4. Rules for Corporate, Sovereign and Bank Exposures
4.1 Risk-Weighted Assets for Corporate, Sovereign and Bank Exposures
Formula for derivation of risk-weighted assets
4.1.1 The derivation of risk-weighted assets is dependent on estimates of PD, LGD, EAD and, in some cases, M, for a given exposure. Paragraphs 4.2.7 to 4.2.13 below discuss the circumstances in which the maturity adjustment applies.
4.1.2 Throughout this section, PD and LGD are measured as decimals, and EAD is measured in Saudi Riyals. For exposures not in default, the formula for calculating risk-weighted assets is 1,2
Correlation ® = 0.12 × (1 - EXP (-50 × PD)) / (1 - EXP (-50)) + 0.24 × [1 - (1 - EXP (-50 × PD)) / (1 - EXP (-50))]
Maturity adjustment (b) = (0.11852 - 0.05478 × ln (PD))^2
Capital requirement 3 (K) = [LGD × N [(1 - R)^-0.5 × G (PD) + (R / (1 - R))^0.5 × G (0.999)] - PD x LGD] x (1 - 1.5 x b)^ -1 × (1 + (M - 2.5) × b)
Risk-weighted assets (RWA) = K x 12.5 x EAD
4.1.3 The capital requirement (K) for a defaulted exposure is equal to the greater of zero and the difference between its LGD and the bank‘s best estimate of EL (see paragraphs 4.5.1, 4.5.2 and 4.5.5 of ―Minimum Requirements for Risk Quantification under IRB Approach‖). The amount of risk-weighted asset for the defaulted exposure is the product of K, 12.5, and EAD.
4.1.4 Purposely Missing.
4.1.5 Under the IRB Approach for corporate credits, banks are permitted to separately distinguish exposures to SME borrowers (defined as corporate exposures where the reported sales for the consolidated group of which the firm is a part is less than SR 15 million) from those to large firms4. A firm-size adjustment (i.e. 0.04 x (1 - (S-5) / 45)) is made to the corporate risk-weight formula for exposures to SME borrowers. S is expressed as total annual sales in millions of SR with values of S falling in the range of equal to or less than SR 15 million or greater than or equal to SR 5 million. Reported sales of less than SR 5 million will be treated as if they were equivalent to SR 5 million for the purposes of the firm-size adjustment for SME borrowers.
Correlation ® = 0.12 × (1 - EXP (-50 × PD)) / (1 - EXP (-50)) + 0.24 × [1 - (1 - EXP (-50 × PD)) / (1 - EXP (-50))] - 0.04 × (1 - (S - 5) / 10)
In the case where total sales are not a meaningful indicator of firm size for particular companies, SAMA may on an exceptional basis allow banks to substitute total assets of the consolidated group for total sales in calculating the SME threshold and the firm-size adjustment. However, banks should not make use of this special treatment to obtain capital relief.
Risk weights for SL
4.1.6 Banks that do not meet the requirements for the estimation of PD under the IRB Approach for corporate exposures will be required to map their internal grades for the SL exposures to five supervisory categories, each of which is associated with a specific risk weight. The slotting criteria on which this mapping should be based are provided in Table 2.
4.1.7 The risk weights for UL associated with each supervisory category broadly correspond to a range of external credit assessments5 as outlined below:
* Strong Good Satisfactory Weak Default 70% 90% 115% 250% 0% BBB- or better BB+ or BB BB-or B+ B to C- Not applicable 4.1.8 Subject to SAMA approval a Bank may assign preferential risk weights of 50% to ―"strong" exposures, and 70% to ―"good" exposures, provided they have a remaining maturity of less than 2.5 years or if SAMA determines that a Banks' underwriting and other risk characteristics are substantially stronger than specified in the slotting criteria for the relevant supervisory risk category.
4.1.9 Banks that meet the requirements for the estimation of PD are able to use the Foundation IRB Approach for corporate exposures to derive risk weights for SL sub-classes.
4.1.10 Banks that meet the requirements for the estimation of PD and LGD and/or EAD are able to use the Advanced IRB Approach for corporate exposures to derive risk weights for SL sub-classes.
