Appendices
Appendix A - How to Request an Update to the Framework
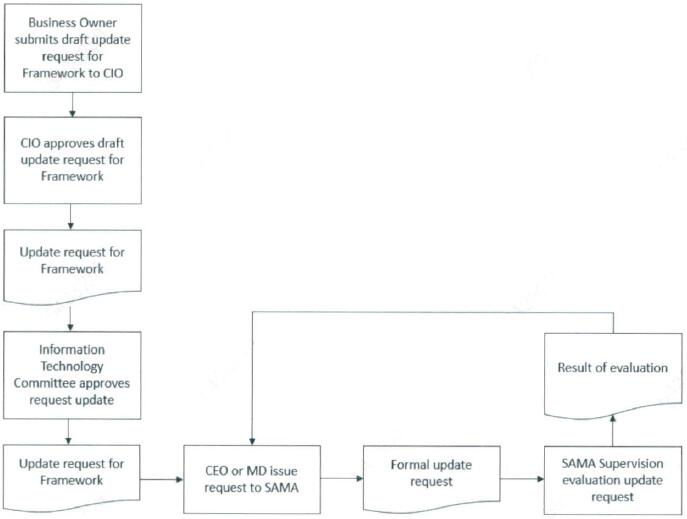
Below the illustration of the process for requesting an update to the Framework.
- Detail information supported by pros and cons about the suggested update.
- The request should first be approved by CIO before submitting to IT steering committee.
- The request should be approved by Member Organization's IT steering committee.
- The request should be sent formally in writing to the manager 'General Department of Cyber Risk Control' via the Member Organization's CEO or managing director.
- 'General Department of Cyber Risk Control' will evaluate the request and informs the Member Organization.
- The current Framework remains applicable while the requested update is being considered, processed and if applicable is approved and processed.
Appendix B - Framework Update Request Form
Request to Update the IT Governance Framework
A submission to the manager of SAMA MA General Department of Cyber Risk Control.
The Saudi Arabia Monetary Authority (SAMA) will consider requests from a member organization (MO) to update its IT Governance Framework based on the information submitted using the form below. A separate form must be completed for each requested update. Please note that all required fields must be properly filled in before SAMA will begin the review process
Requestor Information
REQUESTOR'S SIGNATURE*
xREQUESTOR'S POSITION* DATE* REQUESTOR'S NAME*
MEMBER ORGANIZATION OF REQUESTOR*
FRAMEWORK SECTION*:
PURPOSE OF REQUESTED UPDATE (including detailed information on its pros and cons)*:
PROPOSAL*:
Approvals
1. MO'S CIO APPROVAL*
DATE*
2. MO'S IT STEERING COMMITTEE APPROVAL*
APPROVER'S POSITION*
DATE*
3 SAMA DECISION
SAMA APPROVAL
DATE
* Denotes required fields
Appendix C - How to Request 2 Waiver from the Framework
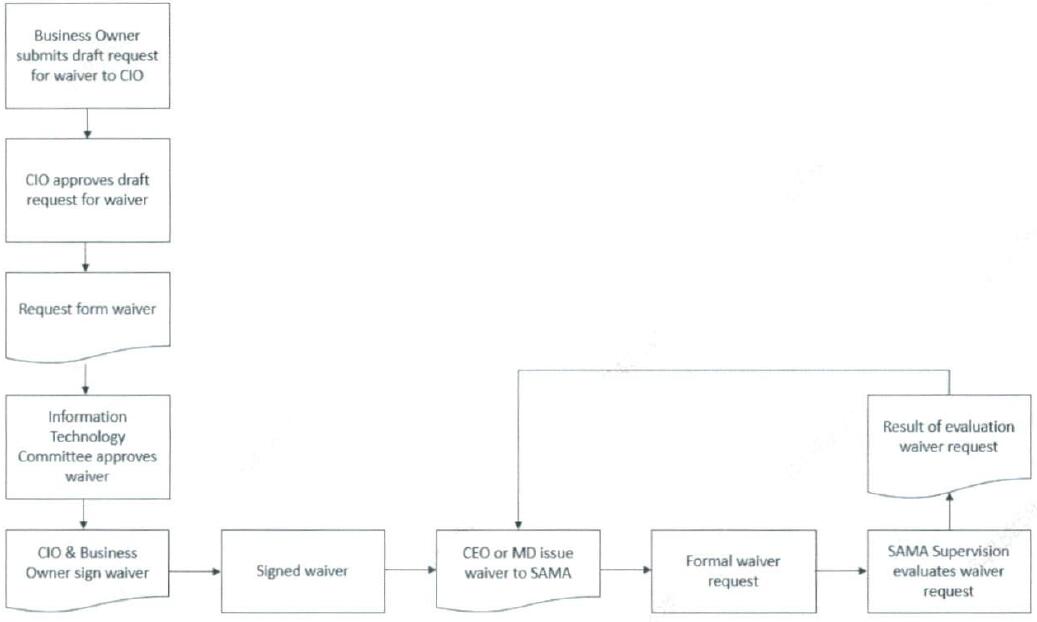
Below the illustration of the process for requesting a waiver from the Framework.
