must consider the following:
6.2.1 Designing and bringing to the market products and services with features, charges and risks that meet the interests, objectives and characteristics of, and are of benefit to the market segment identified for the products and services. In this regard, a formal customer appropriateness and customer fairness assessment must form part of bank’s processes before approval of new products and services.
6.2.2 The products and services offered to customers are fair and suitable.
6.2.3 Avoid any conflicts of interest, potential for mis-selling, terms and conditions that are inherently unfair to consumers, and business practices that restrict the freedom of choice to consumers.
6.2.4 To be proportionate to the nature, scale, risk, and complexity of a bank’s products and services, and designed to identify and control product risk across the value chain, including at minimum the stages of product development, authorization and governance, price, marketing, sale and distribution.
6.2.5 The gradual commercial launch of any new product and service taking into consideration the market segment, riskiness and complexity of the product and service.
6.2.6 Compliance with all applicable rules and regulations issued by SAMA and all other relevant regulators when developing a new product and service as well as any subsequent updates to the rules and regulations. Examples of such rules and regulations (but not limited to):
a. Responsible Lending Principle for Individual Customers (issued in 2018).
b. Financial Consumer Protection Principles and Rules (issued in 2022).
c. Rules for Advertising Products and Services Provided by Financial Institutions (issued in 2023).
d. Debt Collection Regulations and Procedures for Individual Customers (issued in 2018).*
e. SAMA Cyber security Framework (issued in 2017).
f. SAMA Counter-Fraud Framework (issued in 2022).
g. SAMA Business Continuity Management Framework (issued in 2017).
h. Information Technology Governance Framework (issued in 2021).
i. Rules related to touch\face ID, Tahaqaq requirements, digital signature, national and global payment requirements for MADA, Visa, MasterCard, Face recognition.
*These regulations have been replaced by the updated Debt Collection Regulations and Procedures for Individual Customers in accordance with circular No. (106889333), dated 06/09/1446H, corresponding to 05/03/2025G.
6.3 Products and Services Risk Assessments
6.3.1 Banks must establish lines of responsibility for managing risks related to new products and services.
6.3.2 Banks must conduct a full risk assessment of new products and services which form the basis on whether or not to introduce them to the market taking into account reviewing all the associated risk throughout the life cycle of the products and services.
6.3.3 Banks must have risk management standards for developing and launching any new products and services to the market. These include, inter alia, adequate due diligence and approvals, procedures to identify, measure, monitor, report, and mitigate risks, effective change management processes and technologies, ongoing performance monitoring and review mechanisms.
6.3.4 Banks must have risk classification process for each product and service that the bank intend to launch. The classification process must result with an overall risk classification for the product or service (for example: high, medium or low risk).
6.3.5 Banks must have a risk management, controls and monitoring processes in respect of third party risks management, where the bank’s products and services are offered in partnership with Fintech companies, agents or similar entities.
6.3.6 The risk management function must have internal organizational and operational capacity i.e. effective controls, monitoring and reporting systems and procedures in place, to monitor and manage potential risks of the proposed new products and services poses to the bank's own financial health, as well as to the financial well-being of the customers and overall market stability.
6.3.7 The risk management function must document, review and approve risk profile (associated risks) of new products and services before its launch. Risk profile of the new products and services must include at least detailed description of all associated risks i.e. identification, quantification (if possible), assessment, classification and its mitigation plan.
6.3.8 The risk management function must perform comprehensive fraud risk assessment covering fraudulent events across different channels and assessment of prevention, detection, and investigation capabilities from people, process and technology perspective taking into consideration emerging technologies. The risk assessment must also include evaluation of all possible scenarios and dynamic fraud techniques such as social engineering, phishing. that ensures safety and soundness of the bank against dynamic fraudulent scenarios. In addition, the bank must enforce defense in depth mechanism in their environment to ensure deep protection for the customers such as using multichannel technique to ensure customer identity and confirmation of the financial service/transaction for example: registration and activation/approval of services from different channels whenever applicable.
6.3.9 The risk management function must conduct comprehensive risk assessment which cover cyber resilience and data privacy including evaluating threats, vulnerabilities and weaknesses needed to be analyzed for potential impact on the bank that leads to improve member organizations cyber posture.
6.3.10 The risk management function must assure that its people, systems and processes have the ability to adequately capture and report risks and financial commitments relating to its new products and services in a timely manner.
6.3.11 The risk management function must assure that all material risks posed by the introduction of new products and services or by the modification of existing products and services are identified, assessed, monitored and managed appropriately; and must be regularly reviewed in light of the changing market conditions not previously factored.
6.3.12 The risk management function must assess how new products and services will affect the bank's current and projected financial and capital positions.
6.4 Products and Services Compliance
The compliance function must ensure the following:
6.4.1 Review all new products and services from compliance, regulatory and financial crimes perspective and ensure that they conform to all applicable rules and regulations issued by SAMA and all other relevant regulators.
6.4.2 Products and services offered are compliant with all rules and regulations issued by SAMA and all other relevant authorities at all time.
6.4.3 Identify the risks of non-compliance that might arise from products and services, set plans to manage it, and evaluate these risks at least once annually.
6.4.4 Report to the Board at least once annually the risks of non-compliance and how it would be mitigated.
6.4.5 The compliance function must be the main contact point for liaison for submission of all applications for non-objection to introduce new products and services and to notify SAMA of any products and services in cases where non-objection is not required.
6.5 Products and Services Auditing
The internal audit function must ensure the following:
6.5.1 Timely identification of internal control weaknesses, adherence to regulatory requirements and products and services policies and procedures.
6.5.2 To audit all new products and services in a reasonable time i.e. within one year after launching the product or service depending on the nature, type, complexity, and riskiness of the new products and services.
6.5.3 Report to the Audit Committee the results of the audit process that was conducted on the bank’s products and services at least once annually. In case, products and services associated risks increase or violating any rules and regulations issued by SAMA and all other relevant regulators, the internal audit must include them in their yearly audit plan.
6.6 Product Development Function
The product development function (business units) must ensure the following:
6.6.1 They are familiar with products and services policies and procedures and all applicable rules and regulations issued by SAMA and all other relevant regulators.
6.6.2 They are competent and appropriately trained; and thoroughly understand the products and services’ features, characteristics, risks, and ensure that corrective actions are taken to mitigate identified risks related to products and services.
6.7 Products and Services On-going Monitoring and Control
6.7.1 Banks must ensure that the requirement of monitoring products and services on an ongoing basis is in place and implemented, to ensure that the interests, objectives and characteristics of targets market continue to be appropriately taken into account. In addition, the banks must address consumer complaints and rectify them on timely basis.
6.7.2 If the bank identifies a problem/risk related to products or services in the market, or when monitoring the performance of the products or services as required, the bank must take necessary corrective actions and implement measures to prevent future recurrence. The corrective action plan, which may include suspension or withdrawal of products or services must be approved by the senior management function or other functions within the bank accountable for approval of product and services. Banks must also report to SAMA such incidents including the corrective action plan that have been or will be taken.
6.7.3 In the case of product or services suspension or withdrawal, banks are required to notify SAMA at least prior to (45) business days by email before suspending or withdrawing any products or services via (PSBanking@sama.gov.sa). The notification must include justifications for the suspension or withdrawal and the plan to deal with beneficiary customers (exiting plan) affected by discontinuation of products or services.
6.7.4 After the introduction of new products or services, SAMA may, at any time, suspended the product or service if any regulatory incompliance has been identified and/or there is a negative impact on the banking sector or on consumers. SAMA will direct banks to provide corrective actions in such case for approval and implementation.
6.8 Documentations and Reporting Requirement
6.8.1 Banks are required to submit a report to SAMA which include all products and services. The report must be signed by the Chief Executive Officer, and submitted by Compliance Function to Banking Licensing Division via (PSBanking@sama.gov.sa) – by 1st March of each year, according to the table provided in (Annexure 5).
6.8.2 Banks must document all actions taken while implementing the internal policies and procedures, preserve these documents for audit purposes and to make them available to SAMA upon request. In addition, the banks must retain all the documents relating to the risk assessment of the new products and services including key risks from both the bank’s and customer’s perspective, together with the systems and processes that are in place to mitigate these risks.
6.8.3 An inventory of bank’s existing products and services containing information such as (but not limited to): name of a product and service, target market, risk classification, developer of the product or service, reviewer of the product, approver of the product, approval date, launch date, last review date, latest changes made including the description and the date of changes.
7. Notification and Non-Objection Requirements
7.1 Notification Requirements
The following requirements applies to banks that satisfy the required maturity level in Cyber Security Framework, Counter-Fraud Framework, Business Continuity Framework, and Information Technology Governance Framework, which must be independently validated by a qualified and experienced third party on annual basis.
7.1.1 Banks are required to notify SAMA by email at least (10) business days before launching any new products and services via (PSBanking@sama.gov.sa).
7.1.2 SAMA will acknowledge receipt of the notification within (10) business days of receiving the bank’s request. In case, a bank does not receive acknowledgement receipt from SAMA within (10) business days from sending the notifications, it is the bank’s responsibility to follow up with Banking Licensing Division via (PSBanking@sama.gov.sa) for confirming that whether SAMA has received the notification or not.
7.1.3 Banks will be able to launch new products and services once they receive SAMA’s acknowledgement of receipt of the bank’s notification.
7.1.4 Banks must launch their new products and services within (12) months of receiving the acknowledgment receipt from SAMA, otherwise the bank must submit a new notification.
7.1.5 SAMA have the right to ask banks for further information about products and services despite the fact that bank has launched the products and services or not.
7.1.6 SAMA may prohibit a bank from introducing or continuing to offer any products or services if SAMA concludes that such product or service will undermine SAMA’s primary objective of maintaining safety and soundness of the financial sector.
7.1.7 Banks must not reintroduce a product or service that has been stopped or discontinued by the bank for more than (12) months without notifying SAMA by following the notification requirements as per clause (7.1.1).
7.2 Non-objection Requirements for Specified Products and Services
7.2.1 Banks are required to seek SAMA’s non-objection for the below products and services prior launching, as an exception to the notification requirements:
1. Home Loans Products.
2. Financial Lease Products.
3. Financial Derivatives.
4. Products and services that are not covered in existing rules and regulations issued by SAMA.
7.2.2 Banks that do not comply with required maturity level stated in clause (7.1), must apply for nonobjection for all types of products and services.
7.2.3 Banks must launch their new products and services within (12) months of receiving the SAMA’s non-objection, otherwise the bank must submit a new application.
7.2.4 Banks must not reoffer a product or service that has been stopped or discontinued for more than (12) months without a new non-objection from SAMA, as per clauses (7.2.1) and (7.2.2) for products or services that require SAMA’s non-objection.
7.3 Offering of Financial Derivatives Products
Banks must ensure the following are satisfied before submitting a non-objection application to SAMA:
7.3.1 Banks seeking to introduce new financial derivatives products for their customers are required to develop and implement internal customer suitability procedures ensuring that these products are only sold to suitable customers.
7.3.2 Customer suitability procedures must be designed to seek sufficient knowledge about the customer to establish that the customer has a practical understanding of the features of the product and the risks to be assumed.
7.3.3 For complex financial derivatives such as structured products, the complexity of the payoff structure can make it difficult for customers to accurately assess the value and risk of the structured product. Banks must clearly demonstrate to the customer the potential profit and loss scenarios for the structured products over the time horizon.
7.3.4 Banks must ensure that customers are fully aware of risks involved in complex products such as financial derivatives and structured products, the product must meet the customer’s business or investment objectives and risk appetite, the customer have prior investment experience and fully understood and sign-off the terms of contract accordingly.
7.3.5 Banks must not recommend a financial derivative product to a customer unless it is reasonably satisfied that the product is suitable for that particular customer and the nature of the customer’s business. Such a decision must be made based on information sought and obtained from the customer.
7.3.6 Banks seeking to introduce new financial derivative products must demonstrate that the proposed financial derivative instrument has a bona fide economic purpose and does not merely provide means of financial speculation, leverage, or regulatory arbitrage. To meet this test, a bank would have to identify the intended customers for the proposed new financial derivative products and describe (with sufficient specificity) potential uses.
7.3.7 Banks intending to introduce a new financial derivatives products must demonstrate that it has the internal organizational and operational capacity to monitor and manage potential risks of the proposed new products pose to a bank’s own financial health, as well as to the financial well-being of the customers and overall market stability.
7.3.8 Banks must demonstrate that effective control, monitoring & reporting systems, and procedures are in place to ensure on-going operational compliance with a bank’s, the customer’s and the counterparty’s risk appetite. A bank must also have a strong governance process around the valuation of financial derivatives, which includes robust control processes and documented procedures.
7.3.9 Banks intending to introduce a new financial derivatives products will have to demonstrate that the proposed products do not pose potentially unacceptable systemic risk. It is the responsibility of the bank to ensure that suitability of customers for the new financial derivatives product are assessed not only based on a bank’s exposure to an individual customer but also based on the industry’s exposure to the customer. A bank would therefore need to obtain full disclosure from the customers about their financial derivative exposures with other banks and non-banking entities prior to selling new financial derivative products.
7.3.10 Banks must ensure that the new financial derivative such as, structured products that seeks to market is not likely to have a negative impact on broader socio-economic policy goals of the country, for example an impact on SAIBOR or SAR.
7.3.11 Financial derivatives involving SAR against a foreign currency are subject to the requirements of a separate SAMA circular that banks must comply with.
7.3.12 Banks are required to ensure new financial derivative products comply with SAMA Rules on Trade Repository Reporting & Risk Mitigation Requirements for Over-the-Counter ("OTC") Derivatives Contracts issued by SAMA (issued in 2019) and any subsequent updates.
7.4 Documentation Requirements
7.4.1 A bank notifying or seeking a non-objection from SAMA for the introduction of a new product or service must fully complete the checklist and provide the supporting documents as stated in (Annexure 1).
7.4.2 SAMA will not process any application that does not meet or fulfill the above mentioned documentations.
8. Effective Date
This regulation shall be effective by 1st of March 2024. Once effective, this regulation shall supersede the existing SAMA New Banking Products and Services Guidelines issued by circular No. 391000006163 in 18-01-1439H (08-10-2017G).
9. Annexure
Filling Form Instructions 1. This form is for new banking products and services in accordance with the New Banking Products and Services Regulation (second version / Nov 2023). 2. The form must be fully filled out by the bank. 3. The bank must verify the accuracy of the information filled in this form. 4. The form must not be modified in any way. 5. This form and supporting documents such as contracts, terms and conditions should be sent in two formats (Word-PDF) along with the other requirements as shown in annexure (1) to Banking Licensing Division via (PSBanking@sama.gov.sa) Bank name Product or service name Purpose of the application ☐ Notifying SAMA before launching a new product or service.
☐ Obtaining SAMA's no-objection for launching a new product or service according to clause (7.2.1)
☐ Obtaining SAMA's no-objection for launching a new product or service according to clause (7.2.2).
Is it a material change to an existing product or service? ☐ Yes ☐ No Provide date of previous Notification/Non-objection:
Day/Month/Year
Launching date:
Day/Month/Year
New product or service expected launch date:
Day/Month/Year
The rules and regulations that were taken into account in developing this product or service Product or service type
(You can check more than one)☐ Savings ☐ Personal finance ☐ Credit card ☐ Financial Derivatives ☐ Home finance ☐ Prepaid cards ☐ Financial lease ☐ Corporate finance ☐ Banking services ☐ E-service ☐ Treasury product ☐ Other: Annexure (1): Checklist
No. Document Attached Yes No Not Applicable 1 A formal letter signed by the Chief Compliance Officer notifying or requesting SAMA's no-objection to offer new product or service ☐ ☐ 2 Application form for new banking products and services (Annexure 2) ☐ ☐ 3 Statement of compliance (Annexure 3) ☐ ☐ 4 Consumer protection checklist (for retail products and services) signed by the Product or
Service Developer and Chief Compliance Officer (Annexure 4)
☐ ☐ ☐ 5 Copies of supporting documents e.g. terms and conditions, contracts, process workflow (Images), promotional material and any other related documents ☐ ☐ ☐ 6 Contract draft / service level agreement (SLA) / non-disclosure agreement (NDA) if there is a third party in the product and service ☐ ☐ ☐ 7 Risk assessment report which describe the product or service all inherent risks from both the bank's and customer's perspective together with the systems and processes that are in place to mitigate these risks. The following risks need to be considered at minimum:
- Credit Risk
- Market Risk
- Operational Risk
- Strategic Risk
- AML&CFT Risk
- Legal Risk
- Technology Risk
- Cyber Risk
- Fraud Risk
- Business Continuity Risk
- Data Privacy Risk
- Reputational Risk
☐ ☐ ☐ 8 Necessary Shari’ah Committee Approvals for new Shari’ah Compliant Products or Services. ☐ ☐ ☐ I, the undersigned, acknowledge that all the above-mentioned data and information and attached documents are correct, accurate and complete Chief Compliance Officer Date Day/Month/Year Signature Annexure (2): Application Form for New Banking Products or Services
A detailed description of the product or service: Product or Service Risk Classification (For example: High, medium, low risk): Did The bank completed the independent evaluation required under clause (7.1) ? ☐Yes ☐No Evaluation date: Day/Month/Year Is the bank complied with the required maturity level in the frameworks mentioned in clause (7.1) ? ☐Yes ☐No Notes: Product or service objectives: Product or service features: Product or service offering journey: Product or service delivery channel(s): ☐ Bank branches ☐ E-Channels ( ☐ Phone Banking, ☐ Mobile Banking, ☐ Bank's Website) ☐ Relationship Mangers ☐ Other: Targeted customers: ☐ Existing bank customers ☐ Non-existing bank customers Targeted segment: ☐ Retail ☐ Small/Medium enterprises ☐ Corporate ☐ Government sector ☐ Non-profit sector ☐ Other: Customer identity verification mechanism: Fees, commissions and any other additional amounts might be incurred by the customer: Product or service launching plan in the local market: Similar products or services offered in the local market (if any): The potential impact on the bank's liquidity ratios (SAMA Liquidity Ratio, CAR, LCR & NSFR) and any other regulatory indicators: Technological requirements, details and the integration method with third parties and other technological systems, including but not limited to Robot, Cloud, Biometrics: System classification by the entity, whether it is a main or secondary system: In case of storing data, clarify the location of the data storage, the storage method and the type of data shall be clarified in detail, with reasons and justifications: In case of contracting with third parties, the details of the third parties shall be provided, including the name, location, duties, responsibilities, and any relevant information. Third-party remote access method (if applicable): In case of contracting with third parties, what are the type of data will be shared, and what measures will be taken to maintain information privacy and security: Has the verification method been clarified for the product/service, e.g. two factor authentication (2FA) using the password and the one-time password (OTP): Has the product/service been added to fraud monitoring systems with the ability to directly add and modify scenarios: Do third parties comply with the cloud computing cybersecurity controls (in the case of using cloud computing technology): In case of technological integration, explain the integration method in detail: The internal bank function responsible for monitoring the product or service: The method of cancelling the product or service by the customer and cancelation fees (if applicable): Information/correspondences with SAMA regarding the above product or service(If any): Additional information: Product or service developer name and contact information (email, mobile phone, landline): Annexure (3): Statement of Compliance
Product/Service name We, the undersigned, acknowledge that the aforementioned product or service has been fully reviewed and does not violate any laws, instructions or professional practices. We also acknowledge that submitting this application (notification or non-objection) to SAMA does not burden it with any responsibility whatsoever and does not indicate that SAMA guarantees the product or service soundness. In addition, we acknowledge that we bear all the risks that may result from launching the product or service. Furthermore, we confirm that failure to comply with this acknowledgment entitles the authorities to take all measures, including inflicting penalties, holding violators accountable, withdrawing the product or service from the market, committing to correcting any adverse results, and compensating customers for any losses that may occur due to default or negligence on the bank's part. Product or Service Developer Head of Customer Care Head of Legal Affairs Head of Data Privacy Head of Financial Fraud Head of Business Continuity Head of Information Security Head of Information Technology Chief Risk Officer Head of Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorist Financing Chief Compliance Officer Annexure (4): Consumer Protection Checklist
Before or upon concluding a product/service agreement with the customer: No Requirements Cases Yes No Not Applicable 1 Has the bank done a complete study on the product or service suitability to customer needs ☐ ☐ ☐ 2 Were the expected risks to customers from the product or service identified when advertising, and disclosed in the initial disclosure form (before signing the contract) ☐ ☐ ☐ 3 The bank must disclose the discounts and their conditions to customers - if available - and include them in the initial disclosure form (before signing the contract) ☐ ☐ ☐ 4 Ensuring that customer service staff and/or marketers are clearly familiar with the product or service provided helps customers make a decision before entering into a contract ☐ ☐ ☐ 5 The bank must study the customer's financial solvency before granting the product/service and keep it in the customer's file in a way that enables it to:
1. The customer's ability to fulfill the due payments without delay
2. The customer's understanding of the characteristics of the product or service.
3. The product or service meets the customer's need
4. The customer's ability to bear the risks of the product or service
☐ ☐ ☐ 6 The bank must disclose the product/service provider in the initial disclosure form if the product or service provider is a third party ☐ ☐ ☐ 7 Advertising the product or service to customers is appropriate, does not use a seductive or misleading method of marketing, and uses language that is easy to understand and in clear writing, including margins ☐ ☐ ☐ 8 Are the terms and conditions explained in clear language, including fees, and are they fair to customers? A summary of this is provided in the initial disclosure statement, and this is explained to the customer before signing the contract ☐ ☐ ☐ 9 The potential fines and penalties that the customer will bear if the product or service is used on other than the agreed terms must be explained ☐ ☐ ☐ After concluding the product or service agreement with the customer: 1 The product or service must be compatible with SAMA Care's main or sub-classifications of complaints ☐ ☐ ☐ 2 Clarifying the mechanism for submitting a complaint and the contact information with the bank in the product or service contract ☐ ☐ ☐ 3 Providing beneficiaries with a free statement of account (paper or electronic) on a monthly basis showing the payments made and the remaining payments ☐ ☐ ☐ 4 Having specialized staff to provide advice to customers who face financial and technical difficulties during contract periods and providing appropriate solutions for them to overcome these difficulties ☐ ☐ ☐ Product or Service Developer Chief Compliance Officer Date Date Day/Month/Year Day/Month/Year Signature Signature Annexure (5): Annual Report for Banking Products and services
Regulations of Issuance and Operating of Credit and Monthly Charge Cards
No: 361000090389 Date(g): 15/4/2015 | Date(h): 26/6/1436 Status: In-Force Preamble
- These Regulations shall be applicable to the issuance and operations of all aspects of Credit and Charge Cards as issued by a regulated entity (such as Banks, Finance Companies and other Credit and Charge Card Issuers) as licensed and authorized by Saudi Central Bank, (such as VISA, MasterCard, Union Pay & AMEX). Saudi Central Bank is the sole authority empowered to apply these Regulations and to take necessary measures as it deems appropriate regarding any violations of these provisions including imposing punitive charges and/or enforcement actions as applicable under the Banking Control Law and the Implementing Regulation of the Finance Companies Control Law. These Regulations are to be read in conjunction with the Banking Consumer Protection Principles and supplement the Regulations as annotated in the Updated Regulations for Consumer Financing issued in July 2014 and its subsequent updates.
- Saudi Central Bank may, at its discretion, impose a restriction on a Card Issuer under which its Credit Card authorized limit portfolio may not exceed a specified percentage of its total Credit portfolio.
- In all cases where instruction or information is required from Cardholders, Card Issuers may accept Authenticated Communication unless otherwise specified.
- In all cases where instruction or information is required to be sent to Cardholders, Card Issuers may use Guaranteed Communication Means unless otherwise specified.
- Card Issuers must include details about the Card Issuer’s credit advisory services in all monthly statements, default notices and any other correspondence or communications regarding the Cardholder’s account.
Definitions
“Adequate Notice”: Notice to a Cardholder that set forth clearly the pertinent facts so that the Cardholder may reasonably be expected to have noticed it and understood its meaning. The notice may be given by Guaranteed Communication Means reasonably assuring receipt by the Cardholder.
“Advertisement”: A commercial message in any medium that promotes, directly or indirectly, a Credit or Charge Card product.
“Annual Percentage Rate or APR”: The discount rate at which the present value of all payments and instalments that are due from the Cardholder,
representing the total amount payable by the Cardholder, equals the present value of all payments of the Amount of Credit available to the Cardholder on the date on which the Credit amount is available to the Cardholder, calculated in accordance with Annex 1.“Authenticated Communication”: Cardholder instructions received through recorded, verifiable and retrievable medium either paper, electronic or verbal.
“Billing Cycle”: The interval between the days or dates of regular periodic statements. These intervals shall be equal and no longer than a quarter of a year. An interval will be considered equal if the number of days in the cycle does not vary more than four days from the regular day or date of the periodic statement..
“Business Card”: shall mean a Credit or Charge Card issued for the purposes of purchasing goods or services on behalf of a Corporate Entity, where the Corporate Entity bears liability for all amounts charged to the Credit or Charge Card.
“Business Day”: A day on which the Card Issuers are open for business to the general public.
“Calendar Day”: Any day in a month, including weekends and holidays and based on the official calendar of Saudi Arabia: Umm Alqura Calendar.
“Card Association”: shall mean VISA, MasterCard, American Express, Union Pay and Diners Club or similar institutions. Also known as “Payment Systems Operators”.
“Cardholder”: shall mean (a) a holder, or an applicant to become a holder, of a Credit or Charge Card issued by the Issuer or (b) a holder, or an applicant to become a holder who has agreed with the Issuer to pay all obligations arising from the issuance of a Supplementary Credit or Charge Card to a Designated Individual. He/She is the Primary Cardholder. A Cardholder may be a natural person or a Corporate Entity as applicable.
“Card Issuer”: An authorized entity that issues a Credit or Charge Card.
“Card Limit”: The credit line made available to a Credit or Charge Cardholder under a Credit or Charge Card Agreement.
“Cash Advance”: a transaction to withdraw cash by the Cardholder against his/her Credit or Charge Card Limit. A Cardholder receives a Cash Advance when they:
- Withdraw cash from an ATM.
- Withdraw cash from any other source.
- Make a wire transfer.
- Receive any other mode of cash advance as stipulated by the Card Issuer.
“Charge Card”: a card similar to a Credit Card but one that requires the Charge Card holder to repay the full outstanding amount upon receipt of the account statement or on the due date as per the account statement.
“Corporate Card”: shall mean a Credit or Charge Card issued to an employee or Officer of a Corporate Entity where, under the terms of use of the card:
a. The Corporate Entity bears liability for any amounts charged to the card. b. The employee or Officer and the Corporate Entity bear liability on a joint and several basis for any amounts charged to the card: or c. The Corporate Entity bears responsibility for any amounts charged to the card for the purposes of the business of the Corporate Entity. “Corporate Entity”: shall mean a corporation, partnership or sole proprietorship,
“Credit”: the right to defer payment of debt or to incur debt and defer its payment. Credit is extended by a Card Issuer under a plan in which:
a. The Card Issuer reasonably contemplates repeated transactions. b. The Card Issuer may impose a Term Cost from time to time on an outstanding unpaid balance. c. The amount of credit that may be extended to the Cardholder during the term of the plan (up to any limit set by the Card Issuer) is generally made available to the extent that any outstanding balance is repaid. “Credit Bureau”: A licensed national credit bureau offering consumer and commercial credit information services to respective members in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
“Credit Card”: shall mean a card which is issued by an Issuer in association with Credit Card Associations. The card so issued is used by a card holder to obtain in advance, by virtue of the Issuer’s credit, money, goods, services or other benefits from businesses accepting this card domestically and internationally, and repay the relevant indebtedness thereafter or in accordance with other arrangements. This definition includes Corporate Cards and Business Cards but does not include other types of cards issued such as Debit cards, ATM cards and/or pre-paid cards.
“Credit or Charge Card Agreement”: means an agreement for a Credit or Charge Card between the Card Issuers (as licensed and authorized by Saudi Central Bank) and a "Cardholder".
“Default”: any breach of the terms and conditions of the Credit or Charge Card Agreement and the non-payment by a Cardholder of his/her monthly instalment for 90 Calendar Days from its due date.
“Default Notice”: a notice from a Card Issuer to a Cardholder notifying the Cardholder that he is delinquent in payments.
“Designated Individual”: a natural person who has been nominated by a Cardholder to be a holder, or an applicant to become a holder, of a Supplementary Credit or Charge Card issued at the Primary Cardholder’s instructions.
“Fraud”: a deliberate act to dishonestly obtain a benefit (e.g. money, a product or a service).
“Grace Period”: the date by which, or the period within which, any Credit extended for purchases may be repaid without incurring a Term Cost. If a Grace Period is provided, that fact must be disclosed. If the length of the Grace Period varies, the Card Issuer must disclose the range of days or the minimum number of days in the Grace Period, if the disclosure is identified as a range or minimum.
“Gross Salary”: basic monthly salary (less GOSI and pensions contributions) plus all fixed allowances paid to the Cardholder by the employer on a monthly basis.
“Guaranteed Communication Means”: registered mail, hand delivery, and any recorded, verifiable and retrievable electronic medium.
“Initial Disclosure”: the information required to be provided to the Cardholder by a Card Issuer upon opening a Credit or Charge Card account.
“Optional Feature”: features and services which are not part of the standard features or services of the Credit or Charge Card product, requiring payment of additional fees or term cost by the Cardholder.
“Outsourcing”: an arrangement under which a third party (i.e. the service provider) undertakes to provide to a Card Issuer a service previously carried out by the Card Issuer itself or a new service to be launched by the Card Issuer. Outsourcing can be to a service provider in Saudi Arabia or overseas and the service provider may be a unit of the same Card Issuer (e.g. head office or an overseas branch), an affiliated company of the Card Issuer’s group or an independent third party and is subject to the requirement to fully comply with Saudi Central Bank Rules on Outsourcing.
“Primary Cardholder”: a person in whose name a Credit or Charge Card Account is maintained.
“Profit Rate”: applies to credit extended under Sharia Compliant contracts. It means the rate used to derive profits and is expressed as an annual percentage rate ‘APR’.
“Risk”: the potential of any activity to damage the Issuer entity.
“Central Bank”: the Saudi Central Bank.
“Satisfactorily Resolved”: resolution of the error/dispute in accordance with the procedures and timeframes for resolving disputes.
“Term Cost”: the amount of the Term Cost payable by the Cardholder and it may be represented as a fixed or variable percentage of the outstanding balance on the Credit card account.
“Unauthorized Use”: the use of a Credit or Charge card by a person, other than the Cardholder, who does not have actual, implied, designated or apparent authority for such use, including card skimming.
Section One Scope of Application
Application of the Regulations
Article 1
These Regulations will apply to both Credit and Charge Cards, unless a specific exclusion is noted in the relevant article and will apply to salaried and non-salaried applicants.
Article 2
These Regulations are the complete Regulations for the issuance and operation of Credit and Charge Cards in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. They will take precedence over any other regulations issued previously.
Article 3
These Regulations will cover Credit and Charge Cards issued by any regulated entity, licensed by Saudi Central Bank.
Article 4
Companies subject to the provisions of the Implementing Regulation of the Finance Companies Control Law may extend Credit Cards without collateral, based on their Risk assessment methods.
Article 5
Credit and Charge Cards issued by Finance Companies are not subject to the restrictions on fees and commissions stipulated in Article (83) of Implementing Regulation of the Finance Company Control Law as well as Article (9) in the updated Consumer Finance Regulations (July 2014).
Section two Card Issuing
General Requirement
Article 6
All Credit Agreements, application forms, Guarantee Agreements, repayment schedules and other documentation related to Credit and Charge Cards should be in Arabic. An English version of all such documents should be available and provided to a Cardholder if required by them. In the event of a conflict between the two versions of these Regulations, the Arabic version prevails.
Article 7
The Cardholder rights and responsibilities relating to the Credit or Charge Card shall be recorded in the “Cardholder Agreement” that shall meet Saudi Central Bank information disclosure requirements, as provided in Section 5 - ‘Information Disclosure’ of these Regulations.
Article 8
All Card Issuers will fully comply with the international rules and procedures agreed with the relevant Card Association (e.g. Visa Rules / MasterCard Rules / American Express Business and Operational Policies). Where there is any overlap with any Card Association rules, the Articles in these Regulations will take precedence.
Article 9
A Card Issuer may not issue a Credit or Charge Card without receiving a signed application from an applicant.
Article 10
The decision to issue new Credit or Charge Cards requires an effective Risk management strategy to enable an assessment of the eligibility and affirmation of the suitability of the applicant, unless an applicant already holds a Credit or Charge Card(s) issued by the Card Issuer that meets the card issuing requirements provided in Section 2 -‘Card Issuing’ of these Regulations.
Article 11
A Card Issuer shall not issue a Credit or Charge Card to any person who is below 18 years of age (Hijri), except in the case of a Supplementary card as detailed in Section 2 - ‘Card Issuing’ of these Regulations. University students are exempt from this Article, if they can:
a) Provide a Co-signee that meets the card issuing requirements.
b) Provide independent annual income verification and can meet the obligations of the Credit or Charge Card.Article 12
When assessing applications, Card Issuers must perform the following:
a. Verify that the financial information and applicant personal details supplied on the application form are correct. b. Calculate the probability of the applicant’s ability to repay any indebtedness. c. Determine the amount that the applicant can repay. Article 13
The assessment of a request for a Credit or Charge Card should be based on the applicant's ability to meet all the obligations under the Credit or Change Card Agreement, and entity credit policy.
Article 14
A Card Issuer must provide all first time Cardholders with access to free credit advisory services, such as financial education and awareness, before activation of the new Credit or Charge Card can be completed.
Article 15
If the issue of any new, replacement, or supplemental Credit or Charge Card is rejected to a new applicant or existing Cardholder, the Card Issuer must disclose the rejection reasons within I week from the date of the rejection decision.
Article16
The minimum Gross Salary eligibility for new Credit Cardholders is set at SAR 24,000 per annum for bank customers and SAR 30,000 for non-bank customers. Where salary or pension is not used as the main basis of assessment, including for university students, the decision may be based on relationship balances and on the basis of demonstrated good behavior as evidenced in a credit bureau report obtained from a Licensed Credit Bureau.
Article 17
It is the Card Issuers responsibility to make sure that their card manufacturer meets Saudi Central Bank and the Card Association’s standards. A manufacturer must therefore make sure that they keep Cardholder data and cards in a secure environment. Card Issuers must meet and maintain adequate levels of security when they store, process and transmit Cardholder data, in accordance with Card Association rules as a minimum and with Saudi Central Bank circulars as a mandatory obligation.
Article 18
Additional features (such as credit or default insurance products etc.) that require additional payment which are optional to the primary product features of the Credit or Charge cards, must not be added on or embedded to the Credit or Charge Card account and are to be clearly represented as an “Optional Feature”. A Cardholder must indicate his/her approval to obtain such services before their inclusion in the account. Card Issuers must also clearly disclose all fees and Term Cost for these services to the Cardholder within their offer for such Optional Features.
Replacement Cards
ARTICLE 19
A replacement Credit or Charge Card with a new validity period may be issued by a Card Issuer to a Cardholder in the following scenarios:
a. The card has been reported as lost, stolen or damaged. b. The card has been invalidated on suspicion of a fraud or suspicious transaction.
c. The validity period of the card is due to expire, and the replacement card is of the same type as the Credit or Charge Card so replaced.
d. Any other technical reasons including systems and technology enhancements.
e The account is not delinquent.
f A Co-branded card, affinity card or private label card has terminated and a replacement card is issued according to the provisions of the original card Agreement between the Card Issuer and the Cardholder.
g. New or updated requirements and Regulations.
The Card holder has the right to accept or reject the replacement card. A Cardholder shall be deemed to have given their consent if they:
- do not express an objection to the notices referred to in the preceding paragraph within 2 weeks from the issuance of such notices, or
- activates the replacement Credit or Charge Card.
ARTICLE 20
A replacement card shall be treated as being of the same kind as the Credit or Charge Card being replaced including the:
- Type of card
- Terms of use
- Branding
Any fees and Terms Cost relating to the original card held by the Cardholder will apply to the replacement card. The only exception will be where the Cardholder has applied for and activated an upgraded Card, which may have different terms and conditions, including pricing and other features.
Supplementary cards
ARTICLE 21
The Supplementary card may be issued at the Primary Cardholder's request to issue a Supplementary card under their account, to their Designated Individual.
ARTICLE 22
A replacement Supplementary card must be issued in accordance with the Articles for card issuing provided in these Regulations.
ARTICLE 23
The Primary Cardholder shall be liable for all liabilities incurred under the Supplementary card, including any outstanding and or unpaid balances.
Section Three Credit Limits
Article 24
A Card Issuer is not permitted to increase a Credit limit of its Cardholder without receiving an Authenticated Communication from the Primary Cardholder seeking such an increase and according to the Regulations and circulars issued by Saudi Central Bank relating to Credit and Charge Cards. Any confirmation of such prior request by the Primary Cardholder must be documented. This Article does not apply to Charge Cards.
Article 25
When setting initial credit limits, a Card Issuer needs to consider:
a. The results of a debt burden analysis (the ratio of the Cardholder’s debt to his annual income).
b. Account behaviour information (on existing accounts) e.g. typical value of transactions; timeliness of repayments.
Article 26
A Card Issuer may not issue or permanently increase the Credit limit of an existing Credit or Charge Card without seeking the Cardholder’s Credit records from a Licensed Credit Information Bureau, and examining the credit record of the Cardholder to confirm the Cardholder’s solvency, repayment capacity and credit conduct.
Article 27
A Card Issuer is required to carry out proper risk management procedures including the use of Credit scoring models, delinquency behaviour etc., for issuance and for renewal of Credit or Charge Cards and to assign appropriate Credit limits to the Cardholder.
Article 28
The Card Issuer risk management procedures, together with their Credit scoring model, must be reviewed annually at a minimum or as directed by Saudi Central Bank. A fundamental part of this annual review must be the assessment of Cardholder account behavior delinquency.
Article 29
Where a Cardholder has not made the full minimum monthly repayment on 3 consecutive occasions the Card Issuer will immediately:
a) Freeze the account and treat it as a delinquent account.
b) Offer the Credit Advisory Services (regarding how to deal with financial difficulties) free of charge to the Cardholder, and
c) Work towards a mediated settlement before implementing collection and legal system against the Cardholder.
d) A Card Issuer must deal directly with a defaulting Cardholder during this time and can only hand over the case to an internal or external collection agency a minimum of one month after the date when the third consecutive defaulted monthly repayment has occurred. Thereafter and at all times, the Card Issuer must be available to directly offer Credit Advisory Services to the defaulted Cardholder.
Article 30
A Card Issuer is not allowed to lower the minimum monthly repayment required from its Cardholder below 5% of the outstanding balance on the Credit card account.
Article 31
Upon receipt of a request from a Cardholder seeking closure of the Credit or Charge Card account and upon receipt of full and final repayment of the Credit or Charge Card account, the Card Issuer is required to issue a no liability or clearance letter no more than one month from the date of full and final repayment of the outstanding amount and update the Cardholder’s record with any Licensed Credit Bureau within maximum of one week of closing the account.
Section Four Advertising
Article 32
A Card Issuer that advertises a Credit or Charge Card in an Advertisement must disclose, in a manner that is clear to the Cardholder, the name and Annual Percentage Rate (APR) of the advertised product and shall not include other rates such as the Term Cost.
Article 33
A Card Issuer launching a campaign, advertising special term cost free promotions for a specific period, must ensure that the Advertisement discloses in a manner equally as prominent, whether or not term cost accrues during the specific period and is payable after the end of the period, with the end date of the special term cost free promotion period clearly displayed on the Advertisement.
Article 34
The Card Issuer must indicate in all product Advertisements its name, logo, any identifying representation and contact details.
Article 35
SAMA may require any Card Issuer who does not abide by the provisions of the articles within these Regulations to withdraw the Advertisement within one Business Day of notice from Saudi Central Bank.
Article 36
If a Card Issuer offers an introductory promotional term cost, the Card Issuer must remind the Cardholder one week before the end date of the introductory promotional term cost. The Card Issuer will provide the Cardholder with the revised term cost and any change in other terms and conditions that will apply to the period after the introductory period. The Cardholder may have the option to terminate the account. In 10 days if he/she does not accept the new term cost.
Article 37
Advertising by Card Issuers will not be deceptive or misleading and will not exaggerate the advantages of a product or service. All text and numbers, including footnotes shall be clearly visible and understandable with a legible font size (minimum equivalent to Arial 9).
Article 38
The Card Issuer may not carry out any of the following:
a. Provide an Advertisement that includes a false offer or statement or claim expressed in terms that would directly or indirectly deceive or mislead the consumer. b. Provide an Advertisement that includes the unlawful use of a logo, a distinctive mark, or a counterfeit mark.
Section Five Information Disclosure
Disclosure statement
Article 39
A Card Issuer that proposes to enter into a Credit or Charge Card Agreement with a Cardholder must provide an Initial Disclosure. The Disclosure must be clear and easy to understand and highlight the terms and conditions which may affect the Cardholder’s rights and obligations, and the Card Issuer must use any format specified by Saudi Central Bank from time to time for that purpose.
Furthermore, the specific terms contained under Article 74 dealing with ’account statement errors/disputed transactions' must be included in the Initial Disclosure. An Initial Disclosure is deemed to be provided to the Cardholder by any of the following:a) On the day recorded as the time of sending by the authorized Card Issuer’s server, if provided by electronic means, and the Cardholder has consented to receive it by electronic means.
b) On the day recorded as the time of sending by a fax machine, if provided by fax and the Cardholder has consented to receive it by fax.
c) 2 weeks after the postmark date, if provided by registered mail.
d) When it is received, in any other case.
Article 40
The Initial Disclosure must include the following information as a minimum:
a. The initial Credit limit, if it is known at the time the disclosure is made.
b. The APR and the annual 'Term Cost'.
c. The nature and amounts of any recurring non-Term Cost’ charges.
d. The minimum payment during each payment period and the method for determining it.
e. Each period for which a statement of account is to be provided.
f. The date on and after which term cost accrues and information concerning any Grace Period that applies.
g. The particulars of all fees and charges.
h. Information about any Optional Feature in relation to the Credit or Charge Card Agreement that the Cardholder accepts in writing, the fees for each Optional Feature and the conditions under which the Cardholder may cancel that feature.
i. The manner in which the term cost is calculated.
j. If the Cardholder is required by the Credit or Charge Card Agreement to pay the outstanding balance in full on receiving a statement of account:
1. Mention of that requirement
2. The Grace Period by the end of which the Cardholder must have paid that balance and,
3. The penalty fees charged on any outstanding balance not paid when due.
k. Information on all applicable charges including reporting of Default cases to a Licensed Credit Information Bureau or appropriate Regulatory Authorities as per Saudi Central Bank’s approval.
l. An illustrative example of calculations depicting sample conversion of foreign currency charges into Saudi Riyal, showing the foreign exchange conversion fees used when the Card Issuer converts a foreign transaction back to Saudi Riyal. The calculations should include one foreign currency purchase transaction and one Cash Advance transaction at an ATM/POS outside of Saudi Arabia.
Article 41
An Initial Disclosure may be part of a Credit or Charge Card Agreement or an application for a Credit or Charge Card or may be an annex to the foregoing documents. The Card Issuer is required to obtain a signed acknowledgement from the Cardholder of having read and received the Initial Disclosure. This signed acknowledgement must be retained, even after the Cardholder closes their Credit or Charge Card account.
Article 42
If the Cardholder consents, the Initial Disclosure may be provided by electronic means that the Cardholder can retrieve and retain.
Article 43
If the initial Credit limit is not known when the Initial Disclosure is made, the Card Issuer must disclose it in:
a. The first statement of account provided to the Cardholder; or
b. In a separate statement that the Cardholder receives on or before the date of the first statement of account.
General disclosures
Article 44
As part of the Initial Disclosure, Card Issuers must include a summary covering the basic information regarding the Credit or Charge Card product and the main provisions of the Credit or Charge Card Agreement, in a language clear to the Cardholder and in accordance with the format stipulated by Saudi Central Bank. The Cardholder's receipt of such summary shall be documented in the Cardholder record (Annex 2).
Article 45
If a Credit or Charge Card agreement is amended, the Card Issuer must, at least 30 Calendar Days before the amendment takes effect, disclose to the Cardholder, any changes to the agreement, except changes to the following:
a. An extension to the Grace Period.
b. A decrease in fees and charges.
c. A change concerning information about any optional service in relation to the Credit or Charge Card Agreement.
Article 46
The Card Issuer shall mail or deliver to the Cardholder, the monthly account statement at least three weeks prior to due date. Where the Cardholders agree to receive their monthly statement by electronic channel, the Card Issuers may not send the physical statements. The Card Issuer that fails to satisfy such requirement shall forfeit the right to collect any additional fees as a result of such failure.
Article 47
A Card Issuer should include specific warning statements in all Agreements, terms and conditions, application forms and Advertisements, in red colors stating clearly the potential consequences for the Cardholder in;
a) Not meeting the Credit or Charge Card conditions as confirmed in the Agreement.
b) Only making the minimum repayments each month.
Regular account statements
Article 48
A Card Issuer must provide Cardholders with regular monthly statements that contain the following information:
a. Details of Credit Limit: includes approved Credit limit, available and outstanding balances.
b. Previous balance: The outstanding account balance at the beginning of the account statement cycle.
c. Purchases or Advances: Identification of transaction and its merchant description including the date of transaction and the transaction amount in Saudi Riyal or its equivalent if it's in foreign currency.
d. Details of fees or term cost charged to the account, and the dates when those amounts were posted to the account, including fees for 'Optional Features' purchased by the Cardholder.
e. The amount that the Cardholder must pay, on or before a specified due date.
f. The total sum for payments and the total sum for purchases, total sum for Credit advances and total sum for fees.
g. Any payments charged or refunds to the account during the account statement cycle, including the amount and the date of payment and or refund.
h. If the term cost has changed during the account statement cycle, each periodic rate used to calculate the term cost and the value of balances to which it will be applied shall be disclosed. If different periodic rates were used for different types of transactions, the types of transactions to which such rates are applied shall be disclosed.
i. The amount of the balance to which a periodic rate was applied. The manner in which the balance was determined shall be disclosed.
j. The closing date of the account statement cycle on which the balance becomes due and outstanding.
k. The date on which the new outstanding balance of the Credit or Charge Card must be paid fully or partially to avoid term cost and any applicable penalty charges.
l. The address or telephone number to be used for notification of account statement errors or any other enquiries that a Cardholder may have on the account statement.
m. The time period allowed to the Cardholder to verify the accuracy of transactions as annotated in the account statement after which the account statement is binding. This period shall not be less than 30 Calendar days as of the date of sending the statement.
Disclosure of fees, commissions and charges
Article 49
Details of foreign currency transactions, including conversion rate, fees and all charges levied on the foreign currency transaction, must be displayed on the transaction record in the Cardholder’s monthly statement, in the manner stipulated by Saudi Central Bank.
Article 50
If a Card Issuer offers to defer or skip a payment under a Credit or Charge Card Agreement, the Card Issuer must, with the offer, disclose in a prominent manner whether term cost will continue to accrue or if any additional charges will accrue during any period covered by the offer, if the offer is accepted.
Article 51
The Card Issuer is required to promptly advise its Cardholders of any changes in their Credit or Charge Cards agreement by giving them at least 30 Calendar Days prior notice advance notice.
Section Six Cardholder Dealing
General
Article 52
The Saudi Riyal shall be used as a basis for calculating all transactions and charges of Credit and Charge Cards, and it shall be used in all disclosures of monetary values for cards issued and or denominated in Saudi Riyal. For cards issued in currencies other than the Saudi Riyal, the basis for calculation will be their respective currency of issuance.
Article 53
A Cardholder may terminate the relevant Credit or Charge Card Agreement if they do not agree to any amendment, change or modification by notifying the Card Issuer of their desire to terminate the Credit or Charge Card Agreement within 14 calendar Days after their receipt and after paying the outstanding amount. The aforementioned notice from the Card Issuer should advise Cardholders of their entitlement to a 14 calendar Days termination period.
Article 54
The Cardholder is required to keep the Card Issuer's records updated with their latest address and to immediately notify the Card Issuer of any change in their contact details. Failure to provide this information will release the Card Issuer from any liabilities and obligations under Article 56.