1 In denotes the natural logarithm.
2 N(x) denotes the cumulative distribution function for a standard normal random variable (i.e. the probability that a normal random variable with mean zero and variance of one is less than or equal to x). G(z) denotes the inverse cumulative distribution function for a standard normal random variable (i.e. the value of x such that N(x) = z). The normal cumulative distribution function and the inverse of the normal cumulative distribution function are, for example, available in Excel as the functions NORMSDIST and NORMSINV.
3 If this calculation results in a negative capital charge for any individual sovereign exposure, banks should apply a zero capital charge for that exposure.
4 Banks should not apply a firm-size adjustment to a corporate customer which cannot make available the sales figure for the consolidated group of which the customer is a part. Also refer to Table –1 on Page 41 for Illustration.
5 The notations follow the methodology used by Standard & Poor‘s. The use of Standard & Poor‘s credit ratings is for reference only; those of some other SAMA approved external credit assessment institutions ("ECAIs") could equally well be used.
* Refer to Table-2 – Attachment 5.9.4.2 Risk Components
Probability of default (PD)
4.2.1 For corporate and bank exposures, the PD is the greater of the one-year PD associated with the internal borrower grade to which that exposure is assigned, or 0.03%. For sovereign exposures, the PD is the one-year PD associated with the internal borrower grade to which that exposure is assigned. The PD of borrowers assigned to a default grade(s), consistent with the reference definition of default, is 100%. The minimum requirements for the derivation of the PD estimates associated with each internal borrower grade are outlined in paragraphs 4.4.1 to 4.4.9 of “Minimum Requirements for Risk Quantification under IRB Approach”.
Banks where, SAMA has disallowed the application of foundation or advanced approaches to HCVRE must map their internal grades to five supervisory categories, each of which is associated with a specific risk weight. The slotting criteria on which this mapping must be based are the same as those for IPRE, as provided in Annex 6 International Convergence of Capital Measurement and Capital Standards – June 2006, . The risk weights associated with each category are:
Supervisory categories and UL risk weights for high-volatility commercial real estate.
Strong
Good
Satisfactory
Weak
Default
95%
120%
140%
250%
0%
(Refer para 280, International Convergence of Capital Measurement and Capital Standards – June 2006)
Table 1: Illustrative IRB risk weights for UL
Asset Class: Corporate Exposures Residential Mortgages Other Retail Exposures Qualifying Revolving Retail Exposures (%) (%) (%) (%) LGD: 45 45 45 25 45 85 45 85 Maturity 2.5 years Turnover (SR. Mn) 500 50 PD: 0.03 14.44 11.30 4.15 2.30 4.45 8.41 0.98 1.85 0.05 19.65 15.39 6.23 3.46 6.63 12.52 1.51 2.86 0.10 29.65 23.30 10.69 5.94 11.16 21.08 2.71 5.12 0.25 49.47 39.01 21.30 11.83 21.15 39.96 5.76 10.88 0.40 62.72 49.49 29.94 16.64 28.42 53.69 8.41 15.88 0.50 69.61 54.91 35.08 19.49 32.42 61.13 10.04 18.97 0.75 82.78 65.14 46.46 25.81 40.10 75.74 13.08 26.06 1.00 92.32 72.40 56.40 31.33 45.77 86.46 17.22 32.53 1.30 100.95 78.77 67.00 37.22 50.80 95.95 21.02 39.70 1.50 105.59 82.11 73.45 40.80 53.37 100.81 23.40 44.19 2.00 114.86 88.55 87.94 48.85 57.99 109.53 28.92 54.63 2.50 122.16 93.43 100.64 55.91 60.90 115.03 33.98 64.18 3.00 128.44 97.58 111.99 62.22 62.79 118.61 38.66 73.03 4.00 139.58 105.04 131.63 73.13 65.01 122.80 47.16 89.08 5.00 149.86 112.27 148.22 82.35 66.42 125.45 54.75 103.41 6.00 159.61 119.48 162.52 90.29 67.73 127.94 61.61 116.37 10.00 193.09 146.51 204.41 113.56 75.54 142.69 83.89 158.47 15.00 221.54 171.91 235.75 130.96 88.60 167.36 103.89 196.23 20.00 238.23 188.42 253.12 140.62 100.28 189.41 117.99 222.86 Note:
1. The above table provides illustrative risk weights for UL calculated for the corporate asset class and he three retail sub-classes under the IRB Approach to credit risk. Each set of risk weights is produced using the appropriate risk-weight functions set out in this paper. The inputs used to calculate the illustrative risk weights include measures of PD, LGD, and an assumed M of 2.5 years.