- Detail description about the reasons that the member organization could not meet the required control.
- Details description about the available or suggested compensating controls.
- The waiver request should first be approved by CIO before submitting to IT steering committee.
- The waiver request should approved by the members of Member Organization's IT steering committee.
- The waiver request should be signed by the CIO and relevant (business) owner.
- The waiver request should be formally issued in writing to the manager of 'General Department of Cyber Risk Control' via the Member Organization's CEO or managing director.
- ‘General Department of Cyber Risk Control' will evaluate the waiver request and informs the Member Organization.
The current Framework remains applicable while the requested waiver is being evaluated and processed, until the moment of granting the waiver.
Appendix D - Framework Waiver Request Form
Request for Waiver from the SAMA IT Governance Framework
A submission to the manager of 'General Department of Cyber Risk Control'
The Saudi Arabia Monetary Authority (SAMA) will consider requests for waiver from a member organization (MO) from its IT Governance Framework based on the information submitted using the form below. A separate form must be completed for each requested waiver. Please note that all required fields must be properly filled in before SAMA will begin the review process.
Requestor Information
REQUESTOR'S SIGNATURE*
xREQUESTOR'S POSITION* DATE* REQUESTOR'S NAME*
MEMBER ORGANIZATION OF REQUESTOR*
FRAMEWORK CONTROL*:
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF WHY CONTROL CANNOT BE IMPLEMENTED*:
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF AVAILABLE OR SUGGESTED COMPENSATING CONTROLS*:
Approvals
1 .MO's CIO APPROVAL*
DATE*
2. MO'S IT STEERING COMMITTEE APPROVAL*
APPROVER'S POSITION*
DATE*
3. SAMA DECISION
SAMA APPROVAL
DATE
* Denotes required fields
**The validity of this waiver is one year. It is the Member Organizations responsibility to ensure renewal of this waiver.Appendix E - Glossary
Term Description Access Control Means to ensure that access to assets is authorized and restricted based on business and security requirements. Application Architects Application Architects identify needed changes to the portfolio of applications across the ecosystem. They develop and administer application-specific standards such as user interface design, globalization, Web services, portal application programming interfaces, XML, and content. They provide design recommendations based on long-term development organization strategy and develop enterprise level application and custom integration solutions including major enhancements and interfaces, functions and features. Asset Management The systematic process of deploying, operating, maintaining, upgrading, and disposing of assets in a safe, secure and cost effective manner Asset Owner The term Asset owner identifies an individual or entity that has approved management responsibility for controlling the production, development, maintenance, use of the information assets. Authorization Matrix A. matrix that defines the rights and permissions for a specific role needs for information. The matrix lists each user, the business process tasks he or she performs, and the affected systems. Audit Independent review and examination of records and activities to assess the effectiveness of IT governance controls and to ensure compliance with established policies, operational procedures and relevant standard, legal and regulatory requirements. Authentication Verifying the identity of a user, process, or device, often as a prerequisite in order to allow access to resources in a system. Backup Files, devices, data and procedures available for use in case of a failure or loss, or in case of deletion or suspension of their original copies. Business Application Any software or set of computer programs that are used by business users to perform various business functions. Batch Processing Batch processing is the processing of the transactions in a group or batch with no or minimal human interaction. Configuration Item (CI) Component of an infrastructure-or an item, such as a request for change, associated with an infrastructure-which is (or is to be) under the control of configuration management Change Management The controlled identification and implementation of required changes within a business or information systems. Chief Information Officer (CIO) A senior-level executive referred as Chief Information Officer (CIO), Chief Technology Officer (10) / Head of IT or relevant stakeholder who is accountable for IT advocacy, aligning IT and business strategies, and planning, resourcing and managing the delivery of IT services, information and the deployment of associated human resources. Classification Setting the sensitivity level2 of data and information that results in security controls for each level of classification. Data and information sensitivity levels are set according to predefined categories where data and information is created, modified, improved, stored or transmitted. The classification level is