Article 55
A Card Issuer may allow its Cardholder or a Designated Individual to process a Cash Advance using their Credit or Charge Cards up to a maximum of 30% of their Credit limit. ATM cash withdrawals are subject to limits that pertain in the jurisdiction where the Cardholder is making the cash withdrawal.
Article 56
Card Issuers should be advised to incorporate in their Credit or Charge Card agreements a clause which specifies that within 10 days of receiving a Credit or Charge Card, the Cardholder has the right to cancel it free of change and the Card Issuer will not claim any fee unless the Cardholder has activated the Card.
Article 57
The Card Issuer must, upon the approval of the Cardholder, register the Cardholder’s credit information with a Licensed Credit Information Bureau in accordance with the relevant laws, regulations and instructions. Such information shall be updated throughout the period of dealing with the Cardholder.
Article 58
Card Issuers must issue regular SMS, email and other electronic communication awareness messages regarding paying the outstanding amount in time and the actions that a Cardholder needs to take in case of fraudulent transactions and a lost/stolen card with contact details.
Article 59
Card Issuers are expected to have appropriate anti-fraud and monitoring systems and procedures in place to protect itself and its Cardholders. At a minimum, Card Issuers must have systems to detect unusual transactions or account behaviour and must proactively contact Cardholders to verify any suspicious transactions.
Article 60
A Card Issuer should emphasise to merchant customers that they cannot pass on or impose any additional fees or charges (merchant service charge) when Cardholders use a Credit or Charge card for payment of goods or services in their stores. The Card Issuer responsible for accepting the merchant’s deposits should ensure the amounts deposited are aligned with the merchants’ business. A Card Issuer should facilitate training of merchants’ staff on the use of POS devices and provide them with the required rules and regulations to be followed.
Article 61
A Card Issuer engaging in Outsourcing of any component of its Credit or Charge Card business (including marketing for new cards and or collection of dues etc.) shall comply with Saudi Central Bank’s ‘Rules on Outsourcing’.
Article 62
Each monthly statement must include an illustrative information in red colours showing :
a. How long it will take the Cardholder to pay off the amount of SAR 7000 or actual statement balance using the minimum repayment amount only. b. The Term Cost to the Cardholder as a result of paying only the minimum amount due.
Article 63
Card Issuers must issue an SMS message to Cardholders:
(a) Advising when a debit transaction has been authorized, showing the merchant name, date and amount of the debit transaction, updated balance of the account and the credit limit available after the transaction amount has been posted to the account.
(b) Advising when a credit transaction has been processed, showing the payer name, date and amount of the credit transaction, the updated balance of the account and the credit limit available after the transaction amount has
been posted to the account.
(c) Release of pre-authorizations transactions.
Article 64
A Card Issuer must inform Cardholders about outstanding transactions and request payment within a maximum of 90 days from the original date of the transaction. After that, the Card Issuers can only debit a Cardholder’s account for payment after obtaining documented approval from the Cardholder.
Article 65
A Card Issuer is required to implement a clearly defined Code of Conduct for employees engaged in Cards business including sales and marketing of Credit and Charge Card products and follow-up and collection of impaired and delinquent Credit Card and Charge Card Accounts. A Card Issuer must provide those employees with a copy of the Code of Conduct and obtain their acknowledgement of receipt. The Code of Conduct must prohibit the following:
a) Any contact with neighbours, relatives, colleagues or friends of the defaulting Cardholder for the purpose of requesting or conveying information on the solvency of the Cardholder.
b) Any communications (verbal or written) to the Cardholder conveying incorrect information on the consequence of defaulting on their obligations to the Card Issuer. c) Unauthorized repossession of the pledged collateral excluding cash collateral without judicial proceedings or the specific consent of the Cardholder.
d) Communicating with the defaulting Cardholder using envelopes tagged with inscriptions identifying contents as containing debt collection information.
e) Any breach of confidentiality of Cardholder information, conflict of interest and breach of ethical values.
Article 66
Card Issuers are prohibited from increasing the Term Cost on an existing outstanding balance as a result of delinquency or default.
Article 67
Credit and/or Charge Card outstanding amount must be due on the same date each month and payments received up to and including midnight on the due date must be treated as timely. Card Issuers cannot charge a late payment fee unless Cardholders are given at least 21 days to pay their due amount.
Article 68
Late payment fees must be reasonable in proportion to the violation of the account terms in question and must not exceed SAR100. The amount of the late payment fee cannot exceed the outstanding amount.
Article 69
Card Issuers are prohibited from allowing a cardholder to exceed the approved credit limit and paying an ‘over-the-limit- fee and any decision to allow the balance to exceed the authorized credit limit is based on the Card Issuer’s risk assessment.
Article 70
Cash Advance fees must not exceed:
- SAR75 for Cash Advance transaction up to SAR 5000.
3% of transaction amount over SAR 5000, and subject to
a maximum of SAR 300.Article 71
Card issuers are prohibited from imposing any fees for transfer transactions between Cardholder’s current account and the Cardholder’s Credit or Charge Card account at the same bank.
Article 72
Card issuers must immediately credit transfers between their Cardholder’s current account at their bank and the Cardholder’s Credit or Charge Card that has been issued by them.
Article 73
Card issuers must send a notification to Cardholders, one month before expiry of reward points, and repeat one week before expiry date, advising the Cardholder of the number of points due to expire and the expiry date.
Section Seven Disputed Transactions
Account error/disputed transaction
Article 74
The term “account statement error/disputed transaction” shall represent any transaction posted to the Cardholder’s Credit or Charge Card account, resulting in an error in the overall balance. Account statement errors shall include the following:
a. An Unauthorized use transaction that is not made by the Cardholder or person authorized by the Cardholder.
b. A transaction on which the Cardholder requests additional clarification including documented evidence.
c. Failure by the Card Issuer to properly credit a payment or any other amount deposited in the Cardholder’s account.
d. Accounting error made by the Card Issuer, so that a charge would be lower or higher than it should be including the imposition of fees or term cost that are not in accordance with the terms and the agreement in force.
e. The Card Issuer’s failure to deliver a monthly account statement to the Cardholder’s address on record.
f. Any other errors relate to Cardholder transactions.
Article 75
The term “notice of account statement error/disputed transaction" means a notification given by a Cardholder to the Card Issuer, using the contact information as included within the said account statement or other information supplied by the Card Issuer, and it must meet the following requirements:
a. It must be received by the Card Issuer no later than 30 Calendar Days after the Cardholder had mailed or delivered the first account statement which contains the account statement error.
b. The notice shall enable the Card Issuer to identify the Cardholder’s name and account number, and indicate, to the extent possible, the Cardholder’s reasons for believing that an account statement error exists, the nature of such error, the transaction details including posting date and amount related to the error.
c. If the card holder is proven to having being engaged in any fraud behaviours relating to the disputed transactions, and if the card holder refuses to provide relevant necessary materials for the investigation of the disputed transaction, the Card Issuer shall have no liability for the disputed transactions.
d. If an unauthorised transaction or fraud occurs after the Cardholder has notified the Card Issuer by telephone of the loss or theft of the card, then the Card Issuer will bear the responsibility for the amount of the unauthorized transaction or fraud.
Article 76
The Cardholder’s liability for Unauthorized use of the Credit or Charge card shall be limited by the following:
1. In an Unauthorized use of the Credit or Charge card on account of its Loss or Theft, the maximum liability of the Cardholder prior to the Cardholder reporting the Loss or Theft to the Issuer shall not exceed the available credit limit or the amount of unauthorized transactions posted to their account, whichever is lower at the time of such Loss or Theft.
2. The Cardholder shall not bear any responsibility or cost unless the Card Issuer has provided adequate notice of the Cardholder’s maximum potential liability and of means by which the Card Issuer may be notified of loss or theft of the card (such as a telephone number, address,).
3. The Cardholder shall have no liability for any Unauthorized transactions made by the use of the card after reporting its Loss or Theft to the Card Issuer if the following conditions were met:
a) The Cardholder has immediately and without delay notified the card issuer by telephone of the loss or theft of the card.
b) The Cardholder shall also be not responsible if the Card Issuer has failed to receive the notification of loss or theft due to negligence or delay on its part,
c) The Cardholder has exercised vigilant care in safeguarding the card from risk of loss, theft or unauthorized use.
4. If any dispute is found to be a potential or genuine fraud (e.g. counterfeit, skimmed, etc.,) the full amount of the disputed transaction must be reversed on the card account.
Article 77
When informed of the Unauthorized charges by their Cardholders, Card Issuers should ensure appropriate investigations are carried out to determine responsibility and liability. Cardholder are required to provide the necessary information and documentation to assist in the investigations.
Article 78
In any action by a Card Issuer to enforce liability for the use of a Credit or Charge Card, the burden of proof is upon the Card Issuer to show that the use was authorized. If the use was unauthorized, then the burden of proof is upon the Card Issuer to show that the conditions of liability for the unauthorized use have been met.
Article 79
Where a Card Issuer is making refund to a Cardholder account, they must immediately communicate the decision to Cardholder by SMS and refund the due amount.
Article 80
In the case of a Cardholder disputing a transaction, Card issuers must freeze any accruing term cost and must not charge out any term cost on the disputed amount.
Article 81
Card Issuers are required to have systems in place to record and retain Cardholder calls for at least 180 days from the date of recording for verification if required.
Article 82
Card Issuers are required to provide Cardholders with a reference or transaction number at the time of the report of loss, theft or Unauthorized usage.
Article 83
A Cardholder can raise a chargeback claim by sending an Authenticated Communication to their Card Issuer challenging a debit on their card statement within 30 calendar days of the statement date, on which the debit first appears. Such claim include:
a. Charges the Cardholder did not authorize.
b. Charges for undelivered goods or services.
c. Charges for goods or services different from what was represented or of the wrong quantity.
- Upon receipt of the chargeback claim, the Card Issuer must initiate the chargeback claim within a maximum of one week.
Article 84
Where a Card Issuer discovers an internal error, or is informed of an error by a Cardholder making a complaint or a claim, then the Card Issuer should refund all other Cardholders who are affected by a similar error. The Card Issuer should issue a notice to all affected Cardholders, advising them of the error and the steps being taken for corrective action, including the amount of the refund to the Cardholders' accounts. This should be completed within 60 Calendar Days of the original error being identified.
Section Eight Dispute Resolution
Article 85
Card Issuers must have a comprehensive dispute resolution policy and procedures (also known as complaint handling policy and procedures) and comply with Saudi Central Bank Regulations for complaint handling departments A copy of the Card Issuer's complaint handling policy and procedures must clearly be on display in all of their branches and on their websites and they must provide a hard copy to a Cardholder if requested.
Article 86
The Card Issuer must mail or deliver a response to the Cardholder within 30 Calendar Days of receiving the notice of account statement error/dispute advising the Cardholder of the likely timeframe of resolution of the error/dispute and requesting any additional available information or documentation.
Article 87
The Credit or Charge Card Issuer shall conduct necessary investigation and comply with the appropriate dispute resolution procedures (as advised to Cardholder) within two complete account statement cycles, but in no case shall be later than 90 Calendar Days as of the date of receiving the notice of “account statement error/disputed transaction. However, on an exceptional basis the Card Issuer is allowed to extend the resolution date up to 180 Calendar Days from the date of receiving notice of “account statement error/disputed transaction” if the Card Issuer confirms and can prove that the account statement error/disputed transaction falls under the purview of and is being pursued in accordance with the rules and Regulations of the relevant 'Card Association' for the Card.
Article 88
If the account statement error/disputed transaction has not been Satisfactorily Resolved, the Cardholder shall not be obliged to pay the portion of the required payment that the Cardholder believes is related to the disputed amount, including term Cost or fees. The Card Issuer may not try to collect any amount, term cost or fees related to the account statement error/disputed transaction until the dispute is resolved, in accordance with the rules and regulations.
Article 89
The Card Issuer shall not make an improper report about the Cardholder’s Credit standing, or report that an amount or account is delinquent prior to the error/disputed being Satisfactorily Resolved. The Cardholder is not required to pay the disputed amount or term cost or fees during the error/disputed resolution process in any event, not earlier than 90 calendar days (180 days for exceptions cases) from the date of the notice of account statement error/disputed.
Article 90
If the Credit or Charge Card Issuer determines that an account statement error has occurred as stated by the Cardholder, it shall correct the error and pay back any disputed amount and relevant Term Cost and fees debited on the Cardholder’s account and deliver a correction notice to the Cardholder.
Article 91
If the Credit or Charge Card Issuer determines that a different account statement error other than the one identified in the Cardholder’s notice has occurred, the Card Issuer shall mail or deliver to the Cardholder the card issuer’s reasons for believing that a different account statement error has occurred and the reasons for the belief that the error alleged by the Cardholder is incorrect. The issuer shall correct the error and credit the Cardholder’s account with the correct amount and relevant term cost and fees in accordance with procedures in force.
Article 92
If the Card Issuer determines that no account statement error has occurred, it shall mail or deliver an explanation of the reasons of believing that the error alleged by the Cardholder is incorrect and provide the Cardholder with copies of any documented evidence.
Article 93
If the Credit or Charge Card Issuer deems that a Cardholder is liable for all or part of the disputed amount and relevant term cost and fees, it must:
a. Notify the Cardholder of the date when payment is due and the portion of the disputed amount and relevant term cost and fees that the Cardholder is liable for.
b. Report to a Licensed Credit Information Bureau that an account or amount is delinquent because the amount due has remained unpaid after the due date given by the Credit or Charge Card Issuer as defined in the terms and conditions of the Cardholder agreement in force, except for any extension or Grace Period provided by the Card Issuer to the Cardholder.
ANNEX 1
This annex has been updated by circular No (45025707) dated 17/04/1445H (corresponding to 01/11/2023). Please refer to Rules Governing Calculation of Annual Percentage Rate (APR) to read the updated version.ANNEX 1
CALCULATION OF THE ANNUAL PERCENTAGE RATE IN CREDIT CARD
Annual Percentage Rate (APR) is the discount rate at which the present value of all payments and instalments that are due from the Cardholder, representing the Total Amount Payable by the Cardholder, equals the present value of all payments of the Amount of Credit available to the Cardholder on the date on which the Credit amount or the first payment thereof is available to the Cardholder, in accordance with the following equation: where: m: is the number of the last payment to be received by the Cardholder d: is the number of a payment to be received by the Cardholder Cd: is the amount of payment (d) to be received by the Cardholder Sd: is the period between the date of the first payment to be received by the Cardholder and the date of each subsequent payment to the Cardholder, expressed in years and fractions of year, therefore S1=0. n: is the number of the last repayment or payment of charges due on the
Cardholderp: is the number of a repayment or a payment of charges due on the Cardholder Bp: is the amount of repayment or payment of charges (p) due on the Cardholder tp: is the period between the date of the first payment to be received by the Cardholder and the date of each repayment or payment of charges due on the Cardholder, expressed in years and fractions of year X: is the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) Assumptions for the calculation of APR - For the purpose of calculating APR, periods between dates shall be based on a year of 12 equal months or 365 days a year.
- For the purpose of calculating APR, the Total Amount Payable by the Cardholder
shall be determined, including all unavoidable costs and fees with the exception of charges and fees payable by the Cardholder as a result of non-compliance with any of his commitments laid down in the Credit Card Agreement.
- The calculation of the APR must be based on the assumption that the Credit Card Agreement will remain valid for the agreed period and that the Card Issuer and the Cardholder will fulfil their obligations under the terms specified in the Credit Card Agreement.
- If the Credit Card Agreement contains clauses allowing variations in the charges
contained in the APR but unquantifiable at the time of calculation, the APR shall be calculated on the assumption that the charges will remain fixed at the initial level and will remain applicable until the end of the Credit Card Agreement.
- For the purpose of calculating advertised APR, the following shall be assumed:
A) If the ceiling of the credit card has not determined, that ceiling shall assumed to be SAR 10,000;
B) The total amount of credit shall be deemed to be drawn down in full at the start of day 1;
C) The first year unavoidable fees (e.g. application fee, maintenance fee) shall be determined;
D) The credit is provided for a period of one year; and
E) The credit will be repaid in full in 12 equal monthly payments - If the contract contains clauses allowing different ways of drawdown with different charges or Term Cost, the Total Amount of Credit shall be deemed to be drawn down at the highest charge and term cost applied to the most common mechanism.
- If there is a fixed timetable for payment received by the Cardholder but the amount of such payment is flexible, the amount of each payment shall be deemed to be the lowest for which the contract provides.
- If the Credit Card Agreement contains clauses offering charges or term cost for limited period or amount, the term cost and charges shall be deemed to be the highest for the whole duration of the contract.
- The Annual Percentage Rate must be calculated and expressed in percentage points with a minimum of two basis points, and rounding the following decimal place by one point if that place is greater than or equal to 5.
ANNEX 2
Credit card Issuer Logo
Credit Card Agreement Synopsis
Credit card holder Information
Cardholder name
Date of Agreement
National ID / Iqama / CR
Agreement reference number
Credit card information
Credit card limit
APR
Administration fees
Term cost
Annual fees
Minimum amount due
Foreign currency conversion fees
Settlement date
Other fees
Late payment fee
The most prominent provisions
Implications of transactions in foreign currency Implications of paying the minimum amount due Implications of default Implications on cash withdrawals Implications of cash transfer Credit Card Features You will not pay any additional amount when you pay the full outstanding amount in due date.
*Disclaimer: Reviewing this synopsis shall not substitute reviewing the contract, its appendices, and shall not exempt from the obligations stipulated in the contract.
card holder signature Authorized issuer signature and stamp
Credit card issuer contact information
ANNEX 3
FX Illustration Box
Date
Description
Date dd/mm/yyyy
Merchant name on dd/mm/yyyy Debit
Original Currency Amount Currency Conversion Rate Local Currency Amount Other Fees/Charges FX Amount ?? SAR ? SAR ? SAR?
General Rules for Savings Products in Banks
No: 45059688 Date(g): 24/3/2024 | Date(h): 15/9/1445 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Based on the powers vested to Saudi Central Bank under its Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/36) dated 11/04/1442H, and the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/5) dated 22/02/1386H, and based on SAMA's efforts to encourage banks to offer savings products and stimulate customer to benefit from them.
Accordingly, attached are the general rules for savings products in banks, which all banks are required to adhere to, and to complete the necessary procedures in accordance with the established policies and procedures.
Chapter One: General Provisions
Article One: Definitions
The following terms- wherever mentioned in these rules- shall have the meanings indicated next to them, unless the context requires otherwise:
Term
Definition
SAMA
Saudi Central Bank. Bank
Banks and financial institutions licensed to conduct banking activities in the Kingdom according to the Banking Control Law. Customer
A natural or legal person. Savings Products
A product characterized by any or all of the following features:
A. Exchange transactions limited to a specific number.
B. Maintaining a minimum deposit amount.
C. A return due to the customer on the deposit amount, along with the availability of feature (A) or (B).
Deposit Amount
The amount deposited with the bank for savings. Return
The profit on the deposit amount calculated based on the Annual Equivalent Rate (AER). Annual Equivalent Rate (AER)
The annual return rate on the savings product as specified in Disclosure of Interest Rates on Financing and Savings Products. Deduction
A periodic deduction of a specified amount from one of the customer's accounts and its addition to the deposit amount, which the customer can authorize the bank to execute under the product agreement between the customer and the bank. Trusted Communication Channels
A registered communication method that can be verified and is retrievable in written or electronic form. Article Two: Purpose and Scope
- These rules aim to provide a general framework for savings products offered by banks, which contributes to encourage them to launch savings products and stimulate customer benefits from them.
- These rules apply to all banks when presenting and offering savings products to their customers.
- These rules do not override the provisions stated in the relevant regulations, instructions, and instructions issued by SAMA.
Chapter Two: Provisions for Savings Products
Article Three: Design and Development of Savings Products
1 . When designing and developing savings products, the bank must comply to the following: 1.1 Product design quality, and the principles of disclosure and transparency in its presentation and offering. 1.2. Continuous evaluation of the product's effectiveness and risks based on specific performance indicators. 1.3. Transparency, clarity and accuracy in all product documents, including agreements and initial disclosures. 1.4. Flexibility in the terms for customers to obtain and benefit from the product, or cancel it. The bank should make the product available through digital channels and should not require the customer to have or open a current account, except for products that necessitate such mechanisms, like those involving automatic deductions. 1.5. Inclusiveness of products a various customer segments, including those with low income, foreign residents, and individuals under the age of eighteen. 2. The bank should give importance to savings products in its product development process, considering the best local and international standards and practices in this regard. Article Four: Advertising and Disclosure of Savings Products
The bank must give importance to savings products in promotional advertisements. Additionally, it should allocate a section on its website and mobile application to display these products, including at a minimum the characteristics of each product, the terms of use, and frequently asked questions about the product. The section should be regularly reviewed to ensure the information remains up-to-date.
Article Five: Offering and Managing Savings Products
When offering and managing savings products, the bank must adhere to the following:
1. Implement due diligence measures by identifying the customer and any authorized representatives, -if any-, and verify their identities using reliable and independent documents, data, or information, in accordance with the Anti-Money Laundering Law and the Law on Combating the Financing of Terrorism and their implementing regulations. The bank may also refer to the requirements outlined in the Account Opening Rules issued by SAMA when identifying the customer. 2. Provide the customer with an initial disclosure that include the contents of the agreement specified in paragraph (3) of this article. 3. Conclude a product agreement with the customer that includes, -at a minimum- and considering the characteristics of each product, the following: 3.1. Returns and Calculation Mechanism. 3.2. Annual Equivalent Rate (AER). 3.3. Any fees charged to the customer, including administrative fees. 3.4. The scope and areas of investment for the deposit amount. 3.5. The obligations and rights of both parties, such as withdrawal limits from the deposit amount or the minimum amount that must be retained. 3.6. The circumstances under which the customer may not be entitled to returns. 4. Provide the customer with a summarized monthly statement that includes, -at a minimum-, the deposit amount and the returns accrued since the product was obtained. 5. Subject to the provisions in paragraph (1.5) of Article Six, it is preferred that the agreement with the customer be for a fixed term, with either party having the right to terminate it after providing the other party with sufficient notice through mutually agreed reliable communication channels. Upon termination of the agreement or its expiration without renewal agreement by both parties, the bank must transfer the deposit amount to a current account specified by the customer. Article Six: Offering Savings Products to Non-Residents
1. Without prejudice to the provisions of the Anti-Money Laundering Law and the Law on Combating the Financing of Terrorism and their implementing regulations, it is permissible to offer savings products to non-residents in the Kingdom, provided that the bank adheres to the following minimum requirements: 1.1 Compliance with the laws of the customer’s country of residence, -where applicable-, such as obtaining a license from the relevant authorities in the customer’s country of residence, as well as adhering to personal data protection laws, tax evasion laws, and other related regulations. 1.2 Implementation of enhanced due diligence measures, which may include relying on a third party in accordance with the "reliance on a third party" requirements specified in the Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorism Financing (AML/CTF) Guide. 1.3 Establishing limits and methods for withdrawals, deposits, and redemption of the deposit amount in accordance with the customer’s risk level. 1.4 Offering these products exclusively in Saudi Riyals. 1.5 Ensuring that the agreement with the customer be for a fixed term, with either party having the right to terminate it after providing the other party with sufficient notice through mutually agreed reliable communication channels. Upon termination of the agreement or its expiration without renewal agreement by both parties, the bank must transfer the deposit amount to a current account specified by the customer. 1.6 Obtaining written no-objection letter from SAMA before offering the product, including a request detailing the target percentage of total savings products and time deposits held by the bank. 2. Without prejudice to the requirements of Account Opening Rules that mandate the closure of the resident customer's current account upon their final departure from the Kingdom, the customer is permitted to keep the available funds in the bank by utilizing savings products, provided that this is based on the customer's request, whether before their departure from the Kingdom or after their departure and the closure of the current account. Chapter Three: Final Provisions
Article Seven
- These rules represent the minimum requirements that banks must adhere to when designing, developing, offering, and managing savings products.
- These rules will be effective from the date of their issuance.
Regulatory Rules for Prepaid Payment Services in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
No: BCT/15631 Date(g): 2/5/2012 | Date(h): 11/6/1433 Status: In-Force Introduction
The Saudi Central bank* (SAMA), in accordance with the authority vested on it under the following relevant Saudi laws, is the legislative body responsible for exercising regulatory and supervisory control over banks and money exchangers, issuing general rules and overseeing that all banks and money exchangers comply and effectively implement the relevant laws and regulations.
- The Charter of Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency –issued via Royal Decree No. 23 dated 23/5/1377 H, Articles 1 (c) and 3 (d), which entrusts SAMA to supervise and regulate commercial banks and money-changers, and to set relevant rules whenever deemed necessary;
- The Banking Control Law – issued via Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/2/1386 H Article 16 (3).
- Decision No. 3/2149 dated 14/10/1406 H of His Excellency the Minister of Finance concerning the implementation of the provisions of the Banking Control Law.
- Based on the provisions of Articles 4 & 6 of the Anti-Money Laundering Law and its Implementing Regulations issued via Royal Decree No. M/39 dated 25/6/1424 H, empowering regulatory authorities to issue rules related to "Know Your Customer" Principle, and instructions related to precautionary procedures and internal control to detect any of the crimes stated in this Law, ensure compliance of financial institutions with issued instructions; set, apply and update effective written controls and monitor their application to prevent the exploitation of these institutions in money-laundering operations and assist in detecting suspicious transactions.
- Council of Ministers’ Decision, No. 59 Dated 28.3.1420 H which gives the authority to SAMA to authorize the issuance of Electronic Cash Cards and alike, and supervise according to instructions, standards and terms adopted by SAMA.
The Regulatory Rules shall be applicable to the issuance and operations of all aspects of prepaid payments as issued by licensed banks that have been authorized by the Saudi Central Bank*.
SAMA is the sole authority empowered to apply these Regulations and to take necessary measures as it deems appropriate regarding any violations of these provisions including imposing punitive charges and / or enforcement actions as applicable under the Banking Control Law. These rules are to be read in conjunction with and supplement the regulations as annotated in the ‘Rules Governing the Opening of Bank Accounts and General Operational Guidelines in Saudi Arabia’ as issued by SAMA. Financial Service providers in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia are expected to act as responsible businesses, ensuring their customers are educated and informed about the products and services offered, enabling them to make considered decisions about the products and services proffered and their use.
The purpose of the Regulatory Rules is to promote the informed use of prepaid payment services in the Kingdom. The framework defines the scope of prepaid payment services covered by the regulation, the license requirements to issue and acquire prepaid payment services, as well as defining the rights of end users relating to these payments.
The Regulatory Rules prescribes minimum levels of disclosure, gives accountholders the right to cancel prepaid service agreements, regulates certain prepaid payment service practices and provides a means for fair and timely resolution of transaction disputes, thereby providing detailed and sufficient information to educate and enhance the account holder and/or primary cardholder’s knowledge and awareness of prepaid payment service products and their associated terms and conditions.
Where a prepaid payment service is operated utilising the SPAN payment scheme brand these regulations should be read in conjunction with the SPAN Scheme Standard1.
The Regulatory Rules is divided into two sections.
The first section provides a definition of prepaid payment services, of the stakeholders interacting within prepaid payment services and also of the various prepaid payment service segments.
The second section lays down the operating rules and guidelines governing prepaid payment services, including the regulations regarding merchants.
Prepaid payment services operating within the Kingdom, regulated by SAMA, are subject to the rules and regulations defined herein. In addition, Open Loop prepaid services operate through the Saudi Arabian Payments Network (SPAN) and are subject to the applicable Operating Rules and Procedures defined and published by the SPAN Scheme from time to time. These Prepaid Regulatory Rules should therefore be read in conjunction with the ‘SPAN Operating Rules and Regulations’ and ‘SPAN Operating Procedures’, collectively referred to as the ‘SPAN Business Books’.
1The SPAN Scheme Standard relate to the SPAN Business Books, Operating Rules and Procedures
* The Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency was replaced By the name of Saudi Central Bank accordance with The Saudi Central Bank Law No. (M/36), dated 11/04/1442H, corresponding in 26/11/2020AD.
1. Definitions
The regulatory rules presented herein regulate the issuing, acquiring and usage of prepaid payment services. This regulatory rules document focuses primarily on "Cards", but applies to all prepaid services including smart/EMV cards and magnetic stripe card environments as well as other form factors for prepaid payment services, such as contactless and mobile payments.
1.1. Prepaid Payment Service Definition
A prepaid payment service, as regulated under these rules, is defined by the holding of monetary value in a prepaid account/electronic record that can be utilised to purchase goods or services from one or more businesses who agree to participate in the prepaid program. The defining features are:
- Monetary value is held on account for use to purchase goods and services for variable amounts as determined and agreed between the payer and payee at the time of purchase of the prepaid service
- Settlement of transactions can be between otherwise unrelated business entities.
Note: for the purposes of this document the terms "account", "electronic record" and "sub-record" are used interchangeably.
"Open loop" payment services enable the purchase of goods and services from a group of unrelated businesses through a prepaid account utilising a payment brand accepted at the participating merchants, i.e. multiple contracting entities, multiple issuers and multiple acquirers. "Open loop" prepaid services require a clearing and settlement services between different businesses. This includes the ability to encash any part of the prepaid balance through a third party network, such as ATM networks.
“Restricted loop” is a subset of an open loop program, in that the merchant acceptance of the program is limited to a specified merchant or a specified network of merchants. Examples of a restricted loop program include in its broadest form, prepaid accounts for the purchase of specific services or goods across a network of merchants (e.g., a prepaid coffee card accepted across a range of unrelated coffee shops, or a mall card accepted only at merchant locations within a specific mall);
"Closed loop" is the purchase of prepaid goods and services related to the goods and services within a defined contracting entity i.e. single contracting entity, single issuer & single/multiple acquirers. In its most restrictive form, close loop programs prepaid accounts for the purchase of services or goods from a specific merchant or merchant chain utilizing the settlement and clearing functions of the prepaid payment service. (e.g., a nationwide retailer offers a prepaid card valid only at its nationwide locations, an independent merchant offers a prepaid card valid only at its single store location but chooses to utilize the prepaid payment service for settlement and clearing functions).
Examples of closed loop prepaid goods and services include:
- Prepaid accounts for the purchase of specific services or goods, such as prepaid fares for public transport or prepaid airtime for mobile telephony services;
- Vouchers (a paper certificate or a series of electronic digits with a non-reloadable amount associated that allows the holder to make payments up to that value at a specific merchant or merchant chain);
- Gift cards for use at a merchant or merchant chain
A prepaid payment instrument is an access device, or token of identity, that can access a pre-funded account balance held by the issuer (refer to 1.2.1 Issuing Program Manager) to which a transaction can be charged. Such an access device could be a payment card, an internet wallet or a payment device utilising mobile technology.
Prepaid instruments encompassed in this regulatory framework include any access device that can provide transactional services against a prepaid balance, including but not limited to:
- Smart/EMV cards (payment cards with an embedded micro-processor);
- Magnetic stripe cards (payment cards with a magnetic stripe);
- Internet wallets (stored value internet accounts)
- Mobile payments
- Contactless payments (Near Field Communications technology)
1.1.1. Acceptance
Prepaid payment services within these regulatory rules can be used across a range of different acceptance models, or prepaid payment service programmes. These are:
Closed loop prepaid Payment Services2. A closed loop prepaid payment service is a prepaid product that is redeemable at a single merchant or at an affiliated group of merchants with the same name, mark, or logo3. The payment device is purchased on a prepaid basis and is honoured upon presentation at such single merchant or affiliated group of merchants. Closed loop prepaid products may or may not be reloadable.
Examples of closed loop prepaid products are:
i. Merchant branded gift cards
ii. Merchant branded store cards
Restricted loop prepaid payment services: A restricted loop prepaid payment service is a prepaid product that is used to acquire goods and services at a limited network of service providers (e.g. fuel stations), either within a clearly limited area or alternatively that can be used to pay for a limited range of goods and services. Restricted loop payment products may or may not be reloadable.
Examples of restricted loop prepaid products are:
Prepaid payment services that are accepted at different merchants located within a clearly defined area such as shopping cards or mall cards. Other examples include University or campus payment devices, Conference cards, Stadium cards, and other cards that are only accepted within a specific closed venue;
Prepaid payment services that are accepted at different merchants, located in different locations but that can only be used to purchase a limited range of goods and services such as Petrol cards, Meal vouchers or Public transport cards4.
C. Open loop prepaid payment services. Open loop prepaid products are payment instruments that are redeemable at all merchants or service providers where the payment brand is accepted without restrictions.
Open loop prepaid products may or may not be reloadable.
2 While closed loop prepaid payment services may be issued under these Rules in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, it is not anticipated that they will form the bulk of the programmes on offer
3 Where the prepaid payment service can be used to purchase or access a range of goods or services that are not predetermined at the time the prepaid account is loaded with value (e.g. airtime)
4 For example, transport cards that are accepted by transportation companies (cars, trains and others).
2.1.1. Reloadability
The regulatory principle presented herein governs both reloadable and non-reloadable prepaid payment service products.
a. Non-reloadable prepaid payment service. A prepaid payment service is non-reloadable if it has no mechanism for having additional funds added to the initial balance after the initial issuance.
b. Reloadable prepaid payment service. A prepaid payment service is reloadable if it has the ability of having more funds added after the initial issuance.
It is at the discretion of the prepaid Issuer to determine whether a prepaid product should be reloadable or non-reloadable (noting that re-loadable cards are subject to more rigorous KYC and AML requirements).
Common to both reloadable and non-reloadable prepaid services is that there is a deposit account that holds the available balance on the account until such a time as it is redeemed through spend against the balance or a cash withdrawal, when this service is allowed.
1.2. Stakeholder Definition
The implementation of a prepaid payment service payments system in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia will impact a range of stakeholders, including for example: SPAN, prepaid payment service issuers, acquirers, merchants, accountholders and primary cardholders.
1.2.1.The Issuing Programme Manager (Issuer)
A prepaid payment service Issuing Programme Manager (IPM) is a regulated bank in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia that is permitted to accept deposits, according to the Banking Control Law, issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 Dated 22.2.1386 H. The IPM operates the deposit account and collects the funds loaded onto the prepaid account. The IPM is responsible for:
a) Directly reimbursing the acquirers of the service providers (e.g. merchants) that are part of a closed loop payment device, or
b) Reimbursing acquirers through a scheme settlement arrangement if the service providers (e.g. merchants) are part of an open loop payment service.
1. Issuing activities. In order to operate a prepaid payment service programme, IPM’s have responsibility for undertaking the following activities directly, or through partners:
- Prepaid account recruitment. These are the activities associated with marketing to prospective prepaid payment service customers, including the development and distribution of marketing materials;
- Partner recruitment. Activities related to the recruitment of partners into the distribution network, such as an issuing processor, sellers/distributors and the load/reload network representatives (refer to 1.2.1 b);
- Customer recruitment and account set up. Includes the processing of prepaid payment service applications from their receipt by the IPM through to the approval stage (inclusive of the collection of KYC information), setting up new prepaid accounts and the sending out of “service Terms and Conditions” to new account holders;
- Payment product issuing. Includes all aspects related to the delivery of the payment service product to the customers, such as in the case of a prepaid card the production of the card through to the safe delivery of the card and PIN to the primary cardholder; The PIN distribution activity must be undertaken by the regulated entity (i.e. IPM);
- Load /reload network. Relates to the receipt and processing of funds deposited onto the prepaid account. These loads/reloads can potentially be made at a number of different channels, such as affiliated merchants, ATMs, bank transfers, person to person payments or Kiosks;
- Authorisation processing. Refers to the activities related to the approval/decline of an authorisation request associated with the prepaid payment service received by the issuer via SPAN or other payment networks;
- Transaction processing. Activities undertaken by the issuer, from the receipt of the clearing message from the acquirer to the point at which the transaction is posted onto the primary cardholder’s account. These activities also include the research and documentation of transactions disputed by the primary cardholder;
- Overdraft. Drawing more money than the bank accounts holds, prepaid service products are not allowed to go into overdraft;
- Statement production. Activities related to the preparation and delivery of customer statements, which can be via postal mail, web account, email, and SMS or ATM. Paper statements shall however be issued minimum at quarter basis to the primary cardholder (at no additional cost to them) if the cardholder specifically request this option;
- Customer service. Includes the activities associated with the handling and information storage of all general prepaid account related customer enquiries, requests and complaints;
- Fraud investigation. Activities related to the efforts put into preventing and following up suspected or actual cases of prepaid payment service misuse (both processes and systems);
- Usage Monitoring. Activities associated with monitoring the primary cardholder’s activities and customer due diligence that is required to ensure the programme’s on going compliance to AML and CTF regulations in force in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia;
- Programme management. Includes the general administrative and managerial activities involved with operating the prepaid account business, including the analysis of information generated by the programme and the strategic planning and development of the prepaid product.
2. Other participants within issuing activities.
The IPM may share some of the activities described above with third party as regulated by the "Rules on Outsourcing" issued by the Saudi Central Bank. Outsourcing may be used in order to attain a larger distribution network or reduce transaction processing costs.
Examples of organisations with whom the issuer may share issuing activities are as follows:
- The programme manager. A programme manager may administer several aspects of a prepaid programme, which may include transaction processing and the distribution of the payment device and marketing materials;
- The issuing processor. The issuing processor will typically send the responses to the authorisation requests and post the transactions onto the prepaid accounts. It may also manage the customer service;
- The seller/distributor. The seller/ distributor may be an affiliated shopping mall or a merchant that distributes at a fee the prepaid payment service contracts to prospective cardholders;
- The load/reload network. The load/reload network can include, for example, a branch or an ATM, where primary cardholders can load funds onto the prepaid account with cash or via payment with credit or debit cards, within the allowed limits for the product. In accordance with the "SAMA Rules on Outsourcing", July 2008, issuers are required to seek "no objection" from SAMA on the use of 3rd party (merchant sites) for applying load services to prepaid accounts, where such loads shall be governed by the rules set out in section 2.3.
Table 1: Activities that the IPM could share with third parties
(iv)
(iii)
(ii)
(i)
Load/reload network
Seller/ distributor
Issuing Processor
Programme Manager
(Issuing Activities)
Outsource Partner
X
√
X
√
Prepaid Account Recruitment
(i)
X
X
X
√
Partner Recruitment
(ii)
X
X
X
√
Customer Recruitment & Set-up
(iii)
X
√
X
√
Payment Device Issuing (excluding PIN issuing)
(iv)
√
√
√
√
Load/Re-load
(v)
X
X
√
√
Authorisation Processing
(vi)
X
X
√
√
Transaction Processing
(vii)
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Overdraft
(viii)
√
X
√
√
Statement Production
(ix)
X
√
For closed loop only
√
√
Customer Service
X
X
X
√
√
Fraud Investigation
Xi
X
X
√
√
Usage Monitoring
Xii
X
X
X
√
Programme Management
Xiii
1.2.2. The Acquirer
An acquirer of prepaid payment service is a regulated licensed bank, according to the Banking Control Law, issued by Royal Decree, No. M/5 Dated 22.2.1386 H. The acquiring business is governed by the SPAN Scheme Regulations; an acquirer can be either an ATM acquirer or a POS (merchant) acquirer or both.
An ATM acquirer is a regulated bank which is a member of SPAN and which has entered into an agreement with SAMA to acquire ATM transactions.
The POS (Merchant) Acquirer is a regulated bank which is a member of SPAN and which has entered into an agreement with SAMA to acquire Point-Of-Sale (POS) transactions & an agreement with The Merchant to provide him with POS service.
1.2.3.The Contracting Entity
The contracting entity is the individual or Juristic persons or Government entities that enter into the prepaid payment service contract with the IPM. Please note that for the purposes of these rules, the term ‘Contracting Entity’ may not in all cases be the same as the beneficial owner of the funds held on an account, sub account or electronic record supporting the prepaid payment instrument.
For a commercial prepaid product, the contracting entity will be the Juristic person which enters into the service agreement with the prepaid issuer.
For a retail prepaid product, the contracting entity can be the individual who is either the primary cardholder or legal guardian of the primary cardholder.
If the prepaid contracting entity (an individual or a Juristic person) has selected a multi account product (e.g. petty cash card, household cards), the contracting entity will be the primary cardholder and shall determine the value of the funds transferred to secondary card records (Note: secondary cards have no access to the funds on the primary cardholder record).
When the contracting entity is a governmental entity or a Juristic person, the due diligence processes related to KYC and AML for the cardholder (see 2.3 and 2.5) may be shared between the issuer and the contracting entity. However, the issuer remains responsible for satisfactory completion of the KYC and AML requirements in accordance with prevailing regulatory requirements
1.2.4. The Primary Cardholder
The primary cardholder is the individual that uses the prepaid payment service to pay for goods and services at the point of sale and, if applicable, to withdraw cash from ATMs and utilise money transmission services. The contracting entity (an individual or a Juristic person) and the primary cardholder may be the same, but can also be different parties. For example, a guardian could be the contracting entity for a youth card issued to a child.
1.2.5. Merchants
The term merchant refers to a Company, firm, corporation, government entity or other person who:
a) has a Merchant Account and an existing and on-going relationship with an Acquirer, and;
b) is designated to accept any payment by a cardholder using a valid Payment Card to pay for goods and/or services, and;
c) has contractually agreed to accept the payment device as a method of payment at their premises.
1.2.6. Merchant Account
The Merchants Account refers to an account held with the Acquiring Bank used solely for the purposes of settlement of POS transactions. All current SAMA rules are applicable to the opening and maintenance of this account. This account must be settled on a regular basis.
1.2.7. Saudi Arabian Payment Network – SPAN
SPAN operates the payments network and establishes operating rules for card payment device issuers, processors, merchants and ATMs that accept prepaid payment products. The prepaid payment services under this regulation will be accepted throughout the SPAN network, with additional acceptance through non-domestic payment networks, including the GCC countries, as agreed by SPAN.
1.3. Prepaid Payment Services Products Segmentations
1.3.1. Retail payment products
These include general purpose payment products, for example:
a) Payroll Cards (which can include remittance services where the consumer contracts directly for the services with issuer or his agent).
b) Student Cards.
c) Household Cards.
d) Youth Cards.
e) etc.
1.3.2. Government Entities payment products
Government Entities (which include all governmental institutions, ministries, and local juristic entities and the like) payment products are used by government entities to effect payments to recipients of state payment or to purchase products or services for such agencies. Also, to distribute compensation or benefits to employees and/or beneficiaries. Examples of Government Entities oriented cards are as follows:
a) Social Insurance accounts/payment products
b) Procurement accounts/payment products
Funds can only be loaded onto the prepaid account by a government entity itself.
1.3.3. Juristic Persons Payment products
Juristic Persons payment products are used by corporations (which include all appropriately licensed juristic institutions or entities and the like) to facilitate procurement; distribute compensation or benefits to employees, customers or beneficiaries.
Examples of Juristic Persons payment cards programmes are as follows:
a) Payroll cards
b) Employee benefits cards (Health care, transit, etc.)
c) Customers incentive cards
d) Procurement accounts/payment products
2. Rules and Guidelines Governing Prepaid Payment Services
2.1 General Prepaid Payment Service Issuing Rules
2-1-A Closed loop Prepaid Payment Services
A close loop prepaid products may or may not be reloadable. Closed loop prepaid payment services are not allowed to provide cash withdrawal functionality at ATMs or transfer of funds into a bank account.
An issuer (refer to 1.2.1 Issuing Programme Manager) proposing to operate closed loop prepaid programme must seek SAMA’s “no objection” to the proposed programme at a contracting entity level.
A closed loop prepaid payment service issued in the Kingdom is not allowed to provide cross- border payment functionality, unless permitted by SAMA.
2-1-B Restricted Loop Prepaid Payment Services
A restricted loop prepaid products may or may not be reloadable. Restricted loop prepaid payment service product is not allowed to provide cash withdrawal functionality at ATMs or transfer of funds onto a bank account.
Any Issuer (refer to 1.2.1 Issuing Programme Manager) proposing to operate restricted loop prepaid programme must seek SAMA’s “no objection” to the proposed programme at a contracting entity level.
A restricted loop prepaid payment service issued in the Kingdom is not allowed to provide cross-border payment functionality, unless permitted by SAMA.
2-1-C Open Loop Prepaid Payment Services
Open loop prepaid products may or may not be reloadable. An open loop prepaid payment product can, but is not required to, enable cash withdrawals at ATMs or the transfer of funds onto a bank account, including international remittances within the restrictions of Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti Money Laundering (AML)/Combating Terrorist Financing (CTF) rules documented in Section 2-5.
Any Issuer (refer to 1.2.1 Issuing Programme Manager) proposing to operate open loop prepaid programme must seek SAMA’s “no objection” to the proposed programme at a product level.
2-1-D Outsourcing
Regulated Issuers (Refer to The issuing Programme Manager (issuer) 1-2-1) may outsource activities within the KSA to trusted third parties under an outsourced service contract, provided that the regulated issuer assumes the responsibility for all actions undertaken by a third party.
In accordance with the "Rules on Outsourcing", issued by Saudi Central Bank, section 2-3, banks are required to confirm SAMA has "no objection" prior to undertaking any Material Outsourcing.
2.1.1 All disclosures
All disclosures required by these Rules shall be made in the Arabic language and utilise the Hijrah calendar and/or using the Gregorian calendar. Disclosures in the English language shall be provided at the primary cardholder’s request. Any Operator must be a licensed bank in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia that is permitted to accept deposits, according to the Banking Control Law, issued by Royal Decree, No. M/5 Dated 22.2.1386 H.
These rules have been issued in a bilingual form in Arabic and English. In case of any difference in the meaning or interpretation of the text, the Arabic text will prevail. The English language will be referred to only for the purpose of assisting in understanding these rules.
2.1.2 Disclosure requirements
All disclosure requirements contained in these Regulatory Rules apply to products offered in totality by a business approved by SAMA to issue prepaid payment services. Where a joint product is offered the disclosure requirements apply to the business approved by SAMA to issue prepaid payment services.
2.2 License to Issue and/or Acquire prepaid Payment Services
2.2.1 Banking license
To issue a prepaid payment service product or acquire prepaid payment service transactions a financial institution must be a licensed bank in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, according to the Banking Control Law, issued by Royal Decree, No. M/5 Dated 22.2.1386 H, and licensed to provide financial services within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, with SAMA’s “no objection” prior to introduce any prepaid product.
2.2.2 Regulatory Rules
A Prepaid issuer or acquirer operating in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia shall be allowed to issue or acquire prepaid payment services within all acceptance categories (Open Loop, Restricted Loop, Closed Loop) & prepaid payment service segments (Payroll Cards, Youth Cards, etc.) in both the reloadable & non-reloadable variants, as long as the requirements contained within these rules are me
2.3 Know Your Customer Requirements
No: BCT/15631 Date(g): 2/5/2012 | Date(h): 11/6/1433 Status: Modified The general rules for Know Your Customer (KYC) are set out in "Rules Governing Anti-Money Laundering (AML) & Combating Terrorist Financing (CTF)", Issued by Saudi Central Bank, Section 4.3. For prepaid products the entity responsible for KYC purposes is the regulated entity permitted to issue prepaid products.
Depending on the classification of the prepaid payment service proffered, KYC obligations for prepaid payment accounts or electronic records will require either a full verification of the primary cardholder or non-verification.
Specifically,
- KYC requirements for open loop prepaid services will require full verification
- Closed loop cards will not require verification for the primary cardholder within certain constraints.
2.3.1 Full Verification
Open loop and/or reloadable prepaid payment service products are allowed to be issued to an individual provided a Full Verification process has been undertaken:
a) As a result of a written Request from the Contracting entity OR an electronic request in accordance with SAMA E-banking Rules clause 4.1(ii), (which allow for online, internet based account application, provided certain security considerations are taken into account) for the account/electronic record and payment device; b) Where an acceptance by the primary cardholder of the Terms and Conditions relating to the prepaid payment service is obtained by signature;
c) As a renewal of, or substitute for, an existing prepaid payment service.
Full verification is the process by which the Issuer or an authorised third party obtains and verifies the prepaid accountholder’s identity. Accountholders whose identity has been fully verified shall have a prepaid payment service with the full functionality as determined by the Issuer. Full verification is conducted face-to-face (refer to (100-8) interviewing the customer in Rules governing the opening of bank accounts & general operational guidelines in Saudi Arabia).
The face to face verification process requires a government issued document with primary cardholder's full name and photograph. The accepted documents are the same as mentioned in the rules of opening bank accounts. In addition, for those who are not resident in the Kingdom and are in Saudi Arabia to perform Hajj & Omrah or to provide professional consultancy services for government agencies or for a local commercial entity, the accepted documents are a valid passport with valid Saudi visa.
Merchants will not be entitled to conduct the full verification due to the potential conflict of interest.
The Issuer remains responsible for the verification process and is officially required to produce the verification information on demand by SAMA.
d) The issuer may issue prepaid services using existing KYC details provided that one of the following conditions is satisfied:
1. The accountholder is requesting a prepaid payment service from an issuer that has already conducted the full verification of the accountholder , OR
2. The accountholder is replacing a prepaid payment service device from an issuer that has already conducted the full verification of the accountholder.
2.3.2 Card Payment Service Products that use a simpler form of KYC
Card payment service products that use a simpler form of KYC are limited to products providing restricted value, non-reloadable services which can be offered by the issuer (directly or via a third party) without verification of the cardholders identity. This may apply if the prepaid payment service has the following characteristics:
- The prepaid payment service is not reloadable; and
- The amount stored on the device does not exceed 400 SAR; and
- The value is redeemable through a predefined merchant group (closed or restricted loop); and
- The value on the prepaid account cannot be redeemed at ATMs or by transfer to a bank account.
2.4 Account Opening Requirements
For prepaid accounts issued in the Kingdom, the opening of accounts must be in compliance with the current version of “Rules Governing the Opening of Bank Accounts & General Operational Guidelines in Saudi Arabia” issued by SAMA or with the rules defined in sections 2.4.1, 2.4.2, 2.4.3, 2.4.4 .
For closed loop prepaid payment products not requiring KYC the account opening rules are defined in section 2.4.5.
2.4.1 Rules for Opening Prepaid Electronic Records where the Contracting Entity is an Individual
For prepaid payment products where the contracting entity is an individual and where the prepaid payment product is not using a simpler form of KYC the said individual shall be the person for whom the bank will need to identify the required information pertinent to doing financial business with them as a customer for KYC purposes. The individual will also be the person against which the required transaction monitoring of KYC, AML and CTF are applied.
Included within these are all consumer prepaid payment services where the contracting entity is an individual. This includes personal payment service products with a single payment device attached, as well as payment service products with sub-records such as youth cards. Specifically for payment service products for minors less than 18 years old the requirements set out in "Rules Governing the Opening of Bank Accounts & General Operational Guidelines in Saudi Arabia", section 200-1-1 “Minors of less than 18 years' old" apply.
For such a payment service product the following conditions shall apply;
1- A master account shall be opened under the name of the contracting entity.
2- Electronic record or ‘sub-records’ (sub-accounts of the master account) shall be opened for every payment service product issued.
3- Such payment service product shall be branded for use at SPAN access points.
4- Sub-records’ (card accounts) shall not be allowed to accept cash deposits or any credit entries other than the amounts transferred thereto from the master account of the contracting entity.
5- No monthly statements shall be required for issue for such sub-record customers (sponsored cardholders) unless specifically requested by the contracting entity. Instead, the cardholder can get an ATM-generated brief transaction statement.
6- The signature specimens of the customers of such sub-records shall not be entered into the issuer's computer system.
7- The contracting entity shall provide the issuer with completed application forms and copies of the personal documents of sponsored cardholders under its sponsorship and acknowledge that payment services are to be provided to them under its responsibility.
8- Transactions of such prepaid payment services shall be limited to:
- Depositing of funds can only be made by the contracting entity
- Withdrawing (via ATM and PoS)
- POS purchase
- Payment of bills via SADAD
- Remittance outside of the Kingdom by the primary cardholder’s membership of a remittance service if included in the contracted payment services agreed with the contracting entity
9- Such cards shall be delivered to concerned sponsored cardholders by the contracting entity, and personal identification numbers (PIN’s) of the cards shall be delivered by the issuer (the issuer branches or representative) to the primary cardholder under a written form to be kept in the master account file.
10- A special design shall be adopted for the above-mentioned cards which is consistent with the design specification for SPAN Prepaid cards issued from time-to-time by the SPAN scheme.
11- Card expiry is to be within 3 years of issue, Card expiry can be extended for certain categories (i.e. Student cards) subject to SAMA approval.
12- For payroll cards:
- Once the cardholders valid Government issued identity card has expired the card has to be stopped.
- The issuer shall provide necessary technical support and make available sufficient ATM access to serve the above-mentioned customers as near as possible to their work locations.
All programs must comply with the regulatory rules for prepaid payment services in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
2.4.2 Rules for Opening Prepaid Electronic Records where the Contracting Entity a Juristic Person
For prepaid electronic records where the contracting entity is a juristic person and where the prepaid electronic records is not using a simpler form of KYC, the individual(s) who will be provided the payment service product shall be the person for whom the issuer will need to identify the required information pertinent to doing financial business with them as a customer for KYC purposes. The individual will also be the person against which the required transaction monitoring of KYC, AML and CTF are applied.
Included within these are all commercial prepaid payment services where the contracting entity is a Juristic person. This includes salary payment service products, prepaid procurement cards (petty cash payment products) with a single payment device attached, as well as payment service products with sub-records.
Specifically account opening procedures must be compliant with section 300 of the 'Rules Governing the Opening of Bank Accounts and General Operational Guidelines in Saudi Arabia’ as issued by SAMA.
For the opening of accounts of prepaid payment service products where the contracting entity is a Juristic person the following conditions shall apply;
1- A master account shall be opened under the name of the Juristic person for each payment service product contracted by the contracting entity.
2- Electronic record or ‘sub-records’ (sub-accounts of the master account) shall be opened for every payment service device.
3- Such payment service product shall be branded for use at SPAN access points.
4- Sub-records’ (the payment device accounts) shall not be allowed to accept cash deposits or any credit entries other than the amounts transferred thereto from the master account of the contracting entity.
5- No monthly statements shall be required for issue for such sub-record customers (the cardholder) unless specifically requested by the sub-record customer. Instead, the cardholder can get an ATM-generated brief transaction statement.
6- The signature specimens of the customers of such sub-records shall not be entered into the issuer's computer system.
7- (a) The contracting entity shall provide the issuer with completed application forms and copies of the personal documents of its personnel and/or beneficiaries to which payment services are to be provided indicating that they are checked and found valid and identical to their respective originals, that the listed personnel and/or beneficiaries work under its sponsorship and/or that they are under its responsibility. The contracting entity must be compliant with all applicable rules.
OR
(b) The contracting entity shall provide the issuer with a list of the relevant ID numbers of their employees and/or beneficiaries sourced from their valid government identification (e.g. Iqama number). The issuer representative shall source the relevant employee and/or beneficiaries’ information by reference to the Ministry of Interior data held at the National Information Centre and produce the employee and/or beneficiary sub-record application form for later signature by the employee and/or beneficiaries (refer to xii below).
8- The authorized representatives of the issuer shall review the originals of the valid government identification of the cardholder and attest the authenticity of the provided copies attached to the applications of opening the sub-records.
9- A form of opening a sub-record or card account for each employee and/or beneficiary shall be signed by the employee and/or beneficiary (only).
10- No such an individual employee and beneficiary may have more than one sub-record per payment service agreement with the contracting entity.
11- Transactions of the records of such cards shall be limited to:
- Withdrawing (via ATM and/or POS) the amount(s) of the salary and/or other amounts payable to the card holder.
- PoS purchase.
- Remittance outside of the Kingdom by the employee’s membership of a remittance service if included in the contracted payment services agreed with the contracting entity
- Payment of bills via SADAD if included in the contracted payment services agreed with the contracting entity
- For payroll cards only: Transfer from card record to employee’s own current account, in the case of the current account being in the same issuer if included in the contracted payment services agreed with the contracting entity.
12- Such cards can be delivered to concerned employees/beneficiary by juristic person whereas personal identification numbers (PIN’s) of the cards must be delivered by the issuer (the issuer branches or representative) for the primary cardholder under a written form to be kept in the master account file.
13- A special design shall be adopted for the above-mentioned cards which is consistent with the design specification for SPAN Prepaid cards issued from time-to-time by the SPAN scheme.
14- Card expiry is to be within 3 years of issue.
15- For payroll cards:
- Once the cardholders valid Government issued identity card has expired the card has to be stopped.
- The issuer shall provide necessary technical support and make available sufficient ATM access to serve the above-mentioned customers as near as possible to their work locations.
16- The above-mentioned service shall be rendered to eligible Juristic persons having a relationship with the issuer.
17- All programs must comply with the regulatory rules for prepaid payment services in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
2.4.3 Rules for Opening Prepaid Electronic Records where the Contracting Entity is a Government Agency
For prepaid electronic records where the contracting entity is government agency and where the prepaid electronic record is not using a simpler form of KYC, the individual(s) who will be provided the payment service product shall be the person for whom the issuer will need to identify the required information pertinent to doing financial business with them as a customer for KYC purposes. The individual will also be the person against which the required transaction monitoring of KYC, AML and CTF are applied.
Included within these are all commercial prepaid payment services where the contracting entity is a government agency. This includes salary payment service products, prepaid procurement cards (petty cash payment products) with a single payment device attached, as well as payment service products with sub-records.
Specifically account opening procedures must be compliant with the following clauses (Section 500-1-1, sub-clauses 1, 2, 3 and 7 & Section 500-2) of the 'Rules Governing the Opening of Bank Accounts and General Operational Guidelines in Saudi Arabia’ as issued by SAMA.
In addition to the rules laid out in the above, for a prepaid payment product opened under these rules the account terms and conditions must specify the withdrawal functionality and/or value threshold (via POS and/or ATM), as agreed with the Government entity.
For the opening of accounts of prepaid payment service products where the contracting entity is government agency the following conditions shall apply;
1- A master account shall be opened under the name of the government agency for each payment service product contracted by the contracting entity.
2- Electronic record or ‘sub-records’ (sub-accounts of the master account) shall be opened for every payment service device.
3- Such payment service product shall be branded for use at SPAN access points.
4- With the exception of Student card, Sub-records’ (the payment device accounts) shall not be allowed to accept any credit entries other than the amounts transferred thereto from the master account of the contracting entity.
5- No monthly statements shall be required for issue for such sub-record customers (the cardholder) unless specifically requested by the sub-record customer. Instead, the cardholder can get an ATM-generated brief transaction statement.
6- The signature specimens of the customers of such sub-records shall not be entered into the issuer's computer system.
7- (a) The contracting entity shall provide the issuer with completed application forms and copies of the personal documents of its personnel or beneficiaries to which payment services are to be provided indicating that they are checked and found valid and identical to their respective originals, that the listed personnel work under its sponsorship and/or that they are under its responsibility. The contracting entity must be compliant with all applicable rules.
OR
(b) The contracting entity shall provide the issuer with a list of the relevant ID numbers of their employees and/or beneficiaries sourced from their valid government identification. The issuer representative shall source the relevant employee and/or beneficiaries’ information by reference to the Ministry of Interior data held at the National Information Centre and produce the employee sub-record application form for later signature by the employee (see xii below).
8- The authorized representatives of the issuer shall review the originals of the valid government identification of the cardholder and attest the authenticity of the provided copies attached to the applications of opening the sub-records.
9- A form of opening a sub-record or card accounts for each employee/beneficial shall be signed by the employee/beneficial (only).
10- No such an individual employee may have more than one employee/beneficial sub-record per payment service agreement with the contracting entity.
11- Transactions of the records of such cards shall be limited to:
- Withdrawing (via ATM and/or POS) the amount(s) of the salary and/or other amounts payable to the card holder.
- PoS purchase
- Remittance outside of the Kingdom by the employee’s/beneficiaries membership of a remittance service if included in the contracted payment services agreed with the contracting entity
- Payment of bills via SADAD if included in the contracted payment services agreed with the contracting entity
- For payroll cards only: Transfer from card record to employee’s own current account, in the case of the current account being in the same issuer if included in the contracted payment services agreed with the contracting entity.
12- Such cards can be delivered to concerned employees/beneficiaries by the Government Entity, whereas personal identification numbers (PIN’s) of the cards must be delivered by the issuer (the issuer branches or representative) for the card holder under a written form to be kept in the master account file.
13- A special design shall be adopted for the above-mentioned cards which is consistent with the design specification for SPAN Prepaid cards issued from time-to-time by the SPAN scheme.
14- Card expiry is to be within 3 years of issue, Card expiry can be extended for certain categories (i.e. Student cards) subject to SAMA Approval.
15- For payroll cards:
- Once the cardholders valid Government issued identity card has expired the card has to be stopped.
- The issuer shall provide necessary technical support and make available sufficient ATM access to serve the customers as near as possible to their work locations.
16- The above-mentioned service shall be rendered to the government agencies that have a relationship with the issuer.
17- All programs must comply with the regulatory rules for prepaid payment services in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
2.4.4 Rules for Opening Prepaid Electronic Records where the Contracting Entity is a Householder
For prepaid payment products where the contracting entity is an individual householder and the contracting entity has satisfied the normal SAMA Account Opening and KYC requirements, as identified at 2.4.1. The contracting entity will also be the person against which the required transaction monitoring of KYC, AML and CTF obligations are applied.
Included within these are all retail prepaid payment services where the contracting entity is a householder who offers payments cards to household members, for the purpose of effecting purchase payments and cash withdrawals using a SPAN debit card drawn on monies for which the contracting entity is the beneficial owner.
Such household members shall be either:
- A family member (e.g. wife, son) or have a legal relationship with the contracting entity (e.g. legal guardian).
- A contracted employment relationship, where the cardholder is under the sponsorship of the contracting entity.
For such a payment service product the following conditions shall apply;
1- A master account shall be opened under the name of the contracting entity which is directly related to the bank account of the contracting entity.
2- Electronic record or ‘sub-records’ (subaccounts of the master account) shall be opened for every payment service product issued.
3- Such payment service product shall be branded for use at SPAN access points only.
4- Sub-records’ (card accounts) shall not be allowed to accept cash deposits or any credit entries other than the amounts transferred thereto from the master account of the contracting entity.
5- Sub-records credits shall not exceed a cumulative maximum of SAR 13,000 in any twelve month period.
6- No monthly statements shall be required for issue for such sub-record customers (cardholders) unless specifically requested by the contracting entity. Instead, the cardholder can get an ATM-generated brief transaction statement.
7- The cardholder shall not be required to be subjected to the standard KYC requirements.
8- The contracting entity shall remain liable and responsible for all transactions effected by the cardholder as evidenced through the sub-record.
9- The householder has to provide the issuer with completed application details and the National Identification Number for cardholders which have to be validated by the issuer.
10- In the event of a change of cardholder the contracting entity has to submit the National Identification number of the new cardholder in line with condition ix.
11- Transactions of such prepaid payment services shall be limited to:
- Domestic withdrawals (via ATM and PoS purchase)
- POS purchase
- Transfers to and from the prepaid payment service record to the contracting entity's own current account.
12- Issuers will issue cards and personal identification numbers (PIN’s) to the contracting entity for delivery to cardholders (e.g. Household members).
13- Once the cardholders valid Government issued identity card has expired the card has to be stopped.
14- A special design shall be adopted for the above-mentioned cards which is consistent with the design specification for SPAN Prepaid cards issued by the SPAN scheme.
15- Card expiry is to be within 3 years of issue.
16- All programs must comply with the regulatory rules for prepaid payment services in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
2.4.5 Rules for Opening Prepaid Electronic Records that Use a simpler form of KYC
For Prepaid Payment Electronic Records that uses a simpler form of KYC the following applies:
1- A master account shall be opened under the name of the contracting entity.
2- Electronic record or ‘sub-records’ (subaccounts of the master account) shall be opened for every card issued in the programme.
3- Such card can be:
a) used within a closed or restricted loop arrangement different from SPAN access points
b) used at specified SPAN access points.
4- Sub-records’ (the card accounts) shall not be allowed to accept cash deposits or any credit entries other than at the issuance of the card.
5- No statements shall be required for issue. Instead, the cardholder can request a balance enquiry at participating merchant outlets.
6- No signature specimens of the customers are required to be obtained.
7- Transactions facilitated through such cards shall be limited to PoS purchase (excluding cash back option) up to the amount deposited in the card record at the time of activation of the card.
8- A special design shall be adopted for the above-mentioned cards which is different from the design specification for SPAN Prepaid cards. The card will not carry the SPAN Logo
9- Card expiry is to be within 2 years of issue.
10- The above-mentioned service shall be rendered to eligible entities having a relationship with the issuer.
11- Such accounts must be open under the approval of the compliance officer at the bank according to procedures set by the bank based on its customer categorization process.
12- All programs must comply with the regulatory rules for prepaid payment services in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
2.5 Anti-Money Laundering & Control of Terrorist Financing
The general rules for Anti-Money Laundering (AML) are set out in the Saudi Arabian "Anti Money Laundering (“AML”) law" and "Rules Governing Anti-Money Laundering & Combating Terrorist Financing", Section 4.2. Any prepaid product must comply with all anti-money laundering/combating financing of terrorism guidelines already implemented in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
2.5.1 Anti-money laundering regulations
Anti-money laundering regulations are designed to prohibit the funding of prepaid accounts with financial money from criminal activities.
2.5.2 Issuer compliance
Irrespective of the number of parties with whom the Issuer may share the issuing activities, the issuer remains liable for ensuring compliance of its prepaid programme(s). If necessary, additional systems, procedures and controls must be deployed by the issuer to ensure compliance with these guidelines.
2.5.3 Monitoring of payment service activity
The issuer is required to monitor on an on-going basis the prepaid payment service activity by undertaking the following tasks and verifying to SAMA their compliance with the Kingdom's AML legislation:
- Keep up to date the primary cardholder’s verification data (as described in 2.3) held on record as required according to the Anti-Money Laundering (“AML”) law in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Article 5
- Verify transaction records at regular intervals, where the frequency will depend on the level of risk attributed to the primary cardholder, to ensure that these fall within the scope agreed in the contract established with the primary cardholder;
- Maintain a log of all the transactions undertaken using the prepaid payment services. This data must be available for scrutiny by SAMA as appropriate when requested;
- Report suspicious activity promptly to Financial Intelligence Unit if it suspects that funds loaded onto the prepaid account are the proceeds of criminal activity;
- Such monitoring to be undertaken by the Financial Intelligence Unit as defined in the "Anti Money Laundering (“AML”) law" and "Rules Governing Anti-Money Laundering & Combating Terrorist Financing", Section 4.2;
- Conduct transaction screening as well as account and primary cardholder behaviour monitoring, to identify any unusual activity;
2.5.4 Funds transfers
If the prepaid payment service allows the primary cardholder to transfer money to a bank account in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia or abroad, the issuer must conduct the following precautionary measures:
- Obtain adequate levels of information about the beneficiary bank; and
- Assess whether the beneficiary bank’s anti-money laundering controls and risk management procedures are adequate; and
- Screen the beneficiary's bank account against available AML/CFT negative files.
- Consider all the relevant rules relating to remittances and follow Customer Due Diligence (CDD) processes with individual customers and with receiving banks (correspondent banks).
2.5.5 Face to face verification
Further to the customer due diligence measures carried out at the onset of the contract (see 2.3), a further full verification must be carried out face-to- face whenever:
a. There is a suspicion of money laundering or terrorist financing;
b. There are doubts about the veracity or adequacy of the previously obtained primary cardholder identification data;
c. Higher compliance risks are posed.
The prepaid account must be blocked until full verification occurs if any of the above suspicions are raised.
2.5.6 SAMA Examination
SAMA may conduct the following activities:
a. Request the issuer to provide, detailed information about the transaction (e.g. primary cardholder’s identity, transactions history) upon request;
b. Interview staff at the Issuer to investigate potential compliance issues;
c. Conduct an inspection of the books and accounts of a bank, or affiliated third parties;
d. Impose penalties to any issuer who fails to observe the primary cardholder due diligence and the transaction archiving requirements.
2.6 Data Protection
Banks must ensure that card and account holder's confidentiality is maintained at all times and comply with the requirements of:
a) "Rules Governing Anti-Money Laundering & Combating Terrorist Financing", Section 4.10: "Record Keeping & Retention" and
b) "Rules Governing the Opening of Bank Accounts & General Operational Guidelines in Saudi Arabia", Part 2 "Supervisory Rules & Controls" Section 4: "Updating Account Data".
In addition to the requirements described as follows:
2.6.1 Contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) data collection
The issuer is responsible for ensuring that the primary cardholder’s data is collected and processed, irrespective of other parties being involved in providing the service (refer to 1.2.1).
2.6.2 Contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) data storage
The issuer shall ensure that contracting entity (an individual or an organisation) personal data, either in electronic format or paper-based, collected during the contracting entity’s recruitment, as well as from the transactional activity of the payment device is stored in secured facilities within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (see "Rules on Outsourcing" issued by SAMA).
The data storage facilities and the data transmission processes are considered secured if the issuer has taken the necessary technical and organisational measures to comply with the Payment Card Industry (PCI) standards as defined, to protect the data against:
a) Accidental loss;
b) Alteration, unauthorised disclosure or access;
c) All other forms of unlawful processing.
2.6.3 Third party use of contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) and/or primary cardholder data
Prior consent of the primary cardholder is needed when the issuer or a third party wishes to use the primary cardholder’s personal data for services additional to the purpose for which it has been collected (e.g., for e-marketing purposes), except when:
a) The issuer or the third party is required to do so in order to comply with a legal obligation (e.g., responsibility to comply with regulations relating to money laundering); or
b) The data is non-attributable and its use is defined in the contract to which the primary cardholder is party (note: primary cardholders can provide such consent as part of the application process).
2.7 Distance Selling of Reloadable Products
2.7.1Distance selling rules and guidelines
The distance selling rules and guidelines described in this section are applicable whenever a prepaid account and payment device is requested via an internet website, call centre or postal mail. Distance selling applications to an eligible prepaid issuer within the Kingdom for a prepaid account originating from outside the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
2.7.2 Provision of contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) with contractual terms and conditions
All contractual terms and conditions must be provided in a written form (including electronically).
2.7.3 Confirmation of contract receipt by the contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity)
Upon completing the electronic full verification (see 2.3.1), the Issuer must confirm that the contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) has received the contract information by contacting the primary contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) via telephone, postal mail or email or any other electronic means. Contracts can be concluded online.
2.7.4 Cooling off period
The contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) shall be entitled to a cooling-off period of 14 days, during which they may terminate the initial contract without any penalties.
a)
The issuer can start the provision of services during the cooling-off period provided the contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) agrees to such and the full verification where appropriate has been completed. Agreement during the cooling-off period is deemed granted when contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) activates the payment device. Such agreement may not restrict the contracting entity's (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) right to cancel within the 14 day period; b)
If the contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) terminates the contract during the cooling-off period, the contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) will be entitled to a full refund of any unused balance (the difference between any loads and spend, and between withdrawals or fees charged to the prepaid payment service account). 2.8 Consumer Protection
2.8.1 Provision of disclosures
The issuer shall provide the disclosures required under this section on or with any application that is made available to the customers, including one contained in a catalogue, magazine, or other generally available publication, to open a prepaid payment service account.
2.8.2 Disclosures with or upon application
A prepaid payment service issuer shall disclose the following with or on an application:
a) All charges and fees, if any, associated with the use of the instrument, including:
1) Fees for issuance, or availability, such as any annual or other periodic fee, expressed as an annualised amount, or any other fee that may be imposed for the issuance or availability of the prepaid payment service, including any fee based on card activity or inactivity;
2) Minimum commission charge or any minimum or fixed commission charge that could be imposed upon completion of a certain period;
3) Transaction charges or any transaction charge imposed for the use of the payment device for purchases and/or any conditions attaching to such charges;
4) Cash withdrawal fees. Any fee imposed on cash withdrawals from the account (if cash withdrawals are allowed);
5) Any other fee or penalty fee imposed in connection with the usage of the prepaid payment service account. b) The terms and conditions relating to the redemption of the value remaining on the prepaid account. For illustrative purposes, table 2 outlines the "beneficial ownership" of funds held on sub-record accounts.
c) The rights and liabilities of the contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) must be summarised in a set of Terms and Conditions, which shall meet the disclosure requirements contained in these Regulatory Rules;
d) The time limits during which the contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) has the right to cancel the prepaid payment service agreement after it has been signed (the cooling off period);
Table 2: Beneficial owners of funds on prepaid accounts in specific cases
Beneficial Owner
Cardholder
Contracting entity
Account Party
Account Type
Employee Employee Employer (Payroll Card) Child* Child Guardian Youth Card (U18) Student Student University\Student
(Student Card)
Visitor Visitor Committee/visitor Visitor Card (e.g. Hajj and/or
Umrah)
Householder Domestic Staff Householder (Household Card) Company Co. Employee Company Company Card (Petty Cash) Welfare Recipient Welfare Recipient Government (Welfare Card) Cardholder# Cardholder Merchant (Gift Card) Cardholder Cardholder Cardholder (General purpose Card) e) If the payment device is lost, stolen or misused by someone who obtained it without the contracting entity's (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) consent, any consumer liability, or limit thereof, shall be stated:
1) For non-personalised prepaid account products where the contracting entity is anonymous (non-personalised cards) the payment device is considered equivalent to cash.
2) For personalised prepaid account products the following liability rules apply:
1) Notification to the issuer of loss or theft of the payment device is deemed given when the primary cardholder in person, in writing or by telephone has taken steps to inform the issuer about the loss, theft or possible unauthorised use of the payment device.
2) The primary cardholder retains liability for all prepaid payment account usage up to the point of notification to the issuer. No liability shall exist for unauthorised use on the primary cardholder after notification to the payment device issuer;
f) A statement that the primary cardholder should contact the payment device issuer for any change in personal details / information and the issuer should provide a telephone number or a mailing address for that purpose;
g) The expiry period and the terms and conditions pertaining to expiration of the instrument;
h) Any optional additional services shall be presented as a ‘positive option’, which the applicant must indicate, if one wishes to receive them. Any charges for these services must be disclosed;
i) The customer service office, telephone numbers, Email (if exits) and website URL.
* The Child/Accountholder is the beneficial owner of the funds, but the Guardian will typically have Power of Attorney and signing rights on the Account until the Child reaches age of majority (18)
#The value on the Gift Card will be the property of the Cardholder, but may be limited to ‚withdrawal through Purchase‘ at the Merchant outlet. This will be defined in the Prepaid Service Terms & Conditions
2.8.3 Government entities or juristic persons programmes
If the prepaid payment service is a Government or a juristic persons prepaid payment service (see1.3.2 and 1.3.3), the master accountholder/contracting entity shall be responsible for all expenses incurred in processing the payment including bank fees, service provider charges, and all other costs. The Contracting entity is not allowed to share any costs with the primary cardholders, including deducting fees from funds from the account directly or indirectly.
However, in the case of sub-records where the cardholder is the beneficial owner, transaction effected directly by the beneficial owner (e.g. ATM and/or POS transactions) which may be chargeable, can be applied to such sub-record. All other expenses related to production and distributions of cards remain responsibility of the contracting entity.
2.8.4 Written contracts
The issuer must enter into a written contract with the contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) which can be in electronic form.
2.8.5 Contract signature
Contracts must be signed by the contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity). If the contract is entered into online there must be a requirement for a digital signature or exchange of written copies later on.
2.8.6 Contracting entity/Cardholder complaints
The issuer must put in place an effective mechanism to attend to any primary cardholder complaints. The contracting entity (an individual or a juristic person or government entity) will also be able to complain to SAMA in accordance with the SPAN rules.
2.8.7 Communication language
The use of clear and simple language terms is required in all communications. The Arabic language should be the main communication language.
2.8.8 Honouring primary cardholder payment instructions
The issuer shall honour the primary cardholder's instructions for payments, at approved locations, if there is sufficient balance outstanding against the instrument.
2.8.9 Card fees
Periodical fees, such as dormancy fees or inactivity charges, shall not be charged to prepaid payment services, except in the circumstances below and provided that these are clearly stated in the terms and conditions:
a. There has been no purchase activity using the card in the 3-month period prior to the date on which the charge or fee is imposed;
b. Such charge or fee, if any, is reasonable and does not exceed limits set in the circulars "Schedule of Maximum Fees for Prepaid Services", appended and updated by SAMA.
2.8.10 Card expirations
Prepaid Payment Services shall be subject to standard SPAN card expiration date,
a. The expiration date is at least 3 years after the date on which the prepaid account funds were first loaded, where the card is a smart/EMV card
OR
B. two years for magnetic stripe cards;
AND
c. the terms of expiration are prominently disclosed
2.8.11 Unfair contract terms
Any term in the contract will be considered unfair if it causes a significant imbalance in the rights and obligations arising under the agreement to the detriment of the account or primary cardholder. Unfair terms will be considered null and void, but shall not affect the validity of any other provisions in the contract. Where there is any doubt as to the meaning of a contractual term, the interpretation should favour the primary cardholder
2.9 Advertising Prepaid Payment Service Products
Advertising for prepaid payment service products must follow SAMA regulations for advertising Financial Service Products, including the SAMA circular dated 28th Safar 1430H- 8th November 2009, which prohibits banks using names and/or pictures of holy places for any marketing activity. In accordance with the Banking Control Law, issued by Royal Decree, No. M/5Dated 22.2.1386 H, article 23 (5).
2.9.1 Definition of an advertisement
For the purpose of this Regulatory Framework, an advertisement is a commercial message in any medium that promotes, directly or indirectly, a prepaid payment service product.
2.9.2 Minimum level of detail
Advertisement shall clearly state the identity of the issuer making the disclosure (i.e. any public disclosure or communication relating to a prepaid service offering MUST identify the identity of the regulated issuer/IPM notwithstanding any other brand or title under which the service may be offered to market). The minimum level of detail should contain the name of the issuer and the bank address/phone number and specify that the account balance is held by a bank.
2.9.3 Presentation of terms
Advertisement shall only state specific terms that actually are, or will be arranged or offered by the prepaid payment service issuer. The terms shall be presented as a whole with charges shown adjacent to the offer.
2.10 Statementing
For prepaid payment service products requiring full KYC verification, (see section 2.3.1), statement preparation and delivery (either physical delivery by post or notification of electronic statement availability or through branches) must occur, at a minimum, quarterly if requested by the account holder.
The statement must include all transactions credited or debited from the account. The statement shall disclose the following items:
a. Charges/Fees. A disclosure of the amount, itemised and identified by type, of any charges or fees debited to the account during the statement cycle;
b. Address or phone number for notice of statement errors. The address or the phone number to be used for notice of statement errors.
In addition, the issuer shall, upon receipt of an enquiry from the cardholder, provide information about the remaining balance on the payment device, in any appropriate form.
For prepaid payment service products that use a simpler form of KYC, (see section 2.3.2), there are no requirements to issue regular statements. Prepaid payment service customers will be entitled to enquire about the remaining balance on the payment device upon presentment of the payment device at PoS at a participating merchant outlet.
2.11 Cardholder Dispute Resolutions for Prepaid Services
2.11.1 Billing errors
In the following the term “billing error” represents a posting to the prepaid payment service account and which gives rise to an error in the overall balance. Billing errors include:
a) A transaction that is not made by the primary cardholder or by a person who has authority to use the consumer’s prepaid payment service;
b) A transaction for which the primary cardholder requests additional clarification;
c) A failure by the issuer to properly post a transaction onto the prepaid account;
d) An error of computational or accounting nature that is made by the issuer, so that a charge is either over or understated, including application of fees or penalty charges that are not in accordance with the Terms & Conditions of the Agreement in force.
2.11.2 Billing error notice
A billing error notice is an oral or written message from the primary cardholder that:
a. Is received by the issuer at the call centre or address provided in the Terms and Conditions in force no later than 180 days after the transaction date of the alleged billing error;
b. Enables the issuer to identify the primary cardholder’s name and account number, and, to the extent possible, indicates the primary cardholder’s reasons for believing that a billing error exists, the type of error, the date and amount of the error.
c. Such billing error notice shall be taken seriously by the bank (issuer and/or acquirer).
2.11.3 Handling of billing errors
The bank (issuer) shall handle billing errors as follows:
1- The primary cardholder can claim for a billing error within a period of 180 days from the transaction date;
2- Once a bank receives a complaint/billing error from primary cardholder, the bank has to inform the customer by either an oral or a written message of the process by which the bank will deal with the billing error. The bank must ensure that the complaint can be uniquely tracked within the bank's complaint management system as directed by SAMA;
3- Until a billing error is resolved, the disputed amount, including any charges owed, shall be held in a pooled (suspense) account;
4- The bank shall conduct reasonable investigations and comply with the appropriate resolution procedures within 12 working days from receiving a billing error notice. If the investigation takes more than 12 working days, then:
a) The bank will be liable to be penalized (according to Claim Processing System (CPS) rules)
b) The cardholder shall be informed of the current status and revised timeline (which must not exceed additional 18 working days) for resolution by the bank
c) The bank has to indicate that an additional time period is required to resolve this issue in the SAMA CPS;
5- If the bank determines that a billing error occurred as asserted, it shall correct the billing error and credit the prepaid account with any disputed amount and related commissions or other charges from the overages (suspense) account and deliver to primary cardholder by any means, a correction notice;
6- If the bank determines that a different billing error occurred from that identified in the billing error notice, the bank shall deliver to the primary cardholder by mail or other means an explanation of the reasons for the bank’s conclusion that a different billing error occurred and the reasons for the belief that the billing error alleged by the primary cardholder is incorrect. The bank shall correct the billing error and credit the prepaid account with any erroneous amount and related commission or other charges as applicable, and provide the customer with the applicable documents, if its requested;
7- The bank has to resolve the complaint/billing error within these additional 18 working days. If bank does not, then the following will occur:
a) the bank will be liable to be penalized (double the first charge)
b) the bank has to repay the customer (the primary cardholder) the disputed amount
c) close this case in the bank's complaint management system and the CPS;
8- The bank (as issuer) has to provide the complainant (primary card holder and/or the merchant) copies of documentary evidence, especially if the bank determines no billing error occurred, if the complainant requests that;
9- The complainant (primary card holder) retains the right to escalate the complaint to SAMA, if unsatisfied with the bank’s treatment of the complaint;
10- The complainant (primary card holder) retains the right to escalate the complaint to the Committee for the Settlement of Banking Disputes (CSBD), if unsatisfied with SAMA's and the bank’s treatment of the complaint;
11- If the bank has fully complied with the requirements of this section, the bank has no further responsibility if a primary cardholder reasserts substantially the same billing error.
2.12 Merchant Dispute Resolution for Prepaid Payment Services
The prepaid dispute resolution process is as defined in the SPAN Scheme Standard. For avoidance of doubt these are as follows.
2.12.1 Merchant Dispute Resolution
a. The term “statement error” represents a posting to the merchant’s account which gives rise to an error in the overall balance. Statement errors include:
1) A failure by the Operator to credit or debit properly a transaction to the merchant’s account;
2) An error of computational or accounting nature that is made by the acquirer, so that a charge is either over or under stated, including application of fees or penalty charges that are not in accordance with the Terms and Agreement in force.
b. A statement error notice is a written or oral message from the Merchant that:
1) Is received by an Operator at the address or telephone number provided in the Terms and Conditions in force no later than 90 days from the transaction date;
2) Enables Operator to identify the merchant’s name and account number, and, to the extent possible, indicates the merchant’s reasons for believing that a statement error exists, the type of error, the date and amount of the error.
c. The Operator (bank) shall handle statement errors as follows:
1- Once the Operator receives a complaint from merchant, the operator has to inform the customer by either an oral or a written message of the process by which the bank will deal with the statement error;
2- The Operator shall conduct a reasonable investigation and comply with the appropriate resolution procedures no later than 30 working days, after receiving a statement error notice;
3- If the Operator determines that a statement error occurred as asserted, it shall correct the statement error and credit or debit the merchant’s account with any disputed amount and related commission or other charges and mail or deliver by other means a correction notice to the merchant;
4- If an Operator determines that a different statement error occurred from that identified in the statement error notice, the Operator shall inform the merchant with an explanation of the reasons for the bank’s belief that a different statement error occurred and the reasons for the belief that the statement error alleged by the merchant is incorrect, correct the statement error and credit or debit the merchant’s account with any erroneous amount and related commission or other charges as applicable; and provide the merchant with the relevant documentary evidence if the merchant so requests;
5- If an Operator determines that no statement error occurred the Operator shall mail or deliver by other means to the merchant an explanation of the reasons for the bank’s belief that the statement error alleged by the merchant is incorrect, furnish copies of documentary evidence, if the merchant so requests.
6- The Operator has to resolve the issue within these 30 working days from the date of receiving the complaint. If the bank does not, then the following will occur:
a) the bank will be liable to be penalized;
b) the bank has to repay the customer (the merchant) the disputed amount;
c) close this case in the bank system;
7- The complainant (merchant) retains the right to escalate the complaint to SAMA, if unsatisfied with the bank’s treatment of the complaint;
8- The complainant (merchant) retains the right to escalate the complaint to the Committee for the Settlement of Banking Disputes (CSBD), if unsatisfied with SAMA's and the bank’s treatment of the complaint.
9- A bank that has fully complied with the requirements described in this section has no further responsibilities if a merchant reasserts substantially the same statement error.
2.13 Merchant Agreements for Closed Loop Prepaid Payment Services
This section provides the rules for the disclosure of information between the prepayment operator, "Operator", (issuer and/or acquirer) of a prepaid payment service transaction and the merchant where the agreement relates to a closed loop prepaid product.
2.13.1 Regulated financial institutions
A closed loop prepaid payment service Operator must be a bank in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia that is permitted to accept deposits, according to the Banking Control Law, issued by Royal Decree, No. M/5 Dated 22.2.1386 H.
2.13.2 Disclosure of charges
The Operator shall disclose in Merchant Service Agreement all charges, if any, associated with the operation of prepaid payment services and acceptance of prepaid payment service transactions and an explanation of the method of computation of charges as follows:
a. Card account operational fees. Fees payable by the merchant, which may include card issuing fees, annual fees, load fees, etc.;
b. Terminal fees. Any prepaid specific fees for the rental of Point of Sale terminal equipment or any connection charges and frequency of assessment;
c. Merchant Service Commission rates. Any specific prepaid payment service commission rate that is used to compute a commission against the total volume of sales, differentiating between any flat or ad valorem fee, including the frequency of assessment (for example daily, weekly, monthly, etc.). If different rates apply to different types of transactions, the types of transactions and the rates applicable shall also be disclosed;
d. Other charges and penalty charges. The rate of charges, itemised and identified by type, of any charges other than terminal fees and merchant service commission rates charged to the merchant for accepting prepaid payment service transactions and frequency of assessment.
2.13.3 Changes in charges
The Operator shall inform the merchant in writing of any changes in charges at least 60 working days before the changes take effect.
2.13.4 Cancellation of agreement
The merchant shall have the right to cancel a Merchant Service Agreement with a notice period not to exceed 90 calendar days.
2.13.5 Settlement period
The Operator shall disclose within the Merchant Service Agreement the elapsed time between the deposit of transactions, these being either captured on paper or electronically, and the crediting of the value, less any applicable charges according to section 2.13.2, into the merchant’s account. The Operator must pay or credit their contracted Merchants after the transaction reconciliation process is completed according to the terms and conditions stipulated in the Merchant Service Agreement. Payment must cover the transaction totals reduced by the credits (reversals, adjustments and refunds) and any applicable Merchant discounts.
2.13.6 Merchant’s liability for unauthorised use of prepaid payment services
a. The Operator shall disclose the prescribed procedures as follows when accepting prepaid payment service transactions, either in the Merchant Service Agreement or an associated set of operating procedures. The disclosure shall cover:
1- The process that the merchant must follow to verify the identity of the primary cardholder )e.g. ask the cardholder to enter his PIN) ;
2- A statement informing the merchant that it is required to ask for authorisation for all prepaid transactions, (i.e. the floor limit for a prepaid transaction shall be 0 Saudi Riyal, where no offline transactions are permitted)
3- The merchant’s obligations for retaining evidence of the transaction, such as receipts and/or electronic records;
4- Reasonable time periods within which merchants must provide documented evidence, such as signed receipts, to assist the Operator with resolving primary cardholder disputes rose through the issuer.
b. The Operator must disclose any merchant liability arising from an obligation to ensure that the prepaid payment service payment system provided is not misused for acts of fraud, dishonesty or misconduct.
2.13.7 Statementing
The prepaid payment service Operator shall mail or deliver by other means a periodic statement to the merchant relating to prepaid transactions credited to the merchant account. The statement shall disclose the following items:
a. Transactions. A summary of all prepaid payment service transactions, categorised by the charges disclosed in 2.13;
b. Charges. A disclosure of the amount itemised and identified by type of any charges debited to the merchant account during the statement cycle;
c. Address for notice of statement errors. The address to be used for notice of statement errors.
2.14 Non-compliance
If SAMA finds that a bank has failed to comply with the rules contained in this document , it may take one or more of the following measures:
- impose fines on prepaid service providers;
- impose, for any specified period, limitations or other restrictions in relation to carrying out prepaid payment service provision by an issuer or acquirer;
- require a prepaid service provider to provide restitution to their customers; and
- request removal of outsourced service providers.
In applying penalties for non-compliance SAMA will be guided by the level of penalties identified in Article 23 of the 'Banking Control Law', No. M/5 Dated 22.2.1386.
2.15 Account Closure
For prepaid accounts issued within the Kingdom, the closing of accounts must be conducted in accordance with the prevailing legislation.
2.15.1 Account Closure Rules for Reloadable Accounts
If a prepaid payment service account is reloadable, the following closure rules apply:
2.15.2 Disclosure:
The Issuing Programme Manager must provide the accountholder/contracting entity with appropriate methods or options to close their prepaid payment service record (account). Such options must be disclosed to the accountholder at the time of account opening.
2.15.3 Accountholder initiated closure:
The accountholder is permitted to request closure of the prepaid payment service record by advising the issuer directly at an issuers premises or branch (including mobile branches), by authenticated contact through a call centre access, or through written request for record closure to a customer service centre. The issuer must offer the accountholder a mechanism by which they can choose to either transfer any remaining balance to another account/record or withdraw the remaining balance in cash.
The prepaid card(s) associated with the record should be returned to the issuer upon record closure, to be securely destroyed. In the event the prepaid card cannot be provided to the bank during the record closure request, the card should be disabled from further use.
2.15.4 Issuer initiated closure:
Issuer (Bank) can initiate a record closure, at their discretion, after a record has been inactive for at least 180 days and in all cases after 5 years, in accordance with the SAMA ‘Rules Governing the Opening of Bank Accounts & General Operational Guidelines in Saudi Arabia’. If a positive balance remains on the record, the bank must inform the accountholder in cases where the account holder is known, in writing or by other suitable means (e.g. SMS) of their intent to close the record and give the accountholder 30 days prior notice from the date of dispatch of the intent to close.
If after this 30 day period the record remains inactive, the bank must close the prepaid record and disable the associated prepaid card(s). Any remaining balance in the record must be transferred to the Unclaimed Balances Account. Funds will remain at the Unclaimed Balances Account to support any refund in the event the accountholder or his representative was to return in the future and request their remaining funds.
2.15.5 Account Closure Rules for Non- Reloadable Accounts
If a prepaid payment service account is non- reloadable (e.g. Gift Card), the account record expires either:
- When the value on the account record has been exhausted/spent.
- When the expiry date of the card is reached.
2.15.6 Cardholder Balance Refund on Non-Reloadable Accounts
If a cardholder requests redemption of the outstanding balance on a dormant or expired card, the merchant is obliged to honor the cardholder request, upon presentation of relevant ‘proof of ownership’.
Such proof shall include:
- Presentation of the relevant Gift Card
- A receipt that may have been issued by the Merchant or Card Issuer at the point of buying such card or alike.
Upon presentation of such proof, the cardholder shall be entitled to reimbursement of the ‘net outstanding balance’(6) on the account. Such reimbursement may be by way of:
- A re-issued gift card for (at least) the net outstanding balance
- Bankers cheque
- Cash
(6) The net outstanding balance shall be deemed to be the value outstanding on the card following the last recorded purchase transaction, less any legitimate issuer fees (see 2.8.9) that may be applicable up to the time of the ‘redemption’ request.
Rules Governing Disposal of Finance Assets or Their Contractual Rights
No: 605580000099 Date(g): 12/6/2019 | Date(h): 9/10/1440 Status: In-Force These rules were issued by Circular No. (361000145658) dated 18/11/1436H corresponding to 01/09/2015G, and amended in accordance with the Rules Governing Disposal of Finance Assets or Their Contractual Rights No. (99/60558), dated 09/10/1440H, corresponding to 12/06/2019G.Based on the powers vested to SAMA under the relevant laws, regulations and instructions, and the powers vested to SAMA under the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/5) dated 22/02/1386 H, and the Finance Companies Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/51) dated 13/08/1433H, and Article Sixty-Seven of the Implementing Regulations of the Finance Companies Control Law, and SAMA Circular No. (361000145658) dated 18/11/1436 H containing Rules Governing Disposal of Finance Assets or Their Contractual Rights.
Please find attached the updated version of the "Rules Governing Disposal of Finance Assets and their Contractual Rights".
To take note and abide by it as of its date.
Introduction
These Rules shall apply to banks and finance companies licensed and authorized by SAMA. SAMA is the sole authority empowered to apply these Rules and to take necessary measures, as it deems appropriate regarding any violations of these rules, including imposing punitive charges or enforcement actions as applicable under the Banking Control Law promulgated by Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/02/1386H and Finance Companies Control Law promulgated by Royal Decree No. M/51 dated 13/08/1433H. SAMA may update these Rules as and when required.
These Rules have been issued in both Arabic and English. In the event of discrepancy in the interpretation of the two texts, the Arabic text shall prevail.
Chapter One Definitions
- The following terms and phrases, wherever used in these Rules, shall have the meanings assigned thereto unless the context requires otherwise:
Central Bank: Saudi Central Bank*.
Finance entity: Any bank or finance company licensed by SAMA.
Disposal: Encompasses sale of finance assets, or factoring.
First party: A finance entity that intends to dispose its finance assets or their contractual rights.
Second party: An entity that possess finance assets or their contractual rights after being disposed by the first party.
Sale of assets: Transfer of the ownership of finance assets or their contractual rights to the second party.
Factoring: Sale of the rights of finance contracts to the second party, where the ownership of finance assets remains with the first party.
Recourse: Disposal arrangement whereby the first party bears the credit risk of the disposed finance assets or their contractual rights, including default risk.
Partial recourse: Disposal arrangement whereby the first party bears part of the credit risk of the disposed finance assets or their contractual rights, including default risk.
Without recourse: Disposal arrangement whereby the second party bears the credit risk of the disposed finance assets or their contractual rights, including default risk.
Disposal forms: The disposal can be either with recourse, partial recourse, or without recourse.
Finance assets portfolio: A pool of finance assets or their contractual rights, which are intended to be disposed by the finance entity.
* The Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency was replaced by the name of Saudi Central Bank in accordance with The Saudi Central Bank Law No. (M/36), dated 11/04/1442H, corresponding 26/11/2020G.
Chapter Two General Provisions
- These Rules shall apply to all finance entities.
- These Rules govern the disposal of finance assets or their contractual rights, whether the disposal takes the form of sale of asset or factoring.
- SAMA may decline or restrict transactions of disposal of finance assets or their contractual rights based on reasons deemed relevant by SAMA, such as experience, technical capabilities, or risk level.
- SAMA may exempt certain transactions of disposal of finance assets or their contractual rights from certain provisions of these rules when it deems that their nature or volume warrant such exemption.