2. A firm-size adjustment applies to exposures made to SME borrowers (defined as corporate exposures where the reported sales for the consolidated group of which the firm is a part is less than SR 250 million). Accordingly, the firm-size adjustment is made in determining the second set of risk weights provided in second column of corporate exposures given that the turnover of the firm receiving the exposure is assumed to be SR 5 million.
Loss given default (LGD)
4.2.2 Banks should provide an estimate of the LGD for each corporate, sovereign and bank exposure. There are two approaches for deriving this estimate: the Foundation IRB Approach and the Advanced IRB Approach.
LGD under the Foundation IRB Approach
Treatment of unsecured claims and non-recognised collateral
4.2.3 Under the Foundation IRB Approach, senior claims on corporates, sovereigns and banks not secured by recognised collateral will be assigned a 45% LGD.
4.2.4 All subordinated claims on corporates, sovereigns and banks will be assigned a 75% LGD. A subordinated loan is a facility that is expressly subordinated to another facility.
LGD under the Advanced IRB Approach
4.2.5 Subject to the minimum requirements specified in subsection 4.5 of “Minimum Requirements for Risk Quantification under IRB Approach”, banks are allowed to use their own internal estimates of LGD for corporate, sovereign and bank exposures. The LGD should be measured as a percentage of the EAD. Banks eligible for the IRB Approach that are unable to meet these minimum requirements should utilise the foundation LGD treatment described in paragraphs 4.2.3 to 4.2.4 above.
Exposure at default (EAD)
4.2.6 The following paragraphs on EAD apply to both on and off-balance sheet positions. All exposures are measured gross of specific provisions or partial write-offs. The EAD on drawn amounts should not be less than the sum of:
(i) The amount by which a bank‘s regulatory capital would be reduced if the exposure were written-off fully; and
(ii) Any specific provisions and partial write-offs.
When the difference between the instrument’s EAD and the sum of (i) and (ii) is positive, this amount is termed a discount. The calculation of risk-weighted assets is independent of any discounts. Under the limited circumstances described in paragraph 380, International Convergence of Capital Measurement and Capital Standards – June 2006, discounts may be included in the measurement of total eligible provisions for purposes of the EL-provision calculation set out in Section III.G, International Convergence of Capital Measurement and Capital Standards – June 2006
SAMA hereby intimates that the approaches laid in Annexure 4 (Treatment of Counterparty Credit Risk and Cross-Product Netting), of the International Convergence of Capital Measurement and Capital Standards, 2006, (with the exception of clauses applicable to netting) for the purpose of computing the credit equivalent amount of Securities Financing Transactions and OTC derivatives that expose a bank to counterparty credit risk, are available to banks and constitute an integral part of the "SAMA Detailed Guidance Document Relating to Pillar 1, June 2006.
(Refer para 334, International Convergence of Capital Measurement and Capital Standards – June 2006)
Effective maturity (M)
4.2.7 For Banks using the Foundation IRB Approach for corporate exposures, the M will be 2.5 years except for repo-style transactions where the M will be 6 months. Banks using any element of the Advanced IRB Approach are required to measure the M for each facility as defined below.
4.2.8 M is defined as the greater of one year and the remaining effective maturity in years. In all cases, the M will be no greater than five years.
4.2.9 For an instrument subject to a determined cash flow schedule, the M is defined as:
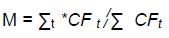
Where CFt flows (principal, interest payments and fees) contractually payable by the borrower in periodt .
4.2.10 If a bank is not in a position to calculate the M of the contracted payments as noted above, it is allowed to use a more conservative measure of M. An example of this measurement is the maximum remaining time (in years) that the borrower is permitted to take to fully discharge its contractual obligation (principal, interest, and fees) under the terms of the loan agreement. Normally, this will correspond to the nominal maturity of the instrument.
4.2.11 For derivatives subject to a master netting agreement, the weighted average maturity of the transactions should be used when applying the explicit maturity adjustment. Further, the notional amount of each transaction should be used for weighting the maturity.
4.2.12 For repo-style transactions subject to a master netting agreement, the weighted average maturity of the transactions should be used when applying the explicit maturity adjustment. A five-day floor will apply to the average. Further, the notional amount of each transaction should be used for weighting the maturity.