an indication of the value or importance of the data and information of the organization. Chief Operating Officer (COO) A senior-level executive responsible for the daily operation of the organization. Critical IT infrastructures These are the information assets (i.e., facilities, systems, networks, processes, and key operators who operate and process them), whose loss or vulnerability to security breaches may result in significant negative impact on the availability, integration or delivery of basic services, including services that could result in serious loss of property, alongside observance of significant economic and/or social impacts. Compensating Control A management, operational, and/or technical control (i.e., safeguard or countermeasure) employed by an organization in place of a recommended control in the low, moderate, or high baselines that provides equivalent or comparable protection for an information system. Containerization Unit of software that packages up code and all its dependencies. Data Masking A. computerized technique of blocking out the display of sensitive information or PII. Database Administrator Database administrator, frequently known just by the acronym DBA, is a role usually within the Information Technology department, charged with the creation, maintenance, backups, querying, tuning, user rights assignment and security of an organization's database. Disaster Recovery Programs, activities and plans designed to restore the organizations critical business functions and services to an acceptable situation, following exposure to cyber and IT incidents or disruption of such services. Enterprise Architect Description of the fundamental underlying design of the components of the business system, or of one element of the business system (e.g., technology), the relationships among them, and the manner in which they support the enterprise's objectives. Feasibility study A phase of a system development life cycle (SDLC) methodology that researches the feasibility and adequacy of resources for the development or acquisition of a system solution to a user need. Formally documented Documentation that is written, approved by the senior leadership and disseminated to relevant parties. Freezing period e.g. Salaries deposit days, public or national holidays. Hypervisor A hypervisor allows one host computer to support multiple guest Virtual Machines (VMs) by virtually sharing its resources, like memory and processing. Incident An occurrence that actually or potentially jeopardizes the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of an information system or the information the system processes, stores, or transmits or that constitutes violation or imminent threat of violation of security policies, security procedures, or acceptable use policies. Incident Management The monitoring and detection of events on an information systems and the execution of proper responses to those events. Information Asset A piece of information, stored in any manner, which is recognized as 'valuable' to the organization. Interdependencies Set of interaction with dependence of information assets on each another in order to deliver set of works or tasks. IT Change and Release Management A holistic and proactive approach to managing the transition from a current to a desired organizational state, focusing specifically on the critical human or "soft" elements of change IT facilities The physical environment where the IT infrastructure is located. IT risk The business risk associated with the use, ownership, operation, involvement, influence and adoption of IT within an enterprise. IT Steering committee An executive-management-level committee that assists in the delivery of the IT strategy oversees day-to-day management of IT service delivery and IT projects, and focuses on implementation aspects. Key Performance Indicator (KPI) KPI is a type of performance measurement that evaluates the success of an organization or of a particular activity in which it engages to achieve particular objectives and goals. Key Risk Indicator (KRI) KRI is a measure used to indicate the probability an activity or organization will exceed its defined risk appetite. KRIs are used by organizations to provide an early signal of increasing risk exposures in various areas of the enterprise. Likelihood A weighted factor based on an analysis of the probability that a given threat is capable of exploiting a given vulnerability. Member Organization Organizations affiliated with SAMA. Need-to-know The restriction of data, which is considered sensitive unless one has a specific need to know; for official business duties. Off-the-shelf system Software that already exists and is available from commercial sources. Outsourcing Obtaining goods or services by contracting with a supplier or service provider. Patch An update to an operating system, application, or other software issued specifically to correct particular problems with the software. Patch management The systematic notification, identification, deployment, installation, and verification of operating system and application software code revisions. Recovery A procedure or