Chapter Three Requirements for Disposal of Finance Assets or Their Contractual Rights
6. The finance entity shall be in operation for at least two years prior to disposing its finance assets or their contractual rights. 7. The finance entity that intends to dispose finance assets or their contractual rights, shall comply with the following: 7-1 If the assets, which are intended to be disposed, are real-estate assets, there need to be a lapse of at least six months from the date of extending credit related to the assets to be disposed of, or six months from the date of first paid instalment, whichever comes later. 7-2 If the assets, which are intended to be disposed, are other than real-estate assets with contract maturity not exceeding five years, there need to be lapse of at least three months from the date of extending credit related to the assets to be disposed of, or three months from the date of the first paid instalment, whichever comes later. 7-3 If the assets, which are intended to be disposed, are other than real-estate assets with contract maturity exceeding five years, there need to be lapse of at least six months from the date of extending credit related to the assets to be disposed of, or six months from the date of first paid instalment, whichever comes later. Chapter Four Procedures for Disposal of Finance Assets or Their Contractual Rights
8. The finance entity that wishes for disposal of finance assets or their contractual rights must apply for SAMA's no-objection attached with the following: 8-1 Disposal of finance assets portfolio or their contractual rights template (appendix 1). 8-2 Overdue Instalments of finance assets portfolio template (appendix 2). 8-3 A historical record of the last (5) disposed finance assets portfolios or their contractual rights, if available (appendix 3). 8-4 A copy of the proposed contracts and agreements between first and second party. The contract shall contain all necessary information including but not limited to the following: A. Details of the underlying parties in the contract. B. Type of the disposal of finance assets or their contractual rights. C. Forms of the disposal of finance assets or their contractual rights and guarantees thereto. D. Expected date of the contract. E. Type of the finance assets portfolio. F. Gross and net value of the finance assets portfolio. 9. The finance entity can provide the second party - when it deems necessary - with data and information regarding the finance assets portfolio that intended to be disposed. 10. The finance entity, which intends to dispose finance assets or their contractual rights, shall apply for SAMA's no-objection, with all the documents, templates and records as specified in these Rules, at least (15) business days prior to the expected date of the disposal. 11. The finance entity must provide SAMA with a copy of all concluded contracts and agreements regarding the disposal within five business days of their conclusion. Chapter Five Effectiveness
- These Rules shall be effective from the date of their issuance.
Appendices
Instructions When Offering Real Estate Finance Products for Individuals
No: 465440000099 Date(g): 16/5/2018 | Date(h): 2/9/1439 Status: In-Force Translated Document
These instructions were issued under Circular No. (46544/99), dated 2/9/1439H, corresponding to 16/05/2018G, and were amended under Circular No. (41059668), dated 16/10/1441H, corresponding to 07/06/2020G.First: Introduction
A. Objective
These instructions aim to establish the minimum provisions that finance providers must adhere to when offering real estate financing products to individuals, in order to help clients make informed decisions when requesting real estate financing, protect the rights of all parties, and enhance the soundness of the real estate financing sector.
B. Scope
These instructions apply to banks and real estate finance companies subject to the supervision of SAMA.
Second: Instructions for Offering Real Estate Financing Products to Individuals
When offering real estate financing products to individuals, banks and real estate finance companies must comply with the following: 1- When a client submits a request for one of the real estate financing products, the finance provider must request and study the necessary information to understand the client's financial circumstances and form a clear picture of the client's ability to meet the obligations arising from the requested financing. The provider must ensure that the product is suitable for the client. A real estate financing offer should not be made if the results of the client's ability to meet obligations do not align with the provider's approved credit-granting policies. 2- The provider must explain the proposed real estate financing product to the client, clarifying the terms and conditions of the financing contract, especially the risks associated with the product. This explanation must be given by a qualified and responsible employee and discussed with the client in a language the client understands, in a simple and clear manner. The provider must document this explanation and may not offer a real estate financing product unless it is clear that the client understands the terms, conditions, and associated risks. 3- The provider must offer the client a real estate financing offer that is valid for no less than fifteen working days from the date it is presented. The offer can be provided to the client in written or electronic form, according to the client's preference. The offer must include all relevant data and documents in the same format as would be signed if the real estate financing contract were executed. The offer must include the following documents: A. The real estate financing contract and its attachments. B. The disclosure form for the real estate financing offer in the format provided in Annex A. C. The acknowledgment form for accepting the credit risk associated with variable-rate real estate financing, in the format provided in Annex B (for variable-cost financing products). The provider must document the client's receipt of these documents, whether provided in written or electronic form, and ensure that if the client opts for a written offer, they can take the documents off the premises. The client is free to consult others for advice. No real estate financing contract may be signed unless these documents have been provided to the client, and the client is allowed to take them off the premises. 4- Before the offer expires, the provider must assign a qualified credit advisor who is well-versed in real estate financing products for individuals. The advisor must provide the client with a clear explanation of the nature of the proposed financing, its risks, the terms and conditions of the contract, and the repricing mechanism (if applicable). The advisor must also answer the client's inquiries transparently and clearly. The credit advisor must not be the same employee who interacted with the client before the offer or presented the offer. Documenting communication with the credit advisor is a key requirement for finalizing the contract, and this can be done through audio recordings or by signing a meeting confirmation form. No real estate financing contract may be signed unless the credit advisor has provided the required explanation to the client, answered all inquiries, and documented it. 5- There must be a waiting period of at least five working days from the date the client receives the real estate financing offer, allowing the client time to review the offer, consult with the credit advisor, and seek external advice. The provider must encourage the client not to make any decisions regarding the property during this five-day waiting period, such as making a down payment or deposit. No real estate financing contract may be signed before the waiting period ends. 6- Banks and real estate finance companies are prohibited from signing any real estate financing contracts for individuals unless all the above requirements have been met and documented in the financing file. Third: Annexes
Annex A
[Financing Entity Logo]
Real Estate Financing Offer Disclosure Form for Individuals
Client Information
Client Name Offer Submission Date National ID or Resident ID Offer Expiry Date Mobile Number Reference Number (File Number) Total Monthly Income ......... (SAR)
Net Available Monthly Income ....... (SAR)
Total Debt-to-Income Ratio (Before Financing) ....... (%)
Total Debt-to-Income Ratio (With Financing) ....... (%)
Financing Information
Financing Amount ......... (SAR)
Financing Type (Ijarah / Murabaha / Istisna / ...Other) …………….
(+) Profit Amount ......... (SAR)
Annual Percentage Rate (APR) ....... (%)
Property Evaluation Fee ......... (SAR)
Down Payment Amount ......... (SAR)
Insurance* ......... (SAR)
Contract Term ..... (Month)
Any Other Fees or Costs* ......... (SAR)
Number of Installments ...... (Installment)
Administrative Fees ......... (SAR)
Monthly Payment Amount (Installment/Rent) ......... (SAR)
(=) Total Amount Payable ......... (SAR)
Type of Profit Rate (Fixed/Variable) …………….
Variable Profit Rate* :.....(%) Fixed Portion: ..... (%)
Variable Portion:..... (%)
Fixed Profit Rate* ....... (%)
Minimum Monthly Payment Amount Throughout the Contract Term* ......... (SAR)
First Period Duration* ..... (Month)
Maximum Monthly Payment Amount Throughout the Contract Term* ......... (SAR)
Date of First Recalculation of Contract Value/Payments* "Client's Signature Acknowledging Understanding of the Difference Between Fixed and Variable Profit Rates" Final Installment Amount* ......... (SAR)
Additional Notes …………….
Key Property Details
Property Type (Apartment / Villa / Land...) Property Value City Neighborhood Title Deed Number Title Deed Issue Date Title Deed Issuing Authority Property Number Land Area Building Area* Property Readiness for Occupancy* Number of Rooms* Property Age Developer's Warranty Period* Note: Reviewing this form does not replace reading the entire contents of the financing contract and its attachments, and does not exempt from the obligations stated therein.
Client's signature acknowledging receipt and confirming that the credit advisor answered all of their questions
(Signature is not required to approve the financing contract)
Signature and seal of the Authorized Person of the Financing Authority
(Signature is required for financing according to the above data unless misleading information is found or there is a change in the client's circumstances)
*The phrase (not applicable) should be inserted if the relevant clause does not apply to the financing contract.
(Financing entity information and contact details)
Annex B
Acknowledgment of Acceptance of Credit Risks for Real Estate Financing with Variable Term Costs
I, [Client’s Full Name Written by Hand], acknowledge that I have applied to [Lender’s Name Printed] (the Lender) for real estate financing in the form of [Real Estate Financing Type], and that the Lender has provided me with a comprehensive explanation of [Real Estate Financing Type], including the terms and conditions of this financing contract, the risks associated with [Real Estate Financing Type], and has answered all my inquiries, specifically: 1- The Lender explained that the term cost associated with [Real Estate Financing Type] is variable, which means it may increase or decrease during the contract period. The agreed-upon installment may rise or fall, and the Lender provided examples showing that the installment amount could significantly increase (e.g., the agreed installment in the contract: 3500 SAR, could become 5500 SAR or 7500 SAR). The Lender explained the mechanism for recalculating the term cost concerning the reference rate and the dates for recalculating the term cost. 2- I reviewed a disclosure form for the real estate financing offer detailing the term cost associated with [Real Estate Financing Type], the minimum monthly installment amount throughout the contract duration, and the maximum possible monthly installment amount. 3- The Lender provided me with the real estate financing offer, which included clear copies containing all data from the real estate financing contract, its attachments, the disclosure form for the real estate financing offer, and this acknowledgment form. I took these documents to review them outside the Lender’s premises and to present them to anyone I choose for opinion and advice. The offer’s validity was not less than fifteen business days. 4- The Lender provided me with a credit advisor who contacted me and provided a [telephone/face-to-face] comprehensive explanation of [Real Estate Financing Type], including the terms and conditions of this financing contract, the risks associated with [Real Estate Financing Type], and answered all my inquiries. After reviewing all details of the real estate financing offer and understanding them clearly, and after studying all my obligations and considering all future possibilities and the related burdens and commitments not previously undertaken before signing the contract, I hereby, of my own free will, accept the obligations arising from this type of real estate financing upon signing the contract and all its attachments. Instructions for Creditors on Dealing with Promissory Notes
No: 43076917 Date(g): 5/4/2022 | Date(h): 4/9/1443 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Based on the powers vested to SAMA under its law issued by Royal Decree No. M/36 dated 11/04/1442 H, and The Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/02/1386 H, and The Finance Companies Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/51 dated 13/08/1433 H.
In order to protect the rights of participants in the financial sector and in pursuit of standardizing the procedures adopted by financing entities in their handling of promissory notes, please find attached the relevant instructions issued in this regard.
For your information and action accordingly as of 01/07/2022 G.
Chapter One: Definitions and General Provisions
1. Definitions
The following terms and phrases, wherever mentioned herein, shall have the meanings assigned thereto unless the context otherwise requires:
SAMA : Saudi Central Bank.
Instructions: Instructions for Handling Promissory Notes.
Financing Entity: Banks, and financing companies are subject to supervision and regulation of SAMA.
Customer: An individual or legal entity receiving a financing product from a financing entity.
Default: The failure of the customer to pay the agreed-upon monthly installments in the financing contract for three consecutive months, or for more than five non-consecutive months during the financing period, or as stipulated in the financing contract for non-monthly payments.
Third Party: An entity contracted to perform services on behalf of the financing entity that were previously carried out by the financing entity or to provide a new service intended for implementation. This may be a unit within the financing entity, an affiliated company, or an independent company.
Documented Communication: A recorded means of communication that can be verified and retrieved in written or electronic form.
2. General Provisions
2.1. These instructions aim to set the minimum requirements that financing entities must adhere to when handling promissory notes.
2.2. These instructions shall not prejudice the provisions set forth in related instructions, including but not limited to the following:
- Debt Collection Regulations and Procedures for Individual Customers issued under SAMA Circular No. (39100008334) dated 26/07/1439H*.
- Model Contract of the Financial Lease of Vehicles for Individuals issued under SAMA Circular No. (41038534) dated 01/06/1441 H.
- Mortgage Finance Model Contract for Individuals in Murabaha and Ejarah issued under SAMA Circular No. (41038504) dated 01/06/1441 H.
-Rules on Outsourcing for Finance Companies issued under SAMA Circular No. (65338/99) dated 07/05/1440 H.
- First Update to the Instructions for Rules on Outsourcing issued under SAMA Circular No. (41027017) dated 18/04/1441 H.
- Controls on the Signatures of Customer on the Bonds of the Order Without Data (Blank) in Exchange for Access to Banking Facilities issued under SAMA Circular No. (271000000743) dated 19/12/1427 H.
- SAMA Circular No. (41044391) dated 25/06/1441 H concerning the "Nafith" Electronic Platform Approved by the Ministry of Justice.
- SAMA Circular No. (41045412) dated 01/07/1441 H concerning the "Nafith" Electronic Platform Approved by the Ministry of Justice.
*These regulations have been replaced by the updated Debt Collection Regulations and Procedures for Individual Customers in accordance with circular No. (106889333), dated 06/09/1446H, corresponding to 05/03/2025G.
Chapter Two: Instructions for Handling Promissory Notes by Financing Entities
3. The financing entity must establish a policy approved by the Board of Directors for handling promissory notes, which must include, at a minimum, the following:
3.1. Procedures to be followed prior to initiating enforcement actions on a promissory note
a. Identifying the department responsible for communicating with the defaulting customer, without prejudicing the communication mechanisms stipulated in the related SAMA instructions.
b. Designating the authorized individual responsible for approving the initiation of enforcement actions on the promissory note before the competent court.
3.2. Procedures to be followed when initiating enforcement actions on a promissory note
a. Identifying the necessary documents for enforcing a promissory note, which must include, at a minimum: (the financing contract under which the promissory note was issued, the promissory note due for payment, evidence of the customer's default, and proof of communication with the defaulting customer).
b. Designating the department responsible for carrying out the enforcement procedures on the promissory note before the competent court.
c. If enforcement tasks are assigned to a third party, the financing entity must adhere to the related SAMA instructions.
d. Identifying the department responsible for coordinating with the third party regarding the enforcement of the promissory note and ensuring their compliance with relevant laws, regulations, and instructions.
e. Limiting the claim under the promissory note to the amount due from the defaulting customer according to the relationship documents and account statements when filing for enforcement before the competent court.
3.3. Procedures to be followed upon the completion of the purpose of the promissory note:
a. The authorized individual must directly endorse the promissory note to indicate that its value has been settled, for the purpose of returning it to the customer.
b. The responsible department must directly contact the customer through a documented communication method to return the promissory note.
c. The promissory note should be returned to the customer either in person at the financing entity’s office or by sending it to the customer's national address upon request. The costs of sending the note may be charged to the customer if delivery is requested, with the customer’s request being documented.
d. If the customer does not respond or cannot be reached to receive the completed promissory note, the financing entity should endorse the note to indicate that the customer has settled its value and keep it in the customer’s file. Additionally, the entity must attach proof of communication attempts with the customer without response and ensure that the note is returned to the customer upon request.
e. In the case of renewing the relationship with the customer or modifying the loan or facility, the financing entity must return the original promissory note or notes related to the renewed or modified contract to the customer and obtain a new promissory note or notes in light of the new relationship.
Chapter Three: Final Provisions
- Enforcement actions on a promissory note before the competent court may only be initiated after fulfilling the requirements specified in the policy referenced in Section (3) of these instructions.
- The financing entity shall be liable for any damages incurred by the customer due to the enforcement of a promissory note that the customer has already settled.
- The financing entity must adhere to the model format for promissory notes prepared by the Ministry of Commerce, as issued under SAMA Circular No. (6876/BC/213) dated 09/06/1410 H.
- When issuing an electronic promissory note, the financing entity must use the approved electronic platforms.
- SAMA reserves the right to take any actions stipulated in the Banking Control Law and the Finance Companies Control Law and its implementing regulations against a financing entity that does not comply with these instructions.
- The financing entity must develop a plan for communicating with customers to return promissory notes that have fulfilled their purpose. This plan should be implemented within one year from the date of publication of these instructions and SAMA should be informed upon its completion.
- SAMA has the authority to amend and update these instructions if needed.
Rules for Comprehensive Insurance of Motor Vehicles Financially Leased to Individuals
No: 441/191 Date(g): 22/7/2020 | Date(h): 2/12/1441 Status: In-Force SAMA has issued this Rules according to the Governor’s Decision number (441/191) dated 02/12/1441G, based on the powers vested to SAMA by The Cooperative Insurance Companies Control Law promulgated by Royal Decree No. (M/32) dated 02/06/1424H (corresponding to 31/07/2003), and its Implementing Regulation issued by the Decision of the Minister of Finance No. (1/596) dated 01/03/1425H (corresponding to 20/04/2004, and The Finance Companies Control Law promulgated by royal decree number (M\51) dated 13\08\1433H and its Implementing Regulation issued according to the Governor’s Decision number (2/ M SH T) dated 14\04\1438H, and Finance Lease Law promulgated by Royal Decree number (M/48) dated 13\08\1433H, and its Implementing Regulation issued according to the Governor’s Decision number (1/M SH T) dated 14\04\1434H.
Article 1 Purpose
The objective of these Rules is to regulate the relationship between the financing entities and their individual customers with regard to the insurance coverage on the financially leased vehicles.
Article 2 Definitions
For the purpose of applying the provisions of these Rules, the following terms and phrases, wherever mentioned herein, shall have the meanings assigned thereto, unless the context otherwise requires:
1. Central Bank: The Saudi Central Bank*.
2. Rules: The Rules for Comprehensive Insurance of Motor Vehicles Financially Leased to Individuals.
3. Insurer: The Insurance Company licensed to practice Motor Vehicle Insurance.
4. Insureds: The Lessor and the Lessee identified in the Policy Schedule.
5. Lessor: The finance companies or the banks licensed to practice finance leasing.
6. Lessee: The beneficial owner of the leased Motor Vehicle according to the finance lease contract.
7. First Beneficiary: The Lessee, being the beneficial owner, in the event of Partial Loss or Damage.
8. Second Beneficiary: The Lessor, being the owner of the Motor Vehicle, in the event of Total Loss.
9. The Unified Comprehensive Insurance Policy for Motor Vehicles Financially Leased to Individuals (the “Policy”): The insurance Policy mentioned in section two of these Rules, whereby an Insurer undertakes to indemnify the beneficiaries of the insurance coverage in the event of damage or loss resulted of a risk covered under the Policy for a Premium paid by the Insureds. This Policy shall include the insurance coverage request, provisions and conditions, exclusions, Policy Schedule and Appendixes (if any) which shall comply with all the provisions set forth under these Rules.
10. Motor Vehicle: The insured Motor Vehicle under the Policy, financially leased to the Lessee by the Lessor.
11. Driver: The person authorized to drive the Motor Vehicle and whose name is stated in the Policy Schedule.
12. Accident: An event wherein the insured Motor Vehicle sustains incidental damage or loss.
13. Claim: A Claim for indemnity for damage or loss caused by a risk covered under the Policy.
14. Claimant: Any natural or juristic person or their legal representatives who sustained damage or loss caused by risk covered under the Policy.
15. Premium: The amount paid by the Insureds or their representatives to the Insurer in exchange for the Insurer’s agreement to indemnify for damage or loss resulting directly from a risk covered under the Policy.
16.Actual Amount of Premium: The Policy price before applying the individuals’ eligible discounts based on the underwriting instructions issued by Saudi Central Bank.
17. Discounts: No claims discount and loyalty discount, indicated in Saudi Central Bank’s underwriting guidelines.
18. Sum Insured: The value of the Motor Vehicle upon submission of the insurance coverage request approved by the Insurer and identified in the Policy Schedule.
19. Material Change: Any change that leads to an increase in the likelihood or magnitude of risk.
20.Insurance Form: The application that is being filled while contracting between the Lessor and Lessee; which includes the details and information of the Insureds along with the Additional Benefits requested by the Lessee, the details of the Motor Vehicle to be insured, the Sum Insured and its yearly depreciation and any other information needed for pricing the Policy, to be relied upon when requesting the insurance coverage from the Insurer.
21. Policy Schedule: The schedule attached to the Policy that forms an integral part thereof. It contains the information of the Insureds and the authorized Drivers (if any), term of coverage, Sum Insured, Premium, details of the insured Motor Vehicle, limits of coverage, and Additional Benefits (if any).
22. Partial Loss: The destruction or damage of parts of the Motor Vehicle that would reduce or prevent the benefit thereof,without exceeding the minimum limit of Total Loss set by the authorized entity in auto damages’ appraisal.
23. Total Loss: Full Loss or destruction of the Motor Vehicle, that the rendition of repairs is technically unfeasible or economically costly, according to the standards set by the authorized entity in auto damages’ appraisal.
24.Deductible: The amount borne by the Lessee for every damage or loss associated with a risk covered under the Policy.
25.Lessee Insurance Account: The account created by the Lessor and endorsed to the finance leasing contract, which states the paid amounts to the Insurer as Premium and what was withdraw from the lessee for the Motor Vehicle’s insurance in accordance to these Rules. for the purpose of liquidation at the end of the leasing contract.
26.Additional Benefits: Any additional insurance coverage requested to be added to the base coverage by the Lessee and for which extra Premium is paid.
27. Endorsement: An agreement between the Insurer and the Insureds subsequent to the issuance of the Policy, whereby items of coverage are added to, amended, or removed on top of the basic coverage and which should be attached to the Policy and deemed an integral part thereof.
* The Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency was replaced by the name of Saudi Central Bank in accordance with The Saudi Central Bank Law No. (M/36), dated 11/04/1442H, corresponding in 26/11/2020G.
Chapter One: Provisions of the Relationship Between the Lessor and the Lessee in Comprehensive Insurance of Motor Vehicles Financially Leased to Individuals
Article 3
Any Motor Vehicle governed by financially leasing contract to individuals shall be insured according to the provisions of these Rules. No amendments shall be allowed to the insurance coverage to go beyond the minimum limits set by these Rules, such as amendments to the coverage, conditions, provisions, or exclusions.
Article 4
The Lessor must include the name of the Lessee in the “vehicle registration” as the “actual user” of the Motor Vehicle.
Article 5
The Lessor shall insure the Motor Vehicle annually during the period of the finance leasing contract.
The Lessor shall obtain insurance offers from at least three Insurers, and chose the best offer and lower price and provide it to the Lessee.
Article 6
1. The Insurance Premium shall be calculated annually by the Insurer based on the changes on the Sum Insured and the pricing factors for the Lessee. The Lessor shall provide the Insurer with the Lessee’s information in the Insurance Form which is required the pricing; after obtaining the Lessee’s approval.
2. The Lessee shall provide the Lessor with any Material Changes to his/her data, which have been previously submitted to the Insurer and which effect the insurance Premium.
3. The Insurer shall provide the Lessor with The Actual Amount of the Premium along with the Premium amount after applying the Discounts, if the Lessee is eligible for any.
4.The Lessor shall calculate the Premium amount on the Lessee at the beginning of the finance leasing contract, based on the Actual Amount of the Premium. (as the explanatory example below)
5.At the end of the insurance year, the Lessor shall calculate the balance amount of what have been paid to the Insurer, and what have been paid by the Lessee, and keep it in the Lessee Insurance Account, and provide the lessee with a copy of the Lessee Insurance Account.
6.At the end of the finance contract between the lessee and the Lessor, the Lessor shall pay back the Lessee the extra amount of Premiums paid by the Lessee or shall ask the Lessee to pay the extra amount paid by the Lessor to the Insurer for the insurance Policy.
7. The accounts settlement related to the insurance Policy shall be made within (30) days from the termination date of the agreement between the Lessor and the Lessee.
Explanatory example:
First year:
Motor Vehicle Value: 100,000 SAR.
The Actual Amount of Premium: 4,000 SAR. SAR.
The Premium amount after applying Discounts: (for example, no claim discount 30%): 2,800 SAR. The Lessor computes the Premium amount on the Lessee based on The Actual Amount of Premium (4,000) SAR and saves the different between The Actual Amount of Insurance Premium and the Premium amount after applying the Discounts: (4,000-2,800=1,200) SAR added to the Lessee Insurance Account.
Second year:
Motor Vehicle value: 80,000 SAR. (after applying depreciation percentage).
The Actual Amount of Premium: 3,200 SAR.
The Premium amount after applying Discounts: (for example, no claim discount 40%): 1,920 SAR.
The different between The Actual Amount of Premium and the Premium amount after applying the Discounts: (3,200-1,920=1,280) SAR added to the Lessee Insurance Account. The Lessee Insurance Account balance: (first year: 1,200+second year: 1,280=2,480) SAR.
Third year:
Motor Vehicle value: 70,000 SAR.
The Actual Amount of Premium: 2,800 SAR.
No amount will be added to the Lessee Insurance Account if he/she is not eligible for any Discounts for having an accident.
At the end of the finance lease contract, the amount withdrew from the Lessee and the amount paid to the Insurer are subjected to liquidation, as follow:
Amount withdrew from the Lessee: 4,000+3,200+2,800=10,000 SAR. Amount paid to the Insurer: 2,800+1,900+2,800=7,520 SAR.
7,520-10,000=2,480 SAR to be paid back to the Lessee.
Article 7
The Lessor and the Lessee shall agree at the beginning of the finance leasing contract on the annual depreciation percentage, which shall be stated in the Insurance Form
Article 8
Only the Lessee shall have the right to request Additional Benefits to the Policy and determine the Deductible amount.
Article 9
The Lessor and the Lessee shall agree on the method of repairs to take place (dealerships or certified auto repair shops) in The Insurance Form.
Article 10
1-The Lessor shall explain to the Lessee the scope of insurance coverage as well as the conditions, provisions and exclusions applicable to the Policy.
2-The Lessor shall provide the Lessee with a hard or electronic copy of the Policy at the beginning of the finance leasing contract and at every renewal of the Policy.
Article 11
Sum Insured Calculation:
The Sum Insured is determined in the first year following registration of the Motor Vehicle at the authorized authority based on the retail price offered by the certified dealership for the insured Motor Vehicle (excluding finance amounts or any other future services), provided that the value will be subject to the annually depreciation percentage, as specified in the Insurance Form as to reflect its real value at the time of renewal.
Chapter Two: The Unified Comprehensive Insurance Policy for Motor Vehicles Financially Leased to Individuals
Article 12
The Policy shall be treated as individual insurance policies regarding -for example but not limited to- pricing, eligible Discounts and Claims settlement.
Article 13
The insurance coverage request that was completed and signed by the insurance applicant or their legal representative shall form an integral part of the Policy; which contains the provisions, conditions, exclusions, coverage limits and schedule; and any Endorsement agreed upon, whether at the start of the insurance coverage or following its effectiveness.
Article 14
Insurance Coverage
Coverage under the Policy shall include loss or damage to the insured Motor Vehicle, and third party civil liability.
Article 15 General Provisions
1. Scope of Coverage:
The Insurer shall compensate the beneficiary for loss or damage to the Motor Vehicle, including any installed accessories, occurring due to any incident, including fire, theft or damage resulting from lightening or natural disasters such as floods or hailstones, according to the Policy conditions provided below.
2.Maximum Indemnity Limit:
a. Partial Loss: The maximum indemnity limit in case of Partial Loss or Damage is the cost of reinstatement of the Motor Vehicle, in addition to the costs of transportation and storage, after calculating the Deductible amount and the depreciation rate if applicable according to the conditions stated in the Policy, and this amount shall be determined by entities licensed to conduct vehicle damage assessments.
b. Total Loss: The Insurer’s maximum liability limit in case of Total Loss shall not exceed the Sum Insured for the Motor Vehicle. The Motor Vehicle is deemed as Total Loss or damaged if the damage assessment shows that the needed repairs are economically or technically infeasible, provided that such assessment is conducted by entities licensed to conduct vehicle damage assessments.
3. Deductible:
a- In the event of Partial Loss or Damage to the Motor Vehicle the Insurer may charge the Deductible amount specified in the Policy Schedule for each Claim.
b- The Insurer’s liability starts after the Deductible has been exhausted, and this is only applicable to damages or losses occurring to the insured Motor Vehicle, and it does not apply on claims arising from civil liability coverage against third party.
c- The First Beneficiary shall not be charged a Deductible if the Lessee or the Driver were not held liable for the Accident, according to the report prepared by the entity attending the Accident scene.
d- In case the First Beneficiary or the Driver is held partially liable for the Accident, the percentage of Deductible amount shall be calculated as per the percentage of liability accounted for by the Lessee or the Driver regarding the Accident only.
e- Under no circumstance shall the Deductible be multiplied within this Policy for a single motor Accident.
4. Storage and Transportation:
The Insurer shall pay the expenses incurred by the Insureds when transporting the damaged Motor Vehicle, due to an Accident covered under the Policy, to a safe location, auto repair shop, certified dealership, or to an assessment center in the case the vehicle was immobile. Such expenses will be limited to a maximum of SAR (500) within the city and SAR (1,000) outside the city; provided that the transportation receipt is submitted when filing the Claim.
6. Claim Settlement Procedures:
a- Either the First or the Second Beneficiary may file a Claim request to the Insurer upon the occurrence of loss or damage covered under the Policy. The Insurer shall provide the Claimant, within (3) business days, with a notice acknowledging receipt of the Claim and informing them of any missing documents. The Insurer may also appoint an assessor or loss adjuster, if necessary, within a period not exceeding (3) business days from receiving the Claim completed with all documents, provided that the Insurer informs the Claimant of whether the Claim is accepted or rejected, within (10) business days from the date of filing the Claim completed with all documents.
b- If the Claim is accepted and deemed to be Partial Loss, the Insurer shall approve repairing the insured Motor Vehicle at the respective certified dealership or the certified auto repair shops approved by the Insurer (as specified in the Policy Schedule) within (5) business days, ensuring that the First Beneficiary receives the Motor Vehicle after it has been reinstated to its former condition before the loss or damage. The Insurer shall also provide details regarding the due indemnity process and what does it cover (the amount of spare parts and labor charges).
c- If the insured Motor Vehicle is deemed to be Total Loss, the Insureds shall compensate the Second Beneficiary with the Sum Insured specified in the Policy Schedule - after calculating the Deductible, if any - and inform the First Beneficiary of the amount indemnified to the Second Beneficiary via a reliable communication means. The Insurer shall settle the Claim sustained under this Policy with integrity and fairness, without any compromises, and within a maximum period of (10) business days from the date of the Claim completed with all documents. The Second Beneficiary shall deliver the Motor Vehicle wreckage to the Insurer.
d-In the event of damage or loss of the Motor Vehicle caused by a third party, The Insurer shall compensate beneficiaries in
accordance to these Rules. The Insurer has the right of recovery against the Insurer of the third party whom caused the accident.
e- The Insurer shall prioritize the First Beneficiary in purchasing the insured Motor Vehicle wreckage when its loss or damage is deemed as economically Total Loss, according to the value determined by the authorized entity in assessing the Motor Vehicle after the occurrence of the damage.
f- In case of Motor Vehicle theft, the Insureds or any of them shall report to the competent authorities and the Insurer promptly, and the Claim shall only be accepted after a period of (60) days from the date of submission of such report.
g- If an Insurer does not issue the necessary approval for repairing the Motor Vehicle or settling the Claim within the prescribed period without a legal justification, both beneficiaries - after filing a complaint to the Insurer- are entitled to submit a complaint against the Insurer via SAMACares website (www.Samacares.com) or with the Committees for Resolution of Insurance Disputes and Violations, so as to compel the Insurer to settle the Claim and compensate such beneficiaries for any costs incurred as a result of their inability to use the Motor Vehicle due to the Insurer's delay in settling the Claim.
h- In case of rejection of the Claim, the Insurer shall:
1.Provide the Claimant with the reasons for rejection.
2.Inform the Claimant of their right to submit a complaint at SAMACares website (www.Samacares.com) or refer their case to the Committees for Resolution of Insurance Disputes and Violations for consideration.
3. Provide the Claimant with a copy of documents related to the Claim upon their request.
Article 16 Coverage Exclusions
This coverage excludes:
1- A Motor Vehicle found to be driven by a person who does not hold a valid license corresponding to the type of vehicle driven, according to the relevant laws and regulations, or in the event that an order is issued by a concerned authority for the forfeiture of the Driver’s license, or if the license was expired at the time of the Accident unless it was renewed within (50) business days from the date of the Accident.
2-The Deductible amount stated in the Policy Schedule.
3-Consequential loss or denial of usage.
4-Manufacturing defects and damages resulting due to the usage of the Motor Vehicle or from mechanical or electrical malfunctions.
5-Damage, loss or theft of tires, rims, and/or hubcaps (wheel covers), unless such loss or damage occurred thereto at the time of the covered Accident.
6-Death or physical injury to the Insured or the Driver.
7-Emergency medical expenses.
8-Loss or damage to goods and/or personal belongings while being loaded, unloaded or transported in or on the Motor Vehicle.
9-Loss or damage to any trailer unless expressly stated otherwise in the Policy Schedule.
10-Loss or damage to a Motor Vehicle as a result of theft or attempt theft due to leaving the Motor Vehicle running or abandoning the keys inside of it, or due to not shutting down the windows or closing the doors.
11-All additional Motor Vehicle’s accessories, apart from those already fitted by the manufacturer and whose price is already included in the original price of the Motor Vehicle, unless the type and value of such accessories are explicitly and specifically stated in the Policy Schedule.
12-If the Motor Vehicle is used in contravention to restrictions set forth in the Policy Schedule.
13-Carrying passengers beyond the permitted loading capacity of the Motor Vehicle or overloaded; if it is proven that the Accident was caused by such violation.
14-If the Motor Vehicle is used for any type of racing or for acceleration, endurance or speed testing.
15-A Motor Vehicle driven by a person under the influence of drugs, alcohol, or medicines which medically prohibit driving after taking it.
16-If the Motor Vehicle is being used or operated as working machinery.
17-Car drifting, running a red light or driving against direction of traffic if it is proven that this was the cause of the Accident according to the report prepared by the authorized entity of traffic Accidents.
18-A Motor Vehicle driven in areas that are normally off-limits to the public, such as airports or seaports.
19-Any liabilities or costs that were directly or indirectly incurred due to criminal and hostile acts committed by the Insureds and/or the Driver.
20-If the Driver escapes the scene of the Accident for no acceptable justification.
21-If it is proven in the report prepared by the authorized entity attending traffic Accidents that the Accident was caused deliberately by the Insured or the Driver.
22-Submitting inaccurate information or concealing material facts in the insurance coverage request.
23-Accidents occurring outside the territorial borders of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabian.
24-Any liability or expenses arising, directly or indirectly, from the following:
a) War, invasion, acts of foreign enemy, hostilities, warlike acts (whether war is declared or not), or civil war.
b) Rebellion, military or popular uprising, insurgence, revolution, usurping authority, martial laws, siege; or any events or reasons leading to declaring or continuation of martial laws, siege, or acts of vandalism and terrorism committed by person(s) working individually or on behalf of or related to any terrorist organization. Terrorism shall mean the use of violence for political, intellectual, philosophical, racial, ethnic, social, or religious purposes. The use of violence includes putting the public and/or a segment of it under panic condition; affecting and/or causing turmoil; intervening in any operations and/or activities or policies related to the government; or causing turbulence negatively affecting the national economy or any of its sectors.
c- Strikes, riots, or civil or labor unrest.
d-What has been caused, or contributed to, by nuclear weapons, ionizing radiations, radioactive contamination due to any nuclear fuel or waste, or contamination due to nuclear fuel combustion. For the purposes of this exclusion, combustion shall include any nuclear fission.
The Lessee may opt to cancel any of the exclusions above, which will be included as an Additional Benefits, unless deemed to be in conflict with relevant laws.
Article 17
Covering Third Party Civil Liability
The determination of coverage in this section is subject to the Unified Compulsory Motor Insurance Policy issued by Saudi Central Bank.
General conditions
1. Subrogation:
Following indemnification of an insurance beneficiary, the Insurer has the right to act on behalf of the Insured in pursuing their Claim against the person at fault, unless it is the First Beneficiary.
2. Right of Recovery:
In the case that an Insurer made indemnity payments to any party whomsoever for damage or loss, and it was later discovered that the payments were made upon a risk excluded from or not covered under the Policy; or if the Claim involved deceit, fraud, misinformation or forgery, the Insurer is entitled to recover against the indemnified person for the indemnity payments. The Insurer is also entitled to recourse against any person at fault in case of attempted theft or theft of the insured Motor Vehicle or when the insured Motor Vehicle is driven by any person without permission from the Insureds.
3. Changes:
The Insureds shall notify the Insurer, within 20 business days of any Material Changes to the information submitted in the insurance coverage request. The Insurer shall notify the Insureds in case it intends to increase the amount of the Premium, or reimburse part of the Premium to the lessor when it is reduced. If no notification is sent to the Insured by the Insurer within five business days, then this shall indicate the Insurer’s agreement to continue providing the coverage at the Premium rate agreed upon at the time of signing the Policy.
5. Obligations of the Insureds or Driver in Case the Occurrence of an Accident Covered under the Policy:
a) Shall inform the concerned entities as soon as an Accident occurs and shall not leave the scene of the Accident until procedures have been completed, except in cases where leaving the scene is required such as the case of physical injuries.
b) Shall not Claim responsibility with the intention of harming the Insurer, pay or undertake to pay any amount to any party involved in the Accident except after obtaining a prior written approval from the Insurer.
c) Shall cooperate with the Insurer, and issue powers of attorney enabling the Insurer to carry out the pleading, defending and settlement procedures on behalf of the Insured or the Driver, if the Insurer expresses its desire to do so.
d) Shall, at the Insurer's expense, perform all actions required to guarantee the Insurer's right for recovering any of its due entitlements from any other party, as a result of indemnity paid in accordance with the Policy.
e) Shall inform the concerned entities in case of theft or any other criminal act and shall cooperate with the Insurer in securing the conviction of the offender.
6. Fraud:
All rights arising from the Policy shall be forfeited if the Claim involves fraud, or if the Insureds or the Driver adopts fraudulent ways or methods to gain benefit under this Policy, or if the liability or damage resulted from a deliberate act by or collusion with, the Insureds, the Driver, or others. The Insurer has the right of recover against any party found to be responsible for such fraud, whether as a conspirator or an accomplice.
7. Cancellation:
Neither the Insurer nor the Insureds has the right to cancel the Policy after its issuance, except in the following cases:
a. The write-off of the Motor Vehicle’s registrar.
b. Transfer of ownership of a Motor Vehicle to another owner.
c. The existence of alternative Policy that provides the same coverage indicated in the Rules and covers the remaining term of the Policy to be cancelled.
d. Termination or cancelation of the finance leasing contract between the Lessor and the Lessee.
The Insurer shall refund the Lessor the due amount payable for the uncovered period by depositing the amount to their bank account via IBAN, and it will be added to Lessee Insurance Account, within three business days from the date on which the Insurer becomes aware of the occurrence of any of the cases mentioned above. The due amount payable to the Insureds for the uncovered period is calculated by subtracting the elapsed days from the total Policy term (in days) and then dividing the result by the total Policy term. The result is then multiplied by the insurance Premium less administrative fees (a maximum of SAR 25), and as follows:
(365 - elapsed days) /365 × insurance Premium less administrative fees (a maximum of SAR 25) = return Premium payable to the Insured.
The Insurer is exempted from paying the return Premium in the case that there is a Claim—related to the Policy to be cancelled and on the Motor Vehicle covered by the Policy—whose value exceeds the amount to be refunded as per the calculation formula mentioned above.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, Insurers, Insureds and Drivers shall remain bound by the provisions of this Policy with respect to the obligations arising prior to its cancellation.
8. Policy Issuance and Renewal Notification:
The Insurer may not issue this Policy unless it is automatically linked to the system of the authorized entity in the collection, maintenance, and sharing of insurance information. The Insurer shall notify the Insureds of the expiry date of the Policy- (45) days as maximum- in advance, in order to enable them to renew the Policy or replace it with another Policy from another insurance company.
Policy Schedule
Policy Schedule for the Comprehensive Insurance for Motor Vehicles Financially Leased to Individuals
Policy No.
Insureds Information
Insured (Lessee)
Insured (Lessor)
National ID number for
Saudi nationals
Commercial
Registration No.
Name of Insureds
Phone number
National Address
Vehicle Details
Chassis No.
Registration Plate No.
Vehicle Registration Expiry Date
Vehicle Color
Customs Card No.
Type of Chassis
Year of Manufacture
Vehicle Make
Names of
Authorized Drivers
Vehicle Model
Premium
Deductible
Percentage of Considering the Motor Vehicle as Economic Total Lost
Sum Insured
Geographic Border
Additional Benefits
Repair Method
(dealerships or certified auto repair shops)
Converge period
The insurance coverage request that was completed and signed by the insurance applicant or their legal representative shall form an integral part of the Policy; which contains the provisions, conditions, exclusions, coverage limits and schedule; and any Endorsement agreed upon, whether at the start of the insurance coverage or following its effectiveness. Insurance Form
Insurance Form
(to be filled by the Lessor and the Lessee at the beginning of the Finance agreement)
Lessor and Lessee Information
(Lessor)
(Lessee)
National ID number for
Saudi nationals
Commercial
Registration No.
Name of Lessee and
Lessor
Phone number
National Address
Vehicle Details
Chassis No.
Registration Plate No.
Vehicle Registration Expiry Date
Vehicle Color
Customs Card No.
Type of Chassis
Year of Manufacture
Vehicle Make
Names of
Authorized Drivers
Vehicle Model
Annual Depreciation Percentage of Motor Vehicle
Actual Value of Motor Vehicle
The approximate value of the Motor Vehicle for the next years from the Motor Vehicles Financially Leased Contract.
First Year: (actual value of Motor Vehicle selling price)
Second Year: (Motor Vehicle value based on depreciation percentage)
Third Year: (Motor Vehicle value based on depreciation percentage)
Forth Year: (Motor Vehicle value based on depreciation percentage)
Fifth Year: (Motor Vehicle value based on depreciation percentage)
Deductible
Additional Benefits
Repair Method (dealerships or certified auto repair shops)
Regulations for Total Loss Settlement of Vehicle Leasing Contracts
No: 498600000099 Date(g): 24/9/2019 | Date(h): 25/1/1441 Status: In-Force Translated Document
With reference to the powers vested to SAMA under the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/5) dated 22/02/1386H, the Finance Companies Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/51) dated 13/08/1433H, and the Finance Lease Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/48) dated 13/08/1433H, and in order to achieve SAMA’s objectives of maintaining fairness in transactions in the finance sector and protecting customers.
Attached are the regulations for the total loss settlement of vehicle leasing contracts, which apply to total loss incidents occurring after (01/01/2020G).
First: Definitions
The following terms and phrases, wherever mentioned in these regulations, shall have the meanings indicated next to each of them, unless the context requires otherwise:
No. Term Definition 1 Lessor A joint-stock company licensed to practice financial leasing, including commercial banks. 2 Lessee The person who owns the benefit of the leased asset under the contract. 3 Advance Lease Payment The payment made by the lessee at the beginning of the contract to the lessor to enable them to use the leased asset. This payment is divided and amortized equally over all lease payments throughout the contract period. 4 Number of Last Due Payment The number of payments due from the lessee from the start of the financing period up to the date of the incident, according to the payment schedule attached to the contract. 5 Financing Period The number of agreed-upon lease payments. 6 Total Loss The total loss or damage to the vehicle, where repairing the vehicle is either technically unfeasible or economically costly, according to the standards approved by the relevant authority in assessing vehicle damage. 7 Settlement in the Event of Total Loss A calculation process through which the remaining debt amount is determined from the date of the total loss of the leased asset (interruption of benefit). 8 Unconsumed Amount of the Advance Lease Payment The amount owed to the lessee from the advance lease payment. 9 Remaining Principal Amount The remaining principal amount as of the date of the incident, according to the repayment schedule in the financing contract. 10 Incident An event that caused damage or accidental loss to the leased vehicle. 11 Insurance Compensation The compensation amount paid by the contracted insurance company. 12 Net Settlement Amount The net credit or debit amount after the settlement in the event of a total loss. Second: Mechanism for Settling a Vehicle Finance Lease Contract in the Event of Total Loss
A. Unconsumed Amount of the Advance Lease Payment:
Unconsumed Amount=(Financing Period–Number of Last Due Payment)×( Advance Lease Payment \Financing Period ) B. Difference Between the Remaining Principal Amount and the Insurance Compensation:
Difference=Remaining Principal Amount (including the last payment, if any)−Insurance Compensation - If the amount is greater than zero, multiply by (Lessee’s Responsibility Percentage for the Accident).
- If the amount is less than or equal to zero, it is taken as is.
C. Net Settlement Amount:
=Unconsumed Amount of the Advance Lease Payment (A)−Difference Between Remaining Principal Amount and Insurance Compensation (B) D. Action Regarding the Net Settlement Amount:
- If the net settlement amount is greater than zero, the lessee is compensated with the full net settlement amount - any outstanding amounts owed by the lessee before the total loss, if applicable.
- If the net settlement amount is less than zero, the lessor is entitled to claim the net settlement amount from the lessee + any outstanding amounts owed by the lessee before the total loss, if applicable.
The Guidelines on Standing Orders for Financing Entity
No: 43033273 Date(g): 18/11/2021 | Date(h): 13/4/1443 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Based on the powers vested to SAMA under its law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/36) dated 11/04/1442H, the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/5) dated 22/06/1386 H, and the Finance Companies Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/51) dated 13/08/1433 H.
To contribute to providing different financing options for customers, reduce the risk of default, and establish a minimum set of regulations that must be adhered to when offering or utilizing this service.
You will find the regulations for the standing payment order in favor of the financing entity, which replace the standing payment order regulations in favor of real estate financiers as notified by SAMA’s Circular No. (41039820) dated 05/06/1441 H. The most notable changes are as follows:
- The service now includes all financing products and is no longer limited to real estate financing products.
- The scope of financing entities now includes banks and funds affiliated with the National Development Fund.
For your information and action accordingly as of this date.
- The service now includes all financing products and is no longer limited to real estate financing products.
First: Definitions and General Provisions
A. Definitions
The following terms and phrases—wherever mentioned in these regulations—shall have the meanings specified next to each of them, unless the context requires otherwise:
Financing Entity: Banks, commercial banks, and financing companies subject to the supervision of SAMA, as well as government financing entities such as banks and funds affiliated with the National Development Fund.
Financing: Credit granted to the customer by the financing entity.
Customer: A natural person who has obtained a financing product from a financing entity.
Standing Payment Order in Favor of the Financing Entity: A service provided by banks through which regular financial transfers are made from the customer's account to the financing entity’s account for a specified period and amount to repay the financing.
Reliable Means of Communication: A registered means of communication that can be verified and retrieved in written or electronic form.
B. Objective
These regulations aim to establish the minimum provisions that must be adhered to regarding the standing payment order in favor of financing entities, promote and protect competition between financing entities, support the availability of financing options for customers, and contribute to reducing the risks of default in repayments.
C. Scope of Application
These regulations apply to all financing products, without prejudice to the Responsible Lending Principles for Individual Customers and the Debt Collection Regulations and Procedures for Individual Customers, as well as other related laws and instructions.
Second: Regulations for Standing Payment Order in Favor of a Financing Entity
A. Bank Obligations
When offering a standing payment order in favor of a financing entity, banks must adhere to the following: 1. Verify the existence of a fixed monthly income for the customer (such as a salary or equivalent) before accepting the request to establish a standing payment order in favor of the financing entity.
2. Obtain the customer’s acknowledgment of their awareness of the consequences of establishing a standing payment order in favor of the financing entity, according to the acknowledgment form specified in the annex.
3. Notify the customer upon establishing the standing payment order in favor of the financing entity via reliable means of communication, with the notification including, at a minimum, the following: the transfer amount, the date the order will begin, the duration in months, the account number to which the amount will be transferred monthly, and the name of the beneficiary financing entity.
4. Execute the standing payment order for the full transfer amount on the due date or within five (5) days of the due date if the amount is not available on the specified date.
5. Notify the customer if the standing payment order is not executed, providing the reason via reliable means of communication.
6. Obtain the beneficiary financing entity’s approval for the standing payment order or receive a clearance letter from the financing entity when the customer requests to amend or cancel the standing payment order.
7. Ensure that the amount to be transferred from the customer’s account is not among the amounts that SAMA has confirmed should not be touched or deducted. Also, comply with the regulations related to account freezing, enforcement, and blocking bank accounts when creating or executing standing payment orders. B. Obligations of the Beneficiary Financing Entity
The beneficiary financing entity of a standing payment order must adhere to the following: 1. Grant the customer approval to change the standing payment order amount when their circumstances change, leading to a rescheduling of the debt. This must be done within (3) working days from the completion of the rescheduling procedures by the financing entity.
2. Provide the customer with a clearance letter and a no-objection certificate for cancelling the standing payment order within (7) working days from the date of the customer’s request in the following cases: a. Full repayment of the outstanding obligations.
b. Exemption from the obligations as specified in the relevant instructions of SAMA, according to the applicable laws and regulations, or as stipulated in the contracts.
