If new information is obtained after deciding on the resolving approach, the bank must re-examine and refresh it. For example, if it turns out that the borrower had been misleading it with certain material information, the approach and the measures must be more conservative. On the other hand, if the borrower puts forward or presents a repayment proposal during the measures, which would considerably improve the bank's position, the bank may mitigate the measures subject to fulfillment of certain conditions or eliminate them completely. This means that there is a certain flexibility of restructuring measures for the company.
|
Banks generally have a choice of choosing to restructure a loan, sell the loan (note sale), or liquidate the underlying collateral either by sale by owner or legal procedures (e.g. enforcement or insolvency). These guidelines require banks to compare the value of the proposed restructuring option against the other alternatives. The analysis will be confined to comparing the value of the proposed restructuring against enforcement and bankruptcy. Choosing the optimal option, i.e., the solution that returns the highest value to the bank is not always clear-cut.
|
Evaluating alternative strategies based on NPV analysis
|
Using a simple Net Present Value (NPV) analysis is recommended in order to provide more quantitative justification for the decision.
|
The general formula to calculate net present value is:
|
| | 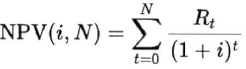
|
Where i = interest rate per period
|
| | N = total number of periods
|
| | Rt= net cash flow per period t
|
| | t = period in which cash flow occurs
|
Net present value (NPV) is the sum of the present values (PV) of a stream of payments over a period of time. It is based on the concept of time value of money - money received in the future is less valuable than money received today. To determine NPV, the net cash flow (cash payments of principal, interest, and fees less the bank’s out-of-pocket costs for legal fees, consultants, etc.) received annually is calculated. Each of these amounts or future values (FV) is then discounted to the present by using an appropriate market-based discount rate. Alternatively, the Banks may also use original effective interest rate used for computation of provisioning under International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS) 9 guidelines.
|
The sum of the PVs equals the NPV. Because of its simplicity, NPV is a useful tool to evaluate which of the possible workout options results in the maximum recovery to the bank.
|
For NPV analysis, the bank's standard risk-adjusted discount rate should be considered. NPV from various options should be considered including below considerations in each option:
|
| i. | Restructuring: evaluation based on estimated cash-flows for a period under negotiation for new tenor of contract. The factors to be considered are interest rate of the new term, any other expenses involved in restructuring and business plan or internal estimations of the bank.
|
| ii. | Enforcement (including legal): the parameters to be considered includes current value of the property, suitable haircuts to be applied, litigation charges and additional time to be taken to conclude these proceedings.
|
| iii. | Insolvency: cost of insolvency procedure, length of time to conclude insolvency proceedings and estimated value to be recovered.
|