process to restore or control something that is suspended, damaged, stolen or lost. Recovery Point Objective (RPO) The point in time to which data must be recovered after an outage. RPO is determined based on the acceptable data loss in case of a disruption of operations. It indicates the earliest point in time that is acceptable to recover the data. The RPO effectively quantifies the permissible amount of data loss in case of interruption. Recovery Time Objective (RTO) The amount of time allowed for the recovery of a business function or resource after a disaster occurs Regression Testing Testing of a previously tested program following modification to ensure that defects have not been introduced or uncovered in unchanged areas of the software, as a result of the changes made. Residual risks The remaining risk after management has implemented a risk response. Retention The length of time that information, data, event logs or backups must be retained, regardless of the form (i.e., paper and electronic). Risk A measure of the extent to which an organization is threatened by a potential circumstance or event, and typically a function of: (i) the adverse impacts that would arise if the circumstance or event occurs; and (ii) the likelihood of occurrence. Risk register Risk register is a table used as a repository for all risks identified and includes additional information about each risk, e.g. risk category, risk owner, and mitigation actions taken. Risk Tolerance The acceptable variation relative to performance to the achievement of objectives. Also refer to 'Risk appetite'. Risk Treatment A process to modify risk that can involve avoiding the risk by deciding not to start or continue with the activity that gives rise to the risk; taking or increasing risk in order to pursue an opportunity; removing the risk source; changing the likelihood; changing the consequences; sharing the risk with another party or parties; and retaining the risk by informed decision.
Risk treatments that deal with negative consequences are sometimes referred to as "risk mitigation", "risk elimination", "risk prevention" and "risk reduction". Risk treatments can create new risks or modify existing risks.Root-cause analysis A principle-based, systems approach for the identification of underlying causes associated with a particular set of risks. RACI Chart Illustrates who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted and Informed within an organizational framework. Security Testing A process intended to ensure that modified or new systems and applications include appropriate security controls and protection and do not introduce any security holes or vulnerabilities that might compromise other systems or applications or misuses of the system, application or its information, and to maintain functionality as intended. Security-by Design A methodology to systems and software development and networks design that seeks to make systems, software and networks free from cybersecurity vulnerabilities/weaknesses and impervious to cyber-attack as much as possible through measures such as: continuous testing, authentication safeguards and adherence to best programming and design practices. Segregation of Duties Key principle that aims at minimizing errors and fraud when processing specific tasks. It is accomplished through having several people with different privileges, required to complete a task. Service level agreement (SLA) Defines the specific responsibilities of the service provider and sets the customer expectations. Stress Testing A type of performance testing conducted to evaluate a system or component at or beyond the limits of its anticipated or specified workloads, or with reduced availability of resources such as access to memory or servers. System Acquisition Procedures established to purchase application software, or an upgrade, including evaluation of the supplier's financial stability, track record, resources and references from existing customers System Configuration Management The control of changes to a set of configuration items over a system life cycle. Third-Party Any organization acting as a party in a contractual relationship to provide goods or services (this includes suppliers and service providers). Threat Any circumstance or event with the potential to adversely impact organizational operations (including mission, functions, image, or reputation), organizational assets, or individuals through an information system via unauthorized access, destruction, disclosure, modification of information, and/or denial of service. Unit Testing A testing technique that is used to test program logic within a particular program or module. User Acceptance Testing (UAT) Taking use cases or procedures for how the system was designed to perform and ensuring that someone who follows the procedure gets the intended result. Vulnerability Weakness in an information system, system security procedures, internal controls, or implementation that could be exploited or triggered by a threat source. Owner Individual or group that holds or possesses the rights of and the responsibilities for an enterprise, entity or asset.