3. Beneficiary financing entities may coordinate and reach prior agreements with each bank individually to obtain immediate notifications or periodic data reports that include details of the standing payment orders executed in their favor.
4. Notify the customer upon receipt of the standing payment order amount via reliable means of communication. Annex
I acknowledge that the standing payment order to settle my obligations from my bank account (IBAN No.: .......) is a result of the financing granted to me by the financing entity, and that I cannot cancel it without providing a clearance letter from the beneficiary financing entity. I also acknowledge that I am not entitled to change the monthly deduction amount or the deduction period without the approval of the beneficiary financing entity. I further acknowledge that the bank has the right to deduct the monthly amount on the specified date or within (5) days of the specified date. I acknowledge that the bank executing the standing payment order is not responsible for any damages that may arise from the standing payment order, and bears no liability resulting from the execution of this order. The bank also reserves the right to seek recourse for any damages it may incur as a result of this order.
The Working Mechanism of Dealing with the Beneficiaries of First Home Regarding Tax Revenues
No: 747280000067 Date(g): 25/8/2019 | Date(h): 24/12/1440 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Referring to the ongoing coordination between SAMA, the Ministry of Housing, and the General Authority of Zakat and Tax regarding the mechanism for refunding Value-Added Tax (VAT) on the first home.
SAMA received a letter from His Excellency the Minister of Housing, No. 703, dated 20/12/1440H, which includes the approval of the VAT refund mechanism for the first home and requests its circulation to financing entities. The mechanism has been in effect since 01/08/2019G.
Attached is the operational procedure for dealing with beneficiaries of the first home concerning tax revenues.
Responsibilities of the Citizen
- If the purchase is made through a financer, the beneficiary must provide the certificate to the financer and cover any additional tax amounts if the value of the residential unit exceeds 850,000 SAR. The beneficiary must also sign a commitment not to present it to any other financing entity, developer, or seller.
- If the purchase is made directly from a developer registered with the Authority, the beneficiary must provide the certificate to the developer and cover any additional tax amounts if the value of the residential unit exceeds 850,000 SAR. The beneficiary must also sign a commitment not to present it to any other financing entity or developer.
- If the purchase is made directly from a developer not registered with the Authority, no tax amounts are payable for the residential unit.
- If the purchase is made through a financer, the beneficiary must provide the certificate to the financer and cover any additional tax amounts if the value of the residential unit exceeds 850,000 SAR. The beneficiary must also sign a commitment not to present it to any other financing entity, developer, or seller.
Responsibilities of Financing Entities
1) If the purchase is made from a developer registered with the Authority:
1.1. The financer will receive the certificate from the beneficiary and any additional tax amounts if the value of the residential unit exceeds 850,000 SAR. The beneficiary must also sign a commitment not to present the certificate to any other financing entity or developer. The financer will then issue a sales invoice for the full tax amount (certificate value + any additional tax amounts).
1.2. The financer will provide the certificate and any additional tax amounts if the value of the residential unit exceeds 850,000 SAR to the developer, and will receive a purchase invoice for the full tax amount (certificate value + any additional tax amounts).
1.3. The financer must record the full tax amount (certificate value + any additional tax amounts) for both sale and purchase in their tax declarations for the above-mentioned case.
2) If the purchase is made from a developer not registered with the Authority.
2.1. No tax amounts are to be paid to the developer.
2.2. The financer should submit a refund request through the portal and attach the deed after transfer of ownership, the sales invoice, financing contract, and the Authority’s declaration confirming the developer’s tax registration eligibility.
Responsibilities of Sales and Development Entities Registered with the Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority, whether individuals or companies:
1) If the sale is made to a financing entity: 2.3. The seller will receive the certificate from the financer and any additional tax amounts if the value of the residential unit exceeds 850,000 SAR. The seller will also obtain a commitment from the beneficiary through the financing entity, confirming that the certificate will not be presented to any other financing entity or developer. The seller will then issue a sales invoice for the full tax amount (certificate value + any additional tax amounts).
2.4. The seller should submit a refund request through the portal, attaching the deed after the transfer of ownership and the sales invoice.
2.5. The seller must record the full tax amount (certificate value + any additional tax amounts) for the sale in their tax declarations for the above-mentioned case.
2) If the sale is made directly to the beneficiary:
2.1. The seller will receive the certificate from the beneficiary and any additional tax amounts if the value of the residential unit exceeds 850,000 SAR. The beneficiary must also sign a commitment not to present the certificate to any other financing entity or developer. The seller will then issue a sales invoice for the full tax amount (certificate value + any additional tax amounts).
2.2. The seller should submit a refund request through the portal, attaching the deed after the transfer of ownership and the sales invoice.
2.3. The developer must record the full tax amount (certificate value + any additional tax amounts) for the sale in their tax declarations for the above-mentioned case.
Transfer of The Real Estate Financing Debts
Based on Article 2 of the Real Estate Finance Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/50) dated 13/08/1433H. which authorizes SAMA to regulate the real estate finance sector, including the issuance of standards and procedures related to real estate financing, further to the circular No. 391000000353 dated 01/01/1439H. Regarding Variable-Cost Real Estate Financing Products for Individuals.
Based on the role of SAMA in protecting the rights of customers of financial institutions under its supervision, and due to the importance of regulating the transfer of customers' debts who meet the conditions of the above circular, it is necessary to adhere to the following:
First: The financing entity (debt seller) must fill out the form for transferring real estate debt (attached) within seven working days of receiving the request from the customer. It should complete all the necessary information while adhering to the accelerate the payment standards mentioned in Article 84 of the Implementing Regulation of the Finance Companies Control Law issued by the decision of His Excellency the Governor No. 2/MFC dated 14/04/1434H. which regulates the accelerated payment process, with the necessity of notifying the customer immediately upon issuing the debt transfer document, provided that the offer period specified in the form is not less than ten working days." Second: After the financing entity (willing to purchase the debt) receives the debt transfer form, it commits to the following: Grant credit equivalent to(100%) of the value of the offer specified in the form. • Obtain a written acknowledgment from the customer that includes all obligations, if any, such as, but not limited to, (property safety, appraisal fees, property guarantee, etc.). Third: Upon the approval of the financing entity (willing to purchase the debt) and completion of the requirements, a cheque in the amount of the debt is issued and the form is returned to the financing entity (the debt seller) to complete the ownership transfer process within a period not exceeding seven working days from the date of receiving the debt transfer form. Fourth: The financing entity (the debt seller) must, after receiving the form and the bank cheque, commit to the following: Initiate the process of transferring the property ownership to the financing party (the debt buyer) from the date of receiving the bank cheque. Update the customer's credit record and issue a clearance letter for the customer. Fifth: Taking into account the aforementioned points, the financing entity (willing to purchase the debt) commits to the following provisions, stated in Article 10 of the Implementing Regulation of the Real Estate Finance Law, issued by the decision of His Excellency the Minister of Finance No. 1229 dated 10/04/1434H. Additional Provisions According to Circular No. (391000086876) dated 09/08/1439H.It has been observed that some real estate financiers, when purchasing real estate financing debt from another financier, provide the customer with an excess cash amount, resulting in an increase in the amount of the new financing.
In order to ensure SAMA's commitment to protecting customers and ensuring that financing entities comply with the relevant regulations and instructions, SAMA would like to emphasize the following:
- Compliance with the provisions of Article (11) of the Implementing Regulation of the Real Estate Finance Law, as well as the subsequent circulars issued by SAMA regarding it, which set the maximum limit for granting credit in real estate financing contracts, in any form of financing, at 90% of the value of the first dwelling for the citizen.
- Compliance with the accelerate the payment standards outlined in Article 84 of the Implementing Regulation of the Finance Companies Control Law, which regulate the process of accelerated payment.
- Compliance with paragraph (Second) of the above-mentioned circular, which states that "Grant credit equivalent to(100%) of the value of the offer specified in the form".
- Compliance with the purchase of real estate financing debt at an amount equivalent to the value of the purchase offer only.
For your information and adherence accordingly. Please note that SAMA will take all legal measures against real estate financiers who do not comply with the provisions of this circular.
Real Estate Murabaha Finance Buyout
Based on the powers vested to SAMA in accordance with the relevant regulations, rules, and instructions, and referring to the instructions regarding the time periods for issuing the clearance letter and transferring the account and debt, issued in accordance with SAMA Circular No. (43023350) dated 15/3/1443 H, and SAMA Circular No. (42013215) dated 4/3/1442 H, regarding the subjection of the mortgage contract concluded between a lender - on behalf of or as an agent for others - and individual customers is subject to the financing regulations and instructions issued by SAMA.
- SAMA wishes to emphasize the following to real estate financiers:
A- Executing customer requests related to the transfer of real estate financing debts according to the Murabaha agreement, while adhering to the specified time frames for transferring real estate financing debts as outlined in the instructions mentioned above. - B- Compliance with SAMA's instructions related to the purchase and transfer of real estate financing debt between financiers.
- C. The working days related to the procedures for lifting the mortgage are excluded from the time periods mentioned in the instructions above, provided that the reason is related to an external party.
- D- Update internal policies in accordance with these instructions.
- SAMA wishes to emphasize the following to real estate financiers:
Self-Build Product Instructions for Retail Mortgage Finance
Based on the powers vested to SAMA under the relevant regulations, laws, and instructions, and based on SAMA's role in protecting the rights of clients of financial institutions under its supervision, and in order to ensure the safety of the real estate finance sector and achieve financial stability, real estate financiers must adhere to the following when granting financing under the 'Self-Build' product for retail mortgage finance:
- Determine the total value of construction payments "financing amount" at the beginning of the contract, and link the payments to specific completion percentages in a single financing contract.
- Reflect the total financing amount in the customer’s credit record at the beginning of the contract, specifying the actual amount granted to the customer in the same record.
- Ensure that administrative fees charged by the financing entity to the beneficiary do not exceed (1%) of the financing amount or SAR 5,000 (whichever is less), in accordance with the instructions issued by SAMA, including those issued under Circular No. 361000091211 dated 30/06/1436H.
- Disburse the specified payment amount within (15) days from the date of the customer's request, provided that the client has met the completion percentages required for each payment as per the contract.
To take note and action accordingly within a period not exceeding (30) days from its date. Additionally, real estate financiers must take all necessary measures to apply the provisions of this circular to existing financing contracts under the 'Self-Build' real mortgage finance.
Collecting Amounts Owed to Finance Entities for Previous Periods in Exchange for VAT on Real Estate Finance Contracts
Referring to the Law of Value Added Tax issued by Royal Decree No. M/113 dated 2/11/1438 H and the Executive Regulations of the Value Added Tax Law issued by the Board of Directors of the General Authority for Zakat and Tax under Decision No. (3839) dated 14/12/1438 H.
SAMA wishes to emphasize the importance for all financing entities to comply with the Law of Value Added Tax, its Executive Regulations, and the guidelines and instructions issued by the General Authority for Zakat and Tax in this regard, and SAMA confirms that financing entities have the right to demand that customers pay the Value Added Tax amounts due for previous periods from real estate finance contracts, To facilitate customers, financing entities may offer all possible options for payment or settlement provided that do not violate the relevant regulations and instructions, and on the condition that written approval is obtained from the customer if they accept any payment or settlement option before proceeding with any payment of the due amount. If the customer does not accept the available options for settling the VAT amounts due for previous periods, the financing entity may seek recourse through the competent judicial authorities to claim the payment of those amounts.
For your information and compliance. SAMA will take the necessary legal measures in the event of non-compliance with these instructions.
Variable-Cost Real Estate Financing Products for Individuals
SAMA would like to emphasize the importance of the Financial Consumer Protection Principles and Rules , particularly the necessity of Equitable and Fair Treatment (Principle No. 1), disclosure and transparency (Principle No. 2), and financial education and awareness (Principle No. 3). Additionally, SAMA highlights the responsibilities of lender toward their customer, particularly the obligation to ensure that the product is suitable for the customer's needs and circumstances, explaining the product’s nature, costs, and associated benefits and risks in a clear and understandable manner. Moreover, lender must provide advice and support to customers facing financial difficulties, working with them to overcome these challenges before proceeding with legal actions.
In light of the challenges some beneficiaries of variable-cost real estate financing products have faced, particularly the increase in monthly installments, and based on a study conducted in this regard, SAMA directs real estate lenders to immediately take all necessary actions to care for their customers. These care measures should include appointing specialists with sufficient knowledge of this type of product to communicate with customers, providing a clear explanation of the product’s nature, its benefits and risks, the relevant contract terms, the repricing mechanism, and addressing any other customer inquiries. The due diligence procedures must also include offering customers one or more options, in addition to the option of continuing with the existing real estate financing contract. These options may include converting the contract to a fixed-rate financing contract, rescheduling the payments, or enabling the customer to transfer the debt to another real estate lender under conditions that suit the customer.
SAMA stresses that none of these options should result in the customer being charged any additional costs for the remaining period, in accordance with the Guide for Calculating the Early Payment Amount outlined in the finance regulations and without imposing any additional administrative fees on the customer.
SAMA clarifies that these directives are issued to ensure the protection of customers' rights and to promote fairness and transparency in transactions. This is based on the powers granted to SAMA under the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority Law, issued by Royal Decree No. (23) dated 23/05/1377H, the Real Estate Finance Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/50) dated 13/08/1433H, the Finance Lease Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/48) dated 13/08/1433H, and the Finance Companies Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/51) dated 13/08/1433H, along with the implementing regulations for these laws. SAMA will take legal action in the event of non-compliance with the above directives.
In light of the inquiries received by SAMA on this matter, SAMA emphasizes that real estate lenders must undertake the following:
- Disclose the reference index for the variable cost of real estate financing products on their website.
- Urgently communicate with all customers benefiting from variable-cost real estate financing products regarding the following points:
A. The ability to access the reference index data for the variable cost of real estate financing products on the lender’s website and provide the dedicated link for this information. B. Provide customers with contact details and grant them a period of no less than one month from the date of receipt to offer them options to amend their contract terms or any other options as outlined in the aforementioned circular. C. Inform customers of their right to communicate with a credit advisor who is well-versed in the characteristics of this type of product to provide a clear explanation of the product’s nature, its benefits and risks, the relevant contract terms, the repricing mechanism, and to answer any customer inquiries in this regard. This communication and the outcomes must be properly documented. Please note that SAMA will take all necessary legal actions in the event of non-compliance with the issued instructions in this regard.
Digital Confirmation of Banking Products for Bank Customers
Further to SAMA's instructions regarding SAMA's non-objection to provide personal finance products and issuing credit cards for individuals by utilizing Digital Confirmation services. In line with SAMA's commitment to enabling all customers to easily obtain their banking and financing needs, and enhancing the strategic goals related to digital transformation.
We inform you that SAMA has no objection to provide all financing products through electronic channels to individual bank customers, as well as small and medium enterprises through digital certification services. This is provided that the requirements in the Electronic Transactions Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/18) dated 08/03/1428 H and the Implementing Regulations are followed, and the bank must assess the risks associated with the service, determine the types of financing covered by this service, and set adequate controls, policies, and precautionary measures. The following minimum requirements must be met:
- The digital certification service provider must be accredited by the National Digital Certification Center.
- The provision of digital certification services must not affect the bank's basic procedures for verifying the eligibility and identity of the customer, agent, or authorized signatory.
- The financing request must be initiated through one of the electronic channels, taking into account the necessary procedural controls and notifying the customer via SMS about the request. Additionally:
- For individuals: the request must be activated through another channel, for example, the controls for adding and activating beneficiaries as detailed in the Cyber Security Framework
- For enterprises: consider the necessary procedural controls, including but not limited to: authorizing multiple approvals for financing requests, activating the request from another channel, etc.
- Ensure that the customer/business owner or authorized representative approves the execution of the request by contacting the customer via a phone call from the call center or customer service.
- It is the bank's responsibility to verify the information provided by the customer/business before executing the transaction.
- Approval of the request must be obtained at least 24 hours after submission for individuals and three business days for enterprises.
- Adequate security standards must be established to protect data and communication with the digital certification service provider, considering the security encryption standards for data as well as data privacy.
- Maintain copies of documents and all legal matters concerning digital certification.
- Update agreements and contracts to clarify that this service is conducted electronically using digital certification and that there shall be no objection to its electronic execution.
- Specify the type of financing and its maximum limit in accordance with the bank's policies and potential risks based on the bank's classification.
- Periodically evaluate and monitor the precautionary controls and ensure their effectiveness.
These instructions replace SAMA's instructions regarding the SAMA’s non-objection to offering personal financing products and issuing credit cards for individuals through digital certification services.
Regulations for Processing Financial Refunds for Bank Cards
Based on the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/2/1386H, and the powers vested to SAMA to apply the Implementation Rules for Banking Control Law under the decision of the Minister of Finance No. 3/2149 dated 14/10/1406H, and referring to the Regulations of Issuance and Operations of Credit and Monthly Charge Cards issued by Circular No. 361000090389 dated 26/6/1436H, and SAMA’s instructions issued by Circular No. 19901/M AT/9006 dated 18/4/1432H regarding instant SMS notification services.
We inform you that all banks operating in the Kingdom must adhere to the following when processing financial refund transactions for bank cards:
First: Credit Cards
- Process and settle financial refund transactions within three working days from the date of receiving the transaction in the acquirer bank's law.
- Process and settle financial refund transactions to credit card accounts within three working days from the date of receiving the transaction in the issuer bank's law.
- Notify customers via SMS immediately upon crediting the refund amount to the card account.
Second: Debit Cards (Mada)
- Process and settle financial refund transactions immediately upon receiving the transaction in the acquirer bank's law.
- Process and settle financial refund transactions to the card account immediately upon receiving the transaction in the issuer bank's law.
- Notify customers via SMS immediately upon crediting the refund amount to the account linked to the card.
For your information and action accordingly as of 01/01/2020G.
Procedural Requirements for Mortgage Registration
No: 391000070455 Date(g): 6/3/2018 | Date(h): 19/6/1439 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Based on the powers granted to SAMA under the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority Law issued by Royal Decree No. (23) dated 23/5/1377 H, and the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/5) dated 22/2/1386 H, and the Financing Companies Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/51) dated 13/8/1433 H, and with reference to the Registered Real Estate Mortgage Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/49) dated 13/8/1433 H.
Given the discrepancies reported to SAMA between the procedures of financing entities and notaries, and in continuation of the cooperation between the Ministry of Justice and SAMA, the Ministry of Justice has issued a procedural guide aimed at standardizing mortgage procedures between financing entities and notaries. Additionally, the Ministry has released forms for mortgage registration and an incident registration form.
Therefore, SAMA requires banks and financing companies to adhere to the following:
First: Adhere to and comply with the procedural requirements for documenting and registering mortgages according to the registration forms (Appendix 1).
Second: Provide SAMA with cases where notaries refuse to act, using the Incident Documentation Form (Appendix 2).
Procedural Requirements for Mortgage Documentation and the Prepared Forms for That Purpose.
First: The presence of the mortgagor or their representative with a power of attorney authorizing the required action.
Second: The presence of a representative from the financer (bank or financing company) with a power of attorney authorizing the required action.
Third: The mortgagee must be a licensed bank or financing company, and the financer must hold a valid license from SAMA for real estate financing.
Fourth: The mortgaged property must be owned by the mortgagor. However, it is permissible for the mortgaged property to belong to a guarantor who offers their property as collateral for the benefit of the debtor, even without the debtor's consent.
Fifth: The mortgaged property must be specifically identified, existing or expected to exist, and capable of being sold.
Sixth: The financer must provide proof that the contract executed between them and the mortgagor complies with Islamic Sharia principles, through a letter from the Sharia board granting approval of the product, rather than approving each individual contract separately.
Seventh: The completion of the transfer of ownership and the mortgage must be done in a single process, in accordance with Ministry of Justice Circular No. 13/T/6973 dated 19/1/1439 H, for the purposes of correcting a previous mortgage.
Eighth: The process must be carried out in accordance with the forms prepared by SAMA and the Ministry of Justice.
Form 1 (Property Owned by the Financing Company)
To His Excellency, the Chief Notary of ............... May Allah protect him
Peace be upon you, and the mercy and blessings of Allah,To proceed:
We inform you that the bank/company: ........................, under Commercial Register No. ............................... dated / / 14 H, owns the property according to the deed issued by your office No. ............ dated / / 14 H. We seek your approval to transfer ownership of the aforementioned property to Mr./Ms. ................... of Saudi nationality, under Civil Registration No. ....................... on the condition that the property is mortgaged to the financing company/bank ................ as collateral for an outstanding amount of .................. SAR (amount in words) under Financing Contract No. .......... dated / / 14 H, approved by the Sharia Board of the financing company/bank under No. .................. dated / / 14 H. Please note that the Sharia Board's approval is still valid and has not been amended or revoked. The execution of this contract, which establishes the debtor's liability, has been or will be carried out according to the Sharia Board's decisions. The debt will be repaid in .......... monthly installments, each amounting to ............... SAR (amount in words), payable on the ............ of each Hijri/Gregorian month, starting from / / 14 H. In case of non-payment, the property will be sold in accordance with the enforcement regulations.
Therefore, we kindly request that you document the mortgage. May Allah protect and care for you ،،،
Representative of the Financing Company / Bank
Form 2 (Property Owned by the Mortgagor)
To His Excellency, the Chief Notary of ............... May Allah protect him
Peace be upon you, and the mercy and blessings of Allah,To proceed:
We inform you that the individual/citizen/organization/company ........................... under Register No. (................) dated / / 14 H, has outstanding dues to the financing company/bank amounting to(Only ................... SAR) under Financing Contract (................) No. (........) dated / / 14 H, approved by the Sharia Board under No. ( ) dated / / 14 H. Please note that the Sharia Board's approval is still valid and has not been amended or revoked. The execution of this contract, which establishes the debtor's liability, has been or will be carried out according to the Sharia Board's decisions. The debt will be repaid in ( ) monthly installments, each amounting to ( ) (SAR), payable on the ( ) of each Hijri/Gregorian month, starting from / / 14 H. The aforementioned party has mortgaged the described property as collateral for these dues, according to the terms outlined in the mortgage contract. In case of non-payment, the property will be sold in accordance with enforcement regulations.
Therefore, we kindly request that you document the mortgage. May Allah protect and care for you ،،،
Representative of the Financing Company / Bank
Form 3 (Property Owned by a Third Party, Sold to the Company, Then Sold to the Client and Mortgaged)
Property Sale and Mortgage Registration Form (Murabaha)
To His Excellency, the Chief Notary of ............... May Allah protect him
We inform you that the individual/citizen/organization/company: ......................, under Register No. ....................... owns the property according to the deed issued by your office No. .................... dated / / 14 H. The mentioned party wishes to sell the described property to the financing company/bank .............. under Commercial Register No. ........................... dated / / 14 H, for a price of .................. SAR (amount in words). The financing company/bank has accepted this sale and then resold it on deferred terms for ...................... SAR (amount in words) to Mr./Ms. ..................... of Saudi nationality, under Civil Registration No. ....................., and accepted this sale on the condition that the mentioned property be mortgaged to the financing company/bank.............................. as collateral for the outstanding dues amounting to ................... SAR (amount in words) under Murabaha Contract No. ................. dated / / 14 H, approved by the Sharia Board under No. .............. dated / / 14 H. Please note that the Sharia Board's approval is still valid and has not been amended or revoked. The execution of this contract, which establishes the debtor's liability, has been or will be carried out according to the Sharia Board's decisions. The debt will be repaid in ............... monthly installments, each amounting to ................. SAR (amount in words), payable on the ........ of each Hijri/Gregorian month, starting from / / 14 H. In case of non-payment, the property will be sold in accordance with enforcement regulations.
Therefore, we kindly request that you document the sale and mortgage. May Allah protect and care for you،،،
Representative of the Financing Company / Bank
Incident Documentation Form
Referring to SAMA Circular No. 381000089828 dated 28/8/1438 H, which mandates banks and financing companies to register mortgage agreements in accordance with the fact of the contract, to cease procedures related to property ownership transfer instead of mortgaging it, and to rectify the status of properties currently registered in the bank's name within a period not exceeding 3 years, while also informing clients of these changes.
We inform you that it has been impossible for us to execute the mortgage due to the following incident:
Notary Office Location Name of the Notary Transaction Registration Number and Date at the Notary Office Deed Number and Date Type of Financing Real Estate Financier (Bank or Financing Company) - SAMA reviewed the mentioned request and found it compliant with the relevant regulations and instructions of the institution.
- Attached to the form is a copy of the letter addressed to the Notary Office.
Representative of SAMA
Financial Market Activities
Banks Investment Rules
No: 43083108 Date(g): 25/4/2022 | Date(h): 24/9/1443 Status: In-Force Based on the Saudi Central Bank Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/36 dated 11/04/1442H and the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/02/1386H, and based on the Central Bank's supervisory and regulatory role, and to ensure that banks establish an integrated internal framework to organize their investments, govern their procedures, effectively manage the resulting risks, and maintain the quality and safety of these investments, you will find attached the first version of the Banks' Investment Rules.
For your information and action accordingly as of October 1, 2022G.
1. Introduction
Banks invest in different asset classes for the purpose of managing liquidity, hedging, diversification of assets, and generating returns. These Investments expose banks to a multitude of risks; therefore, SAMA has decided to issue these Banks Investment Rules.
These Rules are issued in accordance with the authority vested in Saudi Central Bank (SAMA) under the Central Bank Law issued via Royal Decree No. M/36 dated 11/04/1442H, and the Banking Control Law issued via Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/2/1386H.
2. Objectives
The objectives of these Rules are as follows:
2.1 Ensure banks put in place a comprehensive internal investment framework, with proper risk management in accordance with SAMA regulatory requirements.
2.2 Provide guidance for bank investment activities to ensure the alignment with sound risk management and governance practices.
3. Scope of Application
These Rules are applicable to banks’ investments that are reported as net investments in the balance sheet for all banks licensed under the Banking Control Law.
4. Definitions
The following terms and phrases, where used in these Rules, should have the corresponding meanings, unless the context implies otherwise:
■ Rules
Banks Investment Rules.
■ Local Investment
Any investment in both trading and banking book that takes place in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia regardless of the currency and the residency of the issuer.
■ International Investment
Any investment in both trading and banking book that takes place outside the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia regardless of the currency and the residency of the issuer.
5. General Requirements
5.1 Banks should be prudent in managing their investments, and ensure the safety of their capital and liquidity taking into consideration the following:
■ Properly managing investment concentration to avoid the potential loss of one investment negatively affecting the whole investment portfolio.
■ Properly managing the liquidity of their investment portfolio to meet cash requirements and any liabilities as they fall due.
5.2 Banks should review and monitor their investment portfolio and make sure that their decisions and portfolio management practices comply with SAMA’s regulations and the bank’s policies and procedures.
5.3 Banks’ investment decisions must be associated with a proper documented rationale taking into consideration the economic environment, investment maturity, price volatility, market behavior, credit risk, concentration risk, legal risk and all other applicable risks. In addition, banks should focus on understanding the investment structures including any associated risks and potential payoffs.
6. Governance
6.1 Banks should have clear governance structure in terms of the role of the Board of Directors and Senior Management. In addition, banks should have a clear internal controls and audit procedures in terms of protecting the interests of depositors and other stakeholders.
6.2 The Board of Directors of a bank is ultimately responsible for the oversight of the bank’s investments. The Board or its delegated authority is responsible for approving the internal Investment Policy and Strategy. For Foreign Banks Branches (FBB), the responsibilities of the Board of Directors lies with the authority responsible for overseeing the business and operations of the FBB at Head Office/Regional Office.
6.3 Banks should have a committee at management level that will be held responsible and accountable for investment decisions including the approval and allocation of funds, risk assessment, setting investment limits and insuring that the bank’s investments are in-line with its Investment Policy.
6.4 Banks’ Investment Policy should include, but not limited to, the following:
■ Governance requirements including setting controls, responsibilities, and delegation of authority.
■ Investment eligibility criteria.
■ Prudential exposure limits taking into consideration minimum capital, liquidity and reserve requirements set by SAMA.
■ Terms regulating the bank’s local and international investments by setting investment limits in-line with the bank’s core business activity, strategy, risk tolerance, risk profile, market and macroeconomic conditions which include but not limited to setting the following limits:
- International investments (Local/foreign currency) to total investments
- International investments (Local/foreign currency) to total regulatory capital (Tier 1 + Tier2)
- Total investments / Total Assets
■ Guidelines to handle active/passive breaches to an investment limit or any fraudulent activity.
■ Criteria on eligible counterparties for dealing/trading as well as the proper counterparty limits.
■ Guidelines that include valuation of the portfolio, waterfall-pricing system and consistent portfolio calculation performance and reporting systems.
■ Systems for management of various risks and internal controls.
■ Data keeping requirements.
6.5 Banks should develop a clear, robust and demonstrable set of procedures, monitoring tools, governance and contingency plans to enable them to proactively identify any potential difficulties and risks, investigate the drivers and act in a timely manner to mitigate potential investment losses and report to the bank’s senior management and SAMA if needed.
6.6 Banks Investment Policy and procedures should be reviewed at least every three years or more frequently if the bank deems it necessary based on the changes in the relevant regulatory requirements or business practices.
6.7 Banks Investment Policy and procedures should adhere to the investment requirements in the Banking Control Law and all relevant regulations.
6.8 Banks should have a strategy for their investments that articulates in a clear and concise manner the bank’s approach and objectives, including establishing quantitative investment targets /goals and how to achieve them over a realistic timeframe.
6.9 Banks Investment Strategy should take into consideration the credit risk (Sectoral, Geographical, Settlement, etc.), market risk (volatility, interest rate including Interest Rate Risk in the Banking Book (IRRBB), FX, etc.), Operational risk (errors, frauds), liquidity risks, concentration risk and any other applicable risks.
6.10 Banks should oversee the implementation of the Investment Strategy and ensure that it remains appropriate in relation to the bank’s size, complexity, geographical footprint, business strategy, markets and regulatory requirements.
6.11 Banks should have an operational guidelines detailing how the investment strategy will be implemented. This should include clearly defining and documenting the roles, responsibilities, formal reporting lines and individual (or team) goals and incentives geared towards reaching the targets in the Investment Strategy.
6.12 Banks should put in place mechanisms to monitor the operational guidelines effectiveness and its integration into the bank’s risk management framework.
7. Risk Management and Monitoring
7.1 Banks should analyze and assess current and prospective investments, taking into consideration all risks that may arise from such investment. The results and any risks identified in the assessment should be reported to the relevant committee responsible for the bank’s investment activities.
7.2 Banks investments should be in-line with their risk management framework. Banks should have an adequate risk management system to identify, measure, and manage the risks generated from investment activities.
7.3 Before engaging in any investments, Banks should comply with all relevant Anti Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing requirements issued by SAMA.
7.4 The investment portfolio should be in-line with the bank’s investment objectives as specified in their Investment Strategy. Banks should monitor the performance of their investment portfolio on continuous basis and establish benchmark for monitoring purposes where applicable.
7.5 Banks should diversify their investment portfolio to avoid concentration risk; also, they should determine their diversification strategy based on their risk tolerance.
7.6 Banks should perform an annual portfolio level stress-testing taking into consideration macro-economic circumstances to identify the bank’s risk-bearing ability and verify how potential risks are covered, and provide the results of the assessment to SAMA upon request.
7.7 Banks should have adequate resources to manage their investment portfolio including strong managerial /investment capabilities, knowledgeable staff with relevant professional experience.
8. Approval Requirements and Controls
8.1 Banks should obtain SAMA non-objection on investments that require regulatory approval based on the Banking Control Law and Ministerial Decree No. 3/2149, such investments will be approved on a portfolio level. Any changes in these investments’ structure or limits (increase or introduce new limits) will require prior non-objection from SAMA.
8.2 Banks should clarify in their policies the investment channels and approval requirement for each investment product, including that investing in Money Market Funds (MMFs) must be through entities that are licensed by the relevant authority (i.e. the Capital Market Authority “CMA”) and must comply with its Regulations. Such investment must also comply with the following conditions:
■ Saudi riyal-denominated funds must be invested exclusively in the onshore Saudi market.
■ The minimum credit rating requirement for any MMF set by SAMA.
■ The custodian of the MMF must be licensed and regulated.
■ The lending or placement of Saudi riyal-denominated funds, directly or indirectly, is restricted to banks and financial institutions regulated by SAMA or CMA, respectively. Doing otherwise requires SAMA’s prior approval.
8.3 The request for obtaining SAMA non objection must at least include the following:
■ Confirmation of the Board of Directors or its delegated authority approval of the Bank’s Investment Strategy, including investment limits, risk tolerance and allocations for hedging and trading purposes.
■ SAMA’s last non-objection on investment limits.
■ Existing approved limits and utilization amount.
■ Detailed description of each asset class of the outstanding and proposed investments, which includes the followings:
- Strategy for each asset class.
- Ratings (Country issuer instrument) as applicable.
- Book value.
- Market value.
- Expected annual growth rate.
- Projected exposure amount for 3 years (Year-end).
- IFRS9 ECL staging classification, if applicable.
- Asset category in terms of fair value measurements (level 1, level 2, and level 3) as described in IFRS13.
- Asset category in terms of liquidity (High quality liquid assets (HQLA) level 1, level 2a or 2b).
- Revised investment limit.
- Economic sector of security issuer.
- Geographical distribution.
- Currency of denomination.
- Risk Weighted Asset for Credit Risk, Market Risk or Operational Risk.
■ Impact assessment on SAMA regulatory ratios including (Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR), Net Stable Funding Ratio (NSFR), Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR), SAMA Liquidity Ratio (LR), Leverage Ratio) if limits are fully utilized.
■ List and copy of all relevant approved policies and procedures, in particular for monitoring the portfolio performance.
■ Risk assessment for the proposed investment portfolio.
■ Details on the mechanism currently in place for reporting portfolio related to risks/developments to senior management and Board of Directors.
■ The escalation process for any breach of the approved limits.
■ Any other information SAMA may deem necessary for determining SAMA non-objection.
8.4 Banks should review the approved limits (no change/increase/decrease) to be in -line with the bank’s risk tolerance and market position at a minimum every three years.
9. Implementation and Effective Date
9.1 These Rules shall come into force starting from 1 October 2022. All Banks should develop/update their current Investment Policy, procedures and Strategy to be in -line with the requirements prescribed in these Rules.
9.2 Any violation or circumvention of these Rules may warrant the appropriate regulatory action by SAMA.
Guidelines on Repurchase Agreements
No: 43013189 Date(g): 19/9/2021 | Date(h): 12/2/1443 Status: In-Force Based on the Central Bank's supervisory and regulatory role and its keenness to develop and strengthen the financial sector by adopting the best international practices, and based on the powers granted to the Central Bank under the Saudi Central Bank Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/36 dated 11/04/1442 H and the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/02/1386 H.
We inform you that it has been decided to introduce the accompanying Guidelines on Repurchase Agreements, which aim to ensure that repurchase agreements are concluded in accordance with policies and procedures consistent with the Central Bank's regulatory requirements, as well as adopting standardized legal documents for these transactions and ensuring the integrity and comprehensiveness of the risk management of practitioners of repurchase activities.
For your Information and action accordingly as of today.
Part A: Overview
1. Introduction
1.1. The market for repurchase agreements (repo) is an important source of secured short-term funding, complementing other sources of funding in the banking system. A well-developed repo market would also enhance the breadth and depth of Saudi Arabia's bonds and sukuk markets.
1.2. To develop an orderly Saudi repo market, it is important that the Saudi repo market operates with standard market practices in line with global best practices and underpinned by professional conduct as well as prudent and sound risk management practices.
2. Objectives
2.1. These guidelines issued by Saudi Central Bank (SAMA)'s set out policy requirements for repo transactions to:
2.1.1. Ensure that repo transactions are conducted in a manner that is consistent with SAMA's regulatory requirements and the objectives of developing an orderly repo market; and
2.1.2. Ensure that repo market participants practice sound and comprehensive risk management, including the adoption of standard legal documentation.
3. Legal Provisions
3.1. These guidelines are issued by SAMA in exercise of the powers vested upon it under its Charter issued by the Royal Decree No.36 on 11-04-1442H (26 November 2020G) and the Banking Control Law issued by the Royal Decree No. M/5 on 22-02-1386H (11 June 1966G) and the rules for Enforcing its Provisions issued by Ministerial Decision No 3/2149 on 14/10/1406AH.
3.2. All policy requirements in these guidelines are binding on participants in the Saudi repo market.
3.3. These guidelines shall be read together with:
3.3.1. Relevant rules and regulations issued by SAMA;
3.3.2. Saudi Capital Market Law and the relevant rules and regulations issued by the Capital Market Authority (CMA) of Saudi Arabia;
3.3.3. Saudi Bankruptcy Law issued by the Ministry of Commerce (MOC);
3.3.4. Rules and regulations issued by the Ministry of Investment of Saudi Arabia (MISA);
4. Effective Date
4.1. This guideline will come into effect as of the date of issuance.
5. Applicability
Market participants
5.1. These guidelines shall apply to all repo market participants, defined as eligible counterparties in Section 9.
Types of repo transactions
5.2. These guidelines are applicable to any Saudi Riyal (SAR) denominated, outright sale or purchase of eligible securities with an agreement to repurchase or resell the same or equivalent eligible securities at an agreed specified future date or on demand, subject to mutual agreement.
5.3. For avoidance of doubt, there is no prohibition on bank's existing repo transaction entered into with a domestic or foreign counterparty, where the securities or cash leg is denominated in foreign currency and the transaction is governed by the GMRA, subject to compliance to the relevant and applicable rules and regulations in Saudi Arabia.
6. Terms and Definitions
6.1. In these Guidelines, unless the context otherwise requires, the following terms shall have the following meanings:
6.1.1. Custodian: It is a third party that provides services in relation to collateral of a repo transaction, which may include providing custody of the collateral, collateral management, collateral account segregation and other ancillary operations during the life of the transaction;
6.1.2. Eligible Security: an eligible security (or referred to as collateral) that the repo seller provides to the repo buyer to secure funding and meet the requirements in Section 10;
6.1.3. GMRA: Global Master Repurchase Agreements;
6.1.4. Held-in-Custody: It is an arrangement in a repo transaction, where the repo seller retains or a third party is appointed, to retain the collateral security in a segregated account;
6.1.5. HNWI: High Net Worth Individual
6.1.6. ICMA: International Capital Market Association;
6.1.7. Master Repo Agreement (MRA): It is a standardized contract approved by SAMA, that provides all terms and conditions of a repo agreement between a repo buyer and a repo seller;
6.1.8. Repurchase Agreement (Repo): It is an agreement where a seller sells securities to a buyer with a simultaneous promise arrangement for the buyer to resell or for the seller to repurchase the same or equivalent securities for an agreed price at a specified future date or on demand. In addition, repo term will be used commonly in this guideline referring to repo and reverse repo equivalently unless otherwise is specified.
6.1.9. Reverse Repurchase Agreement (Reverse Repo): It is an agreement where a buyer buys financial securities from a seller with a simultaneous promise arrangement for the seller to repurchase or for the buyer to resell the same or equivalent securities for an agreed price at a specified future date or on demand;
6.1.10. Repo Buyer: A market participant who is a cash provider at the repo transaction start date;
6.1.11. Repo Seller: A market participant who is a securities provider at the repo transaction start date
6.1.12. Repo market participants: Eligible counterparties referred to in Section 9;
6.1.13. SOCPA: Saudi Authority of Auditors and Accountants
6.1.14. SARIE: The Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express or any other future instant payments system;
6.1.15. Saudi Repo Market: It is a part of the financial markets in which financial securities are exchanged through an agreement for cash and vice versa in Saudi Arabia;
6.1.16. Tadawul: Saudi Exchange.
Part B: Policy Requirements
7. Legal Agreement
7.1. All repo market participants shall ensure that their repo transactions in Saudi Arabia must be governed by the standard Master Repurchase Agreement (MRA) for the Sale and Purchase of Securities (2020 version) as attached in Appendix A, approved by SAMA.
7.2. Any amendments to the MRA must be incorporated in the Annexures to the agreement and must be mutually agreed by both parties. It should be made clear in trade confirmations or in other alternative agreed forms (e.g. supplementary letter) that the parties mutually agree to a variation of the standard terms and conditions. Parties to the agreement should note that amendments to the MRA may impact the ability of parties to rely on industry legal opinions on the enforceability of the MRA
7.3. At a minimum, the repo agreement shall consist of:
7.3.1. Absolute transfer of ownership of the eligible securities;
7.3.2. Marking-to-market of the repo, unless the eligible security is held by a custodian;
7.3.3. Use of the haircut and margin call, where necessary;
7.3.4. Substitution of the eligible securities where necessary; and
7.3.5. Event of default.
7.4. The MRA shall be subject to and governed by Saudi law.
8. Risk Management Requirements
Risk management policies and procedures
8.1. Banks, including other repo market participants are required to put in place policies and procedures to govern their repo activities. The policies should cover governance, authorization, risk management, internal controls and reporting requirements.
8.2. The risk management policies and procedures must be sufficiently comprehensive covering credit, counterparty, market, legal and operational risks arising from the repo market participant's repo activities.
8.3. Depending on the scale of its repo activities, repo market participants shall ensure effective coordination between the related functional areas (e.g. treasury, back-office, risk management, compliance and IT functions), as well as readiness of the relevant systems and infrastructure to support effective risk management and their repo activities. Such systems may include systems for securities valuation and management, credit control, custody, risk management, record keeping and regulatory reporting purposes.
8.4. Repo market participants shall ensure compliance with the relevant accounting standards for repo transactions as endorsed by SOCPA. Counterparty and credit risks
8.5. Repo market participants must establish exposure limits based on different risk measures, including limits for counterparties and issuers of the underlying collateral securities. These limits must be reviewed on a periodic basis or on a more frequent basis, as market circumstances change.
8.6. Repo market participants shall also take into account the quality of the securities used in the transaction and apply valuation haircut accordingly. Repo market participants shall manage the associated credit risk of collateral securities issued by non-sovereign and corporate and adjust the terms and conditions accordingly such as in terms of repo rates and haircut.
Conduct risk
8.7. The conduct of repo agreements by repo market participants must be in line with the principles of market professionalism and integrity. All repo market participants are prohibited from entering into repo transactions with the intent of manipulating Saudi financial markets.
8.8. Repo market participants shall ensure the confidentiality of the identity of parties to a repo transaction, at all times, except as otherwise required for regulatory reporting to SAMA.
Legal risk
8.9. The ownership of the eligible securities must be fully transferred from the seller to the buyer, even if a custodial arrangement is used to hold the eligible security for parties to the transaction.
8.10. There must be adequate documentation to cover the type of repo that are intended to be undertaken. Any deviation from the normal repo type as described in this document or any other arrangements, shall be mutually agreed between counterparties and properly documented in the legal agreement.
8.11. Repo market participants shall ensure that all the relevant legal and regulatory requirements are fully complied with at all times.
9. Eligible Counterparties
9.1. The following counterparties are eligible to partake in repos transactions, subject to the requirement that at least one principal to the repo transaction must be a bank licensed by SAMA:
9.1.1. Financial institutions, which include banks, insurers and finance companies licensed by SAMA;
9.1.2. Capital market institutions, approved by the CMA;
9.1.3. Corporates, including financial and non-financial corporates incorporated in Saudi Arabia. Corporates should be assessed of their knowledge, sophistication and understanding of risks in the repo market;
9.1.4. Financial and non-financial corporates not domiciled in Saudi Arabia shall not transact repos where the securities have time to maturity of less than one year. For foreign financial corporates, the maturity of securities provided as collateral shall have tenors at least three months longer than the maturity of the repo transaction; and
9.1.5. Non-foreign high net worth individual, subject to suitability assessment that they have the knowledge and understand the risks of the repo market.
10. Eligible Securities
10.1. Eligible SAR denominated instruments shall include:
10.1.1. Bonds/Sukuk issued or guaranteed by the Government of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia;
10.1.2. Securities issued by SAMA;
10.1.3. Bonds’/Sukuk issuances listed in Saudi Exchange; and
10.1.4. Any other eligible securities as may be specified by SAMA.
10.2. The legal maturity (i.e. excluding any optionality) of a security must be at least equal to or longer than the maturity of the repo transaction.
10.3. Securities are not eligible as collateral if they are issued or guaranteed by the repo seller.
11. Price Sources and Valuation
11.1. Counterparties must agree on the price sources to be used to value collateral to minimize disputes between counterparties.
11.2. The market value of the securities should be calculated using dirty prices, in line with the market practice for the accrued interest/profit which is calculated from the last coupon date up to but excluding the margin delivery date. In the event of a dispute about the price used by the margin caller, both parties should agree on an alternative price source, negotiate promptly, reasonably and act in good faith.
11.3. The selection of the price sources should follow a waterfall-based approach to account for any possible failure or unavailability of prices from any single source.
12. Custody
12.1. Prior to engaging in any repo agreements with custodial arrangements, each repo market participant must fully understand the terms and conditions of the custody agreement, including their right and obligations.
12.2. A licensed bank shall have in place custody arrangement and processes for eligible securities held-in-custody on behalf of the repo participants, including comprehensive systems and processes to monitor and segregate the held-in-custody securities to mitigate the risk of duplicative use of securities.
13.Reporting and Settlement Requirements
13.1. A bank repo participant shall report all repo transactions involving eligible securities in Section 10 to SAMA on a daily basis. A bank repo participant is not required to report if there are no repo transactions of eligible securities for that day.
13.2. Other repo market participants shall submit weekly returns on daily positions to SAMA. Weekly reports will cover Sunday to Thursday and should reach SAMA by close of business the following Sunday. Banks are not required to send the weekly returns if there are no repo transactions of eligible securities for that week.
13.3. The Weekly Reports shall include the following:
13.3.1. Name both counterparties (buyer and seller)
13.3.2. Transaction date or deal date
13.3.3. Value date
13.3.4. Currency
13.3.5. Tenor
13.3.6. Due date
13.3.7. Cash amount
13.3.8. Description of securities (i.e. obligor of risk)
13.3.9. Amortized adjusted notional value of securities
13.3.10. Haircut
13.3.11. Initial margin/margin ratio
13.3.12. Profit rate
13.3.13. Profit payment frequency
13.3.14. Profit amount
13.3.15. Total amount due
13.3.16. Market segment for the buyer/seller
13.3.17. First exercisable option date (if applicable)
13.3.18. Any substitution for the securities (if applicable)
13.4. All reports should be sent to email: repo@sama.gov.sa
13.5. The delivery and fund transfer of non-SAMA issued eligible securities with cash must be done through Tadawul and SARIE, respectively in the case where both the counterparties being licensed agents and currency of transaction is SAR.
13.6. The exchange of SAMA issued securities with cash must be done through SAMA and SARIE respectively in the case where both the counterparties being licensed agents and currency of transaction is in SAR.
13.7. The exchange of eligible securities with cash must be done through any agreed systems between the counterparties in the case where one of the counterparties being non-licensed agents or transaction currency is not SAR.
* For the avoidance of doubt, repo market participants are allowed to transact in repos involving perpetual debt with embedded options that could be triggered in less than two years, however the tenor of the repo transaction shall be at least three months shorter than the first exercise date.
Appendix A
Master Agreement for the Sale and Purchase of Securities
Dated as of ____________________________________
Between:
_____________________________________________________________________________________(“Party A”)
and
_____________________________________________________________________________________(“Party B")
1. Applicability
(a) From time to time the parties hereto may enter into transactions in which:
(i) one party, acting through a Designated Office, ("Seller") agrees to sell to the other, acting through a Designated Office, (“Buyer”) Securities against the payment of the purchase price by Buyer to Seller;
(ii) Seller grants a Wa’ad (undertaking) to Buyer to purchase Securities from Buyer on a future specified date, subject to a specified condition being satisfied; and
(iii) Buyer grants a Wa'ad (undertaking) to Seller to sell Securities to Seller on a future specified date, subject to a specified condition being satisfied.
(b) Each such transaction shall be referred to herein as a “Transaction" and shall be governed by this Agreement, including any supplemental terms or conditions contained in Annex1, unless otherwise agreed in writing.
2. Definitions
(a) "Act of Insolvency" shall occur with respect to any party hereto upon -
(i) its making a general assignment for the benefit of, or entering into a reorganisation, arrangement, or composition with, creditors; or
(ii) all or substantially all assets of such party, provided the relevant process is not dismissed, discharged, stayed or restrained within 15 days; or
(iii) its becoming insolvent or becoming unable to pay its debts as they become due or failing or admitting in writing its inability generally to pay its debts as they become due; or
(iv) its seeking, consenting to or acquiescing in the appointment of any trustee, administrator, receiver or liquidator or analogous officer of it or any material part of its property; or
(v) the presentation or filing of a petition in respect of it (other than by the other party to this Agreement in respect of any obligation under this Agreement) in any court or before any agency or the commencement of any proceeding by any Competent Authority alleging or for the bankruptcy, winding-up or insolvency of such party (or any analogous proceeding) or seeking any reorganisation, arrangement, composition, re-adjustment, administration, liquidation, dissolution or similar relief under any present or future statute, law or regulation, such petition not having been stayed or dismissed within 15 days of its filing (except in the case of a petition presented by a Competent Authority or for winding-up or any analogous proceeding, in respect of which no such 15 day period shall apply); or
(vi) the appointment of a receiver, administrator, liquidator, conservator, custodian or trustee or analogous officer of such party or over all or any material part of such party’s property; or
(vii) the filing of any application for the commencement of any protective settlement or any financial restructuring procedure or any liquidation (including any such procedure in respect of small debtors) under the Saudi Arabian Bankruptcy Law (issued pursuant to Royal Decree no. M/50 dated 28/5/1439H (corresponding to 13 February 2018));
(b) "Applicable Rate", in relation to any sum in any currency, the rate selected in a commercially reasonable manner by the Affected Party;
(c) "Appropriate Market", the meaning specified in paragraph 12;
(d) "Base Currency", the currency indicated in Annex1;
(e) "Business Day" means -
(i) in relation to the settlement of a Transaction or delivery of Securities under this Agreement through a settlement system, a day on which that settlement system is open for business;
(ii) in relation to the settlement of a Transaction or delivery of Securities under this Agreement otherwise than through a settlement system, a day on which banks are open for business in the place where the relevant Securities are to be delivered and, if different, the place in which the relevant payment is to be made; and
(iii) in relation to the payment of any amount under this Agreement not falling within (i) or (ii) above, a day other than a Friday, Saturday or Sunday on which banks are open for business in the principal financial centre of the country of which the currency in which the payment is denominated is the official currency and, if different, in the place where any account designated by the parties for the making or receipt of the payment is situated.
(f) “Buyer Exercise Condition”, the meaning specified in paragraph 4(b)(ii);
(g) “Cash Equivalent Amount” has the meaning given in paragraph 6(h);
(h) “Cash Margin”, a cash sum paid or to be paid to Buyer or Seller in accordance with paragraph 4;
(i) "Cash Settlement Amount", the meaning specified in paragraph 12(e)(iii);
(j) "Cash Settlement Payment Date”, the meaning specified in paragraph 12(e)(iii);
(k) "Competent Authority”, a regulator, supervisor or any similar official with primary insolvency, rehabilitative or regulatory jurisdiction over a party in the jurisdiction of its incorporation or establishment or the jurisdiction of its head office;
(l) “Confirmation”, the meaning specified in paragraph 3(b);
(m) "Contractual Currency”, the meaning specified in paragraph 9(a);
(n) "Defaulting Party", the meaning specified in paragraph 12;
(o) "Default Market Value”, the meaning specified in paragraph 12;
(p) “Default Notice", a written notice served by the non-Defaulting Party on the Defaulting Party under paragraph 12(b) designating a day as an Early Termination Date;
(q) “Deliverable Securities”, the meaning specified in paragraph 12;
(r) “Designated Office”, a branch or office which is specified as such in Annex1 or such other branch or office as may be agreed in writing by the parties;
(s) "Distribution(s)”, the meaning specified in sub-paragraph (gg) below;
(t) “Early Termination Date”, the date designated as such in a Default Notice or as otherwise determined in accordance with paragraph 12(b);
(u) “Electronic Messaging System”, an electronic system for communication capable of reproducing communication in hard copy form, including email;
(v) "Equivalent Margin Securities”, Securities equivalent to Securities previously transferred as Margin Securities;
(w) “Equivalent Securities”, with respect to a Transaction, Securities equivalent to the First purchased Securities under that Transaction. If and to the extent that such First Purchased Securities have been redeemed, the expression shall mean a sum of money equivalent to the proceeds of the redemption (other than Distributions);
(x) Securities are “equivalent to” other Securities for the purposes of this Agreement if they are: (i) of the same issuer; (ii) part of the same issue; and (iii) of an identical type, nominal value, description and (except where otherwise stated) amount as those other Securities, provided that -
(A) Securities will be equivalent to other Securities notwithstanding that those Securities have been redenominated into Saudi Riyal or that the nominal value of those Securities has changed in connection with such redenomination; and
(B) where Securities have been converted, subdivided or consolidated or have become the subject of a takeover or the holders of Securities have become entitled to receive or acquire other Securities or other property or the Securities have become subject to any similar event other than a Distribution, the expression “equivalent to” shall mean Securities equivalent to (as defined in the provisions of this definition preceding the proviso) the original Securities together with or replaced by a sum of money or Securities or other property equivalent to (as so defined) that receivable by holders of such original Securities resulting from such event;
(y) "Event of Default”, the meaning specified in paragraph 12;
(z) “Exercise Date”, in respect of a Transaction, the earlier of (i) the date specified in the Confirmation for that Transaction and (ii) the Early Termination Date;
(aa) "Exercise Notice”, a notice substantially in the form set out in Annex III of this Agreement;
(bb) “Exercised Transaction”, in respect of an Early Termination Date, each Transaction in respect of which the Exercising Party has delivered an Exercise Notice to the Undertaking Party in accordance with paragraph 5(a) prior to the occurrence of that Early Termination Date;
(cc) "Exercising Party”, in respect of any Exercise Date:
(i) if such Exercise Date is not an Early Termination Date, if the Seller Exercise Condition with respect to that Exercise Date is satisfied, Buyer, and if the Buyer Exercise Condition with respect to that Exercise Date is satisfied, Seller; or
(ii) if such Exercise Date is an Early Termination Date, if the Cash Settlement Amount is payable to Seller, Seller, and if the Cash Settlement Amount is payable to Buyer, Buyer;
(dd) “First Purchase Date”, with respect to any Transaction, the date on which First Purchased Securities are to be sold by Seller to Buyer in relation to that Transaction;
(ee) “First Purchased Securities”, with respect to any Transaction, the Securities sold or to be sold by Seller to Buyer under that Transaction, and any New Purchased Securities transferred by Seller to Buyer under paragraph 10 in respect of that Transaction;
(ff) “First Purchase Price”, on the First Purchase Date, the price at which the First Purchased Securities are sold or are to be sold by Seller to Buyer;
(gg) “Income”, with respect to any Security at any time, all profit by way of distribution, dividends or other distributions thereon, including distributions which are a payment or repayment of principal in respect of the relevant securities ("Distribution(s)”);
(hh) “Income Payment Date”, with respect to any Securities, the date on which Income is paid in respect of such Securities or, in the case of registered Securities, the date by reference to which particular registered holders are identified as being entitled to payment of Income;
(ii) “Margin Percentage”, with respect to any Margin Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities, the percentage, if any, agreed by the parties acting in a commercially reasonable manner;
(jj) “Margin Securities”, in relation to a Margin Transfer, Securities of the type and value (having applied Margin Percentage, if any) reasonably acceptable to the party calling for such Margin Transfer;
(kk) "Margin Transfer", any, or any combination of, the payment or repayment of Cash Margin and the transfer of Margin Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities;
(ll) “Market Value”, with respect to any Securities as of any time on any date, the price for such Securities (after having applied the Margin Percentage, if any, in the case of Margin Securities) at such time on such date obtained from a generally recognised source agreed by the parties or as otherwise agreed by the parties (and where different prices are obtained for different delivery dates, the price so obtainable for the earliest available such delivery date) having regard to market practice for valuing Securities of the type in question plus the aggregate amount of Income which, as at such date, has accrued but not yet been paid in respect of the Securities to the extent not included in such price as of such date, and for these purposes any sum in a currency other than the Contractual Currency for the Transaction in question shall be converted into such Contractual Currency at the Spot Rate prevailing at the time of the determination;
(mm) “Net Exposure”, the meaning specified in paragraph 6(c);
(nn) the “Net Margin” provided to a party at any time, the excess (if any) at that time of (i) the sum of the amount of Cash Margin paid to that party and the Market Value of Margin Securities transferred to that party under paragraph 6(a) (excluding any Cash Margin which has been repaid to the other party and any Margin Securities in respect of which Equivalent Margin Securities have been transferred or a Cash Equivalent Amount has been paid to the other party) over (ii) the sum of the amount of Cash Margin paid to the other party and the Market Value of Margin Securities transferred to the other party under paragraph 6(a) (excluding any Cash Margin which has been repaid by the other party and any Margin Securities in respect of which Equivalent Margin Securities have been transferred or a Cash Equivalent Amount has been paid by the other party) and for this purpose any amounts not denominated in the Base Currency shall be converted into the Base Currency at the Spot Rate prevailing at the time of the determination;
(oo) “Net Value”, the meaning specified in paragraph 12;
(pp) “New Purchased Securities", the meaning specified in paragraph 10(a);
(qq) “Non-Exercised Transaction”, in respect of an Early Termination Date, each Transaction that is not an Exercised Transaction;
(rr) "Price Differential”, with respect to any Transaction as of any date, the aggregate amount obtained by daily application of the Pricing Rate for such Transaction to the First Purchase Price for such Transaction (on a 360 day, 365 day or other day basis in accordance with the applicable market convention, unless otherwise agreed between the parties for the Transaction) for the actual number of days during the period commencing on (and including) the First Purchase Date for such Transaction and ending on (but excluding) the date of calculation or, if earlier, the Second Purchase Date;
(ss) “Pricing Rate”, with respect to any Transaction, the per annum percentage rate for calculation of the Price Differential agreed to by Buyer and Seller in relation to that Transaction;
(tt) “Receivable Securities”, the meaning specified in paragraph 12;
(uu) “Second Purchase Date", with respect to any Transaction, the date on which Buyer is to sell the Second Purchased Securities to Seller in relation to that Transaction, pursuant to the exercise by the Exercising Party of the undertaking given to it by the Undertaking Party;
(vv) “Second Purchased Securities”, with respect to any Transaction, Equivalent Securities or such other Securities as agreed between Seller and Buyer.
(ww) “Second Purchase Price”, with respect to any Transaction and as of any date, the sum of the First Purchase Price and the Price Differential as of such date;
(xx) "Securities", Shari'ah-compliant securities or financial instruments, or such other securities or financial instruments as specified in Annex 1;
(yy) “Seller Exercise Condition", the meaning specified in paragraph 4(b)(i);
(zz) “Spot Rate”, where an amount in one currency is to be converted into a second currency on any date, unless the parties otherwise agree:
(i) for the purposes of paragraph 12, the spot rate of exchange obtained by reference to a pricing source or quoted by a bank, in each case specified by the non-Defaulting Party, in the Saudi Arabia inter-bank market for the purchase of the second currency with the first currency at such dates and times determined by the non-Defaulting Party; and
(ii) for any other purpose, the latest available spot rate of exchange obtained by reference to a pricing source or quoted by a bank, in each case agreed by the parties (or in the absence of such agreement, specified by Buyer), in the Saudi Arabia inter-bank market for the purchase of the second currency with the first currency on the day on which the calculation is to be made or, if that day is not a day on which banks are open for business in Saudi Arabia, the spot rate of exchange quoted at close of business in Saudi Arabia on the immediately preceding day in Saudi Arabia on which such a quotation was available;
(aaa) “Term”, with respect to any Transaction, the interval of time commencing with the First Purchase Date and ending with the Second Purchase Date;
(bbb) "Termination”, with respect to any Transaction, refers to the requirement with respect to such Transaction for Buyer to sell the Second Purchased Securities against payment by Seller of the Second Purchase Price, pursuant to the exercise by the Exercising Party of the undertaking given to it by the Undertaking Party;
(ccc) “Transaction Costs”, the meaning specified in paragraph 12;
(ddd) “Transaction Exposure”, with respect to any Transaction at any time during the period from the First Purchase Date to the Second Purchase Date (or, if later, the date on which the Second Purchased Securities are delivered to Seller or the Transaction is terminated under paragraph 12(i) or 12(j)) the amount “E” determined as the result of the formula E = R - V, where:
R=the Second Purchase Price at such time; and
V=the Adjusted Value of the Second Purchased Securities at such time
or, where a Transaction relates to Securities of more than one description or to which different haircuts apply, the sum of the Adjusted Values of the Securities of each such description.
For this purpose the “Adjusted Value” of any Securities is their value determined on the basis of the formula, (MV(1 - H)), where:
MV= the Market Value of the Second Purchased Securities at such time
H= the “haircut” for the relevant Securities, if any, as agreed by
the parties from time to time, being a discount from the Market Value of the Securities.
If E is greater than zero, Buyer has a Transaction Exposure equal to E and if E is less than zero, Seller has a Transaction Exposure equal to the absolute value of E;
(eee) "Undertaking Party", in respect of any Exercise Date, the party that is not the Exercising Party; and
(fff) except in paragraphs 16(b)(i) and 20, references in this Agreement to “written” communications and communications "in writing” include communications made through any Electronic Messaging System agreed between the parties.
3. Initiation; Confirmation; Termination
(a) A Transaction may be entered into orally or in writing at the initiation of either Buyer or Seller.
(b) Upon agreeing to enter into a Transaction hereunder Buyer or Seller (or both), as shall have been agreed, shall promptly deliver to the other party written confirmation of such Transaction (a “Confirmation”).
The Confirmation shall describe the First Purchased Securities (including CUSIP or ISIN or other identifying number or numbers, if any), identify Buyer and Seller and set forth -
(i) the First Purchase Date;
(ii) the First Purchase Price;
(iii) the Second Purchase Date;
(iv) the Pricing Rate applicable to the Transaction;
(v) in respect of each party the details of the bank account(s) to which payments to be made hereunder are to be credited; and
(vi) any additional terms or conditions of the Transaction;
and may be in the form of Annex II or may be in any other form to which the parties agree.
The Confirmation relating to a Transaction shall, together with this Agreement, constitute prima facie evidence of the terms agreed between Buyer and Seller for that Transaction, unless objection is made with respect to the Confirmation promptly after receipt thereof. In the event of any conflict between the terms of such Confirmation and this Agreement, the Confirmation shall prevail in respect of that Transaction and those terms only.
(c) On the First Purchase Date for a Transaction, Seller shall transfer the First Purchased Securities to Buyer or its agent against the payment of the First Purchase Price by Buyer in accordance with paragraph 8(c).
(d) Termination of a Transaction will be effected on the date fixed for Termination
4. Undertakings
(a) In respect of each Transaction and subject to paragraph 12:
(i) Seller unilaterally hereby irrevocably and unconditionally undertakes to Buyer that if:
(A) the Seller Exercise Condition with respect to an Exercise Date is satisfied; and
(B) Buyer delivers to Seller an Exercise Notice on, and with respect to, that Exercise Date,
Seller will purchase from Buyer for delivery on the Second Purchase Date the Second Purchased Securities for an amount equal to the Second Purchase Price; and
(2) Buyer unilaterally hereby irrevocably and unconditionally undertakes to Seller that if:
(A) the Buyer Exercise Condition with respect to an Exercise Date is satisfied; and
(B) Seller delivers to Buyer an Exercise Notice on, and with respect to, that Exercise Date,
Buyer will sell to Seller for delivery on the Second Purchase Date the Second Purchased Securities for an amount equal to the Second Purchase Price.
(b) The:
(i) “Seller Exercise Condition” is satisfied in respect of an Exercise Date if the Market Value (or, if an Early Termination Date has occurred, the Default Market Value) of the Second Purchased Securities on such date is lower than the Second Purchase Price on such date; and
(ii) “Buyer Exercise Condition" is satisfied in respect of an Exercise Date if the Market Value (or, if an Early Termination Date has occurred, the Default Market Value) of the Second Purchased Securities on such date is equal to or higher than the Second Purchase Price on such date.
5. Exercise of Undertakings
In respect of each Transaction and subject to paragraph 12:
(a) the Exercising Party, as the recipient of the Undertaking Party’s undertaking, will be entitled to deliver to the Undertaking Party, on each Exercise Date, an Exercise Notice with respect to that Exercise Date; and
(b) following the delivery to the Undertaking Party of an Exercise Notice with respect to an Exercise Date, such delivery constituting an offer by the Exercising Party to the Undertaking Party to enter into the relevant sale and purchase:
(i) the Undertaking Party shall accept such offer orally by telephone or in writing via email, provided that, if the Undertaking Party has not responded to such offer within 5 hours of delivery of the Exercise Notice in accordance with the details specified in Annex I, the Undertaking Party will be deemed to have accepted such offer;
(ii) the Undertaking Party hereby further agrees that not responding to the offer is tantamount to acceptance of the offer;
(iii) Buyer shall deliver to Seller the Second Purchased Securities on the Second Purchase Date; and
(iv) Seller shall pay to Buyer the Second Purchase Price on the Second Purchase Date.
(c) If the Exercising Party has not delivered an Exercise Notice in accordance with paragraph 5(a) above on the Exercise Date:
(i) the Undertaking Party shall be entitled to deliver an offer to enter into the relevant sale and purchase to the Exercising Party, on or prior to the Second Purchase Date;
(ii) if the Exercising Party has not responded to such offer within 5 hours of delivery of the offer in accordance with the details specified in Annex I then the Exercising Party shall be deemed to have accepted such offer;
(iii) the Exercising Party hereby further agrees that not responding to the offer is tantamount to acceptance of the offer;
(iv) Buyer shall deliver to Seller the Second Purchased Securities on the Second Purchase Date; and
(v) Seller shall pay to Buyer the Second Purchase Price on the Second Purchase Date.
6. Margin Maintenance
(a) If at any time either party has a Net Exposure in respect of the other party it may by notice to the other party require the other party to make a Margin Transfer to it of an aggregate amount or value at least equal to that Net Exposure.
(b) A notice under sub-paragraph (a) above may be given orally or in writing.
(c) For the purposes of this Agreement a party has a Net Exposure in respect of the other party if the aggregate of all the first party's Transaction Exposures plus any amount payable to the first party under paragraph 7 but unpaid less the amount of any Net Margin provided to the first party exceeds the aggregate of all the other party's Transaction Exposures plus any amount payable to the other party under paragraph 7 but unpaid less the amount of any Net Margin provided to the other party; and the amount of the Net Exposure is the amount of the excess. For this purpose any amounts not denominated in the Base Currency shall be converted into the Base Currency at the Spot Rate prevailing at the relevant time.
(d) To the extent that a party calling for a Margin Transfer has previously paid Cash Margin which has not been repaid or delivered Margin Securities in respect of which Equivalent Margin Securities have not been delivered to it or a Cash Equivalent Amount has not been paid, that party shall be entitled to require that such Margin Transfer be satisfied first by the repayment of such Cash Margin or the delivery of Equivalent Margin Securities but, subject to this, the composition of a Margin Transfer shall be at the option of the party making such Margin Transfer.
(e) Any Cash Margin transferred shall be in the Base Currency or such other currency as the parties may agree.
(f) A payment of Cash Margin shall give rise to a debt owing from the party receiving such payment to the party making such payment.
(g) Where Seller or Buyer becomes obliged under sub-paragraph (a) above to make a Margin Transfer, it shall transfer Cash Margin or Margin Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities within the minimum period specified in Annex I. or, if no period is there specified, such minimum period as is customarily required for the settlement or delivery of money, Margin Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities of the relevant kind.
(h) Where a party (the “Transferor”) becomes obliged to transfer Equivalent Margin Securities and, having made all reasonable efforts to do so, is, for any reason relating to the Securities or the clearing system through which the Securities are to be transferred, unable to transfer Equivalent Margin Securities then
(i) the Transferor shall immediately pay to the other party Cash Margin at least equal to the Market Value of such Equivalent Margin Securities; and
(ii) if the failure is continuing for two Business Days or more the other party may by notice to the Transferor require the Transferor to pay an amount (the “Cash Equivalent Amount") equal to the Default Market Value of the Equivalent Margin Securities determined by the other party in accordance with paragraph 12(g) which shall apply on the basis that references to the non-Defaulting Party were to the other party and references to the Early Termination Date were to the date on which notice under this paragraph is effective.
(i) The parties may agree that, with respect to any Transaction, the provisions of subparagraphs (a) to (h) above shall not apply but instead that margin may be provided separately in respect of that Transaction in which case -
(i) that Transaction shall not be taken into account when calculating whether either party has a Net Exposure;
(ii) margin shall be provided in respect of that Transaction in such manner as the parties may agree; and
(iii) margin provided in respect of that Transaction shall not be taken into account for the purposes of sub-paragraphs (a) to (h) above.
(j) The parties shall agree and specify in Annex 1 whether Cash Margin shall be held in a manner that results in the accrual of an investment return and if so the basis on which that investment return shall be determined. In the absence of any such agreement between the parties, there shall be no investment return payable by a party in respect of Cash Margin held by it.
7. Income Payments
Unless otherwise agreed -
(a) where: (i) the Term of a particular Transaction extends over an Income Payment Date in respect of any Securities subject to that Transaction; or (ii) an Income Payment Date in respect of any such Securities occurs after the Second Purchase Date but before the Second Purchased Securities have been delivered to Seller or, if earlier, the occurrence of an Early Termination Date or the termination of the Transaction under paragraph 12(j) then Buyer shall on the date such Income is paid by the issuer transfer to or credit to the account of Seller an amount equal to (and in the same currency as) the amount paid by the issuer;
(b) where Margin Securities are transferred from one party ("the first party”) to the other party ("the second party”) and an Income Payment Date in respect of such Securities occurs before Equivalent Margin Securities are transferred or a Cash Equivalent Amount is paid by the second party to the first party, the second party shall on the date such Income is paid by the issuer transfer to or credit to the account of the first party an amount equal to (and in the same currency as) the amount paid by the issuer;
and for the avoidance of doubt references in this paragraph to the amount of any Income paid by the issuer of any Securities shall be to an amount paid without any withholding or deduction for or on account of taxes or duties notwithstanding that a payment of such Income made in certain circumstances may be subject to such a withholding or deduction.
8. Payment and Transfer
(a) Unless otherwise agreed, all money paid hereunder shall be in immediately available freely convertible funds of the relevant currency. All Securities to be transferred hereunder (i) shall be in suitable form for transfer and shall be accompanied by duly executed instruments of transfer or assignment in blank (where required for transfer) and such other documentation as the transferee may reasonably request, or (ii) shall be transferred through any agreed book entry or other securities clearance system or (iii) shall be transferred by any other method mutually acceptable to Seller and Buyer.
(b) Unless otherwise agreed, all money payable by one party to the other in respect of any Transaction shall be paid free and clear of, and without withholding or deduction for, any taxes or duties of whatsoever nature imposed, levied, collected, withheld or assessed by any authority having power to tax, unless the withholding or deduction of such taxes or duties is required by law. In that event, unless otherwise agreed, the paying party shall pay such additional amounts as will result in the net amounts receivable by the other party (after taking account of such withholding or deduction) being equal to such amounts as would have been received by it had no such taxes or duties been required to be withheld or deducted.
(c) Unless otherwise agreed in writing between the parties, under each Transaction transfer of the First Purchased Securities by Seller and payment of the First Purchase Price by Buyer against the transfer of such First Purchased Securities shall be made simultaneously and transfer of the Second Purchased Securities by Buyer and payment of the Second Purchase Price payable by Seller against the transfer of such Second Purchased Securities shall be made simultaneously.
(d) Subject to and without prejudice to the provisions of sub-paragraph 8(c), either party may from time to time in accordance with market practice and in recognition of the practical difficulties in arranging simultaneous delivery of Securities and money waive in relation to any Transaction its rights under this Agreement to receive simultaneous transfer and/or payment provided that transfer and/or payment shall, notwithstanding such waiver, be made on the same day and provided also that no such waiver in respect of one Transaction shall affect or bind it in respect of any other Transaction.
(e) Without prejudice to paragraph 7, the parties shall execute and deliver all necessary documents and take all necessary steps to procure that all right, title and interest in any First Purchased Securities, any Second Purchased Securities, any Margin Securities and any Equivalent Margin Securities shall pass to the party to which transfer is being made upon transfer of the same in accordance with this Agreement, free from all liens (other than a lien granted to the operator of the clearance system through which the Securities are transferred), claims, charges and encumbrances.
(f) Notwithstanding the use of expressions such as “margin”, “Net Margin” and “substitution”, which are used to reflect terminology used in the market for transactions of the kind provided for in this Agreement, all right, title and interest in and to Securities and money transferred or paid under this Agreement shall pass to the transferee upon transfer or payment (and, in respect of transfers of margin, the obligation of the party receiving Margin Securities being an obligation to transfer Equivalent Margin Securities).
(g) Time shall be of the essence in this Agreement.
(h) Subject to paragraph 12, all amounts in the same currency payable by each party to the other under any Transaction or otherwise under this Agreement on the same date shall be combined in a single calculation of a net sum payable by one party to the other and the obligation to pay that sum shall be the only obligation of either party in respect of those amounts.
(i) Subject to paragraph 12, all Securities of the same issue, denomination, currency and series, transferable by each party to the other under any Transaction or hereunder on the same date shall be combined in a single calculation of a net quantity of Securities transferable by one party to the other and the obligation to transfer the net quantity of Securities shall be the only obligation of either party in respect of the Securities so transferable and receivable.
(j) If the parties have specified in Annex I that this paragraph 8(j) shall apply, each obligation of a party under this Agreement (the "first party”) (other than an obligation arising under paragraph 12) is subject to the condition precedent that none of the events specified in paragraph 12(a) (Events of Default) shall have occurred and be continuing with respect to the other party.
9. Contractual Currency
(a) All the payments made in respect of the First Purchase Price or the Second Purchase Price of any Transaction shall be made in the currency of the First Purchase Price (the “Contractual Currency”) save as provided in paragraph 12(e)(ii). Notwithstanding the foregoing, the payee of any money may, at its option, accept tender thereof in any other currency, provided, however, that, to the extent permitted by applicable law, the obligation of the payer to pay such money will be discharged only to the extent of the amount of the Contractual Currency that such payee may, consistent with normal banking procedures, purchase with such other currency (after deduction of any premium and costs of exchange) for delivery within the customary delivery period for spot transactions in respect of the relevant currency.
(b) If for any reason the amount in the Contractual Currency received by a party, including amounts received after conversion of any recovery under any judgment or order expressed in a currency other than the Contractual Currency, falls short of the amount in the Contractual Currency due and payable, the party required to make the payment will, as a separate and independent obligation, to the extent permitted by applicable law, immediately transfer such additional amount in the Contractual Currency as may be necessary to compensate for the shortfall.
(c) If for any reason the amount in the Contractual Currency received by a party exceeds the amount of the Contractual Currency due and payable, the party receiving the transfer will refund promptly the amount of such excess.
10. Substitution
(a) A Transaction may at any time between the First Purchase Date and the Second Purchase Date, if Seller so requests and Buyer so agrees, be varied by the transfer by Buyer to Seller of Securities equivalent to the First Purchased Securities, or to such of the First Purchased Securities as shall be agreed, in exchange for the transfer by Seller to Buyer of other Securities of such amount and description as shall be agreed (“New Purchased Securities”) (being Securities having a Market Value at the date of the variation at least equal to the Market Value of the Equivalent Securities transferred to Seller).
(b) Any variation under sub-paragraph (a) above shall be effected, subject to paragraph 8(d), by the simultaneous transfer of the Equivalent Securities and New Purchased Securities concerned.
(c) A Transaction which is varied under sub-paragraph (a) above shall thereafter continue in effect as though the First Purchased Securities under that Transaction consisted of or included the New Purchased Securities instead of the Securities in respect of which Equivalent Securities have been transferred to Seller.
(d) Where either party has transferred Margin Securities to the other party it may at any time before Equivalent Margin Securities are transferred to it under paragraph 4 request the other party to transfer Equivalent Margin Securities to it in exchange for the transfer to the other party of new Margin Securities having a Market Value at the time at which the exchange is agreed at least equal to that of such Equivalent Margin Securities. If the other party agrees to the request, the exchange shall be effected, subject to paragraph 8(d), by the simultaneous transfer of the Equivalent Margin Securities and new Margin Securities concerned. Where either or both of such transfers is or are effected through a settlement system in circumstances which under the rules and procedures of that settlement system give rise to a payment by or for the account of one party to or for the account of the other party, the parties shall cause such payment or payments to be made outside that settlement system, for value the same day as the payments made through that settlement system, as shall ensure that the exchange of Equivalent Margin Securities and new Margin Securities effected under this sub-paragraph does not give rise to any net payment of cash by either party to the other.
11. Representations
Each party represents and warrants to the other that -
(a) it is duly authorised to execute and deliver this Agreement, to enter into the Transactions contemplated hereunder and to perform its obligations hereunder and thereunder and has taken all necessary action to authorise such execution, delivery and performance;
(b) it will engage in this Agreement and the Transactions contemplated hereunder as principal;
(c) the person signing this Agreement on its behalf is, and any person representing it in entering into a Transaction will be, duly authorised to do so on its behalf;
(d) it has obtained all authorisations of any governmental or regulatory body required in connection with this Agreement and the Transactions contemplated hereunder and such authorisations are in full force and effect;
(e) the execution, delivery and performance of this Agreement and the Transactions contemplated hereunder will not violate any law, ordinance, charter, by-law or rule applicable to it or any agreement by which it is bound or by which any of its assets are affected;
(f) it has satisfied itself and will continue to satisfy itself as to the tax Implications of the Transactions contemplated hereunder;
(g) in connection with this Agreement and each Transaction -
(i) unless there is a written agreement with the other party to the contrary, it is not relying on any advice (whether written or oral) of the other party, other than the representations expressly set out in this Agreement;
(ii) it has made and will make its own decisions regarding the entering into of any Transaction based upon its own judgment and upon advice from such professional advisers as it has deemed it necessary to consult;
(iii) it understands the terms, conditions and risks of each Transaction and is willing to assume (financially and otherwise) those risks;
(h) at the time of transfer to the other party of any Securities it will have the full and unqualified right to make such transfer and that upon such transfer of Securities the other party will receive all right, title and interest in and to those Securities free of any lien (other than a lien granted to the operator of the clearance system through which the Securities are transferred), claim, charge or encumbrance; and
(i) insofar as it wishes or is required for any reason to enter into only transactions which comply or are consistent with the principles of Shari’ah ("Shari'ah Compliant" or "Shari'ah Compliance"), it has made its own investigation into and satisfied itself as to the Shari'ah Compliance of this Agreement, each document entered into pursuant to or in connection with this Agreement and the Transactions entered into hereunder, and all necessary action to confirm that this Agreement, each document entered into pursuant to or in connection with this Agreement and the Transactions contemplated hereunder are Shari'ah Compliant has been taken (including the obtaining of a fatwa where required) and it will not claim any dispute on the grounds of Shari'ah Compliance of this Agreement, any document entered into pursuant to or in connection with this Agreement or any Transactions contemplated hereunder;
(j) it has not relied on the other party or any written declaration, fatwa, opinion or other documents prepared by, on behalf of or at the request of the other party for the purposes of a determination or confirmation that this Agreement, each document entered into pursuant to or in connection with this Agreement and the Transactions contemplated hereunder are Shari'ah compliant; and
(k) it is entering into this Agreement in the ordinary course of its business, and not for speculative purposes.
On the date on which any Transaction is entered into pursuant hereto, and on each day on which Securities, Margin Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities are to be transferred under any Transaction, Buyer and Seller shall each be deemed to repeat all the foregoing representations. For the avoidance of doubt and notwithstanding any arrangements which Seller or Buyer may have with any third party, each party will be liable as a principal for its obligations under this Agreement and each Transaction.
12. Events of Default
(a) If any of the following events (each an “Event of Default”) occurs in relation to either party (the "Defaulting Party”, the other party being the “non-Defaulting Party”) whether acting as Seller or Buyer -
(i) Buyer fails to pay the First Purchase Price upon the applicable First Purchase Date or Seller fails to pay the Second Purchase Price upon the applicable Second Purchase Date; or
(ii) if the parties have specified in Annex I that this sub-paragraph shall apply, Seller fails to deliver the First Purchased Securities on the First Purchase Date or Buyer fails to deliver the Second Purchased Securities on the Second Purchase Date, in either case within the standard settlement time for delivery of the Securities concerned; or
(iii) Seller or Buyer fails to pay when due any sum payable under sub-paragraph (i) or (j) below; or
(iv) Seller or Buyer fails to:
(A) make a Margin Transfer within the minimum period in accordance with paragraph 6(g) or, in the case of an obligation to deliver Equivalent Margin Securities, either to deliver the relevant Equivalent Margin Securities or to pay Cash Margin in accordance with paragraph 6(h)(i) or to pay the Cash Equivalent Amount in accordance with paragraph 6(h)(ii); or
(B) where paragraph 6(i) applies, to provide margin in accordance with that paragraph; or
(v) Seller or Buyer fails to comply with paragraph 7; or
(vi) an Act of Insolvency occurs with respect to Seller or Buyer; or
(vii) any representations made by Seller or Buyer are incorrect or untrue in any material respect when made or repeated or deemed to have been made or repeated; or
(viii) Seller or Buyer admits to the other that it is unable to, or intends not to, perform any of its obligations hereunder or in respect of any Transaction; or
(ix) Seller or Buyer being declared in default or being suspended or expelled from membership of or participation in, any securities exchange or suspended or prohibited from dealing in securities by any Competent Authority, in each case on the grounds that it has failed to meet any requirements relating to financial resources or credit rating; or
(x) Seller or Buyer fails to perform any other of its obligations hereunder and does not remedy such failure within 30 days after notice is given by the non-Defaulting Party requiring it to do so,
then sub-paragraphs (b) to (h) below shall apply.
(b) If at any time an Event of Default has occurred and is continuing the non-Defaulting Party may, by not more than 20 days’ notice to the Defaulting Party specifying the relevant Event of Default, designate a day not earlier than the day such notice is effective as an Early Termination Date in respect of all outstanding Transactions. If, however, “Automatic Early Termination” is specified in Annex I with respect to the Defaulting Party, then an Early Termination Date in respect of all outstanding Transactions will occur at the time immediately preceding the occurrence with respect to the Defaulting Party of an Act of Insolvency which is the presentation of a petition for winding-up or any analogous proceeding or the appointment of a liquidator or analogous officer of the Defaulting Party.
(c) If an Early Termination Date occurs, subject to sub-paragraph (d) below, the Exercise Date for each Transaction hereunder shall occur on the Early Termination Date and the parties acknowledge and agree that the Exercising Party shall have the right to exercise the undertaking(s) of the Undertaking Party in respect of all (but not some only) of the Non-Exercised Transactions (for which purpose, the Seller Exercise Conditions and the Buyer Exercise Conditions shall be disregarded), by delivering an Exercise Notice to the Undertaking Party (and, for the avoidance of doubt, the same Exercise Notice may cover any number of Transactions), on any day in the period from (and including) the date that the statement under sub-paragraph (e)(iii) below is effective to (but excluding) the day falling 30 calendar days after such date (the “Termination Long Stop Date"); provided that, if the Exercising Party has not delivered an Exercise Notice in accordance with paragraph 5 and this sub-paragraph (c) on or prior to the Termination Long Stop Date, such Exercise Notice will be deemed to have been delivered on the Termination Long Stop Date.
(d) If the Exercising Party exercises the undertaking(s) of the Undertaking Party in accordance with paragraph 5 and sub-paragraph (c) above, subject to the following provisions in respect of each Transaction: (i) all Cash Margin shall be repayable and Equivalent Margin Securities shall be deliverable and Cash Equivalent Amounts shall be payable, in each case on the Cash Settlement Payment Date; and (ii) performance of the respective obligations of the parties with respect to the delivery of Securities, the payment of the Second Purchase Price for any Second Purchased Securities, the repayment of any Cash Margin and the payment of Cash Equivalent Amounts shall be deemed to be discharged and replaced with an obligation on the Undertaking Party to pay the Cash Settlement Amount to the Exercising Party in accordance with the provisions of sub-paragraph (e) below.
(e) (i) The Default Market Values of the Second Purchased Securities and any equivalent Margin Securities to be transferred, the amount of any Cash Margin to be transferred and the Second Purchase Prices and Cash Equivalent Amounts to be paid by each party shall be established by the non-Defaulting Party for all Transactions as at the Early Termination Date, provided that, if the parties have specified in Annex I that "Zero Price Differential on Default” shall apply, then, for the purpose of determining the Second Purchase Price in respect of each Non-Exercised Transaction, the Price Differential shall be deemed to be zero;
(ii) on the basis of the sums so established, an account shall be taken (as at the Early Termination Date) of what is due from each party to the other under this Agreement (on the basis that each party's claim against the other in respect of the transfer to it of Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities under this Agreement equals the Default Market Value therefor and including amounts payable under paragraphs 12(h) and 14 (if applicable)) and the sums due from one party shall be set off against the sums due from the other and only the balance of the account shall be payable (by the party having the claim valued at the lower amount pursuant to the foregoing). For the purposes of this calculation, all Transactions shall be deemed to be Exercised Transactions and all sums not denominated in the Base Currency shall be converted into the Base Currency at the Spot Rate; and
(iii) as soon as reasonably practicable after effecting the calculation above, the non-Defaulting Party shall provide to the Defaulting Party a statement showing in reasonable detail such calculations and specifying the balance payable by one party to the other (such balance, the "Cash Settlement Amount”) and such balance shall be due and payable on the later of the Business Day following (A) the date of such statement and (B) the date on which the Exercising Party exercises the undertaking(s) of the Undertaking Party (the later of such dates, the “Cash Settlement Payment Date”).
(f) For the purposes of this Agreement, the "Default Market Value” of any Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities shall be determined by the non-Defaulting Party on or as soon as reasonably practicable after the Early Termination Date in accordance with sub-paragraph (g) below, and for this purpose -
(i) the "Appropriate Market” means, in relation to Securities of any description, the market which is the most appropriate market for Securities of that description, as determined by the non-Defaulting Party;
(ii) "Deliverable Securities” means Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities to be delivered by the Defaulting Party (in the case of Second purchased Securities, following the exercise by the Exercising Party of the Undertaking Party’s undertaking(s));
(iii) "Net Value” means at any time, in relation to any Deliverable Securities or Receivable Securities, the amount which, in the reasonable opinion of the non-Defaulting Party, represents their fair market value, having regard to such pricing sources (including trading prices) and methods (which may include, without limitation, available prices for Securities with similar maturities, terms and credit characteristics as the relevant Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities) as the non-Defaulting Party considers appropriate, less, in the case of Receivable Securities, or plus, in the case of Deliverable Securities, all Transaction Costs which would be incurred or reasonably anticipated in connection with the purchase or sale of such Securities;
(iv) "Receivable Securities” means Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities to be delivered to the Defaulting Party (in the case of Second Purchased Securities, following the exercise by the Exercising Party of the Undertaking Party’s undertaking(s)); and
(v) "Transaction Costs” in relation to any transaction contemplated in paragraph 12(f) or (g) means the reasonable costs, commissions, fees and expenses (including any mark-up or mark-down or premium paid for guaranteed delivery) incurred or reasonably anticipated in connection with the purchase of Deliverable Securities or sale of Receivable Securities, calculated on the assumption that the aggregate thereof is the least that could reasonably be expected to be paid in order to carry out the transaction.
(g) If-
(i) on or about the Early Termination Date the non-Defaulting Party has sold, in the case of Receivable Securities, or purchased, in the case of Deliverable Securities, Securities which form part of the same issue and are of an identical type and description as those Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities (regardless as to whether or not such sales or purchases have settled), the non-Defaulting Party may elect to treat as the Default Market Value -
(A) in the case of Receivable Securities, the net proceeds of such sale after deducting all reasonable costs, commissions, fees and expenses incurred in connection therewith (provided that, where the Securities sold are not identical in amount to the Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities, the non-Defaulting Party may, acting in good faith, either (x) elect to treat such net proceeds of sale divided by the amount of Securities sold and multiplied by the amount of the Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities as the Default Market Value or (y) elect to treat such net proceeds of sale of the Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities actually sold as the Default Market Value of that proportion of the Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities, and, in the case of (y), the Default Market Value of the balance of the Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities shall be determined separately in accordance with the provisions of this paragraph 12(g)); or
(B) in the case of Deliverable Securities, the aggregate cost of such purchase, including all reasonable costs, commissions, fees and expenses incurred in connection therewith (provided that, where the Securities purchased are not identical in amount to the Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities, the non-Defaulting Party may, acting in good faith, either (x) elect to treat such aggregate cost divided by the amount of Securities sold and multiplied by the amount of the Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities as the Default Market Value or (y) elect to treat the aggregate cost of purchasing the Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities actually purchased as the Default Market Value of that proportion of the Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities, and, in the case of (y), the Default Market Value of the balance of the Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities shall be determined separately in accordance with the provisions of this paragraph 12(g));
(ii) on or about the Early Termination Date the non-Defaulting Party has received, in the case of Deliverable Securities, offer quotations or, in the case of Receivable Securities, bid quotations in respect of Securities of the relevant description from two or more market makers or regular dealers in the Appropriate Market in a commercially reasonable size, using pricing methodology which is customary for the relevant type of security (as determined by the non-Defaulting Party) the non-Defaulting Party may elect to treat as the Default Market Value of such Securities -
(A) the price quoted (or where a price is quoted by two or more market makers, the arithmetic mean of such prices) by each of them for, in the case of Deliverable Securities, the sale by the relevant market maker or dealer of such Securities or, in the case of Receivable Securities, the purchase by the relevant market maker or dealer of such Securities provided that such price or prices quoted may be adjusted in a commercially reasonable manner by the non-Defaulting Party (x) to reflect accrued but unpaid coupons not reflected in the price or prices quoted in respect of such securities and (y) in respect of any Pool Factor Affected Security, to reflect the realisable value of such Security, taking into consideration the Pool Factor Distortion (and for this purpose, “Pool Factor Affected Security” means a security other than an equity security in respect of which the decimal value of the outstanding principal divided by the original principal balance of such Security is less than one (as indicated by any pool factor applicable to such security), such circumstance a “Pool Factor Distortion”);
(B) after deducting, in the case of Receivable Securities, or adding, in the case of Deliverable Securities the Transaction Costs which would be incurred or reasonably anticipated in connection with such a transaction; or
(iii) if, acting in good faith the non-Defaulting Party either -
(A) has endeavoured but been unable to sell or purchase Securities in accordance with sub-paragraph (i) above or to obtain quotations in accordance with sub-paragraph (ii) above (or both); or
(B) has determined that it would not be commercially reasonable to sell or purchase Securities at the prices bid or offered or to obtain such quotations, or that it would not be commercially reasonable to use any quotations which it has obtained under sub-paragraph (ii) above, the non-Defaulting Party may determine the Net Value of the relevant Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities (which shall be specified) and may treat such Net Value as the Default Market Value of the relevant Second Purchased Securities or Equivalent Margin Securities.
(h) The Defaulting Party shall be liable to the non-Defaulting Party for the amount of all reasonable and legal and other professional expenses incurred by the non-Defaulting Party in connection with or as a consequence of an Event of Default.
(i) If Seller fails to deliver the First Purchased Securities to Buyer on the applicable First Purchase Date, Buyer may -
(i) if it has paid the First Purchase Price to Seller, require Seller immediately to repay the sum so paid;
(ii) if Buyer has a Transaction Exposure to Seller in respect of the relevant Transaction, require Seller from time to time to pay Cash Margin at least equal to such Transaction Exposure;
(iii) at any time while such failure continues, terminate the Transaction by giving written notice to Seller. On such termination the obligations of Seller and Buyer with respect to delivery of the First Purchased Securities, and their respective undertakings, shall terminate and, unless "Zero Price Differential on Default" is specified as applicable in Annex I and the Transaction is a Non-Exercised Transaction, Seller shall pay to Buyer an amount equal to the excess of the Second Purchase Price at the date of Termination over the First Purchase Price.
(j) If Buyer fails to deliver some or all of the Second Purchased Securities to Seller on the applicable Second Purchase Date, Seller may -
(i) if it has paid the Second Purchase Price to Buyer, require Buyer immediately to repay the sum so paid;
(ii) if Seller has a Transaction Exposure to Buyer in respect of the relevant Transaction, require Buyer from time to time to pay Cash Margin at least equal to such Transaction Exposure;
(iii) at any time while such failure continues, by written notice to Buyer declare that that Transaction or part of that Transaction corresponding to the Second Purchased Securities that have not been delivered (but only that Transaction or part of Transaction) shall be terminated immediately in accordance with sub-paragraph (d) above (disregarding for this purpose references in that sub-paragraph to transfer of Cash Margin, delivery of Equivalent Margin Securities and payment of Cash Equivalent Amount and as if references to the Second Purchase Date were to the date on which notice was given under this sub-paragraph).
(k) The provisions of this Agreement constitute a complete statement of the remedies available to each party in respect of any Event of Default.
(l) Subject to paragraph 12(m), neither party may claim any sum by way of consequential loss or damage in the event of a failure by the other party to perform any of its obligations under this Agreement.
(m)(i) Subject to sub-paragraph (ii) below, if as a result of a Transaction terminating before the scheduled Second Purchase Date under paragraphs 12(b), 12(i)(iii) or 12(j)(iii), the non-Defaulting Party, in the case of paragraph 12(b), Buyer, in the case of paragraph 12(i)(iii), or Seller, in the case of paragraph 12(j)(iii), (in each case the "first party”) incurs any loss or expense in entering into replacement transactions or in otherwise hedging its exposure arising in connection with a Transaction so terminating, the other party shall be required to pay to the first party the amount determined by the first party in good faith and without double counting to be equal to the loss or expense incurred in connection with such replacement transactions or hedging (including all fees, costs and other expenses) less the amount of any profit or gain made by that party in connection with such replacement transactions or hedging; provided that if that calculation results in a negative number, an amount equal to that number shall be payable by the first party to the other party.
(ii) If the first party reasonably decides, instead of entering into such replacement transactions, to replace or unwind any hedging transactions which the first party entered into in connection with the Transaction so terminating, or to enter into any replacement hedging transactions, the other party shall be required to pay to the first party the amount determined by the first party in good faith to be equal to the loss or expense incurred in connection with entering into such replacement or unwinding (including all fees, costs and other expenses) less the amount of any profit or gain made by that party in connection with such replacement or unwinding; provided that if that calculation results in a negative number, an amount equal to that number shall be payable by the first party to the other party.
(n) Each party shall immediately notify the other if an Event of Default, or an event which, upon the service of a notice or the lapse of time, or both, would be an Event of Default, occurs in relation to it.
(o) Any amount payable to one party (the Payee) by the other party (the Payer) under paragraph 12(e) may, at the option of the non-Defaulting Party, be reduced by its set off against any amount payable (whether at such time or in the future or upon the occurrence of a contingency) by the Payee to the Payer (irrespective of the currency, place of payment or booking office of the obligation) under any other agreement between the Payee and the Payer or instrument or undertaking issued or executed by one party to, or in favour of, the other party. If an obligation is unascertained, the non-Defaulting Party may in good faith estimate that obligation and set off in respect of the estimate, subject to accounting to the other party when the obligation is ascertained. Nothing in this paragraph shall be effective to create a charge or other security interest. This paragraph shall be without prejudice and in addition to any right of set off, combination of accounts, lien or other right to which any party is at any time otherwise entitled (whether by operation of law, contract or otherwise).
13. Tax Event
(a) This paragraph shall apply if either party notifies the other that -
(i) any action taken by a taxing authority or brought in a court of competent jurisdiction (regardless of whether such action is taken or brought with respect to a party to this Agreement); or
(ii) a change in the fiscal or regulatory regime (including, but not limited to, a change in law or in the general interpretation of law but excluding any change in any rate of tax),
has or will, in the notifying party's reasonable opinion, have a material adverse effect on that party in the context of a Transaction.
(b) If so requested by the other party, the notifying party will furnish the other with an opinion of a suitably qualified adviser that an event referred to in sub-paragraph (a)(i) or (ii) above has occurred and affects the notifying party.
(c) Where this paragraph applies, the party giving the notice referred to in sub-paragraph (a) may, subject to sub-paragraph (d) below, terminate the Transaction with effect from a date specified in the notice, not being earlier (unless so agreed by the other party) than 30 days after the date of the notice, by nominating that date as the Exercise Date and the Second Purchase Date, and the provisions of paragraph 5(b) shall apply accordingly.
(d) If the party receiving the notice referred to in sub-paragraph (a) so elects, it may override that notice by giving a counter-notice to the other party. If a counter-notice is given, the party which gives the counter-notice will be deemed to have agreed to indemnify the other party against the adverse effect referred to in sub-paragraph (a) so far as relates to the relevant Transaction and the original Second Purchase Date will continue to apply.
(e) Where a Transaction is terminated as described in this paragraph, the party which has given the notice to terminate shall indemnify the other party against any reasonable legal and other professional expenses incurred by the other party by reason of the termination, but the other party may not claim any sum by way of consequential loss or damage in respect of a termination in accordance with this paragraph.
(f) This paragraph is without prejudice to paragraph 8(b) (obligation to pay additional amounts if withholding or deduction required); but an obligation to pay such additional amounts may, where appropriate, be a circumstance which causes this paragraph to apply.
14. Late Payment Amount
(a) Late Payment Amount
If the parties have specified in Annex I that this paragraph 14 shall apply, if all or any part of any sum due and payable by a Party (the "Paying Party") under the terms of this Agreement is not paid to the other Party (the “Affected Party") on the due date (the "Due Date”), a late payment amount (the “Late Payment Amount") shall be payable on such amount as calculated in accordance with sub-paragraph (b) below.
(i) For the purposes of sub-paragraph (b) below, the unpaid amount due from the Paying Party shall be called the “Unpaid Sum”; and
(ii) the period beginning on (and including) the Due Date and ending on (but excluding) the date upon which the obligation of the Paying Party to pay the Unpaid Sum is discharged in full shall be called the “Applicable Period".
(b) Calculation of Late Payment Amount
(i) The Late Payment Amount shall be:
(x) an amount equal to the Unpaid Sum multiplied by the Applicable Rate, multiplied further by the number of days in such Applicable Period and divided by 360 or 365 in accordance with the applicable market convention (or as otherwise agreed between the parties); or
(y) such other amount as may be agreed between the parties at the relevant time.
(ii) If the Applicable Period exceeds one week it shall be deemed to be divided into successive sub-periods, each of which (other than the first, which shall be for a period of seven (7) days commencing on the Due Date) shall start on (and include) the last day of the preceding such period and the duration of which shall be selected by the Affected Party (acting reasonably). The Late Payment Amount shall be calculated for each such sub-period as if the references to Applicable Period above were references to such sub-period and shall be payable at the end of each such sub-period.
(c) Payment of Late Payment Amount
Any Late Payment Amount received by the Affected Party shall be used to pay any actual costs (not to include any opportunity cost) incurred by it as a result of the late payment of the Unpaid Sum and the remaining amount (if any) shall be donated by the Affected Party (on behalf of the Paying Party) to such registered charitable foundations as the Affected Party may select under the supervision of its Shari'ah board. The Affected Party shall, as soon as reasonably practicable following the request of the Paying Party, provide the Paying Party with documentation evidencing any such donation.
15. Single Agreement
Each party acknowledges that, and has entered into this Agreement and will enter into each Transaction hereunder in consideration of and in reliance upon the fact that all Transactions hereunder constitute a single business and contractual relationship and are made in consideration of each other. Accordingly, each party agrees (i) to perform all of its obligations in respect of each Transaction hereunder, and that a default in the performance of any such obligations shall constitute a default by it in respect of all Transactions hereunder, and (ii) that payments, deliveries and other transfers made by either of them in respect of any Transaction shall be deemed to have been made in consideration of payments, deliveries and other transfers in respect of any other Transactions hereunder.
16. Notices and Other Communications
(a) Any notice or other communication to be given under this Agreement -
(i) shall be in the English language, and except where expressly otherwise provided in this Agreement, shall be in writing;
(ii) may be given in any manner described in sub-paragraphs (b) and (c) below,
(iii) shall be sent to the party to whom it is to be given at the address or number, or in accordance with the electronic messaging details, set out in Annex I
(b) Subject to sub-paragraph (c) below, any such notice or other communication shall be effective -
(i) if in writing and delivered in person or by courier, on the date when it is delivered;
(ii) if sent by facsimile transmission, on the date when the transmission is received by a responsible employee of the recipient in legible form (it being agreed that the burden of proving receipt will be on the sender and will not be met by a transmission report generated by the sender's facsimile machine);
(iii) if sent by certified or registered mail (airmail, if overseas) or the equivalent (return receipt requested), on the date that mail is delivered or its delivery is attempted; or
(iv) if sent by Electronic Messaging System, on the date that electronic message is received;
except that any notice or communication which is received, or delivery of which is attempted, after close of business on the date of receipt or attempted delivery or on a day which is not a day on which commercial banks are open for business in the place where that notice or other communication is to be given shall be treated as given at the opening of business on the next following day which is such a day.
(c) lf-
(i) there occurs in relation to either party an Event of Default; and
(ii) the non-Defaulting Party, having made all practicable efforts to do so, including having attempted to use at least two of the methods specified in sub-paragraph (b)(ii), (iii) or (iv) above, has been unable to serve a Default Notice by one of the methods specified in those sub-paragraphs (or such of those methods as are normally used by the non-Defaulting Party when communicating with the Defaulting Party),
the non-Defaulting Party may sign a written notice (a “Special Default Notice”) which -
(A) specifies the relevant event referred to in paragraph 12(a) which has occurred in relation to the Defaulting Party;
(B) specifies the Early Termination Date designated in the Default Notice;
(C) states that the non-Defaulting Party, having made all practicable efforts to do so, including having attempted to use at least two of the methods specified in sub-paragraph (b)(ii), (iii) or (iv) above, has been unable to serve a Default Notice by one of the methods specified in those sub- paragraphs (or such of those methods as are normally used by the non-Defaulting Party when communicating with the Defaulting Party); and
(D) specifies the date on which, and the time at which, the Special Default Notice is signed by the non-Defaulting Party.
On the signature of a Special Default Notice the Early Termination Date shall occur as designated in the Default Notice. A Special Default Notice shall be given to the Defaulting Party as soon as practicable after it is signed.
(d) Either party may by notice to the other change the address or facsimile number or Electronic Messaging System details at which notices or other communications are to be given to it.
17. Entire Agreement; Severability
This Agreement shall supersede any existing agreements between the parties containing general terms and conditions for Transactions. Each provision and agreement herein shall be treated as separate from any other provision or agreement herein and shall be enforceable notwithstanding the unenforceability of any such other provision or agreement.
18. Non-assignability; Termination
(a) Subject to sub-paragraph (b) below, neither party may assign, charge or otherwise deal with (including without limitation any dealing with any interest in or the creation of any interest in) its rights or obligations under this Agreement or under any Transaction without the prior written consent of the other party. Subject to the foregoing, this Agreement and any Transactions shall be binding upon and shall inure to the benefit of the parties and their respective successors and assigns.
(b) Sub-paragraph (a) above shall not preclude a party from assigning, charging or otherwise dealing with all or any part of its interest in any sum payable to it under paragraph 12(c) or (h) above.
(c)Either party may terminate this Agreement by giving written notice to the other, except that this Agreement shall, notwithstanding such notice, remain applicable to any Transactions then outstanding.
(d) All remedies hereunder shall survive Termination in respect of the relevant Transaction and termination of this Agreement.
19. Governing Law and Jurisdiction
This Agreement will be governed by the laws of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Each party submits to the exclusive jurisdiction of the Banking Disputes Committee established in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia pursuant to High Order No. 729/8 dated 10/7/1407H (corresponding to 10/3/1987) and operating under the aegis of the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority, as reconstituted pursuant to Royal Order No. 37441 dated 11/8/1433H (corresponding to 1/7/2012) and its appellate committee and any successor forum thereto.
20. No Waivers, etc.
No express or implied waiver of any Event of Default by either party shall constitute a waiver of any other Event of Default and no exercise of any remedy hereunder by any party shall constitute a waiver of its right to exercise any other remedy hereunder. No modification or waiver of any provision of this Agreement and no consent by any party to a departure herefrom shall be effective unless and until such modification, waiver or consent shall be in writing and duly executed by both of the parties hereto. Without limitation on any of the foregoing, the failure to give a notice pursuant to paragraph 6(a) hereof will not constitute a waiver of any right to do so at a later date.
21. Waiver of Immunity
Each party hereto hereby waives, to the fullest extent permitted by applicable law, all immunity (whether on the basis of sovereignty or otherwise) from jurisdiction, attachment (both before and after judgment) and execution to which it might otherwise be entitled in any action or proceeding in the Courts of England or of any other country or jurisdiction, relating in any way to this Agreement or any Transaction, and agrees that it will not raise, claim or cause to be pleaded any such immunity at or in respect of any such action or proceeding.
22. No Interest Payable
The parties intend and agree that no interest will be payable or receivable under or in connection with this Agreement, and in the event that as a result of any arbitral or judicial award or by operation of any applicable law or otherwise it is determined that any interest is payable in connection with this Agreement, each party agrees to waive any rights it may have to claim or receive such interest and agrees that if any such interest is actually received by it, it shall donate the same to a registered, or otherwise officially recognised, charitable organisation selected by it and whose name shall be disclosed by it to the other party.
23. Recording
The parties agree that each may electronically record all telephone conversations between them.
(Name of Party] (Name of Party] By________________________ By________________________ Title ______________________ Title ______________________ Date Date ANNEX 1 Supplemental Terms or Conditions
Paragraph references are to paragraphs in the Agreement.
1. The following elections shall apply -
(a) paragraph 2(d). The Base Currency shall be:____________________________.
(b) paragraph 2(r). [list Buyer's and Seller s Designated Offices]
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
(c) paragraph 2(xx). Securities shall be: [Shari'ah-compliant securities or financial instruments],
(d) paragraph 3(b). [Seller/Buyer/both Seller and Buyer]* to deliver Confirmation.
(e) paragraph 6(g). Delivery period for margin calls to be:______________________________________.
(f) paragraph 6(j). Details agreed between the parties regarding the accrual of any investment return in respect of Cash Margin transferred to a party:_________________________________________.
[(g) paragraph 8(j). Paragraph 8(j) shall apply.]'
[(h) paragraph 12(a)(ii). Paragraph 12(a)(ii) shall apply.]*
(i) paragraph 12(b). Automatic Early Termination shall apply with respect to [Party A] [Party B]]‘
(j) paragraph 12(e)(1) and 12(i)(iii). Zero Price Differential on Default shall [apply][not apply].
(k) paragraph 14. Paragraph 14 shall [apply][not apply].
(l) paragraph 16. For the purposes of paragraph 16 of this Agreement -
(i) Address for notices and other communications for Party A -
Address:_______________________________________________________
Attention:_______________________________________________________ .
Telephone:___________________________________________________.
Facsimile:_______________________________________________________.
Electronic Messaging System:_______________________________________________________
Answerback:_______________________________________________________
Other:
(ii) Address for notices and other communications for Party B -
Address:_______________________________________________________
Attention:_______________________________________________________
Telephone:_______________________________________________________
Facsimile: _______________________________________________________
Electronic Messaging System: _______________________________________________________
Answerback: _______________________________________________________
Other:
2. The following supplemental terms and conditions shall apply -
[Negative rate transactions
In the case of Transactions in which the Pricing Rate will be negative, the parties agree that if Seller fails to deliver the First Purchased Securities on the First Purchase Date then -
(i) Buyer may by notice to Seller terminate the Transaction (and may continue to do so for every day that Seller fails to deliver the First Purchased Securities); and
(ii) for every day that Seller fails to deliver the First Purchased Securities the Pricing Rate shall be zero.]*
ANNEX II Form of Confirmation
To:_________________________________
From:_________________________________
Date:_________________________________
Subject: Securities Sale Transaction
(Reference Number:_________________________________)
Dear Sirs,
The purpose of this letter, a “Confirmation" for the purposes of the Agreement, is to set forth the terms and conditions of the above repurchase transaction entered into between us on the Contract Date referred to below.
This Confirmation supplements and forms part of, and is subject to, the Master Agreement for the Sale and Purchase of Securities as entered into between us as of_________________________________ as the same may be amended from time to time (the “Agreement”). All provisions contained in the Agreement govern this Confirmation except as expressly modified below. Words and phrases defined in the Agreement and used in this Confirmation shall have the same meaning herein as in the Agreement.
In accordance with paragraph 4 (Undertakings) of the Agreement, in respect of the Transaction documented by this Confirmation and subject to paragraph 12 (Events of Default) of the Agreement:
(i) Seller unilaterally hereby irrevocably and unconditionally undertakes to Buyer that if:
(A) the Seller Exercise Condition with respect to an Exercise Date is satisfied; and
(B) Buyer delivers to Seller an Exercise Notice on, and with respect to, that Exercise Date,
Seller will purchase from Buyer for delivery on the Second Purchase Date the Second Purchased Securities for an amount equal to the Second Purchase Price; and
(ii) Buyer unilaterally hereby irrevocably and unconditionally undertakes to Seller that if:
(A) the Buyer Exercise Condition with respect to an Exercise Date is satisfied; and
(B) Seller delivers to Buyer an Exercise Notice on, and with respect to, that Exercise Date,
Buyer will sell to Seller for delivery on the Second Purchase Date the Second Purchased Securities for an amount equal to the Second Purchase Price.
- Contract Date:
- Purchased Securities [state type[s] and nominal value[s]]:
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
- CUSIP, ISIN or other identifying numbers]:_________________________________________
- Buyer:_______________________________________________________________________________
- Seller:_______________________________________________________________________________
- First Purchase Date:_________________________________________________________________
- First Purchase Price:_________________________________________________________________
- Contractual Currency:_______________________________________________________________
- Exercise Date:______________________________________________________________________
- Second Purchase Date:_____________________________________________________________
- Pricing Rate:_________________________________________________________________________
- Buyer's Bank Account[s] Details:
- Seller's Bank Account[s] Details:
- [ Additional Terms]:*
Yours faithfully,
[SIGNATURE BLOCK FOR PARTY SENDING CONFIRMATION]
Acknowledged and agreed:
(SIGNATURE BLOCK FOR PARTY RECEIVING CONFIRMATION]
ANNEX III Form Of Exercise Notice [Letterhead of the Exercising Party]
To: [ ] (the "Undertaking Party”)
Date: [ ]
Dear:
[We refer to the Confirmation entered into by you and us dated [date] (the "Confirmation”) which supplements, forms part of and is subject to the Master Agreement for the Sale and Purchase of Securities dated [date], as amended and supplemented from time to time, between you and us (the “Agreement").
Unless the context requires otherwise, capitalised terms used in this Exercise Notice and not defined herein will have the same meaning as in the Confirmation.
The Exercising Party hereby confirms to the Undertaking Party that:
- the undersigned is duly authorised to execute and deliver this Exercise Notice on behalf of the Exercising Party;
the Exercising Party is hereby exercising the Undertaking Party’s undertaking in respect of the Exercise Date specified below and accordingly the Undertaking Party is hereby required to [purchase from][sell to] the Exercising Party the following Securities on the following terms:
a. Exercise Date: [ ]
b. Securities: [ ]
c. Second Purchase Date: [ ]
d. Second Purchase Price: [ ]]+
[We refer to the Master Agreement for the Sale and Purchase of Securities dated [date], as amended and supplemented from time to time, between you and us (the “Agreement ').
Unless the context requires otherwise, capitalised terms used in this Exercise Notice and not defined herein will have the same meaning as in the Agreement.
The Exercising Party hereby confirms to the Undertaking Party that:
- the undersigned is duly authorised to execute and deliver this Exercise Notice on behalf of the Exercising Party;
the Exercising Party is hereby exercising the Undertaking Party's undertaking(s) in respect of each Non-Exercised Transaction under the Agreement, and in respect of
+ To be used prior to the occurrence of an Early Termination Dare.
Margin Requirements for Non-Centrally Cleared Derivatives
No: 000042008998 Date(g): 5/10/2020 | Date(h): 18/2/1442 Status: In-Force Introduction
1. The margin requirements are one of the agreed Group of Twenty (G20) reforms to reduce the systemic risk from OTC derivatives.
2. These requirements are issued in accordance with the authority vested in SAMA under the Charter –issued via Royal Decree No. 23 dated 23/5/1377 H, and the Banking Control Law – issued via Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/2/1386 H.
3. These requirements supersede SAMA circulars No. 341000134328 dated 25/11/1434 H, 371000101114 dated 15/9/1437 H, and 51226/67 dated 16/8/1440 H.
Objectives
4. Margin requirements for non-centrally cleared derivatives have two main benefits:
• Reduction of systemic risk: Margin requirements for non-centrally cleared derivatives would be expected to reduce contagion and spillover effects by ensuring that collateral is available to offset losses caused by the default of a derivatives counterparty. Margin requirements can also have broader macroprudential benefits, by reducing the financial system’s vulnerability to potentially destabilising procyclicality and limiting the build-up of uncollateralised exposures within the financial system.
• Promotion of central clearing: Margin requirements are expected to promote central clearing, making the G20’s 2009 reform programme more effective. This could, in turn, contribute to the reduction of systemic risk.
Key Principles and Requirements
Element 1: Scope of Coverage – Instruments Subject to the Requirements
Appropriate margining practices should be in place with respect to all derivatives transactions that are not cleared by Central Counterparties (CCPs)1.
5. Except for physically settled foreign exchange (FX) forwards and swaps, these margin requirements apply to all non-centrally cleared derivatives. These margin requirements do not apply to physically settled FX forwards and swaps.2
6. Initial margin requirements for cross-currency swaps do not apply to the fixed physically settled FX transactions associated with the exchange of principal of crosscurrency swaps. In practice, the margin requirements for cross-currency swaps may be computed in one of two ways. Initial margin may be computed by reference to the “interest rate” portion of the standardised initial margin schedule that is described in Element 3 below and presented in the Appendix A. Alternatively, if initial margin is being calculated pursuant to an approved initial margin model, the initial margin model need not incorporate the risk associated with the fixed physically settled FX transactions associated with the exchange of principal. All other risks that affect crosscurrency swaps, however, must be considered in the calculation of the initial margin amount3. The variation margin requirements that are described below apply to all components of cross-currency swaps.
1 These margining practices only apply to derivatives transactions that are not cleared by CCPs and do not apply to other transactions, such as repurchase agreements and security lending transactions that are not themselves derivatives but share some attributes with derivatives. In addition, indirectly cleared derivatives transactions that are intermediated through a clearing member on behalf of a non-member customer are not subject to these requirements as long as (a) the non-member customer is subject to the margin requirements of the clearing house or (b) the non-member customer provides margin consistent with the relevant corresponding clearing house’s margin requirements.
2 Banks should, however, adhere to Supervisory Guidance for Managing Risks Associated with the Settlement of Foreign Exchange Transactions (as published by BCBS https://www.bis.org/publ/bcbs241.pdf)
3 The only payments to be excluded from initial margin requirements for a cross-currency swap are the fixed physically settled FX transactions associated with the exchange of principal (which have the same characteristics as FX forward contracts). All other payments or cash flows that occur during the life of the swap must be subject to initial margin requirements.Element 2: Scope of Coverage – Scope of Applicability
All covered entities (ie financial firms and systemically important non-financial entities) that engage in non-centrally cleared derivatives must exchange initial and variation margin as appropriate to the counterparty risks posed by such transactions4.
7. For the purpose of this element, Systemically Important Non-financial Entities will be entities whose aggregate month-end average national amount of non-centrally cleared derivatives for the preceding March, April and May exceeds SAR 30 billion, at a consolidated group wide basis.
8. For purposes of determining whether a group’s non-centrally cleared derivatives notional amount exceeds SAR 30 billion, the following shall apply:
• Inter-affiliates trades should not be counted.
• All other non-centrally cleared derivatives must be counted.
9. Covered entities include all financial firms, and systemically important non-financial firms as defined in paragraph 7 above. Central banks, sovereigns5, multilateral development banks, the Bank for International Settlements, and non-systemic, nonfinancial firms are not covered entities6.
10. Only non-centrally cleared derivatives transactions between two covered entities are governed by these requirements. A transaction between a covered entity and one of the aforementioned entities is not covered by these requirements.
11. All covered entities that engage in non-centrally cleared derivatives must calculate, balance and exchange, on a bilateral basis, the full amount of variation margin (ie a zero threshold) on a daily basis. In case of any delay or exception, SAMA should be pre-notified.
12. All covered entities must exchange, on a bilateral basis, initial margin with a threshold not to exceed €50 million. The threshold is applied at the level of the consolidated group to which the threshold is being extended and is based on all non-centrally cleared derivatives between the two consolidated groups7.
13. All margin transfers between parties may be subject to a de-minimis minimum transfer amount not to exceed €500,000.
4 Different treatment is applied with respect to transactions between affiliated entities, as described under Element 6 below.
5 Public sector entities (PSEs) may be treated as sovereigns for the purpose of determining the applicability of these margin requirements.
6 Multilateral development banks (MDBs) exempted from this requirement are those that are eligible for a zero risk-weight under the Basel capital framework (as prescribed in the document published by the BCBS and IOSCO.)
7 Investment funds that are managed by an investment advisor are considered distinct entities that are treated separately when applying the threshold as long as the funds are distinct legal entities that are not collateralised by or are otherwise guaranteed or supported by other investment funds or the investment advisor in the event of fund insolvency or bankruptcy.Element 3: Baseline Minimum Amounts and Methodologies for Initial and Variation Margin
The methodologies for calculating initial and variation margin that serve as the baseline for margin collected from a counterparty should (i) be consistent across entities covered by these requirements and reflect the potential future exposure (initial margin) and current exposure (variation margin) associated with the particular portfolio of noncentrally cleared derivatives at issue and (ii) ensure that all counterparty risk exposures are covered fully with a high degree of confidence.
14. The applicable netting agreements in these requirements are not allowed in Saudi Arabia until relevant laws are enacted and netting is allowed by SAMA. If netting is enforceable in any jurisdiction, positive and negative mark to market exposures in that jurisdiction will be allowed to net.
Initial Margin
15. For the purpose of informing the initial margin baseline, the potential future exposure of a non-centrally cleared derivatives should reflect an extreme but plausible estimate of an increase in the value of the instrument that is consistent with a one-tailed 99 per cent confidence interval over a 10-day horizon,8 based on historical data that incorporates a period of significant financial stress. The initial margin amount must be calibrated to a period that includes financial stress to ensure that sufficient margin will be available when it is most needed and to limit the extent to which the margin can be procyclical.
16. The required amount of initial margin may be calculated by reference to either a quantitative portfolio margin model, or a standardised margin schedule. Banks should use the standardised schedule for initial margin. If a bank wishes to use advanced models, it should be subject to internal governance process, validation, testing and approval by SAMA. Models that have not been granted explicit approval may not be used for initial margin purposes.
17. When initial margin is calculated by reference to an initial margin model, the period of financial stress used for calibration should be identified and applied separately for each broad asset class for which portfolio margining is allowed, as set out below. In addition, the identified period must include a period of financial stress and should cover a historical period not to exceed five years. Additionally, the data within the identified period should be equally weighted for calibration purposes.
18. Quantitative initial margin models must be subject to an internal governance process that continuously assesses the value of the model’s risk assessments, tests the model’s assessments against realised data and experience, and validates the applicability of the model to the derivatives for which it is being used. The process must take into account the complexity of the products covered.
19. Quantitative initial margin models may account for risk on a portfolio basis. More specifically, the initial margin model may consider all of the derivatives that are approved for model use that are subject to a single legally enforceable netting agreement. Derivatives between counterparties that are not subject to the same legally enforceable netting agreement must not be considered in the same initial margin model calculation.
20. Derivative portfolios are often exposed to a number of offsetting risks that can and should be reliably quantified for the purposes of calculating initial margin requirements. At the same time, a distinction must be made between offsetting risks that can be reliably quantified and those that are more difficult to quantify. Accordingly, initial margin models may account for diversification, hedging and risk offsets within well defined asset classes such as currency/rates,9,10 equity, credit, or commodities, but not across such asset classes and provided these instruments are covered by the same legally enforceable netting agreement. However, any such incorporation of diversification, hedging and risk offsets by an initial margin model will require approval by SAMA. Initial margin calculations for derivatives in distinct asset classes must be performed without regard to derivatives in other asset classes.
21. For entities using standardised margin schedule, the required initial margin should be computed by referencing the standardised margin rates in Appendix A, and by adjusting the gross initial margin amount by an amount that relates to the net-to-gross ratio (NGR) pertaining to all derivatives in the legally enforceable netting set.
22. The required initial margin amount should be calculated in two steps. First, the margin rate in the provided schedule would be multiplied by the gross notional size of the derivatives contract, and then this calculation would be repeated for each derivatives contract. This amount may be referred to as the gross standardised initial margin. Second, the gross initial margin amount is adjusted by the ratio of the net current replacement cost to gross current replacement cost (NGR). This is expressed through the following formula:
Net standardised initial margin = 0.4 * Gross initial margin + 0.6 * NGR * Gross initial margin
23. Where NGR is defined as the level of net replacement cost over the level of gross replacement cost for transactions subject to legally enforceable netting agreements. The total amount of initial margin required on a portfolio according to the standardised margin schedule would be the net standardised initial margin amount.
24. Derivatives transactions between covered entities with zero counterparty risk require no initial margin to be collected and may be excluded from the initial margin calculation.
25. In a case where bank is allowed by SAMA to use an approved quantitative portfolio margin model, it will not be allowed to switch between model- and schedule- based margin calculations in an effort to “cherry pick” the most favourable initial margin terms. Accordingly, the choice between model- and schedule-based initial margin calculations should be made consistently over time for all transactions within the same well defined asset class and, it should comply with any other requirements imposed by SAMA. However, a bank may be allowed –upon SAMA’s approval- to use a model-based initial margin calculation for one class of derivatives in which it commonly deals and a schedule-based initial margin in the case of some derivatives that are less routinely employed in its trading activities.
26. Initial margin should be collected at the outset of a transaction, and collected thereafter on a routine and consistent basis upon changes in measured potential future exposure, such as when trades are added to or subtracted from the portfolio.
27. The build-up of additional initial margin should be gradual so that it can be managed over time. Moreover, margin levels should be sufficiently conservative, even during periods of low market volatility, to avoid procyclicality. The specific requirement that initial margin be set consistent with a period that includes stress is meant to limit procyclical changes in the amount of initial margin required.
28. Parties to derivatives contracts should have rigorous and robust dispute resolution procedures in place with their counterparty before the onset of a transaction. In particular, the amount of initial margin to be collected from one party by another will be the result of either an approved model calculation or the standardised schedule. The specific method and parameters that will be used by each party to calculate initial margin should be agreed and recorded at the onset of the transaction to reduce potential disputes. Moreover, parties may agree to use a single model for the purposes of such margin model calculations subject to bilateral agreement and appropriate approval by SAMA. In the event that a margin dispute arises, both parties should make all necessary and appropriate efforts, including timely initiation of dispute resolution protocols, to resolve the dispute and exchange the required amount of initial margin in a timely fashion.
Variation Margin
29. For variation margin, the full amount necessary to fully collateralise the mark-to- market exposure of the non-centrally cleared derivatives must be exchanged.
30. To reduce adverse liquidity shocks and in order to effectively mitigate counterparty credit risk, variation margin should be calculated and exchanged for non-centrally cleared derivatives subject to a single, legally enforceable netting agreement with sufficient frequency.
31. Parties to derivatives contracts should have rigorous and robust dispute resolution procedures in place with their counterparty before the onset of a transaction. In the event that a margin dispute arises, both parties should make all necessary and appropriate efforts, including timely initiation of dispute resolution protocols, to resolve the dispute and exchange the required amount of variation margin in a timely fashion.
8 The 10-day requirement should apply in the case that variation margin is exchanged daily. If variation margin is exchanged – at exceptional cases approved by SAMA as prescribed in paragraph 11 of these requirements- at less than daily frequency then the minimum horizon should be set equal to 10 days plus the number of days in between variation margin exchanges; the threshold calculation set out in paragraph 12 should nonetheless be made irrespective of the frequency with which variation margin is exchanged.
9 Currency and interest rate derivatives may be portfolio margined together for the purposes of these requirements. As an example, an interest rate swap and a currency option may be margined on a portfolio basis as part of a single asset class.
10 Inflation swaps, which transfer inflation risk between counterparties, may be considered as part of the currency/rates asset class for the purpose of computing model-based initial margin requirements, and as part of the interest rate asset class for the purposes of computing standardised initial margin requirements.Element 4: Eligible Collateral for Margin
To ensure that assets collected as collateral for initial and variation margin purposes can be liquidated in a reasonable amount of time to generate proceeds that could sufficiently protect collecting entities covered by the requirements from losses on non-centrally cleared derivatives in the event of a counterparty default, these assets should be highly liquid and should, after accounting for an appropriate haircut, be able to hold their value in a time of financial stress. The set of eligible collateral should take into account that assets which are liquid in normal market conditions may rapidly become illiquid in times of financial stress. In addition to having good liquidity, eligible collateral should not be exposed to excessive credit, market and FX risk (including through differences between the currency of the collateral asset and the currency of settlement). To the extent that the value of the collateral is exposed to these risks, appropriately risk-sensitive haircuts should be applied. More importantly, the value of the collateral should not exhibit a significant correlation with the creditworthiness of the counterparty or the value of the underlying non-centrally cleared derivatives portfolio in such a way that would undermine the effectiveness of the protection offered by the margin collected (ie the so- called “wrong way risk”). Accordingly, securities issued by the counterparty or its related parties should not be accepted as collateral. Accepted collateral should also be reasonably diversified.
32. SAMA only considers eligible collaterals, which are allowed under the standardised approach for credit risk under the Risk-based Capital Framework adopted by SAMA, subject to appropriate haircuts described below.
33. Potential methods for determining appropriate haircuts include either internal or third- party quantitative model-based haircuts or schedule-based haircuts. Banks should apply standardised schedule-based haircuts as defined in Appendix B. If higher haircuts are proposed by different regulators in international jurisdictions, the higher haircut should be applied.
34. Risk-sensitive quantitative models, both internal or third-party, could be used to establish haircuts provided that the model is approved by SAMA and subject to appropriate internal governance standards.
35. Banks should not selectively apply the method for determining appropriate haircuts that would produce a lower haircut, banks should consistently adopt either the standardised tables approach or the internal/third-party models approach for all the collateral assets within the same well defined asset class.
36. In addition to haircuts, other risk mitigants should be considered when accepting noncash collateral. In particular, banks should ensure that the collateral collected is not overly concentrated in terms of an individual issuer, issuer type and asset type.
37. In the event that a dispute arises over the value of eligible collateral, both parties should make all necessary and appropriate efforts, including timely initiation of dispute resolution protocols, to resolve the dispute and exchange any required margin in a timely fashion.
38. Collateral that is posted by a counterparty to satisfy margin requirements may, at some point in time before the end of the derivatives contract, be needed by the counterparty for some particular reason or purpose. Alternative collateral may be substituted or exchanged for the collateral that was originally posted provided that both parties agree to the substitution and that the substitution or exchange is made on the terms applicable to their agreement. When collateral is substituted, the alternative collateral must meet all the requirements outlined above. Further, the value of the alternative collateral, after the application of haircuts, must be sufficient to meet the margin requirement.
Element 5: Treatment of Provided Initial Margin
Because the exchange of initial margin on a net basis may be insufficient to protect two market participants with large gross derivatives exposures to each other in the case of one firm’s failure, the gross initial margin between such firms should be exchanged. Initial margin collected should be held in such a way as to ensure that (i) the margin collected is immediately available to the collecting party in the event of the counterparty’s default, and (ii) the collected margin must be subject to arrangements that protect the posting party to the extent possible under applicable law in the event that the collecting party enters bankruptcy.
39. Initial margin should be exchanged on a gross basis and held in a manner consistent with the principle above.
40. The collateral arrangements should be effective under relevant laws and supported by periodically updated legal opinions.
41. Cash and non-cash collateral collected as variation margin may be re-hypothecated, re-pledged or re-used.
42. Except where re-hypothecated, re-pledged or re-used in accordance with paragraph 43 below, cash and non-cash collateral collected as initial margin should not be rehypothecated, re-pledged or re-used.
43. Cash and non-cash collateral collected as initial margin from a customer may be rehypothecated, re-pledged or re-used (henceforth re-hypothecated) to a third party only for purposes of hedging the initial margin collector’s derivatives position arising out of transactions with customers for which initial margin was collected and it must be subject to conditions that protect the customer’s rights in the collateral, where applicable. In any event, and upon approval from SAMA on a case by case basis, the customer’s collateral may be re-hypothecated only if the conditions described below are met:
• The customer, as part of its contractual agreement with the initial margin collector and after disclosure by the initial margin collector of (i) its right not to permit rehypothecation and (ii) the risks associated with the nature of the customer’s claim to the re-hypothecated collateral in the event of the insolvency of the initial margin collector or the third party, gives express consent in writing to the re-hypothecation of its collateral. In addition, the initial margin collector must give the customer the option to individually segregate the collateral that it posts.
• The initial margin collector is subject to regulation of liquidity risk.
• Collateral collected as initial margin from the customer is treated as a customer asset, and is segregated from the initial margin collector’s proprietary assets until re-hypothecated. Once re-hypothecated, the third party must treat the collateral as a customer asset, and must segregate it from the third party’s proprietary assets. Assets returned to the initial margin collector after re-hypothecation must also be treated as customer assets and must be segregated from the initial margin collector’s proprietary assets.
• The collateral of customers that have consented to the re-hypothecation of their collateral must be segregated from that of customers that have not so consented.
• Where initial margin has been individually segregated, the collateral must only be re-hypothecated for the purpose of hedging the initial margin collector’s derivatives position arising out of transactions with the customer in relation to which the collateral was provided.
• Where initial margin has been individually segregated and subsequently rehypothecated, the initial margin collector must require the third party similarly to segregate the collateral from the assets of the third party’s other customers, counterparties and its proprietary assets.
• Protection is given to the customer from the risk of loss of initial margin in circumstances where either the initial margin collector or the third party becomes insolvent and where both the initial margin collector and the third party become insolvent.
• Where the initial margin collector re-hypothecates initial margin, the agreement with the recipient of the collateral (ie the third party) must prohibit the third party from further re-hypothecating the collateral.
• Where collateral is re-hypothecated, the initial margin collector must notify the customer of that fact. Upon request by the customer and where the customer has opted for individual segregation, the initial margin collector must notify the customer of the amount of cash collateral and the value of non-cash collateral that has been re-hypothecated.
• Collateral must only be re-hypothecated to, and held by, an entity that is regulated in a jurisdiction that meets all of the specific conditions contained in this section and in which the specific conditions can be enforced by the initial margin collector.
• The customer and the third party may not be within the same group.
• The initial margin collector and the third party must keep appropriate records to show that all the above conditions have been met.
44. Banks should disclose the level and volume of re-hypothecation as required in section “Reporting to SAMA” below.
Element 6: Treatment of Transactions with Affiliates
Transactions between a firm and its affiliates should be subject to these initial and variation margin requirements.
45. Banks should apply standardised schedule-based haircuts as defined in Appendix B for transactions between the bank and its affiliates.
Element 7: Interaction of National Regimes in Cross-Border Transactions
Regulatory regimes would interact so as to result in sufficiently consistent and non- duplicative regulatory margin requirements for non-centrally cleared derivatives across jurisdictions.
46. These margin requirements are applicable to legal entities established in Saudi Arabia, which includes locally established subsidiaries of foreign entities, in relation to the initial and variation margins that they collect. SAMA may permit a bank to comply with the margin requirements of a host-country margin regime with respect to its derivatives activities, provided that SAMA considers the host-country margin regime to be consistent with the margin requirements described in this framework.
47. For subsidiaries of Saudi banks in host jurisdictions, they should follow the requirements of the host country.
48. A branch is part of the same legal entity as the headquarters; it may be subject to either the margin requirements of the jurisdiction where the headquarters is established or the requirements of the host country. Foreign Bank Branches (FBB) operating in the Saudi Arabia should be deemed compliant with these requirements if:
• The FBB is required to comply with, and has complied with, the margin requirements of that foreign jurisdiction (home regulator) that have been implemented through Published laws, rules or regulations; and
• The FBB has documentary evidence that the margin requirements of the foreign jurisdiction (home regulator) are comparable to SAMA’s or BCBS-IOSCO’s margin requirements for non-central cleared derivatives.
Element 8: Phase-in of the Requirements
These requirements are phased in so that the systemic risk reductions and incentive benefits are appropriately balanced against the liquidity, operational and transition costs associated with implementing the requirements.
49. These requirements are applicable in a phased manner from 1 September 2016 as described in Margin requirements for Non-centrally Cleared Derivatives paper issued by Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) and Board of the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO)11.
50. The remaining phases –at the time of issuance of this document- to apply the requirement to exchange two-way initial margin with a threshold of up to €50 million are staged as follows:
• From 1 September 2021 to 31 August 2022, any covered entity belonging to a group whose aggregate month-end average notional amount of non-centrally cleared derivatives for March, April, and May of 2021 exceeds €50 billion will be subject to the requirements when transacting with another covered entity (provided that it also meets that condition).
• On a permanent basis (ie from 1 September 2022), any covered entity belonging to a group whose aggregate month-end average notional amount of non-centrally cleared derivatives for March, April, and May of the year exceeds €8 billion will be subject to the requirements described in this document during the one-year period from 1 September of that year to 31 August of the following year when transacting with another covered entity (provided that it also meets that condition). Any covered entity belonging to a group whose aggregate month-end average notional amount of non-centrally cleared derivatives for March, April, and May of the year is less than €8 billion will not be subject to the initial margin requirements described in this document.
51. For the purposes of calculating the group aggregate month-end average notional amount for determining whether a covered entity will be subject to the initial margin requirements described in this document, all of the group’s non-centrally cleared derivatives, including physically settled FX forwards and swaps, should be included.
52. Initial margin requirements should apply to all new contracts entered into during the periods described above. Applying the initial margin requirements to existing derivatives contracts is not required.12
11 Margin Requirements for Non-centrally Cleared Derivatives.
12 Genuine amendments to existing derivatives contracts do not qualify as a new derivatives contract. Any amendment that is intended to extend an existing derivatives contract for the purpose of avoiding margin requirements will be considered a new derivatives contract.Reporting to SAMA
53. All Banks should report relevant initial and variation margin details as prescribed in these requirements in SAMA Q17 returns.
Appendix A
Standardised initial margin schedule
Asset class Initial margin requirement
(% of notional exposure)Credit: 0–2 year duration 2 Credit: 2–5 year duration 5 Credit: 5+ year duration 10 Commodity 15 Equity 15 Foreign exchange 6 Interest rate: 0–2 year duration 1 Interest rate: 2–5 year duration 2 Interest rate: 5+ year duration 4 Other 15 Appendix B
Standardised haircut schedule
Asset class Haircut
(% of market value)Cash in same currency 0 High-quality government and central bank securities: residual maturity less than one year 0.5 High-quality government and central bank securities: residual maturity between one and five years 2 High-quality government and central bank securities: residual maturity greater than five years 4 High-quality corporate\covered bonds: residual maturity less than one year 1 High-quality corporate\covered bonds: residual maturity greater than one year and less than five years 4 High-quality corporate\covered bonds: residual maturity greater than five years 8 Equities included in major stock indices 15 Gold 15 Additional (additive) haircut on asset in which the currency of the derivatives obligation differs from that of the collateral asset 8 Primary Dealer in the Government Securities Market
No: 449950000067 Date(g): 23/3/2019 | Date(h): 17/7/1440 Status: In-Force Further to SAMA Circular No. 32234/67 issued on 23/05/1440 H related to the guidelines and operational principles for Bank Primary Dealers (Bank-PDs) in Government Securities.
Attached are the operational guidelines for Bank Primary Dealers in Government Securities Market in English, which supersede and replace the principles issued under the aforementioned circular.
For your information and action accordingly as of its date.
1. Eligibility conditions for banks proposing to undertake PD business
The following categories of banks would be eligible to undertake PD activities:
A. Banks which meet the minimum capital adequacy ratio as set by SAMA during the ICAAP process.
B. Strong managerial /trading capabilities with treasury operations that is fully computerized, with competent and knowledgeable staff, and with relevant professional experience in main treasury /front and back offices.
C. Adequate risk management systems to measure, manage and provide for the risks emanating from the PD activity. Banks should have a trading desk that has the capacity to hedge risks arising from the PD activities.
D. Adequate physical infrastructure and skilled manpower for efficient participation in primary issues, trading in the secondary market, and to advise and educate investors.
E. SAMA no-objection to undertake Primary Dealership business.
2. General Guidelines and Applicability
A. The bank-PDs' role and obligations in terms of supporting the primary market auctions for issue of Government dated securities, underwriting of Dated Government Securities, market-making in Government securities and secondary market turnover of Government Securities must not contravene any of the prudential rules currently in place for banks.
B. Bank-PDs are required to form a Primary Dealers' Committee and abide by a code of conduct that should be framed by such a committee and such other actions initiated by them in the interests of the securities markets.
C. The investment policy of the bank should be suitably amended to also include PD activities. Within the overall framework of the investment policy, the PD business undertaken by the bank will be limited to dealing, underwriting and market-making in Saudi Government Securities. Investments in Corporate bonds, Commercial Papers, Certificate of deposits and other fixed income securities will not be deemed to be part of the PD business.
D. Bank-PDs should update their investment policy and/or framework and implement a Board approved investment policy and operational guidelines on securities transactions. The policy/framework should include (but not limited to) the following:
- The broad objectives to be followed while undertaking transactions in securities on their own account and on behalf of clients;
- Clearly define the authority to put through deals, and lay down procedure to be followed while putting through deals;
- Various prudential exposure limits;
- Policy regarding dealings through brokers;
- Systems for management of various risks;
- Guidelines for valuation of the portfolio and the reporting systems;
- Operational procedures and controls in relation to the day-to-day business operations to ensure that operations in securities are conducted in accordance with sound and acceptable business practices.
- The effectiveness of the policy and operational guidelines should be periodically evaluated
E. The classification, valuation and operation of investment portfolio guidelines as applicable to banks in regard to "Held for Trading" portfolio will also apply to the portfolio of Government Dated Securities earmarked for PD market-making business.
F. The Government Dated Securities under Bank-PD business will count for SAMA Liquidity Ratios.
G. Bank-PDs should report to SAMA any violations of the terms and conditions of undertaking agreement they sign with the Debt Management Office (DMO).
3. Maintenance of Books, Accounts and Reporting
A. Bank-PDs will have to maintain separate books of accounts for transactions relating to PD business (distinct from transactions in securities on their own account) with necessary audit trails. It should be ensured that, at any point in time, Bank PDs observe the minimum DMO balance of Government Securities earmarked for PD market-making business.
B. Bank-PDs shall submit to their SAMA Team Leaders , an Annual Report on PD activities (with at least information on subscription activities, underwriting activities, primary and secondary markets turnover of the bank) by 15th of February the following year.
C. Bank-PDs should subject the PD transactions and any regulatory returns submitted to the DMO and SAMA to concurrent annual audit. An internal auditors' review report for having maintained the minimum stipulated balance of Government Securities in the PD-book on an ongoing basis and having adhered to these guidelines/ instructions issued by SAMA, should be undertaken and provided to SAMA upon request.
4. Capital Adequacy and Risk Management
A. The capital adequacy requirement and risk management guidelines will be as per the existing guidelines applicable to banks. For the purpose of assessing the bank's capital adequacy requirement and coverage under risk management framework, the PD activity should also be taken into account.
B. The bank undertaking PD activity should put in place adequate risk management systems to measure and provide for the risks emanating from the PD activity.
5. Implementation and Effective Date
A. All Bank-PDs are required to develop and implement the requisite policies and procedures to ensure compliance with these Rules. Any violation or circumvention of these Rules may warrant the appropriate regulatory action by SAMA.
B. Requirement 1(E) (SAMA no-objection) above shall not apply to banks already appointed by the DMO before the effective date of these regulations.
C. These Rules supersede the previous rules issued under SAMA circular 32234 /67 dated 23/05/1440 and shall come into force effective immediately.
Investment Business Activities
Consumer Protection
Regulations for Establishing Customer Care Departments in Banks
No: 44069265 Date(g): 21/3/2023 | Date(h): 29/8/1444 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Based on the Saudi Central Bank Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/36) dated 11/4/1442 H, and referring to the Central Bank Circular No. (351000145194) dated 26/11/1435 H, which accompanies the update of the regulations for handling and establishing complaint units in banks.
These regulations for establishing Customer Care Departments in banks replace the aforementioned regulations and aim to define the minimum instructions that banks must adhere to in order to ensure due care for customers.
For your information and implementation effective from 15/07/2023 G.
Introduction
The Central Bank is the authority responsible for monitoring and overseeing the banks licensed by it. It has regulatory powers that include framing and organizing matters related to the rights of customers of these banks and ensuring their care, based on the Saudi Central Bank Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/36) dated 11/4/1442 H and its Article No. 4 of which states: "The Bank shall carry out its duties in accordance with the provisions of this Law, the regulations and policies issued by the Board, and best international standards and practices. To achieve its objectives, the Bank shall have all the necessary powers and carry out the following duties, powers, and competences: ...9 Issuing directives and developing procedures to protect consumers of financial institutions." Additionally, the Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. (M/5) dated 22/2/1386 H and its amendments, which granted Central Bank the authority to set the conditions and requirements that banks must observe when dealing with customers.
Customer care, handling complaints, and financial education are among the key principles outlined in the Financial Consumer Protection Principles and Rules. This involves enabling customers to access complaint resolution mechanisms easily and enhancing their financial literacy and awareness through the bank. The bank should also facilitate customers' access to clear information regarding their protection, rights, and responsibilities. Moreover, the bank should establish appropriate mechanisms to help customers develop an understanding of the risks associated with the products offered by the bank, allowing them to make suitable choices based on their needs.
To achieve the goals related to the care of customers of banks operating in the Kingdom, the Central Bank issues these instructions, which represent the minimum standards that banks must adhere to in order to ensure due care for customers.
Scope of Application
These regulations apply to banks operating in the Kingdom and licensed by the Saudi Central Bank.
Definitions
Term Definition Central Bank The Saudi Central Bank. Bank Banks licensed to conduct banking activities in the Kingdom in accordance with the provisions of the Banking Control Law. Administration Customer Care Department. Customer An individual or entity receiving services and products from the bank. Complaint Any expression of dissatisfaction related to the provided service, whether justified or unjustified, written or verbal. Inquiry A customer's request for information about the services or products offered by the bank. Request A request made by a customer to obtain a product or service provided by the bank. Electronic System The bank's electronic system for recording complaints and inquiries. Section One: Responsibilities, Policies, and Procedures of the Department
1. Establishment of the Department
1-1 The department shall be established by a decision of the bank's Board of Directors and shall report directly to the highest executive position in the bank, whether the CEO, General Manager, or Managing Director. In the case of temporary absence of this position, the department shall report to their deputy, and it should not be administratively linked to any other department within the bank.
1-2 The department shall be granted the necessary powers, financial, technical, and human resources support to perform its duties efficiently and with high quality.
1-3 The department must consist of at least three units (the bank determines the level of each unit based on its business volume and number of customers): the Complaints Handling Unit, the Quality and Performance Analysis Unit, and the Financial and Educational Awareness Unit.
1-4 Without prejudice to the provisions regarding the Requirements for Appointments to Senior Positions in financial institutions under the supervision of the Central Bank, the bank must obtain written approval from the Central Bank before appointing or assigning a manager to the department.
2. Responsibilities of the Department
2-1 Protecting bank customers.
2-2 Handling customer complaints efficiently and with high quality.
2-3 Responding to any inquiries received.
2-4 Increasing customer satisfaction in the complaint resolution process.
2-5 Addressing and reducing the sources of complaints.
2-6 Enhancing customer awareness of the products and services offered by the bank.
2-7 Developing and updating policies and procedures in accordance with the best local and international practices in customer protection.
3. Policies and Procedures of the Department
3-1 The department must develop the following policies:
- A policy for analyzing complaints and their patterns, addressing their causes and sources (Root Cause Analysis), and obtaining approval from the authorized person in the bank. This policy should also include measuring its effectiveness in addressing the sources of recurring complaints.
- A policy for protecting customer rights and ensuring their care throughout all stages of their interaction with the bank (e.g., marketing and sales procedures, post-sale service quality assurance procedures, complaint handling procedures, customer communication procedures, and credit advisory services procedures).
- A policy for awareness and financial education for the bank’s customers that aligns with the products and services offered by the bank. This policy should include at least the role of the employee responsible for providing a comprehensive explanation of the product or service to the customer, including all obligations associated with that service or product.
3-2 The department manager, or their delegate, must have full authority to make decisions regarding the resolution of complaints with amounts not exceeding SAR 20,000. The bank must establish policies and procedures to organize and monitor this process.
3-3 The department must develop and periodically update (at least once every two years) its operational mechanisms with relevant departments, including service level agreements and escalation processes, to ensure that complaints are handled within regulatory time frames. This mechanism should be technically activated and used to measure compliance, including escalation to the highest executive level.
3-4 To ensure the efficiency and effectiveness of handling complaints, inquiries, and requests, the department should include the following definitions in its internal policies related to customer rights protection and ensure compliance with them: (complaint, inquiry, request, customer), in line with the definitions provided in these regulations.
4. Department Personnel and Their Qualifications
4-1 The bank must employ an appropriate number of staff in the department and its units, commensurate with the number of customers, products, services provided by the bank, and the volume of complaints. An analytical capacity study (Capacity Analysis) should be conducted at least once a year.
4-2 The department manager and staff must have sufficient knowledge and experience in customer care. They should, at a minimum, hold certifications in basic retail banking and credit advisory. The bank is also required to continuously train them through relevant programs suitable for their work, at least once a year. Additionally, the bank must ensure that department staff are well-versed in customer service skills, the bank’s products and services, and the regulations and instructions governing the relationship between customers and the bank.
Section Two: Department Units and Their Responsibilities
First: Complaints Handling Unit
- The unit must provide multiple channels for receiving and handling complaints efficiently and effectively. This should enable customers to submit complaints according to their preferences with ease and at times that are convenient for them. These channels should be clearly displayed on the bank’s website homepage and various platforms. The channels must include at least:Free telephone line,Website,Mobile applications,Email,Branches
The unit must have systems and technical programs that support documenting and tracking the complaint handling process by date and time, allowing for visibility of its status and the actions taken. These systems must, at a minimum, include:
2-1 Recording complaints and documenting their receipt, retaining records, and tracking them through all stages of processing. The customer should be provided with a primary reference number and the processing time frame via a text message on their mobile phone registered with the bank.
2-2 The ability for the customer to register complaints directly in the electronic system, view the final result of the handling process and detailed updates, and receive necessary documents if required.
2-3 Classifying complaints in the electronic system according to the bank’s products and services in line with the relevant central bank instructions.
2-4 Enabling customers to evaluate their satisfaction with the complaint handling results automatically.
2-5 Providing real-time report generation and the ability to automatically submit reports to senior management for performance monitoring.
2-6 Facilitating automatic direct linkage to any databases created by the central bank for supervisory and regulatory purposes.
- The unit must handle complaints within a maximum period of 5 working days from the date of receipt from the customer.
- The unit must establish performance indicators for complaint handling and work on monitoring these indicators to achieve the desired goals. Indicators should, at a minimum, include:
Name of the Indicator Description of the Indicator Desired Objective* Customer Satisfaction Rate with Complaint Handling
Number of Complaints Rated as Satisfied/Agreeable by the Customer Out of Total Complaints Not Less Than 85% Service Level Agreement Compliance Rate Number of Complaints for Which the Bank Was Late in Processing Within the Regulatory Period Out of Total Complaints Not Less Than 95% * The central bank may review and adjust the rates of the above indicators from time to time.
Second: Quality and Performance Analysis Unit
1. The unit must review the quality of the complaint handling procedures and ensure they are processed efficiently and with high quality in accordance with relevant regulations and instructions. It should take corrective actions for complaints that have been handled incorrectly and implement necessary procedures to prevent recurrence.
2. The unit must continuously analyze complaint data and provide corrective plans to address the sources of complaints and measure their effectiveness. These reports should be documented and submitted to the administration manager to be forwarded to the CEO on a monthly basis.
3. The unit must ensure the accuracy of the reports and data contained within them.
4. The unit should submit quarterly reports to the administration manager for forwarding to senior management and the bank's board of directors, covering customer care issues. These reports should, at a minimum, include the following:
- Performance measurement indicators for complaints registered in the "SAMACARES" System.
- Performance measurement indicators for complaints received directly by the bank.
- Compliance of relevant departments with the service level agreement.
- Common complaints during the period.
- Challenges faced by the administration and the approach to addressing them.
Third: Financial Awareness and Education Unit
- The unit must continuously raise customer awareness through all available bank channels and implement annual plans for financial awareness and education. These plans should include, at a minimum: products and services and their risks, fraud, savings, and financial planning.
- The unit must continuously inform customers about all channels for submitting complaints and their right to raise complaints and inquiries. It should also inform them about the possibility of requesting credit advisory services, in cases where the bank is not obligated to provide a credit advisor.
- Unit employees are prohibited from contacting customers for the purpose of marketing the bank's products and services.
The unit should submit semi-annual reports to the administration manager for forwarding to the CEO, which should include the following:
- The number of contacts received by the unit.
- The types of consultations provided to customers.
- Measurement of customer satisfaction regarding the appropriateness of the consultations provided.
Final Provisions
- These instructions are considered a minimum standard for what the bank must do to ensure due diligence in customer care and handle complaints and inquiries efficiently and with high quality. They are closely related to the Financial Consumer Protection Principles and Rules.
- Without prejudice to the provisions outlined in the Principles of Internal Auditing for Local Banks Operating in Saudi Arabia, as well as the Principles of compliance for commercial banks operating in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia; the management must undergo annual review and audit by the Internal Audit Department and the Compliance Department.
- The management must obtain and renew annually the Customer Complaint Management System certification (ISO 10002), in addition to applying the international standard (ISO 10004) related to measuring and monitoring customer satisfaction.
- These instructions replace the controls for establishing complaint units issued under the Central Bank circular number (351000145194) dated 26/11/1435 H.
- All provisions of these instructions shall be effective from the date 15/07/2023 G.
Financial Consumer Protection Principles and Rules
To read the “Financial Consumer Protection Principles and Rules”, click here.
Debt Collection Regulations and Procedures for Individual Customers
No: 106889333 Date(g): 6/3/2025 | Date(h): 6/9/1446 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Chapter One: General Provisions
Article 1: Definitions
The terms and expressions used in these regulations and procedures shall have the meanings assigned to them as follows, unless the context requires otherwise:
Term Definition
SAMA
The Saudi Central Bank.
Creditor: Banks and finance companies.
Debt Collection Creditors collecting the amounts payable by the consumer - or his guarantor in case of default - under the provisions of the finance contract. Creditors Banks, and finance companies subject to the supervision and control of SAMA in accordance with the regulations in force. Consumer A natural person who has obtained the financing product.
Guarantor A natural person who undertakes to perform all or some of the consumer's obligations.
Third Party An external party who practices or initiates any of the collection procedures for the benefit of the creditor
Compelling Change in Circumstances: An event leading to a compulsory change in the consumer's financial circumstances that materially affects the consumer's ability to fulfill his/her financial obligations, such as but not limited to: Inability to work (partially), retirement (compulsory), job loss, loss of fixed allowances given to the consumer by his/her employer on a monthly basis, or salary reduction.
Voluntary Change in Circumstances: An event that leads to a change in the consumer's financial circumstances at the consumer's request, such as but not limited to Early retirement or resignation.
Default: Consumer's failure or delay in paying a certain number of due installments or part thereof agreed upon in the finance contract, in accordance with the provisions of paragraph (1) of Article 9 of the Regulation.
Total Disability A health condition that prevents the consumer from practicing his normal life and results in the consumer being medically unfit for work according to official reports issued or approved by the legally competent authority.
Complaint Any expression of the consumer's dissatisfaction with the provided service or product, whether justified or not, written or verbal.
Documented Communication An official, verifiable and retrievable means of communication in paper or electronic form.
Consumer's Consent Prior consent from the consumer through authenticated means of communication.
Phone Call The call that the consumer responded to and interacted with the employee about.
Communication The process of exchanging information and data by any means of documented communication between the creditors and the consumer, whether oral or non-verbal (such as sign language) for people with disabilities.
Employees Any natural person who works for the interest of the creditors and under their management or supervision for remuneration, including - for the purpose of applying the controls - all employees contracted directly or contracted through a third party.
Day Calendar day including weekends and public holidays.
Article 2: Objectives
These regulations aim for creditors to achieve the following:
- Improve the efficiency of debt collection by implementing effective procedures to reduce the rate of non-performing loans.
- Adhere to professional conduct when dealing with consumers.
- Follow the minimum procedures that must be adhered to when communicating with consumers or their guarantors for the purpose of rescheduling potentially defaulting debts or during collection.
- Protect the privacy of consumers and their guarantors.
- Improve the efficiency of debt collection by implementing effective procedures to reduce the rate of non-performing loans.
Article 3: Scope of Application
These regulations apply to creditors and third parties.
Chapter Two: Communication Regulations with Consumers and Their Guarantors
Article 4: Communication Regulations with Consumers
Creditors must adhere to the regulations, instructions, standards, and professional conduct when communicating with the consumer or their guarantor and comply with the following as a minimum:
- Protect the financial and personal information of consumers and guarantors, maintaining their privacy, and not using such information except for specific professional and legal purposes with the consumer's consent.
- Do not make any phone calls to anyone other than the consumer or their guarantor, and verify the identity of the call recipient at the start of the phone call.
- Limit phone call attempts with the consumer or guarantor to not exceed ten phone calls - at most - every thirty days for each financing product - in case of multiple products, and enable the consumer or guarantor to return the call to the number used to contact them, ensuring communication occurs during official working hours.
- Document communication with consumers or guarantors (incoming or outgoing), and retain records for no less than ten years from the date of communication, and inform the consumer or guarantor at the beginning of the phone call that it is being recorded.
- Enable consumers or their guarantors to evaluate their satisfaction at the end of the phone call, whether for collection purposes or to receive complaints, ensuring this is documented electronically.
- Activate direct channels for communication with consumers to allow inquiries or clarifications regarding existing claims.
- Do not communicate with the consumer or their guarantor using envelopes with phrases indicating they contain debt collection information or similar.
- Do not visit the consumer or their guarantor under any circumstances, whether at their residence or workplace.
- Protect the financial and personal information of consumers and guarantors, maintaining their privacy, and not using such information except for specific professional and legal purposes with the consumer's consent.
Chapter Three: Collection Procedures
Article 5: Communication Mechanism with Consumers
When communicating with consumers or their guarantors for collection purposes, creditors must adhere to transparency and disclosure, and comply with the following:
1- Limit authenticated communication means to:
1-1 Email.
1-2 Registered mail (national address).
1-3 Text messages.
1-4 Phone calls.
1-5 The creditor's app or website.
1-6 Judicial notification.
2- Provide the consumer with the necessary communication-related information, including:
2-1 Creditor's name and the department concerned with collection, or the third party and the name of the creditor they are communicating on behalf of.
2-2 The contact number of the concerned department or third party.
2-3 Working hours of the concerned department or third party.
2-4 The employee's name in case of a phone call.
3- Appoint Arabic as the primary language for communication, except when communicating with non-Arabic speakers, while fully adhering to the regulation.
4- In case the communication is written, all phrases and numbers used must be easy to understand and clearly legible, including headers and footers.
Article 6: Handling Objections
If there is an objection from the consumer or their guarantor regarding the amount claimed, creditors must:
- Document the complaint electronically in the consumer's file, enabling them to view it.
- Register the consumer's or guarantor's complaint based on the instructions issued by SAMA.
- Provide the consumer or guarantor with the expected time frame for resolving the complaint, not exceeding the periods specified by SAMA.
- Do not communicate with the consumer or guarantor to remind them of defaults until the complaint is resolved.
- Present the results of the complaint resolution to the consumer or guarantor and support it with documents justifying the resolution decision.
- If the consumer or guarantor is dissatisfied with the complaint resolution and wishes to escalate it, creditors must provide the consumer with the escalation mechanism and direct them to the appropriate entity.
- Document the complaint electronically in the consumer's file, enabling them to view it.
Chapter Four: Debt Collection Management Regulations
Article 7: Mechanism for Setting Deduction Dates from Consumers' Accounts
Creditors must:
- Set the deduction date in accordance with the salary deposit date for salaried consumers, or as agreed upon with the consumer for non-salaried consumers, ensuring it is specified in the finance contract or repayment schedule, considering changes in salary deposit dates, whether continuous or temporary (e.g., when salary deposit date coinciding with weekends or holidays).
- Deduct the installment on the agreed date, and if the agreed date is exceeded due to a creditor's reason without obtaining the consumer's consent for deduction for each case individually after the agreed date, creditors are obliged to add a similar period at the end of the finance period without calculating any term cost or additional fees, with notification to the consumer through authenticated communication means.
- Set the deduction date in accordance with the salary deposit date for salaried consumers, or as agreed upon with the consumer for non-salaried consumers, ensuring it is specified in the finance contract or repayment schedule, considering changes in salary deposit dates, whether continuous or temporary (e.g., when salary deposit date coinciding with weekends or holidays).
Article 8: Installment Deduction Regulations from Consumers' Accounts
1- Creditors are prohibited from:
1-1 Deducting any amounts from the consumer's accounts without a judicial order or ruling, or without obtaining the consumer's consent, or if the finance contract does not permit deduction for banks and finance companies, Or the agreement to deduct the outstanding finance amounts granted without a salary guarantee through the consumer's bank accounts for finance companies.
1-2 Blocking accounts or balances of consumers, even temporarily, and denying them access to funds available in the accounts without a judicial order or ruling, or without obtaining the consumer's consent, or if the finance contract does not permit blocking, without prejudice to the statutory provisions and related provisions in the regulation.
1-3 Deducting more than one installment for each finance contract within a single salary deposit cycle, unless there is a judicial order or ruling, or with the consumer's consent.
1-4 Deducting the installment before the agreed due date, or withholding the installment amount before the due date.
1-5 Withholding or deducting end-of-service gratuities for national consumers, unless there is a judicial order or ruling, or with the consumer's consent.
1-6 Imposing delay penalties or collection fees exceeding the due amount, with a maximum of one installment value for the entire finance period.
2- Creditors must adhere to the deduction limits from the accounts of joint consumers - for joint finance contracts - as agreed with each consumer individually according to the finance contract.
Article 9: Managing Potential Default Cases
1- For the purpose of applying the regulations, creditors must consider calculating default as follows:
1-1 For consumer default on monthly installments:
When it is proven that the consumer has not committed to paying installments fully or partially for three consecutive months, or delays in paying five separate installments for seven working days or more for each installment from its due date throughout the contract period, and for every five years of the real estate finance contract duration.
1-2 Default in finance contracts granted (non-monthly installments):
When it is proven that the consumer has not committed to paying the due installment (quarterly, semi-annually, annually) for more than 60 working days, or delays in paying four separate installments for 20 working days from the agreed due date in the finance contract, or more than five separate months throughout the finance period, and for every five years of the real estate finance contract duration.
2- Creditors must find proactive solutions when indicators of a change in the consumer's credit status appear that may lead to default, including at a minimum:
2-1 Offering the option to reschedule the debt to the consumer if a change in their circumstances is proven (compulsorily) without granting new finance, without any additional fees, and without any change in the term cost. Creditors must execute the rescheduling - if requested by the consumer - within a period not exceeding 20 working days from the date the consumer provides the necessary documents, and creditors must postpone the deduction of installment amounts until the rescheduling procedures are completed.
2-2 Rescheduling the debt for the consumer if the reason is due to the creditor's failure to assess the consumer's creditworthiness, including but not limited to exceeding the statutory deduction ratios, without granting new finance, without any additional fees, and without any change in the term cost.
3- Creditors may offer the option to reschedule the debt to the consumer if a change in their circumstances is proven (optionally), with the possibility of changing the term cost and without any additional fees, provided that the rescheduling is executed - if requested by the consumer - within a period not exceeding 20 working days from the date the necessary documents are provided by the consumer.
Article 10: Managing Default Cases
1- Creditors must, before resorting to competent authorities, ensure communication with consumers and their guarantors for collection purposes, and exert due diligence in managing the settlement and collection of defaulted debts, including but not limited to:
1-1 Establishing necessary standards to ensure employees adhere to the required professionalism, providing consumers with correct and comprehensive information about their current status, the procedures governing collection, and the legal actions that may be taken in case of default or non-compliance.
1-2 Developing internal work procedures between relevant departments, including service level agreements and escalation mechanisms to ensure consumer objections and complaints are resolved within the statutory period in the instructions issued by SAMA related to this matter, with the mechanism documented electronically and the departments' compliance with it is measured.
1-3 Establishing a written policy to organize collection procedures from consumers or their guarantors, approved by the board of directors or manager, as appropriate, considering at a minimum:
a- Solutions that can be offered to the defaulting consumer based on their creditworthiness, including but not limited to debt settlement between two parties, or rescheduling the debt and deferring installments, avoiding financing solutions that may increase the financial burden on the consumer, such as granting additional finance.
b- Procedures through which creditors ensure the consumer is provided with clear and comprehensive information to the fullest extent possible to help them understand collection procedures and the consequences of default, as well as understanding the proposed solutions and the differences between them if more than one solution is offered.
c- Analysis of complaints and objections and their patterns, addressing their causes and sources, and the role of the department responsible for handling complaints in documenting these reports and measuring their effectiveness in addressing the sources of recurring complaints.
d- Reviewing the policy periodically and ensuring its alignment with best practices, statutory provisions, and related instructions, and updating it as needed or every two years at most.
e- Ensuring that employees of creditors and third parties involved in collection tasks are aware of the policy and provide proof of their awareness.
Article 11: Managing Cases of Total Disability or Death
1- Creditors must exempt the consumer and their guarantor from the amounts claimed under the finance contract or joint finance contract - according to their obligations in the finance contract in the event of death or total disability - without making the exemption contingent on the approval of insurance service providers or any external party. Creditors must complete the procedures within a maximum period of thirty days from the date of receipt of the death certificate or total disability report, refund any amounts deducted in excess from the date of death or total disability, and transfer ownership of the financed asset to the consumer - according to the ownership percentage in joint contracts - or their heirs, or release the mortgage - as appropriate - unless the parties agree to include any of the following exceptions:
1-1 Finance contracts concluded before 01/10/2018G.
1-2 Cases of death or total disability resulting from:
a- The consumer deliberately injuring themselves or attempting suicide.
b- Natural disasters.
c- Judicial rulings issued by Saudi courts.
d- Consumption of alcohol, narcotics, or illegal drugs.
e- Participation or training in dangerous sports or competitions, such as: (horse or car racing).
f- Damage caused or contributed to by nuclear weapons, ionizing radiations, radioactive contamination from any nuclear fuel or waste, contamination due to nuclear fuel combustion, war, invasion, acts of foreign enemy, hostilities, warlike acts, or acts of vandalism and terrorism committed by person(s) working individually, on behalf of, or in relation with any terrorist organization.
2- Creditors are prohibited from delaying the procedures for exempting consumers, and they must immediately request the necessary documents, represented by the death certificate or the medical report issued by a competent authority proving total disability, and exert due diligence to process and complete the exemption process within the time frame specified in the regulations.
Chapter Five: Final Provisions
- Creditors must adhere to the regulations and are responsible for any violations committed by their employees or third parties.
- The regulations set the minimum requirements for creditors to exercise due diligence in all stages of the collection process, and they must continuously develop their internal procedures in line with the nature and size of their business, and according to the best local and international standards and practices, without conflicting with the regulations and related instructions.
- The department responsible for managing collection operations must be subject to review and audit by the internal audit and compliance departments at creditors on an annual basis to ensure the soundness of procedures and their compliance with the regulations and related instructions.
- Creditors are responsible for evaluating and assessing the consumer's credit and financial status and ensuring their ability to fulfill their obligations throughout the contract period, considering and accommodating changes that may occur in their circumstances in accordance with the instructions issued by SAMA.
- The regulations update previous regulations or instructions issued in this regard and replace the provisions of the Debt Collection Regulations and Procedures for Individual Consumers (First Edition), and creditors and third parties must update their policies, procedures, contracts, and agreements in line with them.
- The regulations are effective from the date of publication on SAMA's website.
- Creditors must adhere to the regulations and are responsible for any violations committed by their employees or third parties.
Instructions for services provided to persons with disabilities in financial institutions
To read the “Instructions for services provided to persons with disabilities in financial institutions”, click here.
Code of Conduct and Work Ethics in Financial Institutions
To read the “Code of Conduct and Work Ethics in Financial Institutions”, click here.
Rules for Advertising Products and Services Provided by Financial Institutions
To read the “Rules for Advertising Products and Services Provided by Financial Institutions”, click here.
License Disclosure Instructions
To read the “License Disclosure Instructions”, click here.
A Guide for Calculating the Early Payment Amount
To read the “Guide for Calculating the Early Payment Amount”, click here.
Disclosure of Interest Rates on Financing and Savings Products
No: 41068291 Date(g): 22/7/2020 | Date(h): 2/12/1441 Status: In-Force 1. Introduction
The purpose of these Rules is to provide transparency to the market in terms of APR/AER of various products that Banks and finance companies offer for Retail, Micro and Small enterprises as defined by SAMA. This will further allow Retail, Micro and Small Enterprises to compare APR/AER between different financing and savings products offered by Banks and Finance Companies.
SAMA has issued this update of Disclosure of Interest Rates on Financing and Savings Products that supersede SAMA's circular No. 67/70318 dated 25/11/1440H and complementary circular No. 41044254 dated 25/06/1441H. Added or amended texts are underlined.
2. Scope of Application
All Banks and Finance Companies authorized and regulated by SAMA in Saudi Arabia.
3. Definitions
Annual Percentage Rate (APR)
The discount rate at which the present value of payments and installments that are due from the Borrower, representing the Total Amount Payable by the Borrower, equals the present value of all payments of the Amount of Financing available to the Borrower on the date on which the Financing amount or the first payment thereof is available to the Borrower (As per Article 81 of Implementing Regulations of the Finance Companies Law). Annual Equivalent
Rate (AER)
The rate for a savings account or investment product that has more than one compounded interest/profit during the year. It is calculated under the assumption that any interest/profit paid is included in the principal payments balance and the next interest/profit payment will be based on the slightly higher account balance due to adding the interest/profit paid on the principal payments balance. Credit card purchase rate The rate applied to transactions (cash or credit) made with a credit card. The rate only applies to balances that are not paid in full by the end of the billing cycle. Financing amount Amount of on balance sheet loan granted to the customer. Maturity Contractual maturity of on balance sheet loans granted to customers: This is the final payment date of a loan at which point the principal and all interests/profits are due to be paid.
Contractual maturity of savings products: This is the final payment date of savings products at which point the principal and interests/profits owed to the customer are due to be paid.Monthly payment amount Installment amount the customer is obliged to pay to the Bank or Finance Company each month until the debt is fully repaid. Minimum payment amount Lowest amount the customer can pay on the credit card to avoid late payment penalties. Minimum payments are calculated as percentage of the outstanding balance plus any fees that have been added. Months until balance repaid Number of months remaining if minimum repayment on credit card is made by customer each month. Property market value Price negotiated between a willing buyer and a willing seller in an arm's length transaction after fulfilling valuation criteria set by the bank. The value may not be the current listing price or the amount of the most recent offer on the property. Loan to Value Ratio Ratio of a loan provided by the Bank or Finance Company to the value of a property purchased and determined as property market value. Payment type Interest/profit only payments or, both principal and interest/profit payments or else. Early payment charge A fee the customer will be required to pay to a lender if the customer pays off a loan early and before the scheduled maturity term of the credit facility, also sometimes referred to as a Redemption Penalty. Deposit amount Amount deposited with the Bank in savings or investment products. 4. Disclosure requirements
a) Banks and Finance Companies are required to disclose and publish information for Retail financing and saving products (if any) in a detailed and clear manner on the website, marketing channels, and other marketing materials according to the disclosure tables contained in Section (5) of these Rules.
b) Banks and Finance Companies are required to disclose and publish information for Micro and Small Enterprises financing and saving products (if any) in a detailed and clear manner on the website, marketing channels, and other marketing materials and disclose the price range for each product according to the disclosure tables contained in Section (6) of these Rules.
c) If disclosure tables cannot be included in some marketing channels and materials such as paper publications, prices or competitive benefits should not be included or referred to in a misleading way, and customers should be advised to visit the website for more details about the product.
d) A calculator should be developed for each financing or savings product showing the price and payments based on the consumer's input, and if not possible, disclosure should be made by giving at least three examples that include financing or saving amount, prices, maturity, and the category of the consumer.
e) A calculator should be developed for credit cards to calculate the APR and all commissions and expenses that the consumer will bear in advance or monthly, also, the calculator must clarify the appropriate credit card type and limit based on the consumer's input.
f) Financing limits, charges and tariffs should be subject to the relevant laws, regulations, and any other regulatory requirements.
g) Prices, ratios or rates that do not match disclosure tables and calculator results on the website should not be used in marketing campaigns.
h) The process of calculation and factors that affect the pricing should be clarified for the purpose of transparency e.g. if floating interest/profit rate is used, this should be clarified.
i) Disclosing the minimum or maximum limit for products of which the prices that cannot be determined e.g. savings products whose prices are determined based on the average amount kept in the customer's account.
j) If one of the disclosure requirements in the disclosure forms is not applicable to a product, it should be clarified in the disclosure form as "Not Applicable - N/A" given that a reasonable justification is provided.
k) For mortgage loans, which contain multiple features, Banks and Finance Companies should develop a mortgage calculator on their websites considering the inputs prescribed in section 5 (C) of these Rules. For other printed materials, one example per type should be used.
l) Consumers should be informed, in writing, that prices in the disclosure tables or calculator are examples and customers could be offered different prices based on certain factors such as the consumer credit worthiness.
m) Where applicable, disclosure tables and calculator for financing and savings products (if any) should be consolidated in one page under an icon called "Prices of Financing and Savings Products" in the website. Also, Banks and finance companies should enable direct access to the page by adding the icon on the top right of the website home page to make it easier for consumers to access prices. In addition, disclosure tables and calculators should be included on the page dedicated to each product.
n) Prices should be reviewed periodically, at least monthly, and any modification to prices should be reflected in the disclosure tables and calculator within one business day. In addition, the date of the last update should be mentioned at the top of the page.
5. Disclosure Tables for Retail Customers
Banks and Finance Companies should use the examples below as illustration with the minimum type of information the disclosure forms should include. Additional information can be added to the minimum requirements stated in this section.
a) Different types of financing products
(On balance sheet products, such as loans, should be disclosed, and there is no need to disclose off balance sheet products)
Example: Term loan
Financing Amount Maturity in Years APR* Monthly Payment Amount 100,000 5 years 5.5% 1,901 *The above table is just an example and APR may differ depending on the amount, the maturity period, and the credit scoring of each customer.
b) All Credit Cards types and classes
Example: Platinum balance-transfer card
APR* Credit Card Purchase Rate Minimum Repayment Amount %age Months Until Balance Repaid** 19% 17% 5% 60 months * Banks and Finance Companies should clearly disclose all the elements of the APR and commissions in the contracts, and separate between the commissions and expenses that the consumers will bear in advance and the monthly payments on the outstanding amount.
*lf minimum repayment is made every month, it will take almost 60 months to repay the full amount keeping in view compounded interest/added profits each month.
c) Residential Mortgages
Example: First home buy*
Property
Market
ValueLoan to
Value RatioFixed or Variable Interest/Profit Rate** Annual Percentage Rate (APR) Maturity in Years Payment Type Monthly Payment Amount Early payment Charge 500,000 90% Fixed interest/profit rate 4.5% 25 years Principal and interest/profit 19,378 Profit of future 3 installments *Banks and Finance Companies should disclose the repayment period for off-plan and self-construction products in the mortgage calculator.
**lncluding initial interest/profit rate (interest/profit rate fixed for few years at the start of mortgage) and follow on rate (interest/profit rate to be used once initial rate term is over) e.g. Fixed interest/profit rate for few years and thereafter using variable interest/profit rate e.g. 3 month SAIBOR + 20 basis point.
d) Financial Leasing Products for each type of assets
Example: Auto loan
Asset Type Financing Amount Maturity in
YearsAnnual Percentage Rate (APR) Monthly Payment Amount Residual Value Car 200,000 5 years 5% 4,051 20,000 e) Savings for each Class and Type of Product
Example: 2 years fixed deposits
Minimum Deposit Amount Maturity in Years AER Number of Withdrawals Permitted in the 1st Year Number of Withdrawals Permitted in the 2nd Year 20,000 2 years 1.5% 0 2 6. Disclosure Tables for Micro and Small Enterprises
a) Financing Products
(On balance sheet products for micro and small enterprises, such as loans, should be disclosed, and there is no need to disclose off balance sheet products)
Example: Loan types for small enterprises
Product APR* Administrative Fees Minimum (or) Maximum Administrative Fees Short term loan 4% to 6% 2% to 3% SAR 1000 Medium term loan 3% to 5% 1% to 2% SAR 1000 *The above table is just an example and APR may differ depending on the amount the maturity period, and the credit scoring of each customer.
b) Savings Products
Example: 2 years fixed deposits
Minimum Deposit Amount Maturity in Years AER Number of Withdrawals Permitted in the 1st Year Number of Withdrawals Permitted in the 2nd Year 20,000 2 years 1.5% 0 2 7. Implementation Date
These Rules shall enter into force within 15 days from issuance date.
Consumer Complaints
To read the “Consumer Complaints”, click here.
Regulating Banking Employees' Communications with Customers for Payment of Outstanding Debts
In reference to SAMA receiving complaints from bank customers regarding the numerous phone calls they and their family members, relatives, or friends receive at various and inconvenient times from collection employees working for the banks, aiming to pressure them to pay their outstanding debts to these banks.
In the interest of SAMA in organizing the process of debit collection bank customers and the communications related to this, as well as protecting customer privacy, the bank must establish an appropriate mechanism to limit these communications to the debtors or their guarantors whose names and signatures appear on the banking documents of guarantee and not to other family members, relatives, or friends. Furthermore, these communications should be confined and specified within the official working hours of the banks. In case customers do not respond regarding the bank’s indebtedness, they should be followed up through the specialized authorities. We hope to be informed of the measures taken in this regard within a month from its date.
according to Circular No. (5497/MAT/2346) dated 28/01/1432H. In view of SAMA receiving complaints from bank customers that include threats from collection employees working for or contracted by the banks to record remarks on their credit records with the credit information company "SIMAH" to pressure them to settle their outstanding debts, SAMA wishes to remind banks not to involve the name of SAMA, credit information companies, or other supervisory entities in the communications of debt collectors with customers.
According to SAMA Circular No. (341000059261) dated 11/05/1434H. SAMA has observed that some banks are using unprofessional methods to collect distressed debts and are misleading distressed customers by claiming that their names will be removed from "SIMAH's list" upon settling their debts.
Whereas following such methods with distressed bank customers reinforces a false understanding of the role of credit information companies and negatively impacts the efforts made to educate beneficiaries about the reality of credit reports and their contents. Therefore, SAMA emphasizes the necessity for all banks operating in the Kingdom, particularly the employees of the collection department and contracted collection companies, as well as other relevant departments, to refrain from using unprofessional methods to collect distressed debts. This includes misleading distressed customers into believing that their names will be removed from "SIMAH's list" upon debt settlement, which contradicts the actual mechanisms of the credit reporting system in place.
Control and Awareness Measures for Branch and Customer Service Employees in Banks Operating in the Kingdom
No: 42063179 Date(g): 17/4/2021 | Date(h): 6/9/1442 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Based on the powers vested to SAMA under the relevant regulations and instructions, and in line with the SAMA's supervisory and regulatory role in enhancing the protection of the privacy of customers of the financial institutions under its supervision and their employees, as well as in continuously improving and strengthening sound practices in banks.
Enclosed are the regulatory and awareness procedures for branch staff and customer service employees in banks operating in the Kingdom. These procedures aim to mitigate operational risks related to handling banking laws and to ensure that operations are conducted in accordance with approved regulations, instructions, and powers to protect banks and customers from exposure to losses.
Please take note and act accordingly by the end of the third quarter of 2021.
First: Introduction
A. Objective
These procedures aim to establish the minimum regulatory and awareness measures for branch staff and customer service employees in banks operating in the Kingdom. Compliance with these measures is required to mitigate operational risks related to dealing with banking laws and to ensure that operations are conducted in accordance with approved regulations, instructions, and authorities, thereby protecting banks and clients from potential losses.
B. Scope
These procedures apply to banks operating within the Kingdom. This is without prejudice to any other relevant regulations or guidelines, including but not limited to: Cyber Secuity Framework and the Business Continuity Management Framework.
Second: Definitions
The terms and phrases mentioned in these procedures are defined as follows, unless the context indicates otherwise:
Central Bank: The Saudi Central Bank.
Banks: Banks operating within the Kingdom.
Branches: Branches of commercial banks operating within the Kingdom.
Employees: Employees of branches and customer service.
Customers: Customers of the banks.
Third: Supervisory Procedures
Banks must adhere to the required maturity level as Cyber Security Framework and the Business Continuity Management Framework, with particular attention to the following:
Fourth: Awareness Procedures
Banks are required to adhere to the following:
1. Establish a policy for the secure use of banking laws, including procedures for handling usernames and passwords, and review it periodically. 2. Ensure employees are aware of the importance of checking that they are not being observed when entering their username or password. 3. Provide training and qualification for employees on essential information related to information security. 4. Conduct periodic awareness campaigns for employees regarding the instructions issued by SAMA and the banks' own policies, especially concerning the confidentiality of customer account information and the penalties for non-compliance. This should include ongoing educational materials and be conducted at least every three months. 5. Conduct regular awareness campaigns for employees on information security and financial fraud prevention, with ongoing educational materials provided at least every three months 6. Perform tests and surveys of employees at least every six months to assess the effectiveness of the awareness procedures outlined in points (4) and (5). 7. Obtain a declaration from employees, both upon starting work and annually (either in paper or electronic form), acknowledging that they have reviewed and are committed to all policies related to the secure use of banking laws and the handling of usernames and passwords.
Fifth: General Provisions
1. These procedures should be read in conjunction with all related regulations and instructions.
2. These procedures represent the minimum requirements for banks to implement in terms of enhancing the monitoring and awareness aspects for employees. 3. Existing policies, manuals, and procedures should be reviewed and updated periodically to ensure they align with the requirements set forth in these procedures and related instructions. 4. One of the supervisory departments (Internal Audit or Compliance Department) should be assigned to conduct periodic examinations or reviews (within a maximum of two years) to verify compliance with the requirements outlined in these procedures. Standardization of Notification Elements Sent to Financial Institutions Customers
No: 42023876 Date(g): 29/11/2020 | Date(h): 14/4/1442 Status: In-Force Translated Document
Further to the Saudi Central Bank's (SAMA) letter No. 381000060893 dated 07/06/1438H regarding the standardization of notification elements sent to bank customers for Mada card transactions, and in line with SAMA's commitment to enhancing customer awareness through notification messages for transactions on their accounts, memberships, and electronic wallets:
Attached is an update to the notification templates, which includes adding essential elements to the text notifications according to the procedures outlined in Table No. (1) and Table No. (2) at a minimum. Therefore, financial institutions are required to send notification messages for all financial transactions and apply the requirements as specified in the attached tables within 60 days from the date of this notice, and to provide SAMA with an implementation plan within two weeks. Please be aware that legal actions will be taken if the required procedures are not adhered to within the specified time frame.
Table No. (1)
Transaction Type Minimum Information Required internal purchases Amount, Currency
Store Name
Card Type (Mada, Credit), Executed Through Example (Apple Pay, Mada Pay, Atheer)
Card Number (Last Four Digits)
Date
Time
International Purchases Amount, Currency
Store Name
Country
Card Type (Mada, Credit), Executed Through Example (Apple Pay, Mada Pay, Atheer)
Card Number (Last Four Digits)
Date
Time
International Cash Withdrawal Amount, Currency
Country
Fees
Card Type (Mada, Credit)
Card Number (Last Four Digits)
Date
Time
internal cash withdrawal
Amount, Currency
Withdrawal Location (ATM Location or Branch/Code)Card Type (Mada, Credit)
Card Number (Last Four Digits)
Date
Time
Checks Amount, Currency
Payee Name Check Holder's
Account Number
Date
Time
Cash Deposit Amount, Currency
Deposit Method (e.g., Branch or ATM)
Account Number
Date
Time
Domestic Transfers Transferred Amount, Currency
Fees
Sender's Name (for Incoming Transfers)
Receiver's Name (for Outgoing Transfers)
Sender's Account Number (for Incoming Transfers)
Receiver's Account Number (for Outgoing Transfers)
Date
Time
International Transfers Transferred Amount, Currency
Fees
Sender's Name
Receiver's Name
Sender's Account Number
Receiver's Account Number
Transfer Intermediary Company Name (e.g., Western Union)
Destination Country
Date
Time
Internet Purchases Amount, Currency
Website or Store
Card Type (Mada, Credit), Executed Through Example (Apple Pay, Mada Pay, Atheer)
Card Number (Last Four Digits)
Account Number
Date
Time
Government Bill Payments Amount, Currency
EntityService
Invoice Number
Date
Time
Other Bill Payments Amount, Currency
Biller
Service
Invoice Number
Date
Time
Financing / Refinancing Transactions Financing Type
Total Amount of Financing
Monthly Installment
Account Number
Date
Time
Monthly Financing Deduction Financing Type
Due Installment
Total Remaining
Amount Account Number
Date
Time
Fees Amount, Currency
Reason
Account Number
Date
Time
Refund / Reversal Amount, Currency
Country in External Transactions
Store or Website or Entity
Account Number
Date
Time
Mobile App Transactions App Name (e.g., Apple Pay)
Amount, Currency
Store Name or Website
Card Type (Mada, Credit)Card Number (Last Four Digits)
Account Number
Date
Time
E-Wallet Top-Up Wallet Name (e.g., STCPay)
Amount, Currency
Top-Up Channel (Mada, Credit, SADAD, etc.)
Card Number (Last Four Digits)
Amount, CurrencyDate
Time
E-Wallet Transactions Amount, Currency
Card Type (Mada, Credit) / Transaction
Card Number (Last Four Digits)
Store or Website
Date
Time
Table No. (2)
Arabic Term
English Term
سداد فاتورة
Bill Payment
سداد فاتورة لمرة واحدة
Bill Payment one time
إصدار شيك مصدّق
Certified Cheque lssued
بطاقة ائتمانية الغاء حجز مبلغ
Credit Card Cash Release
بطاقة ائتمانية حجز مبلغ
Credit Card Cash Reserve
بطاقة ائتمانية استرجاع نقدي
Credit Card Cashback
بطاقة ائتمانية تأكيد سداد
Credit Card Credited
بطاقة ائتمانية تسديد
Credit Card Payment
بطاقة ائتمانية استرداد مبلغ
Credit Card Refund
إيداع رسوم
Credit Transaction Fees
حوالة واردة من بطاقة
Credit transfer from card
حوالة واردة بين حساباتك
Credit transfer Between Your Accounts
حوالة واردة حساب مواطن
Credit transfer Citizen Account
سحب نقدي طارئ
Credit transfer Emergency Cash Withdrawal
حوالة واردة من حسابك الجاري
Credit transfer From your Current Account
حوالة واردة من حسابك الاستثماري
Credit transfer From Your Investment Account
حوالة واردة حافز
Credit transfer Hafiz
حوالة واردة داخلية
Credit transfer Internal
حوالة واردة دولية
Credit transfer International
حوالة واردة تمويل
Credit transfer Loan
حوالة واردة محلية
Credit transfer Local
حوالة واردة راتب
Credit transfer Salary
حوالة واردة كفيل
Credit transfer Sponsor
حوالة واردة مكافأة طلاب
Credit transfer Student Reward
خصم رسوم
Debit Transaction Fees
حوالة صادرة الى بطاقة
Debit Transfer to card
حوالة صادرة بين حساباتك
Debit Transfer Between Your Account
حوالة صادرة داخلية
Debit Transfer Internal
حوالة صادرة دولية
Debit Transfer International
خصم قسط تمويل
Debit Transfer Loan Instalment
حوالة صادرة محلية
Debit Transfer Local
حوالة صادرة راتب
Debit Transfer Salary
حوالة صادرة مكفول
Debit Transfer Sponsored
حوالة صادرة الى حسابك الجاري
Debit Transfer To Your Current Account
حوالة صادرة الى حسابك الاستثماري
Debit Transfer To Your Investment account
خصم شيك مصدق
Debit Certified Cheque
خصم شيك ورقي
Debit Paper Cheque
إيداع صراف آلي
Deposit ATM
إيداع فرع
Deposit Branch
إيداع شيك مصدق
Deposit Certified Cheque
إيداع شيك ورقي
Deposit Paper Cheque
شراء عملة أجنبية
Foreign Currency Purchase
سحب صراف آلي دولي
International ATM Withdrawal
مدفوعات وزارة الداخلية
MOl Payments
شراء إنترنت
Online Purchase
امر مستديم سداد فواتير
Permanent transfer Bill Payment
امر مستديم حوالة صادرة داخلية
Permanent transfer Debit transfer Bank internal
امر مستديم حوالة صادرة بين حساباتك
Permanent transfer Debit transfer Between Your Accounts
امر مستديم حوالة صادرة دولية
Permanent transfer Debit transfer International
امر مستديم حوالة صادرة محلية
Permanent transfer Debit transfer Local
امر مستديم حوالة صادرة راتب
Permanent transfer Debit transfer Salary
امر مستديم مدفوعات وزارة الداخلية
Permanent transfer MOl Payments
شراء عبر نقاط البيع دولية
PoS International Purchase
شراء عبر نقاط البيع
Pos Purchase
شراء ونقد عبر نقاط البيع
Pos Purchase & Cashback
تسوية نقطة البيع
PoS settlement
حوالة واردة
Received transfer
استرجاع مدفوعات وزارة الداخلية
Refunding MOl Payments
حوالة عكسية
Reverse Transaction
سحب صراف آلي
ATM Withdrawal
سحب فرع
Branch Withdrawal
Rules Governing Calculation of Annual Percentage Rate (APR)
To read the “Rules Governing Calculation of Annual Percentage Rate (APR)”, click here.
Banking Tariff
No: 381000095093 Date(g): 4/6/2017 | Date(h): 10/9/1438 Status: In-Force The attached banking tariff replaced the tariff for banking services issued pursuant to Circular by SAMA No. (341000134319), dated 25/11/1434 H, corresponding to 29/09/2013 G.According to The Banking Control Law issued by Royal Decree No. M/5 dated 22/2/1386 H. and Ministerial Decision No. 3/2149 dated 14/10/1406 H regarding the implementation Rules for Banking Control Law. SAMA is authorized to set the maximum limit for banking fees on personal accounts and banking services that banks are allowed to charge their individual customers.
Attached is an updated version of the banking tariff and the accompanying instructions, which must be adhered to and implemented within three months from its date.
General Instructions
- The disclosure and transparency principle shall be applied, where all means will be used to inform the customer.
- Disclosing all tariffs at banks’ branches and on their websites in a clear and legible manner to be accessible to customers.
- The maximum banking tariff for banking services as illustrated in the table attached to this circular shall not be exceeded.
- Providing SAMA with all types of tariff or fees according to this circular at the beginning of each Hijri year (Muharram) to be disclosed on website.
- Utilizing banking tariff instructions to encourage the utilization of electronic channels and financial inclusion.
- Obtaining a prior approval from SAMA on tariff or fees for any services or products that are not included in this circular.
- Fees shall be within reasonable and competitive limits as compared with similar services that are conformed to the best applicable applications and practices.
- Not charging any fees associated with the services or products provided to customers except after customers' acceptance for the service and related fee.
- A bank, may opt not to charge any of the tariff set forth herein as it deems appropriate and consistence with its policy of providing services with fair competition.
- Apply the charging policies issued by SAMA for all payment systems (MADA\ SARIE \SADAD…etc.) and its services.
- SAMA will periodically review and update the banking tariff in accordance with approved and licensed products and its fees
Banking Tariff
The banking tariff sets the allowable maximum fees that a bank may, but not necessarily, charge individual customers and beneficiaries for services provided by the bank following their acceptance.
Banking Service Description.
Maximum Banking Tariff
1- Customer Accounts Free
a. opening an account
free b. Balance is less than required limit
None 2- Account statement
At branch:
a. statement for less than one year 25 SAR b. statement for1 - 5 years
30 SAR c. statement for more than five year
50 SAR Electronically (internet, telephone, ATM…):
a. Monthly statement by regular mail or email electronically
Free b. ATM mini statement electronically
free 3- Cash Withdrawal using a withdrawal Form at the Branch
Free 4- MADA ATM and POS Cards:
Free a. issuance of ATM card for a Free account
Free b. ATM cash withdrawal / deposit
Free c. Use of MADA cards at POS terminal by customers
Free d. Renewal of ATM card
Free e. Re-issuance of ATM card retained by an ATM
Free f. NAQAD service (purchase with cash back)
Free g. Re-issuance of ATM card (lost / damaged / 3 invalid passwords)
30 SAR h. issuance of an additional ATM card
30 SAR 5- Electronic Payment of Bills Government Services (SADAD):
a. Government services payment.
Free b. Payment of bills and services..
Free c. SADAD Account for online payment.
Free 6- Banking Transfer & services
At Branch:
a. Transfer to another account within the same bank
Free b. Setting up a standing payment order (one time)
15 SAR c. Transfer to another bank inside the Kingdom through SARIE (same day)
25 SAR d. Transfer to another bank inside the Kingdom through SARIE (forward)
15 SAR e. Transfer to a bank outside the Kingdom.
75 SAR f. Change/cancel transfer outside the kingdom
25 SAR Electronically (internet, telephone and ATM):
g. Transfer to another account within the same bank
Free h. identification of a beneficiary for fund transfer
Free i. Setting up a standing payment order (one time)
10 SAR j. Transfer to another bank inside the Kingdom through SARIE (same day)
7 SAR k. Transfer to another bank inside the Kingdom through SARIE (forward)
5 SAR l. Transfer to a bank outside Kingdom
50 SAR m. Change/cancel transfer outside kingdom
15 SAR 7- Checks
a. Issuance of a checkbook (25 checks)
Free b. Issuance of an additional checkbook (25 checks)
10 SAR c. Issuance of a bank check
10 SAR d. Revocation of a bank check
10 SAR e. Issuance of a bank check (foreign currency)
15 SAR f. Revocation of a bank check (foreign currency)
15 SAR g. Requesting a copy of a check dated to one year
10 SAR h. Requesting a copy of a check dated more than one year
20 SAR 8- GCCNet Transaction Fees
a. Cash withdrawal within Gulf countries
10 SAR b. Balance inquiry within Gulf countries
3 SAR c. Customer use of GCC cards at POS terminals within Gulf countries.
FREE 9. International Network Transaction Fees
a. Cash withdrawal for debit cards
25 SAR Cash withdrawal from credit cards
b. Withdrawal of SAR 5,000 or less
75 SAR c. Withdrawal of more than SAR 5,000
3% MAX 300 SAR d. Credit card dispute fee (if wrong dispute)
50 SAR e. Balance inquiry on ATM
3,5 SAR Model Contracts
The Standard Contract Forms for Opening Current Bank Accounts for Individuals and Juristic Persons
This circular is currently available only in Arabic, please click here to read the Arabic version.Finance Contract Summary Form
No: 351000123114 Date(g): 21/7/2014 | Date(h): 24/9/1435 Status: In-Force This circular is currently available only in Arabic, please click here to read the Arabic version.Mortgage Finance Model Contract for Individuals in Murabaha and Ejarah
This circular is currently available only in Arabic, please click here to read the Arabic version.Consumer Financing Model Contract
No: 44058467 Date(g): 7/2/2023 | Date(h): 17/7/1444 Status: In-Force This circular is currently available only in Arabic, please click here to read the Arabic version.Model Contract of the Financial Lease of Vehicles for Individuals
No: 41038534 Date(g): 26/1/2020 | Date(h): 1/6/1441 Status: In-Force This circular is currently available only in Arabic, please click here to read the Arabic version.Margin Trading System
Other Provisions
Credit